Suppurating atheromas are a disease represented by the presence of a cystic formation on the surface of the skin.
In the absence of an infectious process, the cyst looks like a small round wen with clear edges.
Any mechanical injury can lead to damage to the epidermis and, accordingly, to the development of atheroma. In this case, the disease progresses and affects nearby tissues.
Festering atheromas can reach the size of a chicken egg, causing considerable discomfort to the owner.
Complications of the disease
Suppurating atheromas lead to various complications: the development of an inflammatory process, the formation of phlegmon or an abscess.
Inflammation occurs when an infection enters the cavity of the cyst - it increases in size, becomes hyperemic and painful.
Phlegmon is a disease in which the purulent contents of the atheroma do not come out, but remain under the skin.
An abscess occurs when the capsule ruptures. There are cases when the disease took on an oncological character.
Surgical treatment for atheroma
The essence of the operation is to remove the tumor along with the capsule without opening it. The length of the incision is about 3 cm, but if the atheroma has reached a large size, the incision will be slightly larger. In our clinic, ultrasonic scissors (Harmonic) are used during the operation, so there is no risk of bleeding. The duration of surgery, in contrast to operations using traditional instruments, is much shorter. To close the surgical wound, we use the modern drug Dermobond, while the protective film in the postoperative period protects the wound from infection or moisture. This way, the patient can shower after surgery without fear of getting the surgical site wet. There is also no need for daily dressings, which allows you to minimize visits to the doctor. After 7-14 days, the glue is easily washed off.
We can also offer the patient removal of atheroma using electrosurgery in the Valleylab mode (FORCE TRIAD, Switzerland). This method ensures minimal tissue trauma; the incision is made with simultaneous coagulation, which eliminates the possibility of bleeding. The risk of developing postoperative hematomas and the formation of rough scars is also reduced. Thanks to the bactericidal effect, the likelihood of developing edema or purulent complications is excluded. In addition, it should be noted that there is no pain in the postoperative period and an excellent cosmetic result. Moreover, there is another undeniable advantage of the technique - a short rehabilitation period. The patient can leave the clinic almost immediately; full recovery occurs in 3-5 days.
Diagnosis and treatment
At the first signs of suppurating atheroma, you must contact a surgeon who will conduct a visual examination.
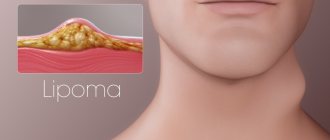
At this stage, it is important to distinguish a cystic formation from a lipoma, hygroma and granuloma.
An ultrasound is performed to get a picture of the cyst cavity.
The treatment for atheroma is surgical removal. Laser and radio wave therapy are not performed in this case.
The operation on the inflamed area consists of two stages:
- opening the abscess, cleaning the cavity from pus and gland secretions;
- removal of the inflamed capsule with formed atheroma.
This manipulation is characterized by local anesthesia (lidocaine, ultracaine). At the final stage, the patient is given a cosmetic suture, which is removed 3-5 days after the operation.
The course of therapy includes antibiotics such as Sumamed, Doxycycline, Lincomycin.
Wen removal is performed on an outpatient basis.
The resulting material is subject to laboratory testing.
Removal of atheroma - planned and urgent
23.09.2019
Removal of atheroma is a small outpatient operation , the trace of which may be practically invisible if cosmetic stitches are applied. Therefore, remove it as planned.
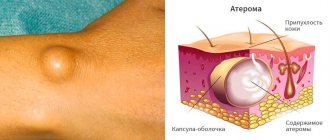
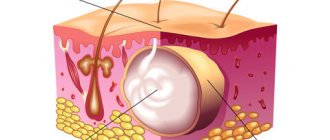
Atheroma is a cyst of the subcutaneous sebaceous gland. The main function of such a gland is to produce fat to lubricate the skin and protect it from environmental influences. Fat enters the surface of the skin through ducts in small portions. If, as a result of injury or inflammation, the ducts of the sebaceous gland become clogged, sebum accumulates under the skin and so-called atheromatous masses are formed. Often atheroma occurs at the site of a former boil . the atheroma through the same duct .
Clinical picture
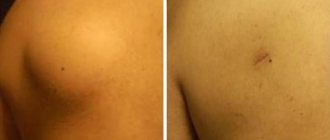
Atheroma looks like a regular round swelling located under the skin. The size of the atheroma is from a pea to a large plum. The formation is painless, moderately mobile, can be located on any part of the body, except the palms , and often occurs on the scalp.
Planned removal of atheroma
Removal of atheroma is carried out for cosmetic reasons or if it is located in the projection of folds of clothing and is injured, causing discomfort when pressed. It is also advisable to remove it in the case when the tumor is constantly injured during its life. It is necessary to remove atheroma on the face and neck , that is, where the absence of scars is important.
