home
/
Articles
/
Consequences of late suture removal
Suturing is a surgical intervention after or instead of surgery, which serves to heal the tissue. Application is resorted to only in cases where the wound is extensive and cannot heal on its own. At the moment, there is a large amount of not only medical materials for this procedure, but also many execution techniques. The technique and materials are selected solely on the basis of the nature of the wound, location and experience of the surgeon, and neither the application nor the removal process is discussed with the patient.
Now such an intervention does not take more than 15 minutes, but recovery can last for weeks. Even if you need to have stitches removed, it is not necessary to stay in the hospital, as it is now quite common to remove stitches at home with the help of specialists.
What types of seams are there and what is their difference?
Depending on the degree of tissue damage, there are many types of sutures and methods of applying them. But they are all divided into external and internal.
External sutures or, as they are also called, superficial sutures: applied to the skin or superficial mucous membranes in one layer, the threads are removed immediately after the tissue has grown together.
Internal seams (plunging) remain deep in the fabric. Most often, absorbable sutures or sutures are used that can later exit through the genitals.
Departure is paid separately - from 550 rubles
Request a call
Call:
+7 (499) 455-08-05
Regardless of what type of seam is used, there are the following types:
- skin;
- muscular;
- tendon;
- capillary;
- intestinal.
The type of suture is selected depending on the depth of the wound and its location. Another important aspect is the patient’s age, since older people have a very low ability to regenerate tissue, which is why submerged sutures are most often used on them.
How is septoplasty performed?
Like classic rhinoplasty, the operation is performed using one of two techniques. The closed technique involves incisions on the nasal septum and the absence of visual control - the surgeon performs manipulations without seeing the working area. The suture in the nose after septoplasty performed using the closed method is small in size, so postoperative marks are completely invisible to others.
With the open technique, incisions are made on the septum between the nostrils and along the mucous membrane of the nostrils. The surgeon then carefully peels away the tissue and works directly with the cartilage structures. After correcting the nasal septum, the doctor returns the tissue to its place and applies stitches. Sutures after closed septoplasty are more voluminous, but a competent application procedure and modern suture material can reduce the visibility of marks to a minimum.
Why and in what cases are stitches applied?
A large cut or wound, whether in an adult or a child, may require stitches. This is done for several reasons:
- for rapid healing of the skin;
- to avoid infection in an open wound;
- for an aesthetic appearance (when a wound has formed on the face).
Only a doctor can determine whether a wound can heal on its own. In doing so, he is guided by the following principles:
- Depth of the wound. Are subcutaneous layers or fatty tissue visible in the wound?
- Disclosure. Is it possible to gently close the edges of the wound?
- Bleeding from the wound. How heavy is the bleeding and can it be stopped?
- Location of the wound. If the wound is on the face, joints, bends of the limbs, or near (inside) the genitals.
- Method of obtaining a wound.
- The presence of a foreign object in the wound.
If the wound is not that serious, then doctors simply apply a bandage and write recommendations for treatment.
Pathology and norm
With any invasive procedure, swelling occurs in the soft tissues. It goes away on its own within a few days. The same can be said about pain. Cheekbones, adjacent teeth, head, and neck may hurt. If after 3 or 4 days the symptoms do not disappear, but increase, then this indicates pathology.
What are the complications after tooth extraction:
- alveolitis, osteomyelitis, most often occurring with dry socket;
- inflammation near the seams;
- damage to the adjacent dental unit;
- perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, if extraction is performed on the upper jaw;
- fracture of the alveolar process, sharp edges of the alveolus that injure soft tissues;
- neuritis of the inferior alveolar nerve;
- postoperative cyst;
- paresthesia, which is characterized by numbness, loss of sensitivity of the cheeks, tongue, jaw and other adjacent areas;
- ondogenic phlegmon, periostitis;
- a hematoma in the neck can occur in people suffering from arterial hypertension (blood leaks out of the vessels into the tissue);
- soft tissue abscesses.
Pus and flux after tooth extraction characterize an acute inflammatory process that requires urgent treatment. Purulent inflammation can occur with insufficient antiseptics during surgery or poor postoperative care, with a dry socket, when food particles get into the hole. A new surgical operation is required to remove necrotic masses.
