Human papillomavirus is one of the most common, along with herpes, chronic infections. Therefore, HPV testing is in great demand in the diagnosis of many diseases. Tests for all types of human papillomavirus are carried out in our clinic daily.
The main types of human papillomas:
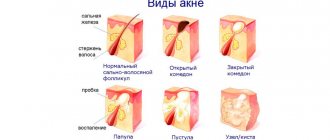
- Skin papillomas: Ordinary thread-like, on a thin stalk. Most often located in the armpits, neck, eyelids, mammary glands and groin
- Flat papillomas are the color of the surrounding skin and rise slightly above it. They are mainly found on the fingers of the limbs and hands.
- Warts are papillomatous formations with keratinization on the surface. They can be everywhere, but more often on the limbs. They especially cause problems when they are located on the soles of the feet and around the nails.
All these types of papillomas develop in the presence of various types of human papillomavirus, detected using special laboratory diagnostics, which will be discussed.
Causes of the disease
A virus is an infection, which means that in order for it to appear in the body, infection must occur.
HPV penetrates the skin and mucous membranes of a healthy person upon their contact with the papillomas of a patient or with visually unchanged skin and mucous membranes of an infected person, provided that there is a large amount of virus at the site of contact and there is damage to the integrity of the epithelium (abrasions, scratches, wounds, erosions, sores). HPV infection is especially common in the presence of herpes simplex rashes, through which the human papillomavirus penetrates the skin and blood.
What tests should I take for HPV?
In our clinic we perform the following tests for human papillomavirus:
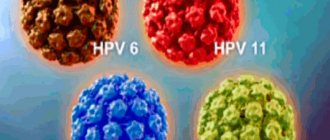
- PCR analysis for HPV types 6 and 11 - a scraping is taken from rashes or mucous membranes of interest to the doctor. The material is placed in a test tube and examined within 1–2 days. Depending on how the analysis is performed, the answer may be:
- Positive - when a virus is detected, indicating the specific type
- If a quantitative method was used, then indicate how many viral particles were detected
Negative - in the absence of HPV in the test material
HPV viruses types 6 and 11 belong to the group of low oncogenic (carcinogenic) risk and, basically, only cause the growth of genital warts or genital warts, which rarely develop into cancer.
The price of analysis for HPV types 6 and 11 is from 300 rubles. for qualitative analysis.
The result of the diagnosis can be either the detection of a certain type of virus or its quantity.
Human papillomaviruses types 16 and 18 are among the most malignant in terms of oncogenic risk and more often than others lead to the development of cancer of the cervix, skin and mucous membranes. Therefore, they are allocated to a separate diagnostic group.
The cost of testing for HPV types 16 and 18 is from 300 rubles. for a qualitative diagnostic option, 800 rubles for a quantitative one.
The analysis period is from 1 day.
- Qualitative without determining the type - the analysis will simply show whether there are viruses of these types in the scraping of cells without detailing
Qualitative with type determination (with genotyping) - the result will contain an indication of the presence of a specific type of HPV
The cost of analysis is from 900 rubles. for a quality option.
Clinical characteristics
The HPV family attracts the close attention of doctors because viruses initially cause benign neoplasms on affected surfaces.
But in the future, they can become the cause of the development of malignant processes.
Among viral infections, they are second only to genital herpes in prevalence.
HPV is mainly transmitted through sexual contact and is more common in women.
The pathogen can be transmitted by any type of sexual contact: oral, vaginal, and anal sex.
For the most part, this pathogen manifests itself as a seemingly harmless process in the form of warts (and on the mucous membranes of the genitals - genital warts).
But certain types of HPV can cause various malignant pathologies (for example, squamous cell skin cancer, cervical cancer).
Infection of a person with one (or several at once) HPV occurs unnoticed.
The incubation period ranges from a week to six months.
Thanks to immunity, after a few months in 70-80% of people the disease completely disappears, leaving no consequences.
But in approximately 15-20% of those infected with HPV, warts and condylomas remain and progress.
In women, erosions also occur on the cervix.
Under unfavorable circumstances, after 5-10 years, cervical cancer forms in this place.
Or a tumor of the skin or mucous membranes.
The risk of malignant transformation is highest for HPV types 16 and 18.
These two types of pathogens in almost 100% of cases lead to cancerous degeneration of tissue at the site of infection.
In addition to them, types 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68 are considered papillomaviruses with a high risk and level of oncogenicity.
There are 5 types of HPV that pose a low risk: 6, 11, 42, 43, 44.
When is the material collected?
