Metrogyl gel: pharmacological properties
Metronidazole (1-(?-hydroxyethyl)-2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole) is an effective antibacterial and antiprotozoal agent from the group of nitroimidazole derivatives. Active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica
and
Giardia intestinalis
, as well as for obligate anaerobes -
Bacteroides spp
.
( B. fragilis, B. distansonis, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus), Fusobacterium spp., Clostridium spp., Peptostreptococcus spp., Peptococcus spp.
Inactive against aerobic microorganisms. The mechanism of action of Metrogyl is due to the biochemical reduction of the 5-nitro group of metronidazole by intracellular transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and protozoa. The reduced 5-nitro group of metronidazole interacts with the DNA of microorganisms, leading to their death. In the presence of mixed flora (aerobic and anaerobic bacteria), metronidazole acts synergistically with antibiotics active against aerobic microorganisms. Improvement usually occurs within 9 days of treatment.
Metrogyl for acne: instructions
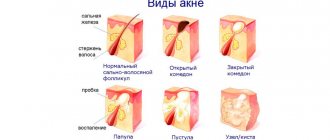
The list of symptoms for which the drug is indicated is quite extensive:
- rosacea (rosacea);
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the sebaceous glands;
- seborrheic lesions;
- ulcers of the lower extremities;
- long-term non-healing wounds;
- soft tissue necrosis;
- haemorrhoids.
Metrogyl is equally effective against acne and hormonal rashes. It can be used to prevent infection of open wounds, chapping of the face and other serious injuries.
You can only buy acne gel at the pharmacy. The product is available without a prescription, but it is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Metrogyl gel: method of application
a thin layer of gel is applied to a previously cleansed affected area of skin 2 times a day (morning and evening) and lightly rubbed. A pronounced clinical effect occurs after 3 weeks of therapy.
Metrogyl gel: contraindications
hypersensitivity to metronidazole, other nitroimidazole derivatives and other components of the drug; I trimester of pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Side effects
local reactions are possible - hyperemia, dry skin, burning sensation and skin irritation. When applied to the skin in the eye area, lacrimation may occur.
special instructions
Avoid getting the gel in your eyes. When applied to large areas of skin or with prolonged use, there is a possibility of resorption of metronidazole and the development of systemic side effects, so the drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with impaired hematopoietic function. If local reactions occur, the drug should be used less frequently or temporarily discontinued. Metronidazole penetrates well into breast milk, so it is not recommended to use Metrogyl during breastfeeding. After applying the gel, you can use cosmetics. During pregnancy, it is prescribed only if absolutely necessary.
Interactions
with external and intravaginal use of Metrogyl gel, an interaction due to systemic absorption of metronidazole is unlikely. However, when prescribing the drug to persons receiving anticoagulants, it should be remembered that metronidazole may enhance the anticoagulant effect of coumarin and warfarin, which leads to an increase in prothrombin time.
Overdose
no messages.
BIBLIOGRAPHY _
Akbulatova L.H. The pathogenic role of the Demodex mite and clinical forms of demodicosis in humans. // Bulletin of Dermatology, 1996, 2, pp. 57-61.
