What is nail onychomycosis and how to treat it?
Onychomycosis is a disease that is localized in the area of the nail plate. Onychomycosis of fingernails and toenails is caused by various types of fungus. According to statistics, pathology is diagnosed in 10-20% of the population. Moreover, the disease occurs in adults and children, which is explained by the almost inevitable infection of all members of the same family.
The infection is most widespread among elderly people over 65 years of age. The reasons for the increase in the number of patients with onychomycosis in this age group are explained quite simply. Aggravating factors contributing to the progression of the fungus in this case are diseases and pathologies such as diabetes, excess body weight, disorders of the cardiovascular system, and osteoarthropathy of the feet.
What it is?
Onychomycosis is a nail disease caused by a fungal infection. This pathology is very common; in total, 10-20% of the world's population suffers from onychomycosis. The causative agents of infection are most often dermatophytes, somewhat less often - trichophytosis, microsporia and epidermophytosis.
Very often, the activity of dermatophytes is complicated by the concomitant development of yeast-like or moldy fungi, which enhance the negative manifestations of the disease and cause resistance to therapy.
How can you get infected?
The causative agent of the disease, a population of fungal spores, thrives in moisture. Therefore, infection most often occurs in the following places:
- public baths;
- saunas;
- swimming pools;
- changing rooms in gyms, showers.
Scales with fungal diseases disappear in patients with onychomycosis, settling mainly on carpets, floors, benches, unpainted wooden objects - there they multiply faster. Nail damage is most often caused by sharing shoes, towels and washcloths. Insufficient cleanliness of premises is often the cause. Inflammation of the nail plates on the hands usually occurs due to the scratching of microorganisms on the skin.
Onychomycosis often affects a person for the second time, even with prior use of antifungal drugs. If the pathogen is not completely destroyed, sooner or later the problem will return. In particular, this applies to treatment methods associated with nail removal - if the operation was performed incorrectly, the disease spreads to neighboring fingers. In addition, there is a possibility of becoming infected with new microorganisms due to unsanitary conditions.
Possible complications
Pessimists who do not believe that onychomycosis is curable should keep in mind that, fortunately, they are mistaken. However, if the disease is ignored or self-medicated without being sure of the correct diagnosis, problems may arise.
Possible complications include:
- the occurrence of mycotic eczema with a large area affected by the fungus;
- burns caused by improper use of keratolytic plaster;
- dysfunction of the liver and gastrointestinal organs, caused by the accumulation of toxins in the body;
- the development of an allergic reaction, also occurring due to the fact that the body is “overloaded” with substances harmful to it;
- psychological problems caused by the fact that a person cannot live an ordinary life - for example, without hesitation, visit the bathhouse, go to the beach.
Information about the manifestations and treatment, classification and photos of symptoms of the Coxsackie virus in children can be found in this material.
Causes and symptoms, treatment methods and photos of carbuncles - all this is in the next article.
Classification
But before treating onychomycosis of the toenails, the form of the fungal infection should be determined.
So, the following types of onychomycosis are distinguished:
- Hypertrophic. This form occurs in the absence of long-term treatment or ineffective treatment of the problem. With this type, thickening of the nail plates and nail bed occurs, which persist for a long time even after successful treatment of hypertrophic onychomycosis of the nails. Such a lesion is typical for a severe stage and requires more serious drug treatment - tablets and antibiotics.
- Normotrophic. With this type, there is no thickening of the nail itself and the subungual area. There is fragility of the nails, and the formation of yellow-gray stripes in the nail plates. With this form, conservative and traditional local therapies are effective - ointments, varnishes, gels, etc.
- Proximal. A lesion that initially affects the base of the nail growth.
- Distal. The most common form of fungal infection. Infection begins in the area of the free edge of the plate. Initially, the nail bed is infected. Outwardly, this manifests itself in the form of a splinter embedded under the nail or a yellow spot. Wearing shoes in patients with this form causes discomfort.
- Atrophic. It manifests itself as a violation of nail growth with subsequent detachment of the plate from the nail bed. Unfortunately, this form cannot be treated with conservative treatment methods and requires surgical removal of the affected plates.
- Side. In this form, the fungus affects the lateral parts of the nail plate and the periungual ridges. Often accompanied by an ingrown toenail.
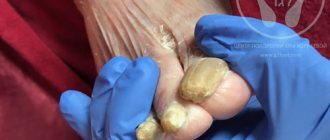
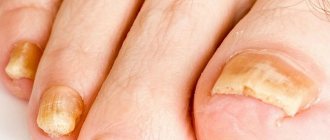
- Total onychomycosis. Signs - the entire plate is affected, it thickens, becomes dull, its color becomes yellow or even brown. As the disease progresses, the nails become deformed and take on a beak-like shape. Furrows of a dirty gray color appear, the free edge of the nail loosens.