If the atheroma is not inflamed, removal is performed routinely on an outpatient basis.
Before the operation the following tests are required:
- clinical blood ;
- Analysis of urine ;
- blood for AIDS and hepatitis;
These examinations are aimed at identifying hidden inflammatory processes to prevent complications.
Under local anesthesia with novocaine or lidocaine, an incision is made in the projection of the formation. the atheroma without breaking its capsule. It is not tightly connected to the surrounding tissues; the capsule peels off quite easily. After removal, the capsule is opened and, if there are atheromatous masses inside, histological examination is usually not performed. Stitches are placed on the wound.
It is advisable to apply special cosmetic sutures. The wound is covered with a sterile bandage , which is changed first daily and then every other day. The sutures are removed after 5-10 days, depending on the location of the atheroma : on the legs the wound takes longer to heal, on the scalp faster.
Laser removal of atheroma
A laser removal technique has now been developed The technique has many advantages:
- tissues are minimally injured;
- complete asepsis during surgery ;
- there will be little bleeding.
After removing the atheroma with a laser, the wound will heal faster and the scar will be practically invisible. But removal is only possible if the cyst is small and has recently formed. The operation is carried out by evaporation. The skin is minimally damaged.
Removal of inflamed atheroma
If the atheroma , inflammation has begun, removal is carried out urgently. In this case, it will no longer be possible to remove it with the capsule, because the capsule is partially melted by pus. In this case, the abscess is opened, the atheromatous masses are removed along with the purulent ones, and the cavity is drained. Purulent and atheromatous masses are drained, and the cavity is washed daily with an antiseptic solution.
The need for antibacterial drugs is determined by the size of the atheroma and the degree of neglect of the process. If a patient comes with a large abscess a week old, with a reaction of the lymph nodes, then antibiotics cannot be avoided. When the inflammation is small and has just begun, the wound can simply be thoroughly drained, disinfected and washed.
In this case, it will no longer be possible to apply cosmetic stitches; the wound will heal by secondary intention, that is, the scar will be very noticeable. It can be adjusted later.
If there is atheroma , it is not necessary to remove it. But atheroma on the face , in the décolleté area, in any place where the scar would be a serious cosmetic defect, must be removed while it is still small. the operation : it is short and very simple.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic
Danger of atheroma
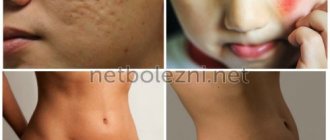
This dermatological disease is a tumor-like benign formation that can be located intra- and subcutaneously. Atheromas can be congenital (as a result of impaired development of the epidermis) or appear secondary due to obstruction of the sebaceous gland duct. Atheroma looks like a dense, painless, round formation, somewhat mobile and can increase in size for a long time and cause significant discomfort; it can also become infected and suppurate. Cases of malignant transformation of these formations have been recorded, but they were observed extremely rarely.
Causes of atheromas
True atheromas are usually called congenital variants of benign tumor-like formations (steatomas), which are formed from the epithelium. Acquired forms (secondary) are called false atheromas - they appear as a result of blockage of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous gland with the subsequent accumulation of sebum and other components of the secretion and the formation of a retention cyst. The appearance of secondary atheromas is promoted by improper extrusion of the acne rod, when a small amount of it remains in the duct and blocks it. Risk factors for the appearance of secondary atheromas are also various hormonal disorders, abnormal structure of the ducts of the sebaceous glands, inflammatory changes in the skin, acne, rosacea, improper use of decorative cosmetics or neglect of personal hygiene rules
The clinical picture is limited to the appearance on the skin of a dense elastic formation of any size (usually from one to several cm) with a favorite localization in the face, neck or back. The formation gradually increases in size and can cause severe discomfort. Tumor-like formations can be single or multiple and are usually characterized by clear contours, mobility, and an elastic, dense consistency. The atheroma itself is represented by a connective tissue capsule that surrounds the contents (cholesterol, sebum, desquamated cells). On the surface of the formation, the opening of the excretory duct may be visible and the contents may periodically be released. When the atheroma becomes inflamed, the color of the skin changes, local soreness and swelling appear, which can be resolved by purulent melting of its contents and the pus breaking out. There is a high probability of recurrence of atheromas if they are not treated correctly. Complications of atheroma, in addition to secondary inflammatory changes, can be the spread of pus with the development of extensive abscesses and phlegmon, recurrence if the contents are not completely removed during treatment.
Atheromas: diagnosis and treatment
A dermatovenerologist and a surgeon are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of atheromas. Differential diagnosis must be carried out with such skin diseases as boils, benign tumors (lipomas, fibromas), syphilitic gummas, hygromas, dermoid cysts. For congenital true atheromas, which are usually located in the scalp, a differential diagnosis is made with cerebral hernias.
