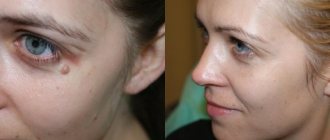
Warts are classified as benign neoplasms.
They can appear on various parts of the skin and mucous membranes.
If a wart appears on the lip, it represents a cosmetic defect and can also cause discomfort to its owner, worsening the quality of life.
Forming on the lip, the tumor affects speech and interferes with eating.
A wart can cause pain, especially if it is localized on the mucous membrane inside the lip.
If measures are not taken to eliminate it, the growth may become injured, which will lead to a secondary infection.
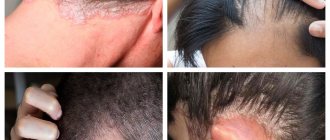
Types of warts
A wart is a growth that rises above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane.
Its dimensions, as a rule, are no more than 1 centimeter in diameter.
The tumor can appear on any part of the body, including the face.
On the face, most often a wart forms on the lip, above or below the lip, on the buccal surface of the oral mucosa.
A warty growth can appear on both the upper and lower lips.
The following types of neoplasms are distinguished:
- Common (vulgar) warts. These are growths that have a dense structure, soft to the touch, flesh-colored or yellowish in color. New growths form on the red border of the lips. They are not painful, but tend to itch. Vulgar warts appear on the lips not only in adults, but also in children.
- Flat- shaped growths may appear on the outside of the lips or on the oral mucosa. Their surface is smooth, oval or round in shape. The color of the growth resembles the color of the skin and almost does not rise above it. The location is also the red border of the lips. Flat warts do not hurt, but they are very itchy.
- Hanging neoplasms are located on a thin stalk. At the beginning of development they resemble a bump. They have a brown, pinkish tint or close to the color of the skin.
- Filiform (acrochords). These are small growths that appear after 35 years, but can occur earlier.
- Genital warts . The localization of such growths is the mucous membrane. The new growths are elongated and arranged in groups, resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower inflorescences. The growths are prone to injury, which causes inflammation and bleeding.
The wart forms gradually and almost imperceptibly.
- At the beginning of development, a small compaction forms, which gradually increases.
- A white dot forms on the surface of the mucous membrane of the lip or in the mouth, which gradually turns into genital warts.
To date, approximately one hundred types of papillomavirus have been discovered.
Some types of growths have a benign course, while others are capable of malignancy.
They can provoke the development of cancer.
In addition to the types of growths listed above, there are also senile warts (keratoma, keratosis).
The difference between keratosis is that its appearance is not associated with papillomavirus, and keratoma does not provoke the formation of cancer.
In their development, senile warts go through several stages:
- ✓ brown spots appear, but the wart has not yet formed
- ✓ formation of papules and nodules
- ✓ appearance of keratoma - when you try to scrape off the scales, bleeding appears
- ✓ transition to the cutaneous horn, which is characterized by excessive growth and keratinization of the neoplasm
According to some experts, keratosis and senile warts belong to different diseases.
How to recognize warts: symptoms and signs
An inexperienced person may confuse warts with other skin growths, for example, moles, calluses, melanomas.
The main differences between warts and moles:
- moles have a dark or black tint, while warts have a light color;
- warts grow tightly together with the skin, moles are separate structures, as if glued to the body;
- moles are soft and smooth to the touch, warts are hard, hard and rough.
It is also easy to distinguish a wart from a callus. When pressing on the growth, painful sensations will occur, and if it peels off, traces of hemorrhages will be visible underneath it. Under the callus is new, tender skin.
You can distinguish a wart from a melanoma by color and shape. This dangerous disease is characterized by heterogeneous red and black shades, proliferation and an uneven contour.
It is not difficult for a dermatologist to make the correct diagnosis using a visual examination. But a good specialist will not be content with just a simple inspection. He will definitely use a special magnifying device - a dermatoscope. If there is a suspicion of a pathogenic process, scraping of the surface layer will be required.
In the case of anogenital warts (located around the anus and on the genitals), consultation with a gynecologist or proctologist is necessary.
The difference between a wart and keratoses and cancer
Keratosis may be similar in appearance to melanoma (a type of skin cancer).
Melanoma can begin as a warty growth or as a seborrheic keratosis.
A dermatologist can distinguish them from cancer.
To exclude an oncological process, a biopsy is performed.
