Erysipelas occurs in 10 people out of 5 thousand people. The name comes from the French word "rouge", which means "red". Main signs: redness and swelling of the body area.
Erysipelas affects people of all ages, but most often it affects women over 50 years of age. The disease is treated with antibiotics and other medications. With proper treatment, the disease goes away after 10 days.
Erysipelas - what kind of disease is this?
Erysipelas is an infectious-allergic disease that affects the skin and subcutaneous tissue. This is a disease with frequent relapses. Erysipelas is caused by group A streptococcus.
In 1/3 of cases, the disease is associated with impaired blood flow and lymph. People with blood group 3 are most susceptible to the disease. The disease occurs in patients with reduced immunity. It can be provoked by frequent nervous disorders and chronic pathologies.
This type of bacteria leads not only to erysipelas, but also to sore throat and rheumatism. True, not all people who get streptococcus into their bodies get sick.
Some of them become carriers. The infection is transmitted through close contact with patients, as well as through airborne droplets.
What does bacterial activity lead to:
- Bacteria have a destructive effect on cells;
- Reduce the level of antibodies fighting against streptococci;
- Affect leukocytes , disrupt their ability to phagocytosis;
- Vessels affected by bacteria dilate and their permeability increases.
Causes
Erysipelas is caused by streptococci - or rather, one of the varieties of bacteria of this group. In an organism with a weakened immune system, streptococcus can cause other diseases - for example, scarlet fever, myocarditis, and sore throat.
About 15% of the world's people are carriers of streptococcus. That is, their immunity is quite strong so as not to get sick, but at the same time they spread the infection. It is transmitted through personal contacts, household objects, airborne droplets, etc.
Predisposing factors for infection:
- Various skin injuries, including insect bites, animal bites, bedsores and ulcers. Even venous catheters can be dangerous in this sense.
- Harmful working conditions - when the skin is constantly exposed to chemicals, it often becomes dirty. People who constantly wear rubber clothing and shoes are also at risk.
- Viral skin lesions - chickenpox, shingles, herpes. They not only violate the integrity of the integument, but also greatly reduce immunity.
- Chronic skin lesions such as eczema, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, etc.
- Purulent lesions of the skin: boil, carbuncle and similar formations.
- Disturbances in the circulatory system - varicose veins, thrombophlebitis. If the skin is deprived of oxygen, it becomes damaged and becomes more susceptible to infection.
- Various scars, the cells of which the body itself can attack, which is why erysipelas develops.
- Fungal diseases of the scalp and feet.
- Serious complications with rhinitis, otitis media, conjunctivitis.
- Injuries to the skin caused by wearing tight clothing that rubs and disrupts blood circulation in the tissues.
- Any reasons that suppress the immune system: taking certain medications, serious illnesses, exhaustion as a result of malnutrition, hypothermia, bad habits, chronic or severe stress and much more.
To summarize, the disease develops against a background of weakened immunity and streptococcal infection, which can occur in different ways.
Causes and symptoms of erysipelas
Causes of the disease:
- Entry into the body of streptococcus;
- Any damage to the skin surface;
- Work in dusty conditions (drivers, miners, farmers);
- Skin diseases caused by viruses (herpes, lichen);
- Diseases of allergic etiology (rash, urticaria);
- Purulent areas (boils, folliculitis);
- Violations of blood and lymph circulation;
- Fungi;
- Complications after colds and infectious diseases;
- Decreased immunity;
- Diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis;
- Blood diseases;
- Oncological neoplasms;
- Frequent nervous disorders;
- Improper lifestyle (smoking, alcoholism).
Areas of the body where erysipelas occurs:
- Legs;
- Shin;
- Hands
- Face;
- Torso;
- Groin areas.
Symptoms:
- A sharp deterioration in health;
- Chills;
- Fever;
- Redness of areas of the skin;
- The area where the inflammatory process occurs quickly increases in size;
- The inflammation has uneven edges (like flames);
- Soreness, burning sensation;
- Swelling;
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
When the first symptoms of erysipelas appear on the skin, you should consult a dermatologist. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out on the basis of an examination of the patient by a doctor, a blood test for SOE and T-lymphocytes, and bacterial culture from the contents of the inflamed area.