Diagnosing atheroma is not difficult. The main method of diagnosis is an external examination with the identification of a characteristic clinical picture: there is a retention cyst on the skin, which has all the properties listed above (dense structure, clear contours, mobility, etc.), but the reference sign is the identification of the opening of the excretory duct in the central part of the formation. In diagnostically difficult cases, it is possible to perform additional examination methods: material is taken for histological examination during surgical treatment.
Removal of atheroma
All atheromas are subject to surgical treatment, regardless of their size and location, because using a conservative method is quite difficult to completely clear the cyst and prevent its reappearance. Small formations, as well as uncomplicated atheromas, can be removed using diathermocoagulation; laser and radio wave therapy techniques are also used. In the presence of inflammatory phenomena, primary conservative anti-inflammatory treatment (ointments, physiotherapeutic techniques, use of antibacterial drugs) is indicated. After the operation, the sutures are removed after 1-2 weeks, depending on the speed of healing. Postoperative complications include secondary infection of the wound during surgery, the formation of a significant postoperative scar after removal of complicated atheromas. There is always a risk of malignant transformation, especially with atheromatosis (multiple formation of atheromas), so this disease should not be taken lightly.
Proper care
If the operation was performed using a scalpel, the surgeon will apply stitches. When using the laser or radio wave method, no stitches are applied. Stitches will be removed approximately a week after the procedure, and sometimes sooner.
If the removal of atheroma involved a serious surgical intervention, for example, a procedure was carried out for enucleation of a giant cyst located on the head under the hairline, bandages will be required.
After removing a large purulent cyst or atheroma, the wound is treated with spruce to prevent inflammation of the scar.
For two weeks after surgery (this is how long the healing process lasts), you must follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- Do not wet the removal area for at least two days.
- If indicated, use anti-inflammatory absorbable agents topically.
- If necessary, treat the wound daily with an antiseptic.
- Wear a bandage or a clean hat (if the operation was performed on the scalp). This will prevent infection from entering the wound.
The speed of wound healing and the likelihood of a scar depends not only on the methods used by the surgeon, but also on the characteristics of the patient’s skin.
Diagnosis of atheroma
It can be located in many places on the body, most often on the face, scalp, torso, arms, and scrotum. Often atheromas are multiple.
Upon examination, atheroma is a tumor-like formation of a round shape, soft consistency, ranging in size from 5 to 40 mm or more. The skin over the atheroma is usually not changed, but if inflammation occurs, it may have a reddish tint. Atheroma is mobile along with the surrounding tissues and is painless. Atheroma can remain small for many years or grow larger.
Sometimes the atheroma communicates with the surface of the skin through a small hole through which atheromatous masses can separate. Often atheromas suppurate; in addition, atheromas may rupture into the subcutaneous tissue. If the atheroma is small and does not bother the patient, then it does not need to be removed. In other cases, surgical treatment is indicated. Atheromas are removed under local anesthesia.
Symptoms of atheroma
Symptoms are not specific and include the presence of a tumor-like formation, painlessness, and a tendency to slowly increase.
During an objective examination, attention is drawn to the spherical formation that has a smooth surface. The growth is associated with the skin, and at the site of the exit of the sebaceous gland, the skin cannot be folded. The content of atheromas are drops of sebum, cholesterol, and keratinized epithelium (can be seen during further laboratory examination).
It is worth remembering that neoplasms such as atheromas can fester when accompanied by a bacterial infection. Then the clinic changes dramatically, the following arises:
- the appearance of pain;
- redness;
- swelling;
- discomfort when opening the jaw, chewing, talking and other movements;
- local temperature increase.
Such processes require quick and efficient solutions. This is all because the process can spread to other areas of the face. A serious complication is the progression of the process into the meninges. This spread occurs due to the penetration of toxic products into the bloodstream. Since the veins of the face do not have valves, the process quickly spreads into the deeper layers precisely because of them.
At the first symptoms of a neoplasm, you should consult a doctor and do not try to cope with the problem on your own. Remember, timely medical care will eliminate the disease in the early stages without any complications.
The main types of treatment for atheroma without surgery
Atheroma is a benign tumor formed as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands.
Atheroma forms mainly on the neck, face, groin area and back. The neoplasm is considered relatively safe, since it has no tendency to degenerate into cancer. Below we will tell you whether it is possible to remove atheroma of the scalp with a laser? and “is it possible for the tumor to re-form, as well as what earlobe atheroma and other forms of the disease look like. Causes of the disease:
- improper skin care;
- injuries, skin cuts;
- excessive use of deodorants;
- hormonal disorders;
- hypersweating (hyperhidrosis);
- pimples, blackheads;
- inflammation of the epidermis;
- metabolic disease.
The main method of treating pathology is surgery. Below we will talk about the types of treatment for atheroma without surgery.
