General information
Prurigo (prurigo) is a chronic disease belonging to the group of neuroallergodermatoses, which is characterized by papular/papulovesicular, nodular rashes accompanied by severe itching.
Clinically, several types of prurigo are distinguished, representing independent nosological units:
- Children's prurigo (syn. urticaria in children, strophulus in children). An allergic skin disease, which occurs mainly in children from one to 5 years of age, less often occurs earlier: in the form of a reaction to a new product introduced into complementary foods or during teething. dysbacteriosis , exudative diathesis and gastrointestinal pathologies are prone to developing prurigo
- Prurigo of adults (syn. prurigo of adults, prurigo of Beignet) is a dermatosis most often found in adults, mainly in old age in persons with gastrointestinal dysfunction, endocrine disorders ( thyrotoxicosis / diabetes mellitus ) or against the background of neuropsychiatric diseases and oncopathology. More often women under the age of 30 suffer from relapses during menopause and men after 50 years ( diabetes mellitus , thyrotoxicosis ). Prurigo often manifests itself in adults who suffered from urticaria / diathesis .
- Nodular prurigo (syn. prurigo Hyde) is a relatively rare form of dermatosis . Nodular prurigo occurs predominantly in females with unstable mental health/reduced immunity, metabolic disorders, endocrine pathology, liver diseases, helminthic infestations, and mosquito bites.
In addition to the indicated nosological forms, there are symptomatic forms of simple prurigo: winter/summer prurigo, pregnant prurigo , lymphogranulomatous / lymphatic (leukemic) prurigo .
The relevance of the problem of prurigo is associated both with its wide prevalence, which accounts for about 5% in the structure of dermatological pathology, and with an increasing upward trend, an increase in severe variants of the course and resistance to traditional therapy. Being a chronic neurodermatosis, pruritus is accompanied by rashes/intense itching, which has a negative impact on the psyche of patients, significantly worsening the quality of life.
Diagnostics
There are diagnostic protocols that require, when identifying signs similar to Hyde’s nodular prurigo, to prescribe the following tests:
- general clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood glucose;
- study of biochemical blood parameters: total protein, liver function tests, including alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, urea;
- immunoglobulin E;
- serological blood test for antibodies to helminths: opisthorchid, roundworm, lamblia, toxocara;
- stool analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- Ultrasound of skin and fiber;
- microscopic examination of nails and skin.
Examinations by various specialists are also necessary. An oncologist - to exclude oncological diseases, an endocrinologist - to diagnose the main diseases of the internal secretion organs. The dentist and ENT specialist must exclude the presence of foci of chronic infection in the oral cavity.
This will help not only make the correct diagnosis, but also establish the cause of the development of Hyde’s nodular prurigo.
The person himself, even based on the coincidence of his own symptoms with those described above, cannot make a diagnosis for himself: Hyde’s nodular prurigo is very similar to other diseases. It is difficult for a non-specialist to distinguish between verrucous lichen planus, late porphyria, warty form of tuberculosis, Hebra's prurigo, one of the forms of sarcoidosis, and lymphoma.
Pathogenesis
In the formation of a pathological process, leading importance is given to the sensitization of the body by various kinds of sensitizers (food, medicinal, insect, environmental, helminthic infestations, enzymopathies, metabolic disorders, tumors, etc.). A significant role in the development of prurigo, especially in children, is played by psycho-emotional development, the connection of which with skin diseases is clearly established.
The syndrome of vegetovisceral dysfunctions is of greatest importance in the development of allergic dermatoses, in which there are functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis , secondary enzyme deficiency, malabsorption/nutrition disorders, which creates a vicious circle.
general information
Each type of disease has characteristic symptoms. The main characteristics are similar for all varieties.
You should suspect pruritus when:
- pustular rashes;
- unbearable itching;
- bloody crusts in places of scratching.
Is pruritus contagious? Despite the abundance of nodular rashes, the itching and poor condition of the skin of a patient diagnosed with prurigo is not dangerous. The disease is not infectious in nature and is not transmitted through contact.
Causes
Prurigo is a polyetiological disease. Among the many reasons, exogenous and endogenous factors are distinguished that cause sensitization of the body.