The method of collecting material for diagnosis and the material itself in general depend on the manifestations of human papillomavirus infection.
If there are elements on the skin and visible mucous membrane, then using a universal urogenital probe, a dermatovenerologist or gynecologist scrapes cells from the surface of the papilloma. The resulting cells are placed in a tube for delivery to the laboratory and PCR analysis for HPV. The manipulation is absolutely painless and takes about 30 seconds.
When diagnosing papillomavirus infection in the urethra, vagina, cervical canal, especially in the presence of cervical erosion, scraping is carried out from these organs, preferably from the erosion itself.
If papillomas are present on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity or rectum, then material is taken from these areas with a probe.
If it is necessary to diagnose diseases of the prostate gland or bladder, urine and prostate secretions can be taken for HPV.
How is an HPV test done by scraping?
This diagnosis depends little on previous training. Although it would be nice if you exclude the effect of antiseptics on the skin and mucous membranes from which the doctor will scrape cells.
At an appointment with a dermatovenerologist, venereologist, urologist or gynecologist, epithelial cells are collected using a special probe from the area of interest:
- Urethra
- The head of the penis, especially rashes, erosions, ulcers on it
- Skin of the penis with rashes
- Skin of the anal area, rectal mucosa
- Labia majora and labia minora
- Vaginal mucosa
- Cervical canal
- Vaginal part of the cervix
- Mucous membranes of the cheeks, tongue, lips, gums
- Mucous membrane of the oropharynx, nasopharynx, larynx.
All manipulations are absolutely painless and low-traumatic.
Only the doctor collects the material! In our clinics, we do not even trust nursing staff with this procedure, because for the quality of the analysis, the scraping itself is even more important than further research.
When examining for human papillomaviruses, you need to take into account, among other things, the following points:
- HPV causes not only the growth of papillomas, condylomas, the development of erosions and cervical cancer. It is associated with a lot of other diseases and clinical manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Therefore, it is worth listening to a venereologist, urologist or gynecologist, who, for a certain clinical picture in a patient, prescribes tests for HPV of one type or another, or a complex test for HPV (human papillomavirus).
- The same person may have several types of HPV, and not all of these types will necessarily manifest themselves simultaneously clinically and be detected in the analysis.
- Therefore, after treatment, it is necessary to undergo a detailed test for HPV, and not be limited to one type, which was determined during the initial diagnosis.
- Sexual partners of patients infected with human papillomavirus are also tested for all types of HPV.
Only your doctor will determine what types of HPV tests you need to take. This depends on the clinical manifestations of the infection, the type of papillomas, the location of the elements and the results of the examination of the partner, if any.
Digen test
In gynecology, there are more than 100 genotypes of the human papillomavirus. Infection of a woman or man may not have clinical manifestations, and sometimes there is a natural cleansing of the pathogen from the body, especially at a young age. But the presence of HPV in the cervical epithelium for a long time can cause its structural atypical changes. Cervical oncology is one of the few types of malignant neoplasms for which a causal relationship with infection with certain types of papillomavirus has been established. To diagnose the most dangerous HPV oncotypes, a Digene test is performed. This method reveals the level of presence of papilloma viruses in the genital organs, leading to the development of neoplastic and atypical processes in the cervical canal and cervix.
The clinic offers 2 types of Digen test:
- “Digen test” is a comprehensive diagnosis of infection of the body with HPV types of high oncogenic risk with genotyping by subgroups indicating quantitative values (the so-called “viral load);
- “HPV Digen test + PAP” is a comprehensive screening test used to identify the type and number of viral particles, as well as to predict precancerous conditions of the cervical canal and cervical cancer, see more here.
HPV complex
| Daijin test | Price | |
| HPV 6/11 | qualitative | 6 200 |
| HPV type determination (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59) | genotyping | |
| HPV quantification (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68) | quantitative | |
| PAP - Digen test | Price | |
| HPV strains 6/11 | qualitative | 8 200 |
| HPV type determination (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59) | genotyping | |
| HPV quantification (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68) | quantitative | |
| Cervical cytology | 2 points | |
Decoding the result of the Digen test
A positive Digene HPV test (+) result in girls under 30 years of age is an indication for repeating the test after 6-9 months, since in young women the infection can be transient.
Positive results of the Digene HPV test (+) in women over 30 years of age may indicate the constant presence of the virus in the body. With certain results of Pap testing, this means that this patient has a high risk of developing cervical cancer and requires additional examination (see HPV screening table below) and special therapy.