Akilov, O.E., Vlasova I.A., Kazantseva S.V., Features of the immune response in patients with dermatoses complicated by severe infestation of anthropophilic mites of the genus // Immunology. 2002. - No. 1. P.43-47
Ambartsum, AM Treating demodicosis / AM Ambartsum // New pharmacy. 2007. -№7. — P.32-35
Beridze, L.R. Changes in immune parameters in primary and secondary demodicosis of the skin // Georg. Med. News. 2004. - No. 6 - P.43-45
Bobrov V.M. Rosacea of the nose, complicated by demodicosis. Bulletin of Dermatology and Venereology 1994; 4:43-44
Butov, Yu.S., Akilov O.E. Clinical features and issues of classification of demodicosis of the skin // Ros. magazine skin and venereal diseases. 2003. - No. 2. — P.53-58
Vartapetov A.Ya. Follicular demodex in skin pathology. // Abstract report at a scientific-practical conference, Moscow Research Institute of Cosmetology of the Ministry of Health of the RSFSR. M., 1972, pp. 38-39
Vasilyeva M.S., Lange A.B. Iron mite populations in perioral dermatitis and rosacea. M: 2006; 135
Vasilyeva M.S., Shif L.V., Vardoyants S.A., Kanbarova L.I. About some clinical manifestations of demodicosis: New cosmetic preparations and treatment of diseases and cosmetic defects. Sat. scientific works of the hospital named after. Y.M.Sverdlova. L 1970; 45-48
Verkhoglyad I.V. Modern antiparasitic therapy of demodicosis // Clinical. dermatology and venereology. 2006. - No. 4. — P.89-90
Vostroknutova T.M. , Mokronosova M.A., Iron mites and problematic facial skin // Attending physician. -2007. No. 9. — pp. 10-12
Zhsltikova, T.M. Is demodicosis a diagnosis or a symptom? // Medical Bulletin. - 2006. - No. 38. — P. 16
Clinical recommendations, Dermatovenereology /edited by A.A. Kubanova// M.: DEX-Press, 2010.-206-209, 230-233
Kogan B.G., Gorgol V.T. Specificity of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis mites, the causative agents of human demodicosis. // Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology, 2001, 21, pp. 37-41.
Kogan, B.G., Gorgol V.T. Diagnosis of demodicosis // Dermatology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology, - 2008. No. 1-2 (11).- P. 286-287
Koshevenko, Yu.N. Demodicosis pseudo-problem of dermatocosmetology // Ros. magazine skin and venereal diseases. - 2004. - No. 4. — P. 6469
Loshakova, V.I. Demodicosis is an urgent problem of modern dermatocosmetology // Vestn. postgraduate honey. education. — 2001. -№1. - pp. 79-80
Petrosyan E.A., Petrosyan V.A. Treatment of rosacea complicated by demodicosis with blood extracorporeally modified with sodium hypochlorite. Vestn Dermatol 1996;2:42-44.
Polunin G.S., Kasparova E.A., Polunina E.G.: Clinical effectiveness of blepharogels in the prevention and treatment of blepharitis. New in ophthalmology No. 1, 2004, pp. 44-47
Akilov OE, Mumcuoglu KY Immune response in demodicosis. //J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol., 2004, v.18, N4, p.440-444
Aylesworth R., Vance JC Demodex foliculorum and Demodex brevis in cutaneous biopsies. //J.American Academy of Dermatology, 1982, v. 7, n. 5, p. 583-589
Ayres J, Ayres S (1961) Demodecidosis in the human. Arch Dermatol 83:816–27
Bassiouni SO, Ahmed JA, Younis AL, Ismail MA, Saadawi AN, Bassiouni SO A study on Demodex folliculorum mite density and immune response in patients facial dermatoses. // J. Egypt Soc. Parasitol., 2005, v.35, N3, p.899-910
Forton F., Cermaux M.A., Brasser T. Et al. Demadecosis and rosacea: epidermiology and significance in daily dermatologie practice. J Am Acad Dermatol 2005; 1:74-87
Forton F., Seys B. Density of Demodex follicolorum in rosacea: a case-control study using standardized skin-surface biopsy. // British J. of Dermotology, 1993, v.128, p.650-659
Kligman AM, Christensen MS Demodex folliculorum: Requirements for Understanding Its Role in Human Skin Disease. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2011; 131:8–10
Kogan BG, Stepanenko VI, Gorgol VT, Pavlyshin AV Role of Demodex mites and Helicobacter infection in etiopathogenesis of rosacea, demodicoses, perioral dermatitis and acne disease. Eur Acad Dermatol Venerol 2003; 15(3): 165.
Lacey N, Kavanagh K, Tseng SC. Under the lash: Demodex mites in human diseases. Biochem (Lond). 2009; 31(4): 2-6
Nutting WB Pathogenesis associated with hair follicle mites (Acari: Demodicidae) // Acarologia, 1975, V.17, p.493-507
Rodriguez AE, Ferer C, Alio JL Chronic blepharitis and Demodex. //Arch. Soc. Esp. Oftalmol, 2005, v; 80, N11, p. 635-42
Rufli T., Mumcuogly Y. Tile hair follicle mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis: biology and medical importance // Dermatolog., 1981, p.162
Is it possible for pregnant and lactating women?