The peculiarity of seborrheic keratosis is that the formation is waxy, flat, and there is no pain when touched or at rest.
With cancer, a growth similar to a keratosis may change shape or color.
In this case, you will need to consult a specialist.
Flat (juvenile) warts
Flat warts are a fairly common type of tumor and the least problematic. They present as small lenticular lesions (several mm in diameter) or smooth papular lesions. They can grow either singly, which is quite rare, or in large numbers, close to each other.
There are several stages of the disease:
- mild – one or several painless warts;
- medium – from 10 to 100 painless growths;
- severe – more than 100 neoplasms.
If they are localized in places that experience excess pressure (friction from clothing, shoes, etc.), they cause pain.
Flat warts are easily identified and have a white, brown, yellowish or pink hue, similar to the color of meat. They are about the size of a pinhead and, compared to other types of warts, are smoother and flatter. In fact, at the point where a flat wart develops, the skin rises slightly (to a height of about 5mm), forming a sort of raised circular area.
The growths typically appear on the face, knees, elbows, back, legs, and arms (especially the fingers). People of absolutely any age become victims of this disease. But most often it affects children and adolescents (20% of schoolchildren have it), hence the second name for warts - juvenile.
In a close group of schoolchildren, 80% show resistance (resistance) to the virus. In adults, irritation and inflammation after shaving contribute to the proliferation of tumors.
The incubation period of infection can last up to 8 months. Mostly the disease is only a cosmetic defect. Juvenile warts are painless unless caused by mechanical pressure or injury and can sometimes cause itching, but are extremely contagious.
The virus is practically not transmitted through shared objects; the main route of infection is skin contact. Flat warts multiply so easily that it is enough to touch a healthy part of the body to cause the birth of a new formation.
The peculiarity of this type of wart is that in most cases no treatment is required: they can disappear as suddenly as they appeared, especially in children. In adults, the disease must be treated, and the virus is very resistant to drug treatment.
Causes of warts
The appearance of warts is caused by infection with papillomavirus or HPV.
Since the skin on the lips is quite thin, it is therefore easily permeable to viruses.
It should be noted that signs of infection with the human papillomavirus do not always occur.
The better the immune system, the less likely it is that symptoms of the disease will appear.
And yet, most of the world's population is infected with HPV.
The incubation period for the development of the disease can be several months or years.
As soon as the immune system fails, the first signs of infection appear.
Activation of the virus is accompanied by the formation of warts.
As a rule, growths appear on the area of the skin or mucous membrane where the pathogen entered the body.
Infection can occur both through sexual contact and through household contact.
Can the virus be transmitted by kissing on the lips?
The most common cases of infection are:
- intrauterine infection of the fetus if a pregnant woman is infected with papillomavirus
- shaking hands or kissing an infected person (if there are wounds or abrasions, the risk of infection increases)
- the use of personal items of an infected person (toothbrush, dishes, lipstick) is unlikely, since the pathogen is not stable in the environment
- sex accompanied by oral sex
- visiting common areas (swimming pool, sauna, shower)
People at risk are those who:
- patients with diabetes mellitus or other pathology of the endocrine system
- suffer from obesity and metabolic disorders
- taking antibiotics for a long time
- have chronic diseases
- suffer from increased sweating, especially on the feet, as this is where plantar warts often form
A malfunction of the immune system can occur for the following reasons:
- If there is a deficiency of essential substances in the body
- After suffering stress or physical exhaustion
- In case of hormone imbalance: during puberty, during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause, during treatment with hormonal drugs
- In case of chronic lack of sleep and overwork
- Due to a recent infectious disease
- If a person abuses smoking and alcoholic beverages
Periungual plantar warts
Periungual warts are small, rough formations with cracks on the surface, located on the hands and feet of a person, namely near the nail plate or deep under it. Externally they resemble cauliflower heads.
They can be flat, pointed or hemispherical. As a rule, periungual warts are gray, but they can also be flesh-colored. They are not too dense, like simple plantar ones, but have a fairly deep root.
This disease mainly affects children and young people. The main factor in contracting the infection is skin microtraumas around the nail. At particular risk are those who bite their nails and pet stray animals, as well as people who carelessly remove cuticles, use undisinfected tools, and work in water without gloves.