HPV test
| HPV screening / Methodology / Price | Standard | Liquid |
| Extended HPV test (with determination of the amount and type of virus, “Digen test”) | 6 200 | 6 500 |
| HPV-PAP test (extended HPV test complex with determination of the amount and type of virus + PAP test) | 8 200 | 8 500 |
| HPV test (with quantification and separate detection of 16 and 18 types of virus) | 4 500 | |
| Coexpression of p16/Ki67 oncoproteins | 8 500 | |
How is the disease transmitted?
You need to know this in order to correctly prescribe a diagnosis. There are many ways of transmission. The virus can be located on any part of the skin or mucous membrane, that is, where there are epithelial cells.
The most common ways of transmitting the human papillomavirus are:
- Sexual vaginal contact.
- Anal sex.
- Oral sex (including cunnilingus) - possible infection of the pharynx and larynx with the development of oncology of these organs.
- Kiss in the presence of microtraumas of the mucous membrane.
- From mother to fetus as it passes through the birth canal.
- In case of close contact of damaged skin with papillomas of another person. The lesions may not be noticeable and often form during sexual contact in the pubic area, scrotum, and labia, which makes it possible to become infected with HPV when using a condom.
- Transfer of the virus from the surface of warts to damaged skin.
Virus prevention
It is possible to prevent both primary infection and infection of a healthy sexual partner, as well as recurrence of human papillomavirus infection.
To prevent the virus from entering during sexual intercourse, it is necessary to use a condom and avoid contact of the skin of a healthy person with areas where there are papillomas in an infected person.
Timely removal of manifestations of papillomavirus infection - papillomas and condylomas - will help reduce the risk of infection. This, of course, does not completely get rid of HPV, but it reduces its amount on the surface of the skin. Antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy directed against the human papillomavirus can also help.
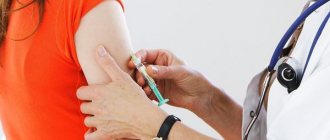
In adolescents who have not had sexual contact and do not have genital types of HPV, a special vaccine is used for prevention, which allows the immune system to produce antibodies against the virus, which prevents it from fixing in cells if infection occurs in the future. This reduces the risk of cervical cancer, which is very often associated with papillomavirus.
Prevention of skin papillomas can be achieved by timely treatment of scratches, abrasions, abrasions, calluses and other skin lesions with antiseptics, which allows you to close the entrance gate to the virus during tactile contact with a sick person.
Office photo
Useful articles
Interesting facts about medicine History of vaccination Vaccination is one of the greatest achievements of medicine, allowing to save 2 to 3 million lives annually. Preview picture in attachment Healthy lifestyle Medical examination: typical misconceptions About the importance of the correct approach to interpreting the results of a medical examination Healthy lifestyle Sleep - strong and healthy Simple rules that will help make your sleep complete.
Show more articles
Make an appointment
- More about the center
- Licenses and documents
- Our vacancies
- Contacts
- Ask a Question
- Leave feedback
- Territorial program
© 2002-2022 LLC 'Medilux-TM' - Network of medical centers | Site map All information, including prices, is provided for informational purposes and is not a public offer (Article 435 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 437 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)
INN: 7725100534 OGRN: 1037700249872
Medilux-TM LLC uses cookies (files with data about past visits to the site) to personalize services and provide user convenience. You can prevent the storage of cookies in your browser settings. MedSwiss takes the protection of personal data seriously - read the terms and conditions for processing it.
Accept user agreement
Get tested for HPV in Moscow with us
To plan preventive methods, of course, HPV diagnosis is important.
You need to know whether you have this virus or not in order to understand the risks for sexual partners and the prospects for the development of this disease. Therefore, even if there are no manifestations, tests for papillomaviruses are necessary during a full examination by a urologist or gynecologist. Where you can get tested for HPV: daily from 10:00 to 21:00 in our clinics, seven days a week and on holidays. If necessary, you can get comprehensive advice on the diagnosis and treatment of human papillomavirus infection from experienced urologists, gynecologists and venereologists.
What are the indications for diagnosis?
Tests are required as screening for women and girls who are characterized by: an active sex life, frequent changes of partners, antisocial behavior, lifestyle, and so on.
And also to those of them who have atypical cells found in cytological smears during medical examinations.
Men should also be periodically screened for HPV infection.
And if condylomas or warts appear in the groin, anus, or perineum, it is imperative to get examined.
In order to get tested for HPV, you need to contact an experienced and professional dermatologist or venereologist.
The doctor will conduct an examination, collect diagnostic material himself and send it for examination to an accredited and certified laboratory.