The pharmaceutical product "Metrogil" can be used in the treatment of demodicosis by pregnant women, but subject to the rules prescribed in the instructions attached to the gel, in order to protect yourself as much as possible from possible side effects. Despite the fact that this medication is safe, specialized doctors still do not recommend using it in the first trimester of pregnancy. Treatment of skin lesions by Demodex mites with the drug "Metrogil" at the beginning of pregnancy is recommended only under the supervision of the attending physician and in cases where the benefit for the expectant mother significantly outweighs the possible risk for the baby in the womb. If you are breastfeeding, you should abandon Metrogyl and use its safer analogues to treat demodicosis.
Is it worth using Metrogyl gel?
If you survey those who have already used Metrogyl acne gel, the reviews will contain the following advantages:
- pronounced anti-inflammatory effect;
- improvement of the general condition of the skin;
- fewer rashes already in the first month of use;
- rapid healing of wounds and abrasions.
If there are no visible improvements within three weeks, contact your dermatologist; you may need to use additional products to enhance the effect of the gel or choose a different drug.
The result of treatment depends on many factors: the causes of the rash, the severity of the disease, the individual characteristics of the body and compliance with the rules of use.
The best drugs for demodicosis
To treat and prevent this infectious disease, external and oral agents can be used. The action of most of them is aimed at destroying pathogens, relieving inflammation, and suppressing the main symptoms. Which gels, ointments, creams, tablets are best to use depends on the degree of skin damage. Judging by the reviews, the best remedies include such medications as:
- Zinc, Sulfur, Ichthyol ointment, ointment;
- gel Metronidazole, Oftagel, Demoten, Blefarogel;
- tablets Ornidazole, Trichopolum;
- eye drops Carbachol, Tobrex, Acular, Dexamethasone.
Detrimental to infection are agents that contain carbolic acid, ether, creosol, tar, sulfur, medical alcohol, and salicylic acid. You can become infected with ophthalmodedecosis through contact with a sick animal or person. If your pet is sick, it must be treated. In such cases, Aversectin ointment helps well.
Composition and properties
The drug "Metrogil", used for the treatment of demodicosis, is produced in tubes with a gel-like consistency inside and contains the following components:
- metronidazole;
- high molecular weight carboxyvinyl polymer;
- caustic soda;
- denodium edetate.
The gel product effectively fights demodicosis.
Penetrating into the pathological environment, these substances have a detrimental effect on microorganisms, which is necessary for demodicosis and other dermatological problems. The antibacterial property of the described gel helps with infectious lesions of the skin, accumulation of pus and mites that have settled on the dermis. The drug also has an antioxidant effect, which creates a protective barrier for the epidermis from the negative effects of radicals and hydroxyl on it.
Analogues of the drug
- "Trichobrol";
- "Deflamon";
- "Metron";
- "Bacimex";
- "Metronidal";
- "Flagyl";
- "Dentamet";
- "Klion";
- "Efloran";
- "Metroseptol";
- "Rosex";
- "Metronidazole";
- "Trichosept";
- "Rozamet";
- "Orvagil";
- "Trichopolus";
- "Siptrogil."
Causes of demodicosis of the eyes
This disease can appear as a result of internal factors:
- decreased immunity after illness;
- chronic microbial and viral diseases;
- the appearance of foci of infection in the body, for example, untreated caries;
- eye refractive diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- acne;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems;
- diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
External factors can also trigger the appearance of demodicosis of the eyes:
- previous ophthalmic surgeries;
- dirty, dusty air;
- high air temperature;
- unhealthy lifestyle, alcohol abuse.
Untreated demodicosis can lead to keratitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, blepharitis and visual impairment. A deficiency of tear fluid is dangerous for the development of secondary infection.