Treatment
Nail fungus causes more than just aesthetic discomfort. Developing in the subungual space, onychomycosis can eventually penetrate the bloodstream, spread throughout the body and cause general allergization. That is why it is necessary to begin treatment when the first signs of the disease appear and continue until complete recovery.
For successful and effective treatment of onychomycosis, it is necessary to strictly follow the prescription of a dermatologist. First of all, it is important to make a correct diagnosis.
At the MedNail clinic you can take tests at a time convenient for you and get results in the shortest possible time.
At your appointment, a dermatologist will scrape the affected area. In a special laboratory, a specialist will perform microscopy. Cultural studies are also carried out (the collected material is placed in a special nutrient medium) and the development of the fungal colony is monitored. This helps determine which species caused the disease.
Treatment of nail fungus involves cleaning off the affected part of the nail plate with a special tool and apparatus in the podiatrist’s office. Treatment with local antifungal agents will then be prescribed. In case of serious extensive lesions, the doctor will prescribe general antimycotic agents. Therapy may also be required to boost overall immunity.
Symptoms of onychomycosis and photos
Each of the three types of onychomycosis has its own individual symptoms (see photo), which also depend on the severity of the disease. The main symptoms that are characteristic of each of the three types of onychomycosis include:
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the area of the periungual fold.
- the presence of dystrophic changes in the nail plate.
- formation of white, yellow spots, stripes inside the nail.
- atrophy of the nail with its separation from the bed.
The disease most often begins with infection of the nail on the big toe. Then the infection spreads to the remaining toes, and then to the hands.
Diagnostic methods
It is very difficult to diagnose yourself: the symptoms of onychomycosis (especially in the initial stages) often resemble the signs of diseases such as psoriasis, eczema, seborrhea, lichen planus, keratoderma. Even a specialist dermatologist will not rely solely on a visual examination to make his conclusions. The patient will undergo a laboratory analysis of bacteriological culture, and a scraping of the nail tissue will be examined (laser microscopy).
If onychomycosis is suspected, fluorescent diagnostics (examination of the diseased nail using a Wood's lamp) is usually used.
How to treat onychomycosis of nails?
Modern effective treatment of onychomycosis consists of the simultaneous use of the following methods and medications:
- Taking systemic antifungal drugs;
- Treating the affected areas of the nail and surrounding skin with local antifungal agents, for example, ointments, gels, varnishes, etc.;
- Removal of the nail plate by surgical or conservative method in case of its total damage and severe thickening;
- Taking medications that improve blood circulation to the peripheral tissues of the feet and hands;
- Courses of physiotherapy, also aimed at improving blood flow in the feet and hands.
Systemic treatment of onychomycosis consists of taking oral antifungal drugs for 6 to 12 months. Currently, the following antifungal drugs are used to treat onychomycosis:
- Griseofulvin, which effectively suppresses protein synthesis in fungi, which leads to their rapid destruction. The daily dose is 500 mg, but in especially severe cases it can be doubled. The product should be taken with meals, and the dose can be divided into 2 doses. The course of therapy can last about six months.
- Terbinafine for the treatment of onychomycosis of the nails of the hands is taken for 1.5 months, and for the feet - 3 months. Cure is observed in 88–94% of patients.
- Fluconazole for the treatment of onychomycosis of the nails of the hands is taken for six months, and of the feet - for 8 - 12 months. Cure is observed in 83–92% of patients.
- Itraconazole is used in two possible regimens: continuous dosing and pulse therapy. With continuous use, the duration of therapy for onychomycosis of the nails of the hands is 3 months, and of the feet – 6 months. Pulse therapy consists of alternating doses of the drug for a week and breaks between them for three weeks. To treat onychomycosis of the nails of the hands, two courses of pulse therapy are necessary, and of the feet – 3–4 courses. Complete cure, even without conservative nail removal, is observed in 80–85% of patients.
- Ketoconazole, which blocks the development of fungi and promotes their destruction. The drug has a strong effect on the liver and can block the action of androgens. It is quite effective against fungi, but it is not recommended to take it for a long time to avoid serious side effects. The daily dosage is 200 mg.
Local treatment of onychomycosis should complement systemic therapy, but in no case replace it. It should be remembered that local treatment of onychomycosis will not achieve a complete cure unless it is combined with oral antifungal drugs in the form of tablets, capsules, solutions and other pharmaceutical forms, since fungal spores can persist in destroyed tissues for a long time in a viable state.
