Causes Symptoms Diagnostics Treatment Advantages of treatment at MGK Prices
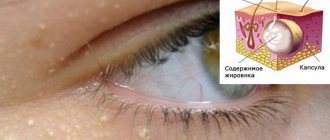
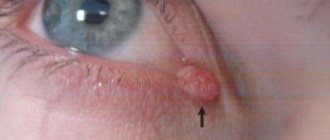
Xanthelasmas of the eyelids look like small single or multiple flat yellowish plaques located at the inner corner of the upper (usually) or lower eyelid. Xanthelasmas are benign formations that are not prone to malignancy; their appearance is associated with general disorders of lipid metabolism.
Prices for treatment for xanthelasma
The cost of surgical treatment of xanthelasma starts from 2000 rubles. (in the presence of a single formation up to 5 mm). The final cost of removal will depend on the number and size of formations, as well as the volume of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures performed.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling (499) 322-36-36 or online using the appropriate form on the website; you can also read the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
Make an appointment
Average cost of xanthelasma removal in Russia
Depending on the type of surgical intervention, the cost of xanthelasma removal in Russian clinics will vary greatly.
The average cost of a classic type surgical operation will be 3,500 rubles for one plaque.
In other cases, the cost will range from 300 rubles and above, and the maximum price for removing formations will be as follows:
- electrocoagulation – 1,800 rubles;
- laser removal – 5,000 rubles;
- cryodestruction – 2,000 rubles.
The cost of other types of operations is discussed on a case-by-case basis with representatives of the selected clinic.
Symptoms
Xanthelasmas of the eyelids are rounded plaques slightly protruding above the surface of the skin, pale yellow in color, and their consistency is soft. The size of such formations can vary from several millimeters to 1.5 cm; the elements themselves can be either single or multiple. In some patients, xanthelasmas may appear as a solid yellowish stripe extending onto the bridge of the nose.
Xanthelasmas in the lower eyelid area (xanthomas) are rarely isolated; they usually occur in addition to the same formations located on the upper eyelid and are a manifestation of xanthomatosis. Patients with xanthelasmas of the eyelids do not present any complaints; the formations are painless and represent mainly a cosmetic defect. Once occurring, xanthomas and xanthelasmas remain for life, very slowly increasing in size.
Diagnosis of the disease
The first thing to do when xanthelasma manifests itself is to make an appointment with a specialist.
After a visual examination, if xanthelasma is suspected, the doctor performs diascopy. The formation is pressed down with glass to bleed it so that the yellowness appears more clearly. Examinations are needed to exclude suspicions of a malignant neoplasm, syringoma, or elastic pseudosanthoma.
Additionally, a blood test for lipid spectrum is prescribed.
It is necessary to identify the risk of developing atherosclerosis, heart attack, and hypertension.
Let's clarify
| Question | Answer |
| Is it possible for xanthelasma to degenerate into a malignant neoplasm? | The patient is not in danger of such degeneration. |
| What complications accompany plaque removal? | There may be bleeding or scarring of the skin at the site of removal. It depends on the skill of the doctor and the correct choice of method. |
| Is there a re-emergence? | Yes. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to carry out a course of special treatment and try to eliminate the provoking factors. |
| Who is at risk? | Women, people with chronic diseases, age category over forty-five. |
| What can be a contraindication to surgery? | The procedure should be postponed for pregnant women, if there is fever or inflammation. It is not recommended to do this if you have oncology or exacerbation of chronic diseases. |
| Is it worth exposing yourself to operational risk? | It is enough to compare photos of patients before and after surgery. Moreover, the risks are minimized. |
| What should be done to prevent this manifestation? | It is important to eliminate possible causes of metabolic disorders in the body.
|
| Is it possible to use decoctions and infusions of plants in addition to medications to reduce cholesterol? | Yes. Some plants contribute to this. Have fewer side effects than chemical drugs. But it can only be used strictly as prescribed by a doctor. Along with other actions, they stimulate bile secretion, so any violations of these organs can lead to serious complications. |
| Which removal method is most popular? | The use of a laser is highly effective for any size of formation and has minimal consequences, since the integrity of the tissue is practically not compromised. The last word always belongs to the specialist. |
| Does laser pose a threat to the eyes? | The laser beam precisely targets the problem area. The mucous membranes of the organs of vision are not in danger. |
| What determines the cost of the operation? | The price for this service is dictated by the chosen removal method and the size of the growth. The larger it is, the more expensive it is. The category of specialist and the level of equipment used also have an impact. |
Diagnostics
Patients with xanthelasma of the eyelids need to consult not only an ophthalmologist, but also an endocrinologist and a dermatologist. The examination must include a general blood test, a study of lipid metabolism (level of lipoproteins and cholesterol in the blood serum).
The characteristic appearance of the formations usually does not pose any difficulties in making a diagnosis. In addition to xanthelasmas and xanthomas, the patient is often diagnosed with obesity, hypertension, metabolic syndrome or diabetes mellitus. Xanthelasma of the eyelids must be differentiated from other similar skin diseases (syringoma, pseudoxanthoma), incl. malignant tumors.