Preparations for injections
Severe forms of erysipelas are treated only with injections of solution antibiotics. The medicine quickly penetrates the systemic bloodstream and destroys pathogenic bacteria.
Injectable drugs are indicated for severe intoxication, which is caused by the accumulation of streptococcal poisons in the body.
Benzylpenicillin
The penicillin antibiotic has a bactericidal effect on pyogenic bacteria. In high doses it destroys enterococci, staphylococci, peptococci, etc.
For purulent inflammation, sepsis, and skin infections, the antibiotic is administered intramuscularly or by drip. A single dose is 250-500 thousand units. In case of gangrenous changes in tissues, the dosage is increased 3-4 times.
Rifampicin
A semi-synthetic antibiotic is used to treat tuberculosis. But it exhibits bactericidal activity against streptococci, so it is also prescribed to eliminate inflammation of a non-tuberculous nature.
Features of application:
- single dose – 900-1200 mg;
- maximum daily dose – 1200 mg;
- frequency of administration – up to 3 times a day.
Rifampicin is not prescribed for children under 6 years of age.
Bicillin-5
A beta-lactam antibiotic has a prolonged bactericidal effect against most pyogenic bacteria. The antimicrobial concentration of Bicillin-5 remains in the bloodstream for more than a day. This ensures rapid elimination of bacterial inflammation in the skin.
The antibiotic is administered exclusively intramuscularly. Adults are prescribed 1,500,000 units no more than once a month. The course of therapy is 3-12 months.
Gentamicin
For complicated forms of the disease, aminoglycoside antibiotics are prescribed. Gentamicin eliminates not only bacterial inflammation, but also complications of erysipelas:
- phlegmon;
- lymphadenitis;
- sepsis.
The solution is injected into a vein or muscle. The dosage depends on body weight - up to 3 mg of the drug per 1 kg of weight intramuscularly. The daily dose is divided into 2-3 injections. The course of therapy is 8-10 days.
Erysipelas is an infectious-allergic disease that requires complex therapy. To quickly remove inflammation, drugs for local, parenteral and oral administration are combined. Uncomplicated erysipelas is treated with antibacterial tablets of the cephalosporin, penicillin and macrolide series.
The bullous-necrotic form is eliminated with injection drugs. To prevent inflammation of healthy tissues, skin lesions are treated with antimicrobial ointments.
Treatment of erysipelas with antibiotics
Before starting treatment, a bacteriological study is carried out to determine which microorganism caused the disease and which antibiotic it is resistant to.
This information helps the doctor choose the right treatment. If the antibiotic is chosen incorrectly, the body is poisoned, the pathogen persists, and erysipelas takes a chronic course.
For erysipelas, complex therapy is carried out. Medicines are prescribed for local treatment of the skin, immunostimulating drugs, as well as antibiotics for oral or intramuscular administration.
Penicillins
Penicillins cause destruction of bacterial cells and their death. Effective against staphylococci, which grow and multiply quickly.
The result of therapy is enhanced by the parallel use of Streptocide and Furazolidone. You can buy medications at a pharmacy only if prescribed by a doctor.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin is a drug active against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci. Available in tablet form (1 tablet contains 250 mg). Contraindicated in case of allergies to penicillins, aphthous stomatitis and pharyngitis, gastrointestinal diseases (severe vomiting, diarrhea). Can be taken by infants up to one year from 3 months at the rate of 20 mg per kilogram of weight (daily dose). For children under 12 years of age, the norm is 30 mg per kilogram of weight. The daily dose is divided into 3-4 doses. It is preferable to give the medicine in the form of a suspension to babies. Adults and adolescents are prescribed 1-3 tablets 3 times a day. Take 30-60 minutes before meals, washing down the tablets with water. Duration of treatment is 5-7 days, for relapses – 10 days. Average cost 50 rubles ;
- Benzylpenicillin is produced in powder form for the preparation of a solution for intramuscular administration. Contraindicated if you are allergic to penicillins. The daily dose for children from 5 months to 1 year is 50-100 thousand units. per kg of weight, from a year - 200-300 thousand units. per kg of weight. Adults are administered 4-6 million units. per day. The frequency of administration is 4 times. Duration of use is 7-10 days. Add 1-3 ml of water for injection, 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 0.5% novocaine solution to the contents of the bottle. Price for one bottle – 10 rubles ;
- Bicillin-5 is a dosage form in powder form for intramuscular injection. Contraindications: allergies, renal failure, lactation and pregnancy. Prescribed to children and adults to prevent relapses once a month for 2-3 years. To prepare the solution, use sterile water for injection, sodium chloride solution, novocaine (0.25-0.5%). Dosage for adults – 1 ampoule, for children over 8 years old – 0.8 ampoules, for preschool children (from 3 years old) – 0.4 ampoules. The average cost for 1 bottle is 26 rubles .