Currently, effective local antifungal drugs that are indicated for use in the complex therapy of onychomycosis are the following:
- Econazole preparations (Pevaril, etc.);
- Isoconazole preparations (Travogen, Travocort);
- Terbinafine preparations (Atifin, Binafin, Lamisil, Myconorm, etc.);
- Naftifine preparations (Exoderil);
- Preparations containing clotrimazole (Amiclon, Imidil, Candibene, Kanison, etc.);
- Preparations containing miconazole (Daktarin, Mikozon);
- Bifonazole preparations (Bifasam, Bifonazol, Bifosin, Mikospor);
- Amorolfine preparations (Loceril);
- Ciclopiroxolamine preparations (Batrafen, Fongial).
To improve microcirculation and accelerate the growth of a new healthy nail plate, the use of the following physiotherapeutic procedures as part of complex therapy for onychomycosis is indicated:
- Amplipulse therapy on the paravertebral areas in the lumbosacral and cervicothoracic regions for 7 to 10 days in a row;
- UHF therapy on the paravertebral areas in the lumbosacral and cervicothoracic regions for 7 to 10 days in a row;
- Supravascular laser irradiation of blood in the area of peripheral blood vessels. Irradiation is carried out at a power of 15 to 60 mW for 6 to 10 minutes per area;
- Diathermy on the paravertebral areas in the lumbosacral region for 7 to 10 days in a row.
These drugs improve blood supply to the fingers and toes, and, therefore, guarantee the delivery of the antifungal drug to the nails in the required concentration.
For this purpose, it is advisable to use the following drugs:
- Pentoxifylline (Trental, Agapurin, etc.) 400 mg 2 – 3 times a day;
- Calcium dobesilate (Doxi-Chem, Doxium) 250 – 500 mg 3 times a day;
- Nicotinic acid 150 – 300 mg 3 times a day or 15 injections of 1 ml of 1% solution.
All of the above medications have serious side effects, so the choice of drug is made only by a doctor based on microbiological data and taking into account individual contraindications. If there are any signs of intolerance, the drug should be stopped and another drug should be selected.
Types of nail plate lesions
There are 3 variants of onychomycosis:
- Normotrophic.
- Hypertrophic.
- Atrophic.
Normotrophic type of onychomycosis on the legs
In the normotrophic type, the infection is localized in the upper layers of the nail plate. Its thickness and color do not change during the disease, but spots and stripes are visible in the depths. The color of nails varies from white to deep yellow. After some time, the spots and stripes merge. The affected area extends to the entire nail plate, excluding the lunula. No brittleness or crumbling is observed. Sometimes there is a slight loosening of the free edge. With adequate treatment, cure is possible.
Rice. 21. Normotrophic type of lesion.
Hypertrophic type of onychomycosis on the legs
This type of onychomycosis is the most common. As a result of the development of subungual hyperkeratosis, the nail plate becomes significantly thicker, deformed and loses its shine. Nails become uneven, dull, acquire a brownish-gray color and crumble. The lunula area is not affected. The disease causes significant discomfort to the patient. In elderly patients, onychogryphosis develops - the nails thicken, lengthen and bend like a bird's claw.
Rice. 22. Hypertrophic type of onychomycosis on the legs.
Rice. 23. Hypertrophic type of onychomycosis on the legs. Onychogryphosis.
Atrophic type of onychomycosis on the legs
With the atrophic (onycholytic) type, the nail plate quickly loses connection with the nail bed, many voids appear in its layers, it fades, becomes thinner and changes color to whitish or yellowish-whitish. The surface remains smooth for a long time. Over time, its partial destruction occurs.
Rice. 24. Atrophic type of nail damage.
Rice. 25. Onycholytic (atrophic) type of onychomycosis on the legs.
Nail removal
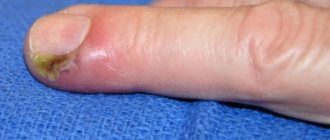
Currently, surgical removal of nails affected by fungus is almost never practiced. The main indication for this is the addition of a bacterial infection or a complete lack of effect from drug treatment (resistant forms of fungi). The addition of a secondary infection occurs quite often with advanced onychomycosis, severe destruction of the nail plate and poor personal hygiene.
If a fungal infection is usually limited to the nails and the surface of the skin, then the bacteria can also infect neighboring tissues. This leads to the formation of pus, its accumulation and the development of a serious inflammatory process. In such cases, it is recommended to remove the nail to more thoroughly treat the bacterial infection. It should be understood that even removing a nail is not a radical solution to the problem of onychomycosis. Regardless of this, antifungal medications must be continued, since the infection is still present in the body and there is a risk of affecting other nails.