Exogenous sensitizers include:
- food allergens: tropical fruits (bananas, citruses, kiwi, pineapples, mangoes, pomegranates, peaches, grapes); berries (blackberries, strawberries, watermelon, raspberries, strawberries, etc.); vegetables (hot/sweet peppers, eggplants, garlic, tomatoes, etc.); fish/seafood (crayfish, mussels, shrimp, red fish, lobster, squid, octopus); milk (mother, goat/cow); seasonings/spices; sauces (mustard, mayonnaise, ketchup); eggs; nuts; honey; chocolate; coffee, cocoa, smoked, fatty, pickled, salty and spicy foods; nectars/juices; carbonated drinks containing alcohol/energy drinks.
- medicines: hormonal, antibacterial drugs, vitamins;
- insect allergens: stings/bites/contact with insects; inhalation of their body particles and waste products;
- environmental allergens: nitrates in soil; contaminated drinking water, gas contamination of inhaled air.
Endogenous sensitizers include:
- endocrinopathies: metabolic syndrome ; diabetes mellitus , adrenal/thyroid diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis , colitis , pancreatitis , gastroduodenitis , cholecystitis , dysbacteriosis ; dry food, lack of proteins, fats and vitamins in the diet;
- neuropsychic disorders: psychoses of various origins , neuroses , stress , obsessive states;
- neoplastic diseases: benign/malignant tumors, lymphogranulomatosis , leukemia ;
- helminths ( enterobiasis / ascariasis , etc.);
- protozoal infections: giardiasis , trypanosomiasis , amebiasis , toxoplasmosis , leishmaniasis , malaria .
Especially often, strophulus in children develops against the background of a constitutional tendency of the child’s body to allergic reactions, manifesting itself in the form of exudative diathesis , as well as fermentopathy of the digestive tract.
Sunny or summer prurigo
Pathology occurs in people suffering from liver diseases and metabolic disorders. The provoking factor is exposure to sunlight.
The manifestations are similar to other types of pathology; the affected areas of the skin have signs of neurodermatitis.
Treatment:
- photoprotective ointments;
- corticosteroids;
- furatsilin paste;
- ichthyol ointment;
- hepatoprotectors;
- a nicotinic acid;
- cyanocobalamin;
- thiamine;
- antihistamines;
- gentle diet.
Symptoms
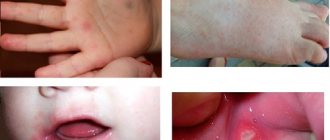
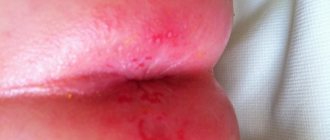
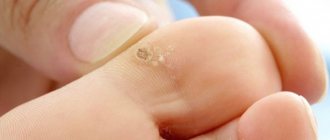
Infantile prurigo manifests itself by the appearance of scattered/abundant bright pink edematous rashes on the skin in the form of nodules with a diameter of 3-5 mm, on which small blisters form over time, which, as a result of scratching, burst with the formation of pinpoint erosions with serous crusts. The predominant localization of rashes is the face, torso, buttocks and extensor surfaces of the extremities.
Symptoms of prurigo may be accompanied by the appearance of a papulovisicular rash. Papulovesicles are larger in size (5-7 mm), have an inflammatory rim and an edematous base. May be located on the skin of the palms/soles. The appearance of the rash is accompanied by intense itching, which leads to the formation of multiple excoriation in the areas of the rash with the development of pyogenic infection, mainly in the form of vulgar impetigo.
In children with prurigo, against the background of rashes, neuropsychic disorders are observed: tearfulness, moodiness, increased irritability, poor sleep, which can be caused both directly by the sleep disorder against the background of itching/autointoxication of the body, and by the specific constitution - congenital lability of the central nervous system.
Often, when infant formula/cow's milk is excluded from the child's diet, the symptoms of pruritus undergo spontaneous regression. However, strophulus in children is accompanied by a high risk of developing into adult prurigo, atopic dermatitis or pruriginous eczema . Symptoms of this type of transformation are anhidrosis , dry skin, enlargement of the inguinal/femoral lymph nodes, the appearance of white dermographism, disappearance of the plantar/decreased abdominal reflex.
