Demodicosis is a disease caused by mites of the genus Demodex (Demodex), which can affect either the skin of the face or spread on the eyelids and especially in the eyelash hair follicles , concentrating on the eyelash follicles. Unlike cutaneous demodicosis, which is relatively easy to treat by treating with various external preparations, the treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids must be approached with caution.
It is necessary that large quantities of medications do not come into contact with the eyes (this can cause irritation).
Note! The main treatment for such cases is ointments against demodicosis.
Indications for the use of ointments and gels for demodicosis of the eyelids
Ointments for demodicosis should be used at the first symptoms of this disease, namely the following signs:
- swelling of the edges of the eyelids;
- eye fatigue against the background of developing inflammatory infectious processes;
- loss of eyelashes that lose their strength;
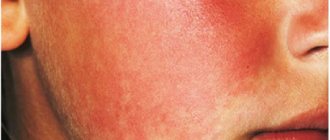
- redness of the eyelids.
Such inflammatory reactions can be noticed already in the first days of the development of the disease.
And if inflammation affects only the eyelids and practically does not spread to the conjunctival membrane, it is necessary to use ointments and gels for demodicosis.
Causes of demodicosis of the eyes
This disease can appear as a result of internal factors:
- decreased immunity after illness;
- chronic microbial and viral diseases;
- the appearance of foci of infection in the body, for example, untreated caries;
- eye refractive diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
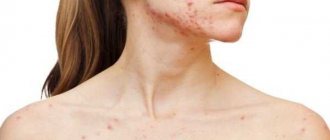
- acne;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems;
- diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
External factors can also trigger the appearance of demodicosis of the eyes:
- previous ophthalmic surgeries;
- dirty, dusty air;
- high air temperature;
- unhealthy lifestyle, alcohol abuse.
Untreated demodicosis can lead to keratitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, blepharitis and visual impairment. A deficiency of tear fluid is dangerous for the development of secondary infection.
Popular ointments for demodex
It is worth noting! Depending on the stage of the disease and the presence of individual intolerance to a particular drug, the doctor may prescribe one of these ointments for the treatment of demodicosis:
- Metrogil . An antimicrobial agent that is active against many bacteria, parasites and other harmful microorganisms. The drug is applied to the edges of the eyelids in a thin layer in the morning and evening. Depending on the progress, treatment can last from 1 to 4 months. In most cases, the effect is noticeable already by the fourth week of using Metrogil.
- Syntomycin ointment . A group of antibiotics based on chloramphenicol. This substance penetrates the cells of pathogens and disrupts the functioning of the mechanisms that produce cell-forming proteins. Depending on the severity of demodicosis, you can use a 5% or 10% medicine, applying it 1-2 times a day to the mite-affected eyelids.
- Stop demodex . A broad-spectrum agent used to treat many bacterial and parasitic dermatological pathologies. The medicine is made on the basis of herbal components; to enhance its effect, it is recommended to additionally use other drugs of similar action. The product is applied twice a day, treating the edges of the eyelids with a cotton swab with gel applied to it. The drug can be removed half an hour after application with a clean cotton swab.
- Permethrin ointment . The composition includes pyretoids - synthetic insecticides that destroy various types of ticks and other parasites. The principle of action of pyretoids is to provoke the development of mutations in the cells of microorganisms. As a result, they cannot reproduce, and after their death, new colonies of ticks do not form. It is enough to apply the medicine once a day, but in case of severe lesions, two or three times application is possible. In this case, the product should be removed no earlier than 12 hours after application. To completely eliminate the pathogen, a two-week course is sufficient, but it can be repeated after a break of a couple of days if the signs of demodicosis have not completely disappeared.
- Ichthyol ointment. Local antiseptic with anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. The drug not only destroys pathogens, but also has a healing effect. Therefore, ichthyol ointment is sometimes prescribed to be used even after the complete destruction of ticks for preventive purposes. You can use the ointment up to three times a day until symptoms disappear completely.
- Sulfuric ointment. The main active component is sulfur, which affects mites of any kind, and also helps eliminate a number of dermatological pathologies, including mycoses, seborrhea, sycosis, psoriasis. Depending on the intensity of symptoms, the medicine can be applied one to three times a day.
- Blepharogel-2. A drug containing sulfur, hyaluronic acid and aloe extract. In this combination, these components have a calming effect, normalize metabolic processes in the affected areas of the skin, destroy mites and moisturize the edges of the eyelids, which become dry and irritated in such diseases. The gel is applied twice a day, after which the edges of the eyelids are gently massaged, rubbing in the product. The duration of the course of treatment is not limited: the gel can be used until the disease completely goes away.
- Demalan. Plant-based cream including chamomile extract, olive oil and glycans. The drug destroys pathogens and has an anti-inflammatory effect, promoting rapid healing of damaged skin. The medicine is applied to the edges of the eyelids twice a day for half an hour, after which the remaining product can be wiped off with a napkin or cotton swab. The total duration of treatment is usually one and a half months.
- Metronidazole . An antibacterial medicine that is used to combat various microorganisms that cause dermatological pathologies - from protozoa to parasites. The product is used on average for about two months, applying it twice a day.
Keep in mind! Most of these drugs are well tolerated by patients and do not cause serious problems even if they come into contact with the eyes.
Although this sometimes results in short-term irritation and burning, it does not cause serious damage to the eye tissue.
How is demodicosis of the eye transmitted?