This type of neoplasm does not pose a threat to human health; it is mainly only a cosmetic defect. Periungual plantar warts do not cause discomfort or pain when pressed. However, a wart under the nail is not so harmless - over time, the neoplasm provokes depletion of the nail plate and its further destruction.
In addition, various bacteria and viruses enter through cracks on the surface of the growths, which easily form due to frequent hand work, causing re-infection. Also, as warts grow, the cracks can cause pain. The cuticle is often lost and a tendency to become inflamed (paronychia) develops.
Removal of the tumor is necessary to stop the proliferation of growths, which easily spread to healthy fingers. Localization of the wart under the nail plate makes treatment and removal very difficult. When it appears in childhood or adolescence, it can go away on its own.
Diagnosis of warts
The main diagnostic method is to examine the patient's face for the presence of warts on the lips and oral mucosa.
To confirm or refute the presence of HPV, it is enough to take tests:
- ✓ Blood tests for antibodies
- ✓ To conduct a histological examination (biopsy), a small part of the tumor is taken for analysis
- ✓ The PCR technique allows you to detect the genetic material of a pathogen with one hundred percent probability
Before getting rid of the growth, you should visit an oncologist.
A specialist will use dermatoscopy to determine the condition of the wart to rule out signs of malignancy.
Senile (age-related keratomas, seborrheic keratoses) warts
Senile warts are one of the most common skin lesions that appear in old age as a general sign of skin aging. Despite their name, they are not caused by the human papillomavirus.
Seborrheic keratoses are extremely common. According to statistics, more than 90% of the population over the age of 60 have one or more of them. They are equally common in both men and women. It is not uncommon for the disease to affect people aged 30-40 years, as well as young people under 20 years of age.
Keratomas and keratoses can appear on any part of the body, including the scalp, face and genitals. The exception is the palms, soles of the feet and mucous membranes. It is rare for a person to develop only one growth. Over time, age-related keratomas become more and more numerous. Many people inherit a tendency to develop a very large number of these tumors. Some of them may have hundreds of wart-like growths scattered throughout their body.
In the early stages, aging warts appear as slightly raised light brown spots or papules. They can remain very flat and resemble freckles in appearance, or they can gradually thicken and develop a rough, warty surface, like a tumor on the skin. In most cases, they darken slowly and may eventually turn black.
These color changes are harmless. Many senile warts remain pinkish in color. Typical of these are small keratin plugs that can be seen on the surface of the wart.
Keratoses are usually round or oval in shape. Some seborrheic warts are irregular in shape. Their size can vary from one to several centimeters in diameter.
The cause of age-related keratomas is unknown. They are generally considered to be degenerative in nature and appear in large numbers as the skin ages. It is assumed that ultraviolet radiation increases the likelihood of their development.
There are five traditional forms of age-related warts:
- Spotted, or popularly “death freckles” . They form in numerous clusters on the hands and face. Such growths are round with an uneven contour and a smooth or slightly rough surface. It has several color options: light brown, brown-brown or pinkish-yellow;
- Papular or nodular . Larger growths tend to grow. Their typical color is gray or yellow. The surface of the wart is covered with horny layers;
- Classic keratoma . It is a collection of plaques tightly connected to each other. It is characterized by a jagged outline and a copper or pinkish color. As it grows, the middle part of the wart sinks;
- Cutaneous horn. It is a modification of keratoma. It is expressed as a cluster of dense keratinized dark brown plaques up to 1.5 cm.
Adverse reactions to certain medications and many chemotherapy drugs can contribute to the formation of irritated seborrheic keratoses—inflamed, red, crusty lesions. This leads to the development of eczematous dermatitis around the growth. Dermatitis can also cause new seborrheic keratoses to appear.
Age-related keratomas are always benign. This means that they do not spread and do not degenerate into a malignant form. The main problem is a cosmetic defect, especially if they develop on the face.
There are rare cases of skin cancer called melanoma that develops in a seborrheic wart. It is unknown whether this is just a coincidence or represents a true change in the cells in a seborrheic wart. A large number of age-related keratomas may be a sign of cancer of internal organs.
Typically, seborrheic keratoses are treated for cosmetic reasons or because they become itchy and irritating. If the growths, especially large and warty ones, are injured (rubbed against clothing, touched by something), they may bleed or become inflamed.