The first signs of prurigo appear at the age of 6 months and up to 3 years. Children's pruritus occurs chronically with periodic remissions and, upon reaching 3–5 years of age, goes away on its own or transforms into neurodermatitis .
Prurigo in adults manifests itself as nodular, intensely itchy rashes on the skin of the extensor surface of the arms/legs, back, abdomen, and buttocks. As a rule, the flexor surface of the limbs and the face are not affected. For adult prurigo, dense conical/hemispherical papules of a reddish-brownish color with a diameter of up to 5 mm are typical, the appearance of which is accompanied by severe itching, which leads to the formation of multiple excoriation covered with crusts. The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. In a chronic course, skin symptoms are accompanied by a neurotic syndrome in the form of severe emotional lability, irritability, and sleep disturbances. Below are photos of the symptoms and first signs of pruritus.
Scabies Beignets . Rashes in the form of dense papules of a hemispherical shape, 6-15 mm in size, with a predominant localization on the skin of the extensor surface of the legs, torso, and arms. The rashes can be either single or multiple, less often with a tendency to group. Characterized by long-term persistence of rash elements and subsequent resolution with the formation of circumferentially pigmented scars. Infection of the elements during scratching can lead to the development of pyoderma , ostiofolliculitis / folliculitis or furunculosis . The disease begins with severe itching, which recurs 3-5 times a day. Characterized by a long, chronic course.
Therapy
Treatment for Hyde nodular pruritus begins with a strict diet. A sick person will have to exclude chocolate, seafood, foods with food dyes, preservatives, and large amounts of simple carbohydrates from their diet. You will have to give up spicy foods, very salty foods, and alcohol.
Drug therapy is also prescribed.
Treatment with drugs
The first-line drugs for the treatment of Hyde's nodular prurigo are antihistamines - selective blockers of type 1 histamine receptors. Histamine released from immune cells will not be able to exert its “allergic” effects: itching, increased permeability of blood vessels, due to which part of the liquid part of the blood leaves the vessels, bronchospasm. The optimal antihistamines of the latest generation, which are taken once a day and do not cause drowsiness, are: Zodak, Erius, Loratadine.
The following are also prescribed as complementary antiallergic and, accordingly, antipruritic effects of antihistamines:
- calcium preparations: calcium pantothenate, calcium gluconate and glycerophosphate;
- complexing agents with antiallergic effect: sodium thiosulfate;
- treatment of prurigo nodules with ointments containing glucocorticoid hormones: “Prednisolone”, “Cutivate”, “Dermovate”;
- if there is no regression of rashes and itching despite the therapy, systemic glucocorticoids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) are prescribed for a short course in small doses;
- in case of severe itching, injection of nodules with glucocorticoid hormones can be used.
Enterosorbents are required for the treatment of Hyde nodular pruritus - products that will “take over” particles of food and drugs that can intensify allergic manifestations. These are “Enterosgel”, “Polysorb”, “Atoxil”. They, unlike other drugs, can be used when the disease develops during pregnancy.
If the patient suffers from neuroses, or itching causes exhaustion of the nervous system, sedatives based on natural ingredients (tincture of motherwort, valerian, peony) are prescribed.
Locally, to accelerate resorption and prevent infection, elements of Hyde's nodular prurigo are treated with antiseptics: boron-ichthyol or boron-naphthalan ointments, and other agents prescribed by a dermatologist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is also carried out: electrosleep, phonophoresis of hydrocortisone on points of the back located near the spine. The effects of diadynamic currents on the areas of the sympathetic nodes of the neck, inductothermy, and microwave therapy are used. The use of sulfide and radon baths is also effective in combination with drug therapy.
Cosmetology procedures
As an alternative to drug therapy or if it is ineffective, some cosmetic procedures may be prescribed. This is PUVA therapy, carried out 4 times a week (15-20 sessions in total), including a combination of ultraviolet irradiation with the use of special medications.