Reasons for the development of xanthelasma
The factors causing the appearance of xanthelasma have not been sufficiently studied. However, in the course of a considerable number of clinical studies, a relationship between the defect and metabolic disorders caused by the deposition of fats in the epidermis was revealed. It has been noted that xanthelasmas are more often detected in people suffering from diabetes mellitus, obesity, liver cirrhosis, myxidema and pancreatitis. Xanthomatosis can be inherited and in this case it manifests itself already in the first year of a child’s life.
Who is at risk?
Most often, xanthelasma occurs in middle-aged and elderly people. As a rule, the “victims” are women who have crossed the age mark of 45 years and suffer from diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia (abnormally high levels of lipids in the blood). However, plaques around the eyelids can also form in men.
Treatment of xanthelasma of the eyelids
Since xanthelasmas and xanthelomas in most cases accompany lipid metabolism disorders, liver disease, etc., it is imperative to treat the underlying disease. It is recommended to follow a diet limiting the consumption of animal fats and replacing them with vegetable fats. If hypercholesterolemia is detected, drugs that normalize lipid metabolism (statins, lipoic acid, berlition) are prescribed. The use of drugs that normalize liver function (choleretic agents, Essentiale, multivitamins) is indicated.
There is no drug treatment for xanthelasma of the eyelid; the formation (at the request of the patient) is removed using a laser, electrocoagulation or surgery. The intervention is performed under local infiltration anesthesia. During removal, a specialist uses tweezers and miniature scissors to separate the base of the plaque, then treats the skin in the wound area with an antiseptic. If the size of the lesion to be removed is not large, the edges of the wound are treated with a solution of iron albuminate, which promotes effective healing. In the case of a more extensive wound surface, its edges are treated with electric current (diathermy) or cosmetic sutures are applied.
Possible complications after xanthelasma removal
- Relapse of the disease. If high blood cholesterol levels are not changed and lipid metabolism is not normalized, xanthelasma may return. It is in order to prevent this that the patient is recommended to switch to a diet that is suitable in this case (vegetable protein);
- Formation of a scar (hypertrophic or keloid) at the suture site after surgical removal of the plaque (possible with a predisposition to the formation of keloid scars).
As a rule, treatment of xanthelasma is complex, and the risk of complications is quite low.
Advantages of xanthelasma treatment and prices at MGK
By contacting the Moscow Eye Clinic, you can be assured of a quick and reliable diagnosis of xanthelasma of the eyelid and its effective treatment. Removal of xanthelasma of the eyelid can only be performed by a specialist with appropriate professional skills. To avoid possible complications, this procedure should be entrusted to an experienced doctor. At the Moscow Eye Clinic you will be able to undergo all the necessary tests, based on the results of which the attending physician will recommend you the most effective treatment methods. The Clinic employs specialists with extensive professional experience who enjoy well-deserved respect both among colleagues and among patients.
Removal of xanthelasma of the eyelid is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. During the operation, sterile instruments and disposable consumables are used, which eliminates the risk of infectious complications.
Author:
Yakovleva Yulia Valerievna 5/5 (1 rating)
Honey. portal:
Methods for removing xanthelasma of the eyelids
Removal of eyelid xanthelasma is carried out using different methods on an outpatient basis:
- Traditional - using a scalpel. Surgical intervention is accompanied by suturing. Scar formation is possible. Bleeding inevitably occurs and there is a possibility of infection. This method is used for large growths or if there is sagging of the upper eyelid. At the same time, formation and excess skin are removed. There is a possibility of relapse. Therefore, plaque fusion should not be allowed to occur.
- Low temperature most often uses liquid nitrogen as a refrigerant. At a temperature of minus one hundred and ninety degrees, freezing and destruction of the structure of the fatty plaque occurs with excellent cosmetic consequences. It is difficult to protect the eye from cold temperatures, but there is minimal risk of infection.
- Radio waves act with waves of a given frequency. Under the influence of heat emanating from a thin electrode, the neoplasm cells die, providing a good aesthetic effect. Minimal risk of complications and recurrence after resection.
- A chemical is used to burn out the plaque, usually using trichloroacetic acid. Rarely used due to the risk of the reagent getting into the eyes.
- Electrocoagulation works using high frequency current. An electrode is placed on the tumor, current is applied to it, and the cells of the growth are destroyed. The cauterization site finally heals after ten days. Special ointments are applied to it. The method is suitable for small formations. There is no risk of retinal burns.
- Laser evaporates the formation with a laser beam. The method of laser treatment of tumors is considered today the most effective and safe, but quite expensive. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The patient's eyes are protected with special glasses. The wound heals under a crust in a few days. An experienced doctor is able to remove all formations in one visit.
Advantages of laser xanthelasma removal:
- No injury to adjacent tissues of healthy skin;
- bloodless, sterile method;
- high accuracy of the beam hitting the affected area to the required depth;
- absence of scars;
- fast recovery;
- harmless to the mucous membranes of the eye.
Benign neoplasms on the eyelid
More than half of all tumors on the eyelids are classified as safe formations.