An alternative to surgery is to artificially “dissolve” the affected nail (avulsion). There are a number of drugs (nogtivit and its analogues) that promote rapid keratinization of nails and their layer-by-layer death. This method is now widely practiced because it is painless and can be performed at home. However, you should resort to it only after consulting a dermatologist.
Causes and risk factors
Onychomycosis is a contagious disease, the main cause of the disease is the transmission of infection from a sick person to a healthy person. The scales that peel off from the infected nail plate can end up on the floor, carpet, tiles in the pool, sand on the beach, along which a healthy person will walk barefoot.
The fungus can get inside the nail plate if it is injured as a result of:
- wearing tight and non-breathable shoes;
- various injuries (domestic, industrial, sports);
- an unsuccessful pedicure, in which the nail was filed too far.
Risk factors are:
- ignoring personal hygiene standards (using other people's towels, shoes);
- weakened body defenses and use of medications that reduce immunity;
- problems with blood circulation (varicose veins);
- chronic diseases (AIDS, diabetes, stomach diseases).
The risk group includes:
- athletes using shared equipment, visiting swimming pools, gyms, baths;
- visitors to nail salons (not all of them provide high-quality treatment for the tools they use);
- representatives of professions who often have to use shared showers (military personnel, miners, healthcare workers).
By the way, when the nail softens from hot water in the shower or bath, it is much easier for infection to get inside and begin its destructive activity.
Folk remedies
As mentioned above, complete cure of onychomycosis is possible only with the help of medications with a strong antifungal effect. However, some traditional medicine recipes can help slow down the destruction of the nail plate or even stop the process for a while. Many doctors even encourage the use of these drugs after a course of treatment to prevent relapses.
To prevent relapses of onychomycosis, it is recommended to use the following traditional methods of treatment:
- A well-known remedy for combating nail fungus is a kombucha compress. For this purpose, take a piece of mature kombucha and wrap it around the nail with a bandage, after thoroughly washing and steaming your feet. This compress is applied throughout the night. In the morning, you need to remove the compress, rinse your nails with warm water and remove dead areas, then treat the nail and adjacent skin with an alcohol solution of iodine or any other antiseptic. Kombucha treatment should be continued for several weeks.
- One method is to treat the affected areas of the nail with a 5% iodine solution 2 times a day. In this case, a burning sensation may be felt. If it is weak, then everything is in order - the product produces the desired effect. If the pain is intense, then iodine treatment should be stopped.
- Traditional medicine recommends a decoction of calamus, which should be taken two to three times a day. Along with this, treating nails for onychomycosis should become a regular procedure; it is necessary to cut off growing nails and rough skin. The effect will be noticeable within a few weeks. To prepare the decoction you need 1–2 tsp. Grind calamus rhizomes and pour boiling water (100 ml). Boil for 1 minute, then strain. The product can be washed down with water, as it has a bitter aftertaste.
Regardless of the recipe chosen, feet or hands must first be steamed, thoroughly washed and dried. It is also advisable to remove all dead particles that appear. It is better to leave all applied compositions overnight, which will significantly enhance the overall healing effect.
Reviews
Georgy, 44 years old: “When the doctor determined my diagnosis, onychomycosis, she immediately prescribed me not only ointments, but also tablets. I admit, I didn’t drink them, I’m afraid to take antibiotics again, so as not to damage my liver. I smeared my nails with Batrafen, took vitamins and echinacea (this is also a doctor’s recommendation). I got rid of the fungus in 3.5 months.”
Svetlana Sergeevna, 64 years old: “I have varicose veins, so I have problems with my legs every now and then. Recently my big fingernail started turning yellow. I know that it is impossible to cause nail fungus, so I used folk remedies - garlic paste, iodine, steaming in water with sea salt. I recovered quickly."
Victoria, 52 years old: “At first my husband did not want to admit that not everything was going well with his nails, and then he did not agree to go to the doctor. I saw enough advertisements on TV and decided that I would treat myself with Lamisil varnish. We bought it and applied it, but it didn’t help. I still had to turn to medicine. The doctor prescribed Griseofulvin tablets and Clotrimazole ointment. My husband was cured in six months, although he could have been sooner if not for his stubbornness.”
Prevention
After completing the treatment program, special attention should be paid to the subsequent prevention of the disease. Doctors recommend following simple rules that will help avoid onychomycosis infection in the future:
- Use individual shoes in saunas, swimming pools, gyms and other common areas.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, perform procedures that strengthen the body's immune system.
- Adhere to the rules and regulations of hygiene, in particular, regularly wash your feet and hands.
Maintaining hygiene requirements is also necessary during the treatment process. Only in this case will it be possible to completely get rid of the unpleasant disease.