Hyde nodular prurigo is also treated with nitrogen. In this case, an applicator is dipped into liquid nitrogen, which has a very low temperature. After this, it is brought one by one to the elements of the rash located in a separate area and touched for a few seconds. Low temperature leads to necrosis of areas or the entire prurigo nodule. The nerve endings going to the elements of the rash also die off - the itching decreases. The areas after treatment take about 3-4 weeks to heal. In their place, new, healthy skin is formed.
An alternative to nitrogen treatment is irrigation with chloroethane, a substance that also has a low temperature and causes wet necrosis in certain areas.
You can resort to diathermocoagulation, “burning out” nodules with high-frequency current, and laser destruction of loose elements. In this case, the nodes die off through dry necrosis - with the formation of a crust. Such a wound heals faster and is less likely to become infected.
Traditional treatment
Sometimes it is possible to treat Hyde's nodular pruritus with folk remedies, which do not remove the cause of the disease, but can help eliminate the itching. For this we use:
- Baths with starch. To do this, dissolve 50 g of starch in a small amount of cold water, which then pour into a warm bath.
- Baths with infusion of birch buds. Take 4 tbsp. birch buds, pour boiling water, let it brew for 3 hours, strain, pour into the bath.
- Propolis ointment. Grind 30 g of propolis, mix it in a clay bowl with 300 g of sunflower oil, place in an oven heated to 120-150°C. Let the butter sit in the oven until it turns dark in color. Once this is achieved, use it to lubricate the rash.
- Celery lotions. Take 250 g of celery roots, chop and add a glass of water. Let it brew for 3 hours, after which you can use it as a lotion.
Hyde nodular prurigo is a pathology that can be cured. It is important that the treatment is comprehensive and includes not only the use of medications, but also diet. Also, the patient should not forget that pruritus can become chronic. With repeated exposure to unfavorable factors, a relapse is possible.
Do you think it is possible to cure Hyde’s nodular prurigo with folk remedies? Or is it better to give preference to medications?
More information about the disease in the video:
During pregnancy
In rare cases, prurigo occurs in pregnant women. Most likely, it is caused by changes in the endocrine, immune, nervous and digestive systems, as a result of which the condition of the skin changes. The disease is also associated with an increase in a woman’s weight during pregnancy, especially during multiple pregnancies, in which the skin of the abdominal wall is greatly stretched. Prurigo develops in the last weeks of pregnancy or after childbirth. Itchy papules appear on the skin, which merge into plaques. Prurigo rashes initially appear in the areas of abdominal stretch marks, and then spread to the buttocks and thighs. In places where the muscles are severely stretched, the connective tissue is sometimes damaged, and this leads to a more pronounced inflammatory process and aggravates the course of the disease. The rash goes away within 4-5 weeks. Prurigo does not affect the fetus, but may recur during subsequent pregnancies.
Propolis-based ointment
According to the observations of traditional healers, it is possible to get rid of the manifestations of pruritus by treating the foci of the disease with an ointment prepared using propolis. Prepare the product according to the following recipe:
- take 100 grams of butter;
- heat 15 grams of propolis in a water bath;
- the ingredients are mixed and kept over low heat until a substance of homogeneous consistency is obtained;
- The ointment is cooled and then poured into a dark glass bottle.
The product is used to treat rash-affected skin areas 3 times a day. Due to the anti-inflammatory properties of propolis, regeneration of damaged skin is observed. Oxidative reactions in local tissues are eliminated. The patient ceases to be bothered by the sensation of itching. There is a general improvement in well-being. Under the influence of butter, the epidermis is qualitatively moisturized and becomes elastic.
Diet
Hypoallergenic diet
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 21-40 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1300-1400 rubles. in Week
Diet for allergies in children
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 15-21 days
- Time frame: until the allergic reaction to the food allergen disappears
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
Hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers with child allergies
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 30 days
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 1600-1700 rubles. in Week
Regardless of age, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet. Completely excluded:
- Products containing dyes and preservatives.
- Citrus.
- Eggs.
- Seafood.
- Sugar.
- Dried fruits, baked goods and other high-carbohydrate foods.
- Chocolate.
- Coffee and cocoa.
- Smoked meats.
- Spices.
- Canned food, marinades.
- Alcohol.
- Fatty and fried foods.
