A wound is damage to the skin and underlying body tissues. Such damage can be caused primarily by mechanical stress, as well as by the influence of excessive temperature or chemical factors. The wound healing process is absolutely physiological and occurs independently: the body, using natural mechanisms, restores the integrity of tissues and integuments, thus protecting internal organs. The only thing that can ensure faster wound healing is stimulation of regeneration processes and the elimination of the development of complications.
What types of wounds are there?
The healing process and time of damage largely depend on its type. Wounds, according to the factors that caused them, are divided into the following types:
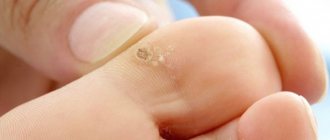
- puncture wounds are injuries caused by a thin object pointed at the end (an awl, a knitting needle), which are distinguished by significant depth in relation to width. In the vast majority of cases, puncture wounds practically do not bleed and this can cause a dangerous misconception that they are not dangerous and, as a result, late seeking medical help. In fact, with a stab wound, damage to internal organs is often observed, as well as internal bleeding, often intense. In this case, blood accumulates, for example, in the abdominal cavity. A narrow wound channel blocks the access of oxygen to the damaged surface, which becomes fertile ground for the development of extremely dangerous gangrenous bacteria;
- incised wounds are injuries caused by a narrow, pointed object. They can also penetrate to a considerable depth, but, unlike stab wounds, they bleed much more, since in the process of inflicting such a wound a large number of blood vessels are damaged. The edges of such a wound are smooth;
- chopped wounds are injuries inflicted by a heavy pointed object (axe, shovel). The edges are often uneven, crushed, the wounds are usually deep;
- lacerations - usually occur with intense mechanical impact on a large area of skin. The edges are uneven, often the skin peels off from the underlying tissues with the formation of a scalped wound, and intense bleeding is not uncommon;
- Bite wounds are wounds that occur as a result of the impact of the teeth of an animal or a person on the body. On the teeth, as a rule, there is plaque with specific microorganisms, which often provoke significant inflammation in the wound;
- Contusion wounds are wounds caused by blunt force trauma. The skin and underlying tissues in the damaged area often become dead. Bleeding is usually minor, interstitial with the formation of a hematoma;
- A gunshot wound is a wound caused by a firearm. It is characterized by significant damage to the tissue around the wound channel due to the impact of bullet energy on them, as well as the presence of particles of clothing and gunpowder in the channel;
- burn wounds are wounds caused by exposure of the skin to thermal energy or concentrated alkalis/acids. The intensity of damage to the skin and underlying tissue depends on the severity of the burn.
Causes of facial allergies
Atypical reactions of the immune system to foods, chemicals and biological substances can cause rashes, pimples, redness, swelling and itching. The person experiences physical and moral discomfort. The manifestations of allergic reactions are varied and depend on the individual characteristics of the body. Most often, localization is observed on the forehead, temples, cheeks, behind the ears, in the décolleté area and on the neck. The most common prerequisites for allergies are:
- heredity;
- consequences of long-term use of medications;
- unfavorable environment;
- constant stress;
- reduced immunity;
- too high a concentration of certain substances;
- insect bites;
- cold or direct sunlight.
There may be other reasons; you need to approach the problem individually.
Allergies to foods and medications
There is often cross-reaction to the protein in this group, making it difficult to find the source. The speed of onset of symptoms can vary from immediate to a period of 2-3 hours. In the case of medications, the prerequisite is overdose, long-term use, too many drugs taken during the day.
Sun or cold
The body’s response is characteristic not only of winter. This could be water or food at a certain temperature. The appearance of photodermatitis is promoted by internal and external causes. Within a day or a little later after exposure to the sun, soreness and itching of the skin begin to bother. When an allergic rash appears on the face of an adult, treatment should begin immediately, otherwise the situation will worsen with each passing hour. As part of complex therapy, immunostimulating cosmetics such as Laennec are effective. Before use, you should consult with specialists.
Reaction due to eczema
Skin diseases significantly reduce the body's resistance, and any violation provokes their exacerbation. Most often, the reaction appears externally in the form of small bubbles with liquid. The acute form can become chronic, which subsequently leads to relapses.
Errors in diet
Various dietary restrictions do not go out of fashion. There are programs based on the consumption of one or just a few products for a long time, which leads to an oversaturation of the body with certain elements, since in this case there can be no talk of balance. You should not be surprised at the deterioration in well-being, since such restrictions become the causes of severe allergies on the face of an adult, the treatment of which is carried out comprehensively and will take a lot of time.
We recommend
GHC Placental 3D Mask withQ10
Serum concentrate
Repairing cream with a moisturizing effect
Placental antioxidant lotion concentrate
Contact with animals, insect bites
A swollen nose and watery eyes when trying to pet a pet are a true classic of the genre. Mosquitoes, bedbugs and other blood-sucking creatures can also cause itching and redness on the skin. The toxins they inject in large quantities cause a rash, often accompanied by fever. In this case, external agents and antihistamines are recommended; dosages should be confirmed with a doctor.
