The family of human papillomaviruses (HPV) includes about one hundred types of pathogens (at least that is currently known).
They differ from each other in individual sections of genetic material; about 80 of them have been well studied by modern medicine.
According to some data, more than 60% of cervical cancer cases are associated with papillomaviruses.
Therefore, timely and accurate diagnosis of HPV infection is an essential component of the fight against tumors of the reproductive system of women and men.
Human papillomavirus - HPV test at the Paracelsus clinic, Aleksandrov
ATTENTION:
You can independently make an appointment with a doctor and for a diagnosis of COVID-19 in the Mobile application "PARACELSUS Clinic"
Online consultations with doctors (more than 18 specialties) are available.
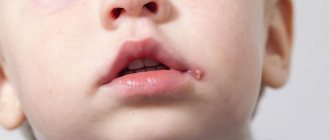
The term HPV (papillomavirus) refers to the human papillomavirus - a group of different types of related viruses that behave differently in the human body. Some of them are harmless and do not manifest themselves in the body, others are the direct cause of the well-known warts and condylomas, and others trigger the growth of malignant tumors.
The activity of papillomavirus in the body causes the growth of genital warts - skin formations of different sizes, which are localized in different areas, but mainly in the anal and/or genital area, oral mucosa in both men and women.
Each virus is assigned its own number or type; in general practice, there are 2 types of HPV:
- low oncogenic risk - types 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 72, 81.
- high oncogenic risk - 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73, 82 types.
The most serious are HPV type 16 and HPV type 18, which cause cervical cancer in women in approximately 70% of cases.
How to identify the HPV virus
In order to prevent fatal developments, it is necessary to be tested for HPV from time to time.
If suspicious foci are identified, no matter where - on the cervix in women or on the head of the penis in men, it is necessary to identify the type of pathogen (there may be several of them) and determine the number of virions.
Quantitative analysis of HPV also helps to make a forecast for malignancy (degeneration of the formation into cancer) - the more copies of the oncogenic HPV type in the sample, the higher the risk.
In modern dermatovenerology, it may be recommended to undergo several types of analyzes and tests:
- Cytology. This microscopy of cells from a suspicious lesion can find signs of cancer. Not suitable for identifying the type of viruses or early diagnosis at the stage of precancerous phenomena.
- Colposcopy with treatment of the lesion with acetic acid and Lugol's solution. Allows you to accurately determine the boundaries of the lesion.
- PCR analysis for HPV. An excellent molecular genetic method, which we will look at a little below.
- Serological tests. They are not very informative for clinical practice; they are more often used to conduct epidemiological studies on HPV.
Throughout the civilized world, a key role in the diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection is given to molecular genetic methods - PCR, Digene test.
How is HPV transmitted and what diseases can it lead to?
Human papilloma virus causes diseases:
- uterine cancer;
- condylomas;
- cervical cancer;
- genital and anal papillomatosis - the formation of warts;
- malignant neoplasms of the anus, penis, larynx, esophagus.
The disease is transmitted mainly through unprotected sexual contact. If the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes is compromised, a domestic method of infection in common areas through household items associated with high humidity (towels, handrails and the floor in a swimming pool, bathhouse/sauna) cannot be ruled out.
During childbirth, the mother's virus is transmitted to the newborn and can have a negative impact on psychophysical development. Therefore, it is important when planning a pregnancy to undergo examination and testing for HPV.
When and to whom should I give it?
The optimal age to start testing (PAP test and HPV test) is 21 years.
It is not recommended to examine younger women, due to the fact that in young women, in most cases, spontaneous elimination (“self-disappearance”) of HPV and HPV-associated lesions occurs. A PAP test must be taken annually.
It is important to test for HPV after each change of partner.
If we take into account that you have a monogamous relationship, and your HPV is negative, and there are no abnormalities in the cytological test result, then the next time a Pap test (and without an HPV test) can be done in 3 years.
But, of course, the frequency of examinations must be discussed with the attending gynecologist, because each case is individual!
You can stop the examination at the age of 69 years, provided that the results of previous examinations are normal and there are no diseases of the cervix for 20 years.
Diagnosis of HPV
Diagnosis and treatment of HPV in women is carried out by a gynecologist; men can consult a urologist and dermatovenerologist. To diagnose papillomavirus in the human body, Pap tests and HPV tests are used.
One of the ways to diagnose HPV in women is colposcopy, which allows you to visually assess the condition of the cervix and vagina.
If the presence of intraurethral formations is suspected, an endoscopic examination of the urethra may be indicated, and a biopsy for oncological diagnostic purposes.
How to prepare for the test?
It is recommended to take a smear no earlier than on the 5th day of the menstrual cycle and no later than 5 days before the expected start of menstruation.