Phenoxymethylpenicillin Benzylpenicillin Bicillin-5
Macrolides
Macrolides inhibit the growth of dangerous bacteria. Antibiotics of this group stop the spread of microorganisms throughout the body. Causes the death of bacteria at high concentrations.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Erythromycin - tablets of 100 or 250 mg. Contraindications are allergies to the components of the medication, children under 14 years of age, and lactation period. Take one tablet 4 times a day one hour before meals. Duration of treatment is 5-14 days. Cost 95 rubles ;
- Olethetrin - used in tablet form. Contraindications are allergies to the components of the medication, kidney/liver pathologies, leukopenia, children under 8 years of age. Dose for adults – one tablet 4 times a day, but not more than 2 grams per day. For children – 20-30 mg per kilogram of weight 4 times a day. Duration of treatment is 5-10 days. Price 180 rubles per package;
- Azithromycin is an antibiotic with a bacteriostatic effect. Available in the form of tablets, capsules, suspensions. Contraindications: macrolide intolerance, kidney/liver pathologies, pregnancy and arrhythmia. Prescribed one capsule (500 mg) or 2 tablets (250 mg) 1 time per day for 5 days. For children from 6 months of age, it is used in the form of a suspension of 5-10 mg per kilogram of weight 1 time per day for 3-5 days. The average cost is 70 rubles .
Erythromycin Oletetrin Azithromycin
Lincosamides
Lincosamides have bacteriostatic activity. They do not cause allergies, but can lead to diarrhea. At high concentrations, the drug can exhibit a bactericidal effect.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Clindamycin is produced in the form of granules for the preparation of syrup, capsules (0.15 g), solution for intravenous or intramuscular administration (1 ampoule per 300 mg). Contraindications: children under 1 month, liver/kidney pathologies, ulcers, asthma, myasthenia gravis, pregnancy, lactation. Take regardless of food intake. Adults take 1-2 capsules orally every 6 hours, children – 8-25 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day (divided into 3-4 doses). Injections: adults - one ampoule every 8 hours, children - 10-40 mg per kg of body weight per day (divided into 3 doses). Duration of use is 7-10 days. Cost – 200 rubles ;
- Lincomycin is available in the form of capsules (0.5 g), solution for injection (1 ml ampoule 0.3 g). Take 1 hour before meals. Orally, adults: one capsule every 6 hours, children – 30-60 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day (divided into 3 doses). Parenteral: adults - 2 ml every 12 hours, children - 10-20 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day (divided by 2 times). Duration of use is 7-10 days. Price – 100 rubles ;
- Dalacin C Phosphate is a solution for injection. Contraindications: allergies to the components of the drug, kidney / liver pathologies, pregnancy, lactation. Used by infusion over 10-60 minutes, the dose for adults is 1800 mg per day (divided by 3 times). The dose for children from one month is 20-40 mg per kg of body weight per day (the norm is divided into 3 times). Cost – 400 rubles .
Climycin Lincomycin Dalacin C Phosphate
Aminoglycosides
Aminoglycosides are most effective in combination with penicillins. Antibiotics are ineffective when taken orally. Intramuscular administration is recommended.