Complications after removal of atheroma
Complications that arise after elimination of atheroma occur in extremely rare cases. When performing any surgical procedure, there is a risk of bleeding during or after surgery. After eliminating the atheroma, bleeding is extremely rare. In some cases, after removal of the atheroma, fluid may accumulate in the cavity; this can be either serous fluid or a small amount of blood. To prevent fluid accumulation during surgery, a thin drainage is installed and a bandage is applied to compress the cavity.
In the first days after removal of the atheroma, there may be a slight rise in temperature. If the temperature rises to high levels, swelling occurs, or intense pain appears in the wound area, you should immediately contact the clinic; this may be inflammation. Although inflammation rarely develops after surgery to remove atheroma, antibiotics are always prescribed as a preventive measure.
Cost of treatment of atheroma
The cost of the operation depends on the size of the tumor; more detailed information can be found by calling.
Causes of atheroma
There are true and false atheromas.
The true form occurs when there is an abnormality of the skin as a result of heredity. The rudiments of the sebaceous glands, which should be on the surface of the skin, are located deeper and do not come to the surface.
- False atheroma develops as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the gland, which leads to the accumulation of secretions in a gradually enlarging cavity. The cause of blockage may be metabolic and hormonal disorders in the body, hyperhidrosis, neglect of personal hygiene, use of low-quality cosmetics, etc. In addition, atheroma can appear when the hair follicle is damaged or the sebaceous gland ruptures due to an inflammatory process. Unfavorable risk factors that increase the risk of tumor development include acne and skin damage.
Symptoms of atheroma
The tumor has clear boundaries; when palpated, it is soft and mobile. In the center of the formation, you can notice a blocked sebaceous duct; often whitish contents are released from it. The tumor, in addition to psychological discomfort, can cause pain if it is in contact with clothing. An atheroma that has increased in size can compress nearby tissues and vessels.
Significant discomfort occurs when there is a complication, the signs of which are swelling around the tumor, pain when pressed, and redness. An attempt to get rid of the formation on your own is fraught with the development of an abscess, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, swelling, redness, and then the opening of the abscess. After a breakthrough, fistulas may appear; if the capsule is preserved, relapses will occur in the future.
Diagnosis of atheroma
The diagnosis can be made based on examination, but atheroma must be differentiated from fibroma, lipoma, dermoid cyst, or malignant soft tissue tumors.
Atheroma in a child
When examined by a specialist, it is extremely important to distinguish atheroma from lipoma. Atheroma in a child is a smooth, round neoplasm located deep in the skin. When palpated, it is soft and motionless. In most cases, the cyst does not cause any discomfort to the baby. There is no threat to health. When an inflammatory process occurs, the situation is completely different. The main symptoms include: redness of the tumor, pain when pressed, discharge of blood or pus. With such manifestations, urgent medical attention is required.
On our website Dobrobut.com you can make an appointment with a doctor and find out how to treat atheroma of the eyelid in a child. Consultations are conducted by specialists with many years of experience. If necessary, a diagnosis and course of treatment will be prescribed.
Possible consequences of atheroma
There are several most likely types of consequences of atheroma:
- Inflammation. This is the most likely and dangerous consequence of atheroma. Sebum and exfoliated epithelium, which are contained in the cavity of this cyst, are an excellent environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. It is not known for certain what exactly provokes inflammation of a previously stable atheroma, but it can happen at any time. After this, it is necessary to clean out the accumulated pus from the cavity as quickly as possible, treat it with an antiseptic and install drainage. Of course, all this should only be done by a professional doctor.
- Relapse. If, after inflammation, the atheroma capsule was not removed or part of it remained, it may reappear in the same place. The same thing, with a certain degree of probability, can happen with high-quality removal of atheroma. The cause of the relapses is not yet known.
- Phlegmon. The most severe consequence of atheroma is purulent melting of the capsule and its spillage into the subcutaneous layer or its breakthrough inside. The result can be phlegmon - diffuse inflammation of the subcutaneous tissues. Without urgent and adequate treatment, it can lead to the most severe consequences, including inflammation of nearby tissues and organs, and if it penetrates the circulatory system, sepsis.
- Inflammation of the postoperative scar. Of course, even after removal of the atheroma, there may be certain problems, for example, inflammation of the wound. As a rule, the cause is non-compliance with safety and care rules. It is worth considering that the larger the size of the lipoma, the longer the scar and the higher the likelihood of inflammation.
- Malignant degeneration. In extremely rare cases, a cancerous tumor may develop from the cells of the lipoma capsule. The probability of this is quite low, but it cannot be completely ruled out. Because of this, in controversial situations, the contents of the capsule are sent to a histology laboratory.
Thus, there are very likely unpleasant consequences of atheroma that should be avoided.