Diagnosis of the disease is usually made through a clinical examination. This type of wart is difficult to distinguish from skin cancer without histological examination. Therefore, very dark lesions that have changed in some way or that are growing rapidly require a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out the possibility of cancer. Darker lesions should also be checked by a doctor to make sure they are not melanoma.
Clinical manifestations of warts on the lip
A wart on the lip does not appear the next day after the papilloma virus enters the body.
The incubation period can last from six months to several years.
This often occurs when the immune system malfunctions.
Having penetrated the skin or mucous membrane, the virus integrates its genetic material into human cells and thus begins to multiply.
As a result, characteristic neoplasms appear at the site of virus introduction.
The pathogen provokes warty growths, disrupting the processes of keratinization of the skin.
Oncogenic strains of papillomavirus change the genetic apparatus of cells in such a way that a malignant formation is formed.
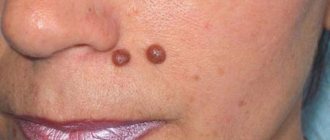
Filiform (acrochord) warts
Filiform warts, also known as facial warts, are the most unusual type of these growths. They are thin, long, racem-like shoots that are usually found on the eyelids and surrounding areas, on the neck, near the lips and nose, and less commonly on the legs, in the groin folds, under the mammary glands and in the armpits.
The typical color of acrochords is flesh-colored, which is why people do not immediately notice them. Sometimes they may turn yellow, brown or pink. Usually they reach a length of 5 to 10 mm, extremely rarely - several centimeters. Depending on the severity of the virus, acrochords form singly or in multiple clusters. This distinctive type of filamentous wart is usually diagnosed visually.
Filiform warts form when a strain of the human papillomavirus causes the top layer of skin to grow too quickly. At the inception stage, the growth looks like a yellowish bump. As it grows, it stretches out, transforming into an elongated formation on a stalk. To the touch, the wart has an elastic and dense structure.
People of absolutely any age can become a “target”, but often elderly patients suffer from this disease. According to statistics, about 50% of the world's population over 50 years of age have facial warts.
Infection with the virus often occurs through cracks and abrasions on the face, so people with dry skin are at high risk. Also, the appearance, growth and spread of facial warts is facilitated by various hormonal changes (pregnancy, obesity, menopause, ovarian dysfunction, diabetes, etc.).
Although highly contagious (infectious) and unattractive in appearance, this type of wart is benign, painless, and often responds well to treatment.
When they appear in sensitive areas, such as skin folds, or areas often subject to pressure and injury, some symptoms may occur:
- itching;
- bleeding;
- soreness;
- irritation.
This type of wart almost never develops into a malignant form. However, if the acrochord is injured, there is a high risk of developing an inflammatory process. Unlike many other similar neoplasms, the filamentous type does not disappear on its own. When a wart falls off, a new one grows in its place. Sometimes there is keratinization of the growth and its transformation into a cutaneous horn.
Facial papillomas are contagious and can be spread by sharing towels or facial cosmetics. Touching the acrochords puts a person at risk of spreading them to other parts of the body. Warts will increase in size and number if they are not removed.
Their location and ugly appearance make facial growths a cause of emotional stress and embarrassment for many people, sometimes affecting their self-esteem and self-confidence.
Is it necessary to remove a wart on the lip?
Removal of the tumor is carried out if there are indications for this.
The growths sometimes disappear spontaneously.
Therefore, if the wart is small and does not cause much concern, then there is no need for removal.
The decision to excise the growth must be made by a specialist.
If a wart causes discomfort in the form of itching, burning, pain, grows, becomes inflamed, or changes in appearance.
If it has increased in size, changed shape and color, or is bleeding, then it must be removed by resorting to excision by one of the methods.
Removing a tumor at home is not safe.
As a result of incorrect actions:
- It may not be possible to remove the wart completely, which will cause its reappearance
- the risk of injury to healthy tissues that surround the growth increases
- scars and cicatrices may form
Are warts always dangerous?
Most warts are completely harmless and can theoretically disappear in a few weeks or at most a month. In this case, patients are more likely to be concerned about a serious cosmetic defect, which causes psychological discomfort and interferes with leading a full lifestyle.
Warts are often painless unless they are on the soles of the feet or another part of the body that is subject to shock or constant contact. But there are cases of itching and discomfort in the affected area.