Due to high toxicity, the dosage is calculated taking into account the weight of the patients.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Gentamicin is a solution for injection. Do not use if you are allergic to the components of the drug. For adults, a single dose is 1-1.7 mg per 1 kilogram of weight, but not more than 3-5 mg per kilogram of weight per day. The frequency of administration is 2-4 times, depending on the severity of the disease. Duration of use is 7-10 days. For newborn children, the daily dose is 1-2 mg per kilogram of weight, and for children over two years old - 3-5 mg. The daily norm is divided into 3 times. Average cost 40 rubles ;
- Amikacin - powder for the preparation of solutions (500 mg). Dilute with water for injection or novocaine. Contraindications: allergy to the components of the drug, kidney disease, pregnancy, lactation. Administered intramuscularly. Dose for adults: 15 mg per kilogram of body weight 1 time per day. The norm for children from 4 weeks is 15 mg per kilogram of weight per day. Duration of use is 7-10 days. Average cost 120 rubles ;
- Kanamycin is a solution for intramuscular injection (1 ampoule – 250 mg). Contraindications: allergies to the constituent drugs, pathologies of the kidneys, liver, pregnancy, lactation. The norm for adults is 15 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, but not more than 1.5 grams. For children – 10 mg per day. Duration of use is 7-10 days. The average cost is 10 rubles .
Gentamicin Amikacin Kanamycin
Cephalosporins
Cephalosporins have low toxicity compared to other antibiotics, so they are well tolerated by people with kidney or liver failure, but they should be prescribed with caution.
Medicines can be used to treat pregnant women, but only as directed by a doctor. Contraindications for medications in this group: allergic reaction to the components of the medications.
Before using medications, you need to do a tolerance test.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Ceftriaxone - in powder form (0.5 g and 1 g in one bottle). Dilute with water for injection, novocaine, lidocaine, saline solution of sodium chloride. Administered intramuscularly. Adults and adolescents over 12 years of age are prescribed 1-2 grams once a day. The daily norm should not exceed 4 grams. For infants from 2 weeks – 20-50 mg per day (dose divided into 2 doses). For children under 12 years of age, 50-75 mg per kilogram of weight (in 2 administrations). Duration of use is 7-10 days. Cost 25 rubles for 1 bottle;
- Cefepime is a powder for injection. Dissolve with water for injection, sodium chloride solution. Injected intramuscularly. Dosage for adults: 1 g every 12 hours. The norm for children from 1 month is 30 mg per kilogram of body weight, from one year and older with a body weight of up to 40 kg - 50 mg every 12 hours. Duration of use is 7-10 days. Cost 250 rubles per package;
- Rocephin - powder for the preparation of solutions (250 mg, 500 mg, 1 g). Dissolve with water for injection. Injected intramuscularly. Dose for adults 1-2 g 1 time per day. The norm for newborns (from the 14th day of life) is 20-50 mg per kilogram of body weight. The dose for children under 12 years of age is 20-80 mg per day. Duration of use is 7-10 days. Cost 390 rubles .
Ceftriaxone Cefepime Rocephin
Sulfonamides
Sulfonamides are very toxic. Often cause allergies and stool disorders. Antibiotics are effective when taken orally. They have a bactericidal effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Biseptol - tablets (240 mg). Contraindications: allergic reaction to the components of the drug, kidney / liver pathologies, diseases of the cardiovascular and circulatory system, pregnancy, lactation, children under 6 weeks. Take after meals with plenty of liquid. Dose for adults: 4 tablets 2 times a day. The norm for children from 2 to 5 years old is one tablet twice a day, from 5 to 12 years old - 2 tablets twice a day. Duration of treatment is 5-14 days. Cost 90 rubles ;
- Co-trimoxazole - tablets (480 mg). Contraindications: children under 3 months, up to 5 years are prescribed a suspension, allergies to the components of the drug, liver and kidney diseases, blood diseases, pregnancy, lactation. Adults and children over 12 years old are prescribed 2 tablets twice a day, children from 5 to 12 years old - one tablet twice a day, from 2 to 5 years old - 0.5 tablets twice a day. Duration of treatment is 5 days. Cost 25 rubles ;
- Bactiseptol - suspension (100 ml). Contraindications: allergies to the components of the medication, kidney/liver disease, children under 6 weeks, pregnancy, lactation. Children from 7 months. up to 2 years – 1 tsp. every 12 hours, from 2 to 12 years – 2 tsp. once every 12 hours, adults – 2-3 tsp. every 12 hours. The suspension is used after meals. Duration of treatment is 5-14 days. The average cost is 120 rubles .
Biseptol Co-trimoxazole Bactiseptol
Fluorochonolones
Fluorocholonols are used to treat skin infections. These are antibacterial medications for systemic use of the quinolone group.