When to see a doctor:
- on the second and third days the swelling does not subside, but the cheek continues to swell;
- the pain becomes more intense and is difficult to eliminate with medications;
- the high temperature lasts for several days, normally it should decrease within 24 hours;
- no appetite, nausea, weakness;
- when pressing on the gum, pus is released, and its edges turn red;
- when palpating the hole with the tongue, no blood clot is detected.
If inflammatory processes are started, this can lead to the melting of bone tissue, an abscess and the spread of infection.
Technique for applying postoperative sutures
Suturing is the final chord that completes the operation and leaves behind the entire journey of saving the patient’s life. Sutures can be continuous or interrupted. The choice depends on the location of application.
Order suture removal at home
Promotion
Included in the price:
- Antiseptic treatment
- Removing suture material (suture removal)
- Secondary treatment with antiseptic
- Applying healing ointment
- Applying a bandage
- Necessary materials and preparations
More details about the service
A continuous suture is placed on the abdominal cavity with one thread if there is no separation of the edges. There are several types of continuous seam, each of which has its own technique:
- Furrier. The first suture is placed with a knot near the corner of the wound. Subsequent ones are at the same distance from the edges of the wound.
- Purse string. Applied to temporarily close natural openings in the skin.
Intermittent or knotted sutures are stronger; after they are applied, several knots can be removed to administer medications or wash the wound. There are:
- simple;
- loop-shaped;
- suture with the formation of a skin fold;
- situational.
Despite the wide variety of interrupted sutures, they are applied using the same technology. It is necessary to have several threads in the needle from 15 to 25 cm. The stitches are placed 1.5 cm apart, after each stitch you need to tie a knot.
Suture care after abdominoplasty
Not only the skill of the plastic surgeon who performed abdominoplasty affects the speed of rehabilitation. The joint efforts of the patient, the attending physician, medical staff, and relatives supporting the person after a complex operation are required. It is necessary to carefully follow all the instructions of the plastic specialist in order to speed up recovery and return to normal everyday life. Proper care of scars, a diet that guarantees the rapid formation of collagen and elastin, and constant wearing of compression garments have a positive effect on the rate of wound healing. According to statistics, the popularity of tummy tuck is steadily growing. Men and women want their belly to look sculpted, beautiful, and complement their impeccable curves.
On a note!
The less postoperative complications there are, the better the scars will look. The aesthetic appeal of the image will be impeccable. The patient will not have to use additional services of cosmetologists to make the scars less noticeable.
Hospital care after abdominoplasty
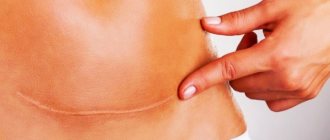
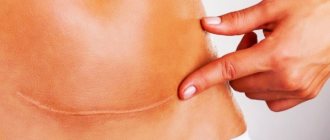
A tummy tuck is always done under general anesthesia. Depending on the complexity of the chosen technique and the duration of the operation, general or local anesthesia or epidural anesthesia is used. Classic abdominoplasty lasts up to five hours. The tissue above the pubic area is cut, and most of the skin is peeled off from the bottom of the anterior abdominal wall to the upper edge of the hypochondrium. After this, hernias are removed, if any, and excess skin is excised. Then the surgeon tightens the skin to eliminate sagging, ptosis, and stretch marks. The rectus abdominis muscles are sutured in case of diastasis. A scar after surgery up to 60 cm long cannot be hidden under underwear.
After the plastic surgeon completes the work, a bandage is put on the patient and he is moved to the hospital room, where he waits until the anesthesia completely stops working. A special bed makes it possible to create conditions for rest so that the body is slightly bent at an angle of 45 degrees. This reduces stress on the scar while the patient is lying down. In addition, a special cushion is placed under the knees to elevate the legs, thus reducing the risk of seams coming apart. Drainage tubes are inserted to drain accumulated fluid from damaged cells and disrupted lymphatic ducts in order to minimize the risk of seroma formation on the anterior abdominal wall.
In the hospital, the patient is monitored by qualified medical staff, who ensure regular treatment of scars with a disinfectant and anesthetic solution, give the necessary injections, and bring prescribed medications strictly at the appointed time. The nurse controls all the patient’s movements and, if necessary, helps to stand up or lie down in order to minimize abdominal tension and minimize the risk of unhealed sutures coming apart. Having discovered that ichor is protruding from the incision, suppuration or necrosis has begun, the surgeon immediately takes the necessary measures to eliminate the complication. The examination is carried out daily; if there are complications, the doctor checks the condition of the scars several times a day. Ideally, the edges of the wound are dry and smooth.