Demodectic mange of the eyes can be contracted at home - by sharing hygiene items, towels, bed linen, and cosmetics with the patient.
To prevent re-infection, you need to change your pillowcase and towel (or use paper towels) daily, and throw away contaminated cosmetics.
To treat each eyelid, you must use a separate (new each time) cotton swab.
1 Diagnosis and treatment of demodicosis
2 Diagnosis and treatment of demodicosis
3 Treatment of demodicosis
Side effects
Such drugs have common side effects , which, according to patients, develop quite rarely when used correctly.
The most common side effect is allergic reactions.
They occur due to individual intolerance or sensitivity to certain components of the drug.
Allergies can manifest as itching, burning and redness of the treated areas of the eyelids.
Additional symptomatic treatment in such cases is not required, but the use of the drug should be discontinued and treatment with any of the analogues should be continued.
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyes
It should be kept in mind that demodicosis of the eyes is caused by parasites, and the disease will not go away on its own. It must be treated over a long period. If you do not follow all the doctor’s instructions, demodicosis quickly becomes chronic, which is more difficult to treat. The insidiousness of the disease is that after some time the external signs of the disease disappear, but repeated self-infection may occur.
Therefore, treatment of demodicosis is quite long and includes a number of measures, including the following:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules, disinfection of bed linen;
- treating the eyelids with special products, cleaning the skin from crusts and plaque;
- treating the base of the eyelashes with drops or bactericidal gel;
- regular application of medicinal ointment prescribed by a doctor to the eyelids;
- regular massage of the eyelids and removal of discharge along with mites;
- the use of physiotherapeutic methods - magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, etc.;
- following a diet excluding sweets, spicy and salty foods;
- increasing immunity, eliminating foci of chronic infection.
How to eat during treatment?
Now many people do not accept drug therapy and prefer folk remedies. This is an erroneous and ineffective method. Only a qualified doctor can conduct the necessary examination to prescribe proven and safe medications.
But we will give you some nutritional tips. Remember the words of Pythagoras: “Man is what he eats”? Exclude from your menu anything that dilates blood vessels. These products cause blood to rush to the face, which is undesirable if you have demodicosis. Drink coffee less often (especially with sugar), avoid herbs and hot spices. Do not over-salt your food under any circumstances!
During therapy, avoid fatty and smoked foods. Reduce your intake of citrus fruits and soda, all of which cause allergic reactions.
What is the risk of demodicosis?
Should you worry if you have been diagnosed with this? Of course not. The disease has long been studied by doctors and is quickly eliminated with simple effective drugs. Don’t be afraid if the parasite finds another “object” among your pets. After all, there are more dangerous eye problems. Therefore, when you hear the word “demodex”, don’t panic! The syndrome can be easily healed in adults and children.
The main thing you need to know is that conservative treatment of demodex prescribed by an ophthalmologist only smoothes out the visible symptoms of the lesion. But it is impossible to completely expel a tick from the body; it performs many important functions.
With the correct diagnosis and effective therapy, your illness will go away without a trace. No eyelash loss or eyelid scarring. There will only be a possibility of relapse and recurrence of demodicosis again. Usually, this does not happen in the majority of patients. Already having experience in treatment and knowing the routes of infection, people try to monitor hygiene and control immunity.
Diagnosis of the disease
Demodectic mange is not difficult to detect. A laboratory microscope will be required, since it is not possible to visually recognize a tick. But it is quite easy to understand that a patient is affected by Demodex. The patient exhibits three signs:
- the skin of the eyelid is inflamed;
- the mucous membrane and part of the eyeball are damaged;
- the disease is seasonal (often progressing in summer).
The disease is aggravated by cosmetics, in particular the application of mascara. The use of eyelash care products also has a negative effect. They contain components that activate the spread of ticks.
How is the disease diagnosed? What worries an ophthalmologist first of all?
- Swelling and inflammation of the edge of the eyelids.
- The appearance of barley.
- Redness and dryness of the conjunctiva.
- Peeling skin around the eyes.
- Severe eyelash loss.
- Dried pus along the contour of the eyebrows.
- Increased lacrimation.
- Photophobia.
An accurate indicator of demodicosis will be a thick yellowish discharge from the eyes. The secretion is formed in pustules - purulent vesicles that, when infected, are created near the eyelash bulbs. Later they burst and leave small yellow crusts. They are clearly visible in the morning after sleep.
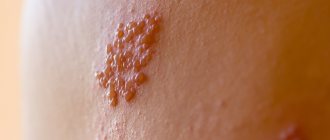
Since Demodex and its waste products are powerful allergens, the disease often occurs with a skin rash that is not visible to the naked eye. If you photograph an area of the epidermis and enlarge the photo, you can easily notice the rash. This is another symptom to diagnose the problem.
1.What is demodicosis and the factors that provoke it?
Demodicosis (demodex, skin mite)
microscopic mite Demodex folliculorum, which inhabits the sebaceous glands of the skin and hair follicles of the eyelids.
This parasite most often causes problematic facial skin and acne on the body (back, chest, shoulders). There is an opinion that inflammation and ulcers on the skin are associated with adolescence and do not require treatment.
However, the disease often remains with a person throughout his life. This indicates that adolescence is only a background for the onset of skin parasite activity. Hormonal changes and immune instability during growing up only create favorable conditions for the activity of skin mites, with which the body is already infected for some reason. The mite lives everywhere, and sooner or later it gets on the skin of any person. However, