- What is nail hyperkeratosis?
- Causes
- Treatment methods for hyperkeratosis of the nail plate
Hyperkeratosis of the nail bed is an excessive thickening of the stratum corneum against the background of slow desquamation of dead cells. As a result, the nail takes on a spherical shape, its color becomes yellow and uneven, and the nail plate becomes brittle and inelastic. The disease occurs in a chronic form. The pathological focus can spread to neighboring structures - affecting other nails and skin of the foot. Against the background of mycoses, itching and an unpleasant odor are possible.
Ingrown toenail: from acute pain to slight gait
“It would seem that only the big toe should suffer from an ingrown toenail. But it was not there. The whole foot of a person hurts. And it doesn’t just hurt, but the pain is exhausting and does not allow you to think about anything else, does not allow you to be distracted and forgotten for a minute” [1].
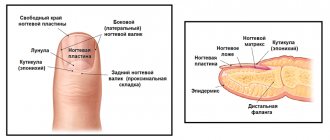
| Ingrown toenail (onychocryptosis) – a common inflammatory disease of the periungual folds and nail plates of the toes. Mostly occurs on the big toes. Ingrowth occurs in the lateral direction, which leads to injury to the soft tissues of the nail fold and, subsequently, to tissue proliferation with the development of chronic inflammation and suppuration in the area of ingrowth. |
“Why does an ingrown toenail cause such suffering? The fact is that there are many sensitive nerve endings in the tissues of the fingertips. Therefore, an ingrown toenail, especially when walking in tight shoes, makes itself felt by excruciating pain, sometimes causing a person to limp. Growing into the surrounding soft tissues, the lateral edges of the nail plate irritate and damage them until ulcers form.
How severe the pain is depends on the degree of inflammation
. Most often, the nail grows from the outside, where it experiences pressure from tight shoes. Initially, pain appears along the edge of the nail. Redness and swelling of the soft tissues occurs in this area. When pressing on the site of inflammation with a finger or wearing shoes, pain occurs. Over time, it becomes constant and interferes with normal walking.
suppuration may also occur.
. Due to the proximity of the bone of the phalanx of the finger, there is a risk of developing inflammation of the periosteum of the phalanx - periostitis, and even inflammation of the bone itself - osteomyelitis" [1].
How to treat onycholysis?
The sooner you contact a podologist or dermatologist to identify the cause of nail detachment, the higher the chances of successfully eliminating the problem.
During the restoration of fingernails or toenails, there is a strict ban on any traumatic procedures, nail extensions, the use of decorative varnishes and aggressive chemical liquids.
If fungal spores have entered the cavity under the nail and onycholysis is infectious in nature, then treatment for onychomycosis is prescribed by a dermatologist.
If the nail plate on your ring finger periodically comes off, then there is a possibility that you need to seek treatment from an endocrinologist and adjust your hormonal levels.
Etiology of ingrown toenail
“Currently, there is a unified point of view on the causes of ingrown toenails.
No. There is an opinion that ingrown toenails are a hereditary disease and can be passed on from generation to generation among members of the same family.
According to most authors studying this problem, the main reason
This disease is an anatomical disproportion between the growing nail plate and the nail bed.
At the same time, it is obvious that anatomical discrepancy and this disproportion, in turn, can be a consequence of the influence of a variety of factors. These factors
include:
- impaired blood flow in the first toe,
- edematous syndrome with an increase in the volume of soft tissues of the finger,
- hyperhidrosis of the feet, which contributes to maceration of the stratum corneum of the skin of the nail folds,
- an innate tendency to narrow the nail bed and excessive mobility of the nail folds themselves.
It is possible that infection of the nail sinus
, which can support the inflammatory process in the area of the nail fold, promoting its swelling and infiltration.
To factors
that contribute to the development of ingrown toenails, a number of authors include:
- flat feet,
- arthrosis of the metatarsophalangeal joint and hallux valgus,
- osteoporosis of the terminal phalanx of the first toe, although, as practice shows, a significant proportion of patients do not have these diseases.
- pressure from tight or uncomfortable shoes with the effect of chronic compression and impaired blood and lymph circulation,
- improper cutting of the nail - cutting the free edge of the nail too deep,
- prolonged exercise (walking or standing) with congestion in the feet,
- infection and onychomycosis,
- chills or frostbite of the feet,
- microtraumatization of the nail matrix or soft tissues.
Thus, according to most authors, ingrown toenails should be considered as a disease with many causative factors
, however, it should be noted that
almost all patients with this pathology are characterized by the presence of an infected sinus between the edge of the nail plate and the skin of the nail fold
. The presence of such a sinus in the form of a narrow slit, especially as its depth increases, probably makes it difficult to carry out adequate hygienic measures for the patients themselves and to perform effective sanitizing procedures in these nail sinuses for medical personnel. All this, along with the above factors, can be the basis for the development of inflammation with an ingrown toenail.
Causes of ingrown toenails in children
- Insufficient care - it is necessary to regularly trim the plate evenly, without rounding.
- Lack of vitamins in the diet - deformations of the nail occur, it injures soft tissues.
- The appearance of fungus means the surface becomes uneven, increasing the risk of developing pathology.
- Flat feet - the uniform distribution of the load on the foot is disrupted.
- Rickets - too thin and brittle nails.
- Incorrectly selected shoes are narrow, tight, which compress the foot and lead to ingrown hairs.
- Genetic predisposition - if close relatives have a tendency to ingrown nails, you need to carefully monitor your baby’s nails.
- Trauma - if a child hits or injures a finger, pathology may occur.
Clinical picture and diagnosis
An ingrown toenail is characterized by complaints of pain in the area of the 1st finger.
, especially when walking, which makes it difficult or impossible to use normal shoes.
Local manifestations are characterized by hyperemia and swelling
of the nail fold on the affected side.
Most often, the lateral edge of the nail
, but a number of patients have
bilateral lesions - the medial and lateral edges of the nail
.
The most common complication of an ingrown toenail is the presence of purulent inflammation.
in the area of the nail folds in the form of paronychia, the presence of pyogenic granulomas and maceration of the skin of the finger.
Differential diagnosis for ingrown toenails
The diagnosis of an ingrown toenail is usually not difficult to establish, but in some cases it is necessary to differentiate an ingrown toenail from certain diseases of the nail, nail bed, nail folds and the terminal phalanx of the toe, which are probably less common.
1. Pyogenic granuloma of the nail bed.
When localized under the edge of the nail and on the nail fold, it initially looks like an inflammatory small nodule, which gradually increases to the size of a pea or nut. The surface is reddish, smooth, sometimes bleeds or becomes covered with serous-purulent plaque or dries out in the form of a crust.
2. Pyococcal and candidomycotic paronychia
. On the first toe, pyococcal paronychia is usually a complication of an ingrown toenail. Characterized by a rapid onset with the development of severe inflammatory phenomena of the soft tissues of the nail fold.
3. Subungual exostosis
– a benign tumor-like growth of normal bone tissue of the terminal phalanx of the finger, which is not classified as a true tumor. The cause is not always known, but in some cases patients indicate a finger injury. It is predominantly localized under the inner edge of the nail phalanx of the toe or at the free edge of the nail, but sometimes it is detected at the lateral edge of the nail. Initially, a hard small formation appears under the nail, which gradually increases in size and causes pain when walking, and then the pain becomes permanent.
4. Subungual and periungual fibroma
- a benign mesenchymal neoplasm of a soft or densely elastic consistency that occurs on both the toes and fingers. They can be of different sizes and shapes, painless, most often localized on the nail folds, but can spread to the nail bed. The gradually increasing pressure of fibroma on the nail or on the eponychium can lead to dystrophic disorders of the nail plate, including its destruction.
5. Subungual and periungual chondroma
- a benign tumor of hyaline and, less commonly, fibrous cartilaginous tissue, formed from the rudiments of cartilage in the bone. More often it develops from the bone of the terminal phalanx of the toes and hands. It looks like a solitary tumor of varying sizes (up to 2 cm), very dense and even hard. But at the beginning of the disease, it is a small hard formation at the free edge of the nail, which, gradually increasing in size, lifts the nail plate (onycholysis), and in some cases leads to its deformation and destruction.
6. Dermoid cyst of the nail bed
– a malformation of tissue with the formation of a cavity lined with epithelium. It is localized in various parts of the body, but can appear in the dermis of the nail bed on the toes. The cyst cavity may contain keratinized scales and hair. As the cyst grows and its size increases, deformation of the nail plate may occur.
7. Glomus subungual tumors (Barais-Masson disease)
– a benign vascular tumor that forms in the area of arteriovenous anastomoses (glomus). They are vascular glomeruli with a capsule of connective tissue and nervous tissue, ranging in size from 5 to 10 mm. When a glomus tumor is localized on the nail bed, it takes on the appearance of a bluish spot, usually at the proximal edge or in the center of the nail. Characterized by severe pain, slow development and benign course.
8. Malignant tumors of the nail bed and nail folds
. Sarcoma and melanoma of the nail bed are rare diseases, but in some cases they can simulate paronychia, pyogenic granuloma and ingrown nails” [2].
Courses for pedicurists “Correction of nail shape using Fraser spring clips” - Course 1 day.
Read more >>>
Ingrowth stages
1. No inflammation. It is characterized by pressure, pain, and the appearance of calluses (core calluses along the nail groove).
2. With inflammation. It is characterized by all 5 signs of inflammation: redness (=hyperemia), local increase in temperature (=hyperthermia), pain, swelling, suppuration.
3. With functional limitation. Characterized by excessive size of nail folds and weeping hypergranulations. Pain not only when walking, but also at rest.
Course for pedicurists “Correction of nail shape using 3TO staples” – Practitioner course 2 days
Read more >>>
Symptoms of the disease
The manifestation of onychocryptosis in children is difficult to detect when the child cannot explain what is bothering him. Mom may notice swelling and redness of the nail fold. If pus is released, you should consult a doctor to treat and treat the affected area. Independent actions can aggravate the problem and lead to the need to remove a child’s ingrown toenail.
Main symptoms:
- pain that gradually increases;
- redness and swelling, if infection occurs, suppuration occurs;
- overgrowth of the affected area with soft tissues;
- increased body temperature as a consequence of the inflammatory process.
Methods for correcting an ingrown toenail
Surgical methods (truncation of the lateral part of the nail plate)
When cutting the nail plate, even an experienced surgeon cannot always give a predictable guarantee of how onychoblasts, the cells in the cuticle area from which the nail grows, will behave. Will they grow, or are they completely removed, where will the keratinized cells grow: up or down, and as a result - a new ingrowth. Up to 70% of relapses. Another important point is the unaesthetic appearance of the nail with a truncated, damaged nail plate.
Orthonyxia methods
This is a corrective method of treating ingrown nails using staples and plates, as a result of which, in addition to solving the problem, the aesthetic appearance of the nail intended by nature is restored.
Consequences of the problem
It is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner so as not to aggravate the situation and not lead to complications. Ingrown toenails come with a risk of infection in the affected area. As a result, suppuration may occur.
In the absence of proper therapy, ingrowth can lead to abscess, osteomyelitis and sepsis. In children, the infection spreads quickly. This is especially dangerous for weakened children with diabetes. Source: I.P. Zhurilo, V.K. Litovka, G.A. Sopov, K.V. Latyshov, I.N. Inozemtsev The problem of ingrown toenails in children // Child's Health, 2012, No. 2(37), pp. 139-141
Doctors take the problem of ingrown toenails seriously and recommend promptly starting therapy and carrying out a set of measures.
We care and treat according to the rules
“Knowing about your ingrown toenail, you will have to subordinate a lot in life to this problem, or rather, to ensure that this problem does not bother you. First of all, for those who have ingrown toenails:
- you need to give up narrow shoes that restrict your feet
; - it is necessary to constantly maintain foot hygiene
, wash them daily with warm water, change socks and stockings; - After the hygiene procedure, rub and knead the fingers
and the entire foot in the direction from bottom to top. This will improve blood circulation throughout the entire foot; - It is very important to cut your nails correctly
- not too short and without cutting off the corners, that is, in such a way that the edge of the nail is almost a straight line and protrudes above the soft tissues. In this case, the nail will not grow into the skin” [1].
Literature
1. Savelyeva E. M. Pain in the foot, flat feet, spurs, arthritis, bone deformation and other problems. best treatment methods /[Savelyeva E. M.]. - St. Petersburg: Vector, 2011. - 128 p.
2. Korobkov V.N. Ingrown toenail of the first toe. training manual / V.N. Korobkov, I.S. Malkov; Ministry of Education and Science of Russia. Federations, State education institution of higher education prof. education "Kazan. state tech. University", State University education establishment of additional prof. education "Kazan. state honey. acad. Roszdrav". - Kazan: Publishing house of Kazan State Technical University, 2010. - 40, [1] p.