Allergies due to stress
In addition to nervous tics, there are other reactions to emotional overload. Unconsciously, a person may scratch or clench their hands tightly. If such situations happen regularly, then health problems may begin. Itching, swelling of certain areas, redness, and difficulty breathing appear. The main direction of stabilizing the condition is the prescription of sedatives, breathing exercises aimed at calming the nervous system, ointments and gels to relieve external manifestations on the skin.
How does wound healing proceed?
Wounds with smooth edges that are brought together as close as possible, without infection, heal by primary intention. If the edges of the wound are uneven, the wound surface is large, or an infection develops on it, we speak of secondary intention. Of course, the first way is preferable; it helps prevent the formation of a rough scar.
Wound healing occurs in three stages. The first of them is self-cleaning of the damaged surface. It occurs due to the physiological reaction of increasing the permeability of the walls of blood capillaries in response to damage. As a result, part of the blood plasma is released into the tissue, which appears on the surface of the wound, helping to cleanse it of contaminants and microorganisms.
The next stage is the inflammatory process, a natural consequence of the presence of contaminants on the surface of the wound, as well as tissue damage itself, which is accompanied by cell death and intoxication of the wound. When healing by primary intention and high-quality cleansing of the wound, inflammation is minimal.
Following inflammation, the stage of regeneration begins, it is manifested by the proliferation of granulation tissue, after which epithelization of the wound occurs, that is, the formation of new integumentary tissues. According to some classifications, the phase of wound epithelization is distinguished as a separate stage of healing, while other experts consider it an integral part of the granulation process.
How to speed up wound healing?
First of all, you should remember: the process of wound healing is an absolutely natural mechanism, the wound heals itself, and a person’s task is not to interfere with this process, not to disrupt it in any way. However, it is possible and necessary to speed it up and avoid possible complications. To do this, it is necessary, first of all, to provide competent first aid to the victim. In addition, it is important to consult a doctor promptly. Sometimes there is no need to treat a wound in a hospital setting; treatment can be carried out at home, but consulting a specialist in any case will not be superfluous. The organization of the wound treatment process also plays an important role. If all conditions are met, the regenerative capabilities of the body will help to quickly eliminate the damage, and soon epithelization and granulation of the wound will occur.
How can hematomas be dangerous?
Often, a more serious damage to facial tissue is hidden under a hematoma - a fracture. Therefore, most facial soft tissue injuries require careful analysis and careful x-ray examination. For a more detailed study of the bones of the facial skeleton of the skull, we use a computed tomograph. With its help, you can identify even subtle damage to bone structures and prevent possible complications.
Unfortunately, there are “folk methods for treating bruises and hematomas,” which result in complications in the form of their suppuration. Any warming compresses, ointments, bandages can only aggravate this situation.
All that is needed to prevent the process of suppuration is cold, a pressure bandage and a thorough examination by a specialist.
Facial wounds.
Wounds and abrasions on the face have a number of specific features. This is the superficial location of the vessels, the presence of facial muscles, as well as the close location of important organs.
However, wound healing in the maxillofacial area has a high regeneration potential due to increased blood supply and good innervation in the facial area.
At the first aid stage
The process of its healing in the future largely depends on how effectively and competently first aid is provided when receiving a wound. Therefore, as first aid you need:
- stop the bleeding,
- wash the wound, clean it of dirt and foreign bodies.
To stop bleeding, a tourniquet is used (when applied, be sure to indicate the time when it was applied) or a pressure bandage. It is advisable to wash the wound with an antiseptic solution, hydrogen peroxide (which, by the way, helps stop bleeding) or, in extreme cases, with clean water. It is important to remove any foreign particles from the wound surface - each of them can subsequently become a source of purulent inflammation and, as a consequence, complications of wound healing. Large debris, slivers, and fragments are removed using tweezers.
Doctor's consultation: when is it necessary?
It is recommended to see a doctor, even if the wound does not seem serious. In addition, there are a number of cases when you cannot do without the help of a specialist. Such cases include:
- continued bleeding from the wound - it may be necessary to stop it by ligating the vessel, applying a suture, or using a hemostatic sponge;
- foreign bodies remaining in the wound, contamination;
- wounds caused by heavily contaminated, rusty, painted, grease-coated objects;
- wounds with signs of inflammation;
- wounds caused by animals;
- suspicion of a fracture, dislocation, ligament rupture.
In addition, it is not recommended to try to use certain medications on your own. The doctor prescribes an ointment for wound epithelization.
What can affect the wound healing process?
In addition to the type of wound (wounds with smooth edges heal faster), regeneration processes directly depend on the condition of the body itself. Consequently, sufficient rest, good nutrition, intake of vitamins and minerals into the body, and giving up bad habits have a positive effect on wound healing. It should also be taken into account that there are a number of diseases that can significantly inhibit the healing process. These are endocrine diseases (in particular, diabetes mellitus); pathologies of the vascular system, which are accompanied by a decrease in the intensity of blood microcirculation; anemia; hypovitaminosis conditions; cachexia (exhaustion); some cancers; obesity; pathologies of the urinary system; liver diseases; skin pathologies, including those of an allergic nature; immunodeficiency states. Therefore, in the presence of such pathologies, attention should be paid to their treatment, or at least compensation - this will have a positive effect on the healing time and will ensure accelerated epithelization of the wound.