Rarely used due to possible side effects: headache, convulsions, anorexia, leukopenia, phlebitis, Quincke's edema and others.
Effective drugs in this group:
- Levofloxacin is a solution for infusion. It has a number of contraindications: age under 18 years, pregnancy and lactation, allergy to the components of the medication. The infusion duration is 30 minutes for 250 mg and 60 minutes for 500 mg. The medicine is administered 1-2 times a day. Duration of use is 7-14 days. Cost 150 rubles ;
- Abiflox is a solution for infusion. Contraindications: sensitivity to the components of the drug, pregnancy, lactation. Adults are administered 500 mg 1-2 times a day. Duration of use is 7-10 days. Price 390 rubles ;
- Ciprofloxacin is in tablet form. Contraindications: allergy to the components of the drug. Dosage for adults – 500 mg 2 times a day, for children over 5 years – 20 mg per 1 kg of body weight. Take regardless of food. Duration of treatment is 7-14 days. The average cost is 60 rubles .
Levofloxacin Abiflox Ciprofloxacin
In case of erysipelas, antibiotic treatment should be used immediately. Local treatment will not lead to recovery of the patient.
Signs of inflammation
In most cases, erysipelas occurs suddenly: within a few hours. Less often, it is preceded by an incubation period of up to 3–5 days. The first symptoms of the disease are characteristic of influenza and many other infections:
- chills;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- muscle weakness;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Intoxication and fever develop due to increased activity of pathogens and the release of many of their antigens into the blood. The immune system reacts to the growth of streptococci, as well as to other foreign agents. The feeling of poor health persists for 1–2 days, then other symptoms appear:
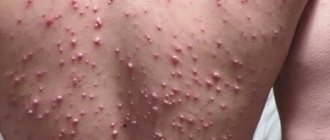
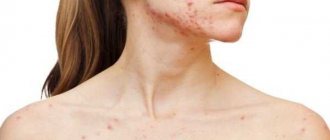
- On the lower leg, thigh, chest area, less commonly: in the area of the external genitalia, on the arm, scalp or face, a sharp burning sensation, itching, swelling, a feeling of fullness appears, the skin turns red.
- In the area of the outbreak, erythema forms - a large spot with ragged edges, reminiscent of flames or land areas on a geographical map. Its surface becomes denser, the color becomes darker: bluish-red or brown. When pressed, pain is felt.
- In the serous form of inflammation, the erythema does not have ulcerations or blisters. Hemorrhagic inflammation provokes multiple small hemorrhages. With bullous erysipelas, translucent blisters with liquid appear on the surface of the lesion, many of which burst with the release of ichor or pus. Sometimes small ulcers remain in place of the blisters, and then scars form.
The acute period of inflammation lasts 1–2 weeks. With a mild form of the disease, health quickly returns to normal. In moderate and severe cases, the fever persists for a long time, attacks of vomiting, and loss of coordination of movements due to toxic shock are possible.
Recovery occurs gradually:
- first the symptoms of fever disappear;
- appetite is normalized, physical strength is restored;
- skin inflammation decreases, swelling resolves, lymph nodes return to normal;
- the dark color of the integument remains for some time, the erysipelas site remains flaky and pigmented for up to 2–4 weeks.
In a recurrent process, inflammation develops again after a short period of remission: from several days to 2 years. Repeated lesions appear in the same place or move throughout the body. Single inflammations are called localized; if there are many of them, they are called widespread.
Additional treatments
In addition to antibiotic treatment, patients with erysipelas are prescribed:
- Antiallergic medications - Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin, take 1 tablet 2 times a day for 7-10 days;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Nimesulide, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac are taken to reduce pain, swelling, normalize temperature - one tablet 3 times a day for 3-5 days, contraindicated in hemorrhagic erysipelas;
- Nitrofurans - Furadonin, Furazolidone are used to suppress the growth and reproduction of bacteria, take 2 tablets 4 times a day;
- Glucocorticosteroids - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone are used for severe complications with the formation of lymphostasis, 4-6 tablets are prescribed per day;
- Biostimulants - Methyluracil is used to accelerate skin regeneration, increase immunity, prescribe 1-2 tablets 3-4 times a day for 15-20 days;
- Multivitamin medications - Ascorutin, Ascorbic acid strengthen blood vessels, increase immunity;
- Proteolytic enzymes - Trypsin, Lidaza are used for subcutaneous injections to improve nutrition in tissues and lymph resorption.