Caring for scars at home after abdominoplasty
If wound healing proceeds without complications, the drainage is removed on the second or third day, and the patient is discharged from the hospital home. It is necessary to take into account that you will have to get there by taxi or your own car; public transport will not provide a safe crossing. It is necessary to adjust the seat in such a way as to minimize the load on the rumen. During the move, shaking should be minimal, since each impact is dangerous for the seam.
Before going home, the patient receives detailed instructions for scar care, which he must strictly follow so that the tissue regeneration process occurs as quickly as possible without complications.
- Carry out disinfection procedures several times a day every day.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor strictly at the right time to ensure rapid healing of wounds.
- Use only what is prescribed by your doctor, without using the advice of acquaintances, friends or the Internet.
Important!
In case of any deviations caused by allergic reactions or individual characteristics of the body, you must immediately contact your doctor.
Pay special attention to a balanced diet during the rehabilitation period. Bowel movements should not cause abdominal tension. Constipation and flatulence can disrupt the integrity of the scar. Be sure to include in your diet dishes that contain ingredients that help speed up the synthesis of collagen and elastin for faster scarring. Pay special attention to foods that enhance the effectiveness of the immune system and help speed up blood production.
It is necessary to constantly wear a bandage that protects the scar from any stress. Even when the wound from the operation heals completely in a month, you should not take risks by walking without compression garments. Special high-waist panties or bodysuits will provide maximum protection when bending or turning the body, creating comfortable conditions for the skin, which needs regular light massage that restores capillary blood flow and lymph movement.
Types of scars after different abdominoplasty techniques
The chosen method of eliminating pathologies is reflected in the postoperative marks that appear on the patient’s body.
- With classic tummy tuck, the scar will stretch from side to side just above the pubis by 6 cm. If it was necessary to move the navel, there will be additional scars in the form of a horseshoe or a triangle.
- With a vertical abdominoplasty, a classic transverse incision will complement a vertical scar extending to the base of the sternum.
- When excess fatty tissue on the sides is removed, two vertical ones will be added to the transverse scar, running parallel at equal distances from the white line of the abdomen.
- If ideal contours of the hip area are formed, a pair of lateral ones are added to the horizontal incision, running along the lower back.
- Mini abdominoplasty is the most gentle type of plastic surgery, in which a 20 cm scar is located just above the pubis and is easily hidden behind underwear.
- The most traumatic is circumferential abdominoplasty. Scars will appear on the stomach, around the waist, on the sides, and back.
Possible complications after abdominoplasty and aftercare
Strict adherence to the rules prescribed by the attending physician reduces the risk of pathological changes due to tissue scarring. However, you need to know what problems can be encountered if you neglect the rules of wound care.
- Infiltrate. Appears in approximately 7-10 percent of patients after tummy tuck. Exudate forms on the anterior abdominal wall above five centimeters from the incision, which oozes, delaying tissue scarring. The seam gets wet, irritated, and hurts. The cause may be a surgeon's error, poor-quality threads used when suturing the incision, or improper placement of drainage tubes. Treatment is prescribed in the form of antibiotic injections, novocaine blockade, repeated surgery to clear suppuration, and installation of a new drainage. If any discharge continues to appear from the wound, you should immediately inform your surgeon.
- Divergence of the edges of the scar. To prevent the suture from coming apart, you must strictly adhere to the rules specified by the surgeon, constantly wear a bandage, do not lift heavy objects, and do not make sudden movements until the scar is completely formed. If you notice that the wound has split open, you should immediately consult a doctor to have new stitches applied. Special ointments and gels that are used to regularly treat the seam will help speed up the scarring process.
If you strictly follow the rules of scar care throughout the year, it will be practically invisible. If necessary, you can use additional cosmetics so that the scar does not stand out on the skin.
What affects the time for suture removal?
The main indicator for removing a suture is wound healing. If the sutures are removed too early, the tissues may separate again, resulting in the need for repeated intervention or an unsightly scar that will then have to be removed. If the suture is removed too late, it can cause suppuration or inflammation of the tissue. It is believed that the optimal period for removal is 10 days after application, but the period may vary, depending on the type of operation:
- amputation of limbs - from 12 days to 2 weeks;
- abdominal surgery – up to 1 week;
- Caesarean section - on the 10th day;
- eye surgery – from 6 to 8 days;
- Chest surgery - 2 weeks.