But as mentioned above, warts are viral in nature, so you cannot expect that the neoplasm will go away on its own or will not bother you for the rest of your life. Any wart should be shown to a dermatologist, and if he deems it necessary, it should be removed using one of the safe methods.
Wart treatment
Treatment of any growth on the lips begins with a medical examination and determining whether the growth is malignant.
Next, the doctor selects a method of therapy.
In case of a malignant form, the patient is referred to an oncologist, who will decide how to treat the patient.
Treatment of the disease is complex.
Treatment consists of the main stages: removal of the growth and drug therapy.
Removal of the tumor can be done in one of the following ways:
- ✓ Using pharmaceutical products
- ✓ In a medical institution where modern excision techniques will be used
- ✓ Folk remedies. The use of alternative medicine methods must be agreed with a doctor
general information
A common wart is a growth on the skin that has a rough surface and protrudes to a certain height above the surface of the epidermis. The color of warts is lighter or darker than the surrounding tissues; on large formations, internal vessels can be seen. The main cause of warts is infection with the human papillomavirus. HPV enters the body through damaged or water-soaked skin. Sometimes infection is possible even if there is no damage to the body. The difficulty of identifying the cause of infection is due to the fact that some warts in adults appear on the body only six months after infection.
HPV mainly affects children and young people. Patients who have a history of chronic skin diseases are susceptible to the problem:
- Psoriasis;
- Dermatitis;
- Eczema, etc.
Patients who have a weakened immune system are also at risk. We are mainly talking about people infected with HIV or those who have undergone organ transplantation. If a patient has problems with immunity, treatment difficulties may arise in the future. In this case, a viral wart most often recurs after removal.
Warts can be found on the skin anywhere on the body. Moreover, most often they are localized in the area of the fingers, elbows, knees, and hands.
Pharmacy products for removing warts
You can buy medications at the pharmacy that will help you deal with warts at home.
Among them:
- Super clean . The product is an alkaline solution that has a chemical effect on the growth, causing cauterization.
- Cryopharma, Wartner . These agents cause cryodestruction of the wart; as a result of cold exposure, the neoplasm is frozen.
- Solcoderm . A drug containing acids that have a cauterizing and mummifying effect on pathological tissues.
- Immunomodulators – Viferon, Oxolinic ointment will help increase immunity and the body’s fight against the virus.
- Antiviral agents – Isoprinosine, Interferon.
The use of cauterizing agents on the lips and face is extremely undesirable; application of these agents to the oral mucosa is especially dangerous.
Human papillomavirus: symptoms and treatment
There are about 200 different types of HPV, of which more than 40 can infect the genitals, mouth and throat. Most people infected with HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) do not know they are infected. Some types cause common warts when they affect the skin. Other types cause sexually transmitted diseases. In fact, HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) can cause serious health problems, including genital diseases and some types of cancer.
Most people who have sexual contact and become infected with HPV do not develop any symptoms. Most HPV infections go dormant within two years. But in some cases, the infection causes long-term problems. These problems include cervical cancer in women, penile cancer in men, some types of rectal cancer in both sexes, and oropharyngeal cancer (cancer of the nasopharynx, tongue, and tonsil).
Previously, nasopharyngeal cancer was associated with smoking or alcohol abuse. Today, oral and nasal cancers associated with smoking and alcohol are much less common, while HPV cancers are on the rise. By 2022, HPV-related cancers of the mouth and throat are predicted to be more common than cervical cancers. Unfortunately, cancer of the oral cavity and oropharynx is most often invisible to the patient, provided it is at an early stage of development with minimal symptoms. This is why the main goal of the dentist or surgeon is to rule out or confirm this diagnosis. As with other cancers you know about, such as cervical, skin, prostate, colon and breast tumors, correct diagnosis is the only factor in effective treatment in the early stages of development.
At the first stage, a full examination by an ENT doctor is carried out, including an analysis of the medical history (symptoms, duration of symptoms, taking into account the patient’s profession, marital status, etc.). This is followed by an initial examination with examination of the nose, mouth, throat, palpation of the tonsils, and tongue. The diagnosis also includes examination of the cervix in women and a basic endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx with a flexible endoscope.
If there is some suspicion, we also perform other tests (blood tests, cultures, ultrasound, CT, MRI, etc.). If an HPV infection is suspected, a tissue sample can be taken and sent for histological and immunohistochemical examination.
What is HPV?