The purulent-inflammatory process that begins in the wound surface significantly slows down and complicates the healing process. Therefore, one of the most important tasks in wound treatment is the prevention of purulent complications. For this purpose, first of all, a thorough initial treatment of the wound by a surgeon is performed. During it, if necessary, dead tissue in the wound is removed, the edges are smoothed, bleeding stops, and the wound itself is thoroughly cleaned of clots, dirt, and foreign bodies. After this, surgical sutures are placed on the wound, or, if there is a need to monitor the wound, it is left open (in this case, sutures will be applied later). The treated wound is covered with a sterile sticker or bandage, which prevents additional trauma to the wound surface and its contamination. Also, in order to prevent purulent complications (or if purulent inflammation has already begun), antibiotics may be prescribed to the victim.
The use of ointments with an antimicrobial effect - for example, Sulfargin - plays a major role in accelerating the healing of a superficial wound, which does not require the intervention of specialists. The active substance of the drug - silver sulfadiazine - has an antibacterial effect, which is prolonged due to the gradual release of silver ions from the ointment. In this regard, one application of the drug per day is sufficient. Sulfargin not only has an antiseptic effect, but also keeps the wound in a moderately moist state under the bandage, which helps make dressings less painful and traumatic. Applying a bandage with Sulfargin ointment to the wound after cleaning it helps speed up the healing process and prevent the development of complications.
Also, to speed up wound healing, ointments with hemoderivat of dairy calves (banned in Europe and America, but used in Russia), preparations based on polyethylene oxide, methyruracil, ichthyol, propolis, syntomycin, plant extracts (in particular, aloe, tea tree, eucalyptus) can be used ), ointments with vitamins (B5, A, C). You should know that drugs that accelerate wound healing should be used only as prescribed by a specialist.
Competent first aid and further treatment of the wound are the most important conditions for its speedy healing and the absence of complications.
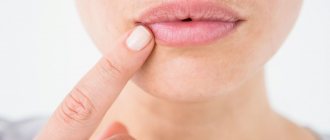
Types of allergies on the face
If in children the most vulnerable area is the buttocks, where signs appear that indicate certain foods or unfavorable conditions, then in adults this is the nasolabial triangle, eyelids, lips, tongue, neck and hands.
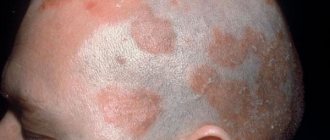
Atopic dermatitis
Chronic inflammatory skin disease. Most often begins in early childhood. The priority prerequisite is genetic predisposition. It can be a concomitant disorder with bronchial asthma and conjunctivitis. There are infant, child and adult forms of the disease.
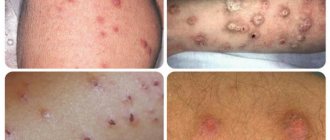
Hives
Allergies and rashes in the form of pimples on the face, the photo of which most often appears on advertising posters of the newest antihistamines, occurs with a seasonal variant. It is characterized by lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, obsessive itching, and redness of certain areas of the body.
Food reactions can occur instantly when certain foods enter the mouth and esophagus. Most often they are milk, eggs, red or yellow fruits, and nuts. Peanuts are the most dangerous in this regard.
Contact dermatitis
Recognizable by clear zones of irritation. The causes are hygiene and cosmetic products, chemicals that come into contact with unprotected skin, jewelry, piercings, latex products, extracts and juices of certain plants. It manifests itself in the form of weeping erosions, in place of which dry scales then appear. To understand how to remove facial allergies, you need to find and eliminate the substance that causes your health to worsen. Often a good result comes from moving to another region. This way, it is possible to cut off some of the options; for the rest, you will have to take special tests in the laboratory.
Toxicoderma
A distinctive point is inflammation not due to external factors, but due to the penetration of a provoking substance into the body. In some cases, it can cause secondary damage to internal organs and anaphylactic shock, since it develops rapidly from the ingestion of an allergen from the inside. One way to prevent inflammation is to take antibiotics, especially penicillin. At the same time, timely treatment gives good results.
The alimentary variety is included in a special group; the deterioration of the condition is provoked not by products, but by food additives in their composition. It is quite dangerous due to the fact that it can occur suddenly, since manufacturers do not indicate all the ingredients in the composition.
Quincke's edema
It poses a direct threat to life. In the question of what an allergy on the face and neck looks like in this case, what to do and how to treat it, time is of the essence. Choking occurs quickly, and the slightest delay can have fatal consequences. An acute inflammatory reaction of the body, which occurs locally in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, affects deep layers, including the muscles of the respiratory system, and in a third of cases is localized in the larynx. It is impossible to prevent the development of Quincke's edema. Women suffer from this disorder more often. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and requires medical attention. Signs may persist for several days and disappear gradually. Treatment includes the administration of potent antiallergic drugs. In severe cases, the patient requires urgent hospitalization in an intensive care unit or intensive care unit.