Treatment of affected areas:
- Compresses with 50% Dimexide solution;
- Powder from crushed Neo-Enteroseptol tablets;
- Dressings with solutions of Microcide and Furacilin;
- Treatment with Oxycort aerosol.
It is prohibited to use Vishnevsky's liniment, Ichthyola and Syntimycin ointment.
Local ointments:
- Tetracycline ointment;
- Erythromycin ointment.
Tetracycline ointment Erythromycin ointment
Ointments are applied to the affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day until symptoms disappear. With their help, pain, swelling, and redness are relieved. If you feel a burning sensation, you should stop using the ointment.
Basic principles of treatment of erysipelas
Treatment with antibiotics is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis. For purulent-necrotic lesions of the skin and tissue, systemic drugs are used, which are administered parenterally (by injection) or orally. Antibiotics from the following groups exhibit the greatest activity against Streptococcus pyogenes:
- penicillins;
- tetracyclines;
- macrolides;
- fluoroquinolones;
- cephalosporins.
To treat lesions, local bacteriostatic drugs are used - tetracyclines, sulfonamides, macrolides.
What antibiotics can be taken by pregnant women?
Treatment of pregnant women with antibiotics is undesirable, since many active components penetrate the placenta and affect the development of the fetus. If a woman has a serious infectious disease, then these medications cannot be avoided.
The doctor selects medications for therapy depending on the timing and condition of the woman. During this period, it is not recommended to experiment. It is necessary to take only those antibiotics to which the sensitivity of the causative agent of the disease has been revealed.
Pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimester can use the following antibiotics to treat erysipelas:
- Benzylpenicillin, Ampicillin;
- Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin;
- Erythromycin, Vilprafen.
In the early stages (in the 1st trimester), antibiotic treatment should be postponed until the 2nd trimester. During this period, the formation of all important organs occurs, and bactericidal drugs can cause disturbances in the development of the unborn child.
During pregnancy, it is allowed to take only penicillin antibiotics, cephalosporins, and macrolides.
What antibiotics are acceptable for children to take?
For children, starting from infancy, the same antibiotics are used to treat erysipelas as for adults.
The only exceptions are medications from the fluorochonolon group, for example, Levofloxacin. These medications can cause a number of complications due to their overly toxic composition.
All other drugs can be used. Only a medical professional can prescribe treatment and select a course of antibiotics.
Self-administration of medications is prohibited.
special instructions
Severe forms of erysipelas are treated only in a hospital. Medical professionals need to monitor the patient’s condition and his reaction to taking medications. Mild forms of erysipelas can be treated at home.
Rules for treating erysipelas at home:
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor regularly;
- Change underwear and bedding daily;
- Take a shower every day, do not wipe the affected areas, but dry them;
- Wash the inflamed area with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, coltsfoot;
- At the healing stage, wash the affected area with aloe or Kalanchoe juice.
Erysipelas is a common problem that can affect anyone. Modern medicine with the help of antibiotics is able to overcome this disease in 7-10 days.
Prevention
Since the disease can affect anyone, prevention of erysipelas is important both for those who have already had the disease once, and for those who have only heard about such a disease.
Prevention consists of following the following tips:
- Treat any inflammation on the skin or mucous membranes in a timely manner.
- Maintain personal hygiene. In the event that work or lifestyle is associated with additional pollution, hygiene should be even more thorough, but not excessive, so that the skin does not suffer - otherwise the effect will be the opposite.
- Use special products (gels and oils) for washing that do not dry out the skin. Regular soap is not suitable for regular use.
- Carefully monitor the condition of your skin in hot weather or if you have folds that constantly sweat. In this case, it is necessary to use special powders.
- Pay close attention to your health if you have problems with blood vessels or lymph stagnation. Such people are recommended for massages and various procedures that disperse fluids in the body.
- Treat your skin immediately if you have frostbite, chapping, or sunburn.
- Wear comfortable, breathable, natural clothing if possible that fits loosely on the body.
- Carefully monitor your immunity and eliminate all factors that can weaken it.
Remember that you cannot insure against this disease, but you can do everything to reduce the risks of its occurrence.