The same types of HPV that are localized in the genital area can infect the mouth and throat. Some types of HPV in the mouth, which have a high risk of malignancy, can cause cancer in the head and neck area. Other types of HPV lesions (known to have a low chance of becoming malignant) cause warts to appear in the mouth, throat, and tongue. In most cases, infection with all types of HPV can cause various health problems.
HPV is transmitted by direct contact with the skin or mucous membrane. However, simple transmission of the virus from person to person does not usually cause acute symptoms. The conditions for the virus to penetrate the epithelium imply the presence of abrasions and microtraumas. People often become infected through oral sex.
Is there a risk
Risk factors for HPV are:
- Increased sexual activity is a risk factor, especially if you have many sexual partners. If you have had 20 or more sexual partners, your chance of contracting HPV may be greater than 20%.
- Smoking is a risk factor. Inhaling tobacco reduces the protection of the mucous membrane, making the mouth more susceptible to infections. Oral leukoplakia (symptoms of leukoplakia are a firm, hard, white, slightly raised plaque or patch on the cheek, gum or tongue, and sometimes on the lower lip).
- Alcohol consumption is a risk factor. You are even more at risk if you smoke and drink.
- Men are more susceptible to oral HPV infection than women.
- Age is a risk factor for oropharyngeal cancer. These cases are more common in adults.
Symptoms
HPV in the mouth is often asymptomatic, so people do not know they are infected. At the same time, patients, out of ignorance, are less likely to take the necessary measures to limit the spread of the disease.
In some cases, it is possible to develop warts on the tongue, mouth or throat, but this is not common.
Some types of HPV can develop into oral and tongue cancer. With oropharyngeal cancer, cancer cells can be found on the tongue, tonsils, and throat walls. These cancer cells can “grow” from HPV in the mouth to become malignant.
How can I reduce my risk of getting oral HPV?
There are currently no experts who have researched how to prevent HPV infection. However, it is likely that condoms, when used frequently and correctly, can significantly reduce the likelihood of contracting HPV during sexual intercourse because they act as barriers and prevent the transmission of HPV from person to person.
More research is needed to understand how HPV (Human Papillomavirus) is transmitted, how infection can be prevented, and who is most susceptible to health problems from oral HPV infection.
Is there HPV testing for me to find out if I have oral HPV?
There is not yet a test to diagnose HPV in the mouth or throat. But if there is a suspicion of involvement of the mouth or throat, histological and immunohistochemical examinations can be carried out to identify HPV and its subtypes.
Can the HPV vaccine prevent oral and oropharyngeal cancer?
There are currently HPV vaccines on the market that prevent cervical cancer and other less common cancers. It is likely that HPV vaccines may also prevent oropharyngeal cancer because vaccination prevents initial infection with various types of HPV that can cause oropharyngeal cancer. However, no studies have been conducted to determine whether HPV vaccines will prevent oral cancer, tongue cancer, and nasopharyngeal cancer.
How is HPV in the mouth treated?
It takes a long time after you are infected with most types of HPV before they begin to cause damage to your mouth. If you have HPV-related warts in your mouth, a surgeon can remove them in the clinic under local or general anesthesia. Treating oral warts with topical therapy can be difficult as recurrences are unfortunately very common.
A doctor can use any of the following methods to treat warts: classical surgical removal, removal of warts using laser or radio frequency, cryotherapy, interferon alpha-2b (Intron A, Roferon-A) in injection form. Usually, if you have warts in the throat, tongue or mouth, they can be removed with a local anesthetic without pain.
If you notice any of these symptoms and you know or think that you may be infected with HPV, you should be examined by an ENT doctor to confirm the diagnosis.
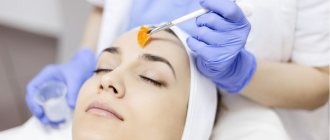
Wart removal in the clinic
The clinic uses modern hardware techniques to excise growths:
- Laser therapy . The method allows you to quickly and without blood remove the growth. There is no discomfort during the procedure, as pain relief is performed. During one session, you can get rid of several tumors in a very short time. The method is suitable not only for adults, but also for children. The likelihood of relapse is minimized. Skin defects in the form of scars after laser use are very rare.
- Radio wave therapy . The technique is considered the safest. When excising a wart using a radio wave, there is no contact with the skin. It is not always possible to completely remove the growth. The procedure leaves no traces of impact.