Swabs should not be taken:
• earlier than 48 hours after sexual intercourse;
• during menstruation;
• earlier than 48 hours after using suppositories and other substances containing fat, vinegar or Lugol solution, tampons or spermicides;
• after a vaginal examination (pelvic ultrasound, colposcopy), douching;
• during the treatment of urogenital infections.
Indications for HPV testing
A person who is infected with HPV may not know about it for a long time. For example, genital warts may appear several weeks after exposure to an infected partner. In this case, the carrier of the virus may not know that he is infected, since he does not have any symptoms.
The incubation period is usually about 3 months, although latent HPV infection can remain in the body for years.
Signs that you should undergo HPV testing:
- the appearance of various formations and growths on the body;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- presence of blood after sexual intercourse;
- discomfort during bowel movements and urination;
- painful sensations during intimacy;
- itching, redness and discomfort in the vaginal and anal areas;
- spotting that is not associated with the menstrual cycle.
An additional indication is to monitor the effectiveness of antiviral therapy.
Testing is also included in screening for precancerous conditions.
Collection of biomaterial and preparation
The material that is taken for HPV analysis is epithelial cells, which are taken from the cervical canal in women, and from the urethra in men. For this purpose, a small diagnostic brush is used, which is inserted into the endocervix or into the urethra. After removing the brush, epithelial cells settle on its villi. The instrument with the resulting biopsy is lowered into a sterile container and sent to the laboratory. For the patient, the collection of material does not cause any particular discomfort, but if HPV is detected in the analysis, then the benefits of it significantly outweigh the discomfort.
You need to prepare specifically for an HPV test. Before the examination, you are not allowed to use antibacterial and antiseptic products for intimate hygiene, douche, use vaginal suppositories, or have intimate relations for two days. If the patient is undergoing antibacterial therapy or taking anticoagulants, you need to notify the doctor about this, the drugs may distort the result. Before collecting biomaterial, you need to urinate.
HPV testing method at the Paracelsus clinic
In Medical, 2 methods are used to determine the human papillomavirus: Real-Time and Digene HPV test.
Real-Time
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technique.
Real-Time measures the amount of viral DNA in the material being tested. The method is prescribed to identify viruses that are normally present singly in the body. Counting the number of viral particles provides a diagnostic result.
When diagnosing papillomavirus, PCR determines the number of viral agents at the time of the study. A high level of virus in the body increases the risk of tumor formation. The method allows the doctor to determine the correct treatment tactics for the patient.
HPV testing methods
In modern medicine there are several effective examinations for human papillomavirus. With their help, you can determine the presence of infection and find out the type of HPV. The patient is referred for testing for papillomavirus by the attending physician, a dermatologist, gynecologist or urologist.
The most common HPV tests are:
- colposcopy;
- histological diagnosis;
- cytological examination;
- amplification and non-amplification test;
- detection of antibodies to HPV.
Colposcopy is prescribed to women to detect papillomas localized in the cervix. Diagnosis is considered simple and routine microscopy of a sample of the vaginal and cervical mucosa at high magnification. The duration of the procedure varies from 10 to 30 minutes. The doctor hands over the results 10-15 minutes after the examination.
Histological diagnosis is almost always prescribed in conjunction with cytological tests. Using this method, a small biopsy sample is examined - a small fragment of tissue. After special treatment, the biomaterial is examined under a microscope to identify affected cells. This technique allows you to determine whether a tumor is malignant or benign. The duration of the manipulation takes no more than 15 minutes. The patient can receive the results 2-3 days after the examination. Most often, after histology, the patient is sent for a non-amplification test or PCR study.
To conduct a cytological examination, the doctor takes a smear of skin cells. The resulting material is examined under a microscope to detect modified cells and tissues that indicate HPV. The technique is simple and not expensive, but at the same time it quite often shows a false negative result. The result form is given to the patient after 4-6 days.
The amplification test in modern traditional medicine is considered accurate because it shows the type of infection and its oncogenicity. The sample is taken from the urinary canal or vaginal mucosa. This analysis is often prescribed by a gynecologist in conjunction with cytological diagnostics.
PCR analysis is used to determine the oncogenicity of a growth or papilloma. The biomaterial is urine, blood plasma, a smear from the mucous surface or amniotic fluid. The accuracy of the survey is close to one hundred percent. Human papillomavirus can be detected even with a small concentration of the pathogen in the sample. With the correct collection of biomaterial and accurate interpretation of the results, it is possible to know for sure whether there is HPV or not just 1-2 days after the manipulation.
Some patients are surprised when the test result is “positive”, but there are no condylomas on the body. This indicates that there is an infection in the body, but the immune system is restraining it in every possible way. Doctors recommend that if the result is “positive,” you undergo a course of treatment, and if there are papillomas, remove them using a laser or other methods.