An anti-allergenic menu may include buckwheat, turnips, zucchini, greens, dairy products, plain yogurts, cucumbers, cabbage, spinach, plums, green apples, olive oil, boiled rabbit and veal, dried apples, bread (corn, oat, buckwheat), juices and fruit drinks. More detailed recommendations can be found in the diet for allergies in children and the hypoallergenic diet.
Burdock root ointment
Burdock contains an abundance of biologically active substances that eliminate allergic and inflammatory reactions in the structure of epidermal tissues. To prepare a healing remedy, take the dried root of the plant. The raw materials are thoroughly crushed and ground in a mortar to a powdery state. The resulting substance is combined in equal proportions with medical Vaseline. The ointment is placed in a dark glass container. The product is allowed to brew in a place where the sun's rays do not penetrate for several days. The medicine is used to treat the rash-affected areas of the epidermis after taking a warm bath.
Prevention
Preventive measures for this disease have not been developed, but following general recommendations on lifestyle and nutrition can to some extent prevent the occurrence of this disease.
- Healthy eating during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Avoid taking medications unless necessary or prescribed by a doctor.
- Elimination of bad habits.
- Healthy sleep and proper rest, avoiding emotional stress.
- Elimination of dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Give priority to breastfeeding.
- If your baby is prone to allergies, strictly monitor your diet.
- Careful care of the child’s skin (bathing, using natural-based moisturizers, powders without synthetic ingredients).
- Using diapers and baby clothes made from natural fabrics.
- Treatment of helminthic infestations and giardiasis in children, as well as gastrointestinal dysfunction.
You can prevent the exacerbation of a chronic disease by eating right, eliminating stressful situations and treating gastrointestinal diseases in a timely manner.
"Linex"
To remove intestinal dysbiosis during pruritus, doctors prescribe Linex. The combined probiotic is a source of lactic acid bacteria, which help restore healthy intestinal microflora. The action of the drug ensures the creation of an environment that is not suitable for the active reproduction of pathogenic organisms. The result of therapy is the active production of food enzymes, the synthesis of essential vitamins, and the restoration of the metabolism of bile secretions. Taking the medication ensures normalization of hormonal levels and strengthening of local immunity in the intestines.
Consequences and complications
- Sleep disorders.
- Neurotic disorders ( depression , anxiety , irritability ).
- Decreased performance.
- Attachment of a secondary infection. skin lesions with itching are the entrance gate for bacterial infection: boils , osteofolliculitis , vulgar impetigo , folliculitis lymphadenitis and lymphadenopathy develop .
- Transition to atopic dermatitis .
- Neurodermatitis.
- Pruriginous eczema.
- Weakening of the immune system.
Healing decoction of walnut, woodruff and linden blossom
To disinfect the skin, relieve inflammation and eliminate the itching sensation during scratching, healers advise using the following remedy. Combine a tablespoon of walnut leaves, woodruff grass and linden blossom. The mixture is poured with boiling water in a volume of 0.5 liters. The resulting composition is placed on the stove and boiled for 10 minutes. The medicine is allowed to cool to room temperature. The liquid is expressed through gauze or a fine strainer. Drink 3 tablespoons of the decoction in the morning and evening, which significantly alleviates the course of the disease.
List of sources
- Zaslavsky D.V. Aspects of pediatric dermatology: from strophulus to atopic dermatitis / Medical advice. — 2022, No. 19 p. 154-157.
- Gorlanov I.A., Milyavskaya I.R., Leina L.M., Zaslavsky D.V., Olovyanishnikov O.V., Kulikova S.Yu. Pediatric dermatovenereology. M.: IG GEOTAR-Media, 2022. 512 p.
- Dermatovenerology. National leadership. Brief edition / ed. Yu. S. Butova, Yu. K. Skripkina, O. L. Ivanova. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2013. - 896 p.
- Zaslavsky D.V., Novikova V.P., Chuprov I.N. Probiotics in the prevention and treatment of atopic dermatitis in children. Questions of Practical Pediatrics, 2016, 11(2): 51-57.
- Ermilova A. I., Menshchikova G. V., Pilguy E. I. Pruritic dermatoses: approaches to treatment / Consilium medicum. Pediatrics. 2014 No. 3, pp. 74-77.