- Electrocoagulation . The procedure requires anesthesia. Using an electrode to which a high-frequency electric current is applied, the wart is burned out, followed by cutting off the growth with a special metal loop. Scarring may appear after removal.
- Cryodestruction . Liquid nitrogen is used and the wart is treated until it turns white. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, the growth tissues die. There is no need for anesthesia for the manipulation. The disadvantage of the technique is the lack of control over the depth of nitrogen exposure. For this reason, frequent relapses occur.
- Surgical. Removal is done using a scalpel. The disadvantage of the procedure is the formation of a scar, so this technique is used only for certain indications (in case of malignancy of the process and large size of the wart).
Mosaic plantar warts
Mosaic warts are a special type of neoplasm. They are plaques, so-called clusters, formed as a result of the fusion of many small plantar warts tightly pressed together. The arrangement of the plaques resembles a mosaic (hence their name).
This formation is usually observed in a small and localized area. It can reach a diameter of about 6-7 cm. In the early stages of development, mosaic warts look like small black punctures. As they develop, they take on the appearance of a white, yellowish or light brown cauliflower, with dark spots in the middle. These spots are formed due to thrombosis of blood vessels.
This type of wart is quite rare. They usually affect the hands or soles of the feet, and are especially common under the toes. Unlike simple plantar warts, mosaic warts cause little or no pain when walking because they are flatter and more superficial.
Mosaic warts are highly contagious. They are difficult to treat due to the multiplicity of foci of viral infection. The success of treatment is facilitated by its timely initiation. As a rule, mosaic growths are prone to recurrence even after surgical removal.
Self-medication is harmful
Do not try to diagnose and treat HPV infection on your own! Firstly, there is a risk of improper use of drugs. Secondly, only a doctor can distinguish papilloma from a malignant tumor. In addition, self-treatment is fraught with consequences.
Today, there are celandine-based preparations on sale that are intended to eliminate warts. Celandine juice is similar in composition to iodine. Therefore, prolonged exposure to the drug causes skin burns. In this case, papillomas are seriously injured and can provoke the development of skin cancer. Cauterization with iodine is even more dangerous - it is more aggressive than celandine. Trying hard to get rid of papillomas with iodine, you can get scars on the skin. Vinegar is no better in this regard. Attempts to bandage warts and papillomas with a thin silk thread often only provoke the growth of these formations.
If you suspect the appearance of warts or genital warts, you should definitely seek advice from a dermatologist, urologist or gynecologist, depending on the location of the source of infection. Only a professional can correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Strengthening the immune system
Modern medicine has not yet learned to kill viruses. But an important fact is that HPV carriage is not lifelong. In addition, medicine has a small number of means at its disposal that allow it to remove some of the viruses from the body. The use of these drugs is fully compatible with immunomodulatory therapy.
The amount of virus in the body is directly related to the state of the body’s immunity - the better the immunity, the less virus. Therefore, the most promising way to reduce the concentration of HPV in the body is to strengthen the immune system. For this purpose, a separate course of treatment is carried out, after which the person begins to feel much better.
Finally, there are very effective preparations for topical use - creams, gels, sprays that increase local immunity and reduce the concentration of the virus in the affected tissues.
Diagnostic methods
At the first appearance of growths on the lips, you should consult a dermatologist. Only he will be able to identify the formation and determine that it is papilloma or condyloma, and not a manifestation of any other disease.
As a rule, after consulting a doctor, an HPV test is prescribed, a tissue biopsy of the growth is performed, and only then appropriate therapy or radical removal of the tumor is prescribed.
In addition, this neoplasm can be malignant. It cannot be treated with the same methods as regular warts. In laboratory conditions, it is possible to identify both the nature of the growth and its benign quality.
Prevention
Since the virus is activated only at those moments when the human body is weakened, patients with HPV will need to constantly maintain their immunity at the proper level. This can be done with proper nutrition, hardening the body and taking immunostimulating drugs. At the moment the formations appear, the patient can infect other people. Therefore, those who are not sick with papillomavirus should avoid oral contact with a person on whose lips neoplasms are noticeable.
You should definitely use protective equipment during sexual intercourse, because the virus is easily transmitted during intimacy. At the same time, the infected person himself may not know that he is sick, which means he can infect his partner unintentionally.