They vary in size. Some are almost invisible, while others grow very large and sometimes even interfere with opening your eyes normally.
The easiest way to find out what kind of neoplasm has appeared on the lower or upper eyelid is from a doctor. The dermatologist will tell you in detail about the types of formations and their dangers.
Tumors often form on the eyelid:
- Acquired moles
These neoplasms are formed from melanocyte cells. They never appear at birth - only in childhood. During puberty they darken, and in the third decade of life they rise slightly above the skin. In old age they lose color, but do not disappear.
They usually do not need to be treated. Moles rarely develop into cancerous tumors. In such cases, they must be removed.
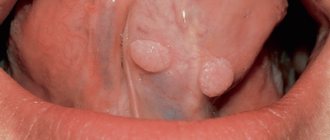
- Papillomas
Neoplasms with legs or a wide base. Either one papilloma or a whole cluster can grow on the eyelid. Appears due to the papilloma A virus and is especially common when the immune system is weakened. Sometimes the formation degenerates into cancer.
- Keratoacanthoma
Dense red growth, up to three centimeters in diameter. There is a small depression in the center of the formation. Often several tumors grow at once, not only on the face, but also on the neck and arms. Usually the formation disappears on its own. After it, an atrophic scar remains. In rare cases, the formation develops into squamous cell skin cancer.
- Seborrheic keratosis
Appears for an unknown reason. The surface of oval or round formations is similar to crust, wax or scales. Neoplasms develop only in older people. No removal required. Only if itching occurs or due to cosmetic discomfort.
- Fibroma
A smooth nodule on a thin stalk, which is formed from connective and fibrous tissue. It grows slowly. Diameter up to several centimeters. Almost never degenerates into a malignant formation.
- Lipoma
One of the varieties of these formations grows on the skin - soft tissue lipoma. Most often on the upper eyelid. A soft and mobile neoplasm of yellow color.
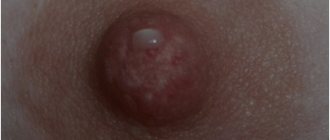
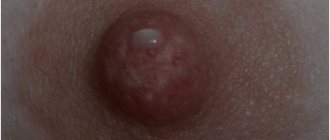
- Hydrocystoma
This formation is also known as a sweat gland cyst. The standard size is up to four millimeters, although some formations grow more than ten millimeters. The neoplasm on the eyelid looks like a dome-shaped nodule with a bluish tint.
Of course, the formations described above are unlikely to please you with their appearance, but for the most part they are harmless. Some are reborn, but extremely rarely.
Cancers are much more dangerous.
Diagnosis of eye tumors
Since neoplasms are caused by a variety of reasons, the diagnosis must be comprehensive. First of all, it is necessary to conduct a urine and blood test. This will provide information about the general state of health and the presence of diseases that can manifest themselves in the form of neoplasms.
At the same time, you need to contact an ophthalmologist and examine the organ of vision using special equipment. The doctor will determine the condition of the tear ducts, retina, and fundus of the eye. In general, diagnosis is performed by exclusion.
Causes of fatty hernias of the eyelids
The main reason that results in fatty hernias of the lower and upper eyelids is the constant contraction of the facial muscles responsible for maintaining the skin of the eyelids in the required position, which leads to their stretching. Even if a person carefully monitors the condition of his skin and performs the necessary procedures to maintain its tone, it is impossible to stop this process. The only thing that can be done is to slow down the speed of this process.
In the process of filling saggy soft tissues with subcutaneous fat, a person develops a disease such as lymphedema - a violation of the outflow of lymphatic fluid, impairing the ability of blood to circulate in the required quantity in the eyelid area.
As mentioned above, age negatively affects the quality of the skin around the eyes, and given the fact that there are a small number of sebaceous glands in the eyelid area, which makes it quite dry, ptosis occurs much earlier than in other areas of the skin.
A significant role in this process is played by the structure, complexion of a person and the genetic characteristics of the skin.
Factors such as:
- frequent exposure to stressful situations;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- lack of the required amount of sleep;
- work that requires visual concentration;
- hormonal imbalance;
- prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, visiting solariums;
- use of cosmetics that are not suitable for your skin type;
- frequent use of decorative makeup;
- smoking.
If a person suspects the formation of fatty hernias of the eyelids, then to establish the correct diagnosis, he should consult a specialist. Fatty hernias of the eyelids are easily confused with other lymphatic edema of the eye area, which can be caused by dysfunction of the cardiovascular system of the body.
Prevention
It is impossible to prevent the appearance of such formations. This will not succeed due to the differences between the reasons that cause the formation of seals. After all, it cannot be ruled out that dust particles, grains of sand or the development of pathologies of the arterial system will enter the eyelid. At the same time, the immune system should be strengthened, which will prevent the development of the disease.
General strengthening procedures will be effective means of prevention. For example, taking vitamin complexes, giving up bad habits such as smoking or drinking alcohol. A proper diet is also important, avoiding fatty and toxin-laden foods.
In addition, you need to protect yourself from the sun's rays by using safety glasses and caps. This will prevent the development of melanoma, which is a malignant tumor.