But a specialist can determine whether to remove the stitches or not, based on the patient’s current condition. If it is necessary to hold the suture for a long time, daily treatment of the wound will be required to ensure that the wound does not become inflamed.
In addition, there are several types of postoperative sutures, which also have their own removal times. These include:
- Primary suture - it is applied immediately after surgery. The duration of removal depends on the operation and the current condition of the patient.
- Secondary - applied in case of consumption of the primary seam. It happens:
- early - 1-2 weeks after surgery;
- late - within a month after surgery.
It is important to remember that only a specialist can remove postoperative sutures.
Departure is paid separately - from 550 rubles
Request a call
Call:
+7 (499) 455-08-05
Stages of scar formation
There are several stages of scarring of the damaged area:
- the first lasts about 5-7 days,
- the second lasts up to 1 month,
- the third lasts for 6 months,
- the fourth lasting about 12 months.
The first phase is also called the inflammatory phase. At this time, granulation cells form at the site of the incisions. It is at this moment that the mark from the operation has the most pronounced red or burgundy tint, and also protrudes noticeably above the level of the rest of the skin.
The location of the scars depends on the type of correction.
The second stage, proliferation, is characterized by the formation of a new capillary network at the site of damage, the removal of swelling and redness. During the third phase, over six months, the scar becomes lighter and less prominent.
Finally, at the final fourth stage, the scar after abdominoplasty gradually acquires its normal, natural appearance, becoming light, flat and inconspicuous against the background of normal skin.
What thread are used to stitch the stitches?
Now there are quite a few types of threads that surgeons use; they can be classified both by brand and by characteristics. There are these types of threads:
- Absorbable. Able to be independently excreted from the body, incapable of rejection. These types of threads are used if the tissue is able to grow together quickly.
- Non-absorbable. Used for stitching tissues of internal organs or if long-term (permanent) stitching of tissues is necessary.
Absorbable threads are created from materials such as:
- nylon;
- polypropylene;
- catgut;
- lavsan.
When using this type of thread, it is necessary to accurately determine the rate of tissue fusion, since if the thread is removed from the body earlier than necessary, this can cause a number of problems.
Non-absorbable threads consist of the following materials:
- cotton;
- linen;
- silk.
This type of thread has a number of disadvantages. The most important thing is the ability to form microbes in tissue. When choosing, the doctor is guided not only by the purpose of the thread, but also by his own experience, and the patient’s preferences are not taken into account.
Materials used in osteoplasty
Osteoplasty uses both natural implants and artificial ones (allosynthetic materials). Natural ones include:
- Autogenous grafts are those that were taken from the same patient and transplanted into him. This material survives better than all other grafts, but you need to understand that another operation will be performed to remove tissue from the donor site.
- Allografts are material that has been taken from a donor's dead body for medical purposes. The material is carefully processed, disinfected, it perfectly restores bone tissue and is used in osteoplasty with great success.
- Xenografts are material taken from certain species of animals and corals. It is also carefully processed, sterilized and prepared for further use in invasive dental procedures associated with implantation.
Synthetic (alloplastic) implants are made on the basis of calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite; they are also widely used by all specialists around the world.
How long does it take for threads to dissolve after surgery?
Absorbable threads are used both in surgical operations on the face and in deep tissue layers, and are also used in organ transplants. The main function is to maintain tissues in a stable state until they grow together.
The main factors due to which material can be excreted from the body include:
- chemical reactions of the body when interacting with protein;
- contact with water in the body.
The rate of removal of threads from the body is influenced by the material from which it was created:
- Catgut begins to dissolve after one month, and is completely eliminated from the body after 4 months.
- Lavsan dissolves within 12-13 days, but dissolution may take 1-1.5 months. Most often this material is used in cosmetology.
- Vicryl begins to be eliminated from the body after 2-3 months.
In this case, it is necessary to follow all the rules for wound treatment, since the healing process can not only be delayed, but also cause inflammation or suppuration.
If your gums are inflamed
It is not always possible to avoid infection of the wound surface, especially when the patient neglects the advice of the dentist. In case of inflammation, you should consult a doctor for examination and identification of the causes of inflammatory reactions.
If the hole is not closed after tooth extraction, alveolitis develops. The natural plug can come off due to intensive rinsing, licking the wound with the tongue, resumption of bleeding and improper actions to stop it. Alveolitis is accompanied by acute pain syndrome. Not only the injured area may hurt, but also the throat, head, jaws, and neighboring teeth.
How long the gums heal after tooth extraction depends on various factors:
- complications of surgical intervention;
- the presence of inflammation or other complications;
- age criterion, the older the patient, the longer the healing and tissue restoration takes place;
- state of immunity, individual characteristics.
When should stitches be removed?
The main indicator for removing stitches is wound healing. Factors such as:
- presence of complications;
- patient's age;
- Current state;
- nature of the surgical intervention.
The location of the seam plays a special role; depending on it, the timing of thread removal is set:
- areas of the body with active blood supply - 5-6 days after application;
- shins, feet, arms, knees - approximately on day 10-12, since in such areas there is a slower recovery rate;
- infected wound - the sutures are removed the next day, as treatment and openness are necessary for speedy healing;
- clean wound - a week after application.
Only a surgeon can determine whether removal is necessary at the moment or not during an examination. In addition, for elderly people, sutures are removed no earlier than after 2 weeks, since they have a very low ability to regenerate.
Techniques used in bone grafting
- Alveolar process resorption is used for horizontal bone splitting when it is necessary to increase the density of the alveolar process. It is performed on both jaws, and today is the most popular method for increasing the volume of the alveolar process, while having a low cost compared to more expensive procedures. Again, there are variations of this technique, but it’s worth paying attention to “Split Control”. The technique makes it possible to simultaneously expand the space and install an implant.
- To increase the volume and length of the alveolar process, a bone block transplantation technique is used. Autogenous material is more often used here. The principle is to screw a bone block taken, for example, from the maxillary region of the zygomatic-alveolar ridge to the bone, using medical mini-screws made of titanium alloy. Then it’s all covered with bone shavings and covered with a connective tissue membrane, which is secured. Subsequently, the surgical wound is tightly sutured with synthetic thread. The disadvantages of autogenous material were discussed above, which should be taken into account when choosing therapy.
- Guided tissue regeneration is a method in which it is possible to both increase the height and expand the volume of the alveolar processes. This technique also involves the simultaneous installation of an implant.
The guided bone regeneration technique includes two components:
- implanted bone material;
- a special barrier membrane that protects against the effects of various infectious agents and other unpleasant factors.
It is important to understand and take into account that the technique of directed bone regeneration does not always provide a sufficient effect. When using this method, bone material is “planted” on the outside of the cortical plate of the upper or lower jaw. The bone structure is very different from its own and is prone to incomplete splitting. Therefore, such an operation should be performed by an experienced doctor who knows all the nuances of the technique and can adequately assess further treatment tactics.
Suture removal technique
Following the correct algorithm for removing sutures and maintaining sanitary conditions allows you not only to avoid infection of the wound, but also to speed up healing. Specialists explain the procedure to the patient before performing it and place him on the couch. The procedure has the following algorithm:
- Removing the protective bandage.
- Inspect the wound and determine the number of stitches to remove.
- Treating the wound with an antiseptic. It must be carried out 2 times to prevent infection, near the wound and inside.
- The suture knot is grabbed with tweezers and lifted.
- The thread that appears after pulling is cut.
- The suture is pulled back with tweezers and the knot is removed.
- Checking the integrity of the skin.
- Treating the wound with an antiseptic.
- The area is covered with a sterile napkin and then fixed with either a bandage or adhesive tape.
This procedure is performed in a hospital, but it is now quite common for postoperative sutures to be removed at home by a specialist.
How to speed up healing?
To help the body recover faster and cope with the consequences of surgery, it is necessary to follow the rules of rehabilitation. To combat edema, you should avoid:
- salty food
- smoked meats,
- smoking,
- alcoholic drinks.
All of the above can slow down the resorption of swelling. Thus, salt retains water in the body, and nicotine provokes vasospasm, which, in turn, leads to the fact that nasal swelling after septoplasty goes away more slowly than it could.
You should also not sleep on your stomach, tilt your head, play sports, wear glasses, visit the sauna or solarium, or take hot baths. Of course, these restrictions are not forever, but only for the period of rehabilitation. After successful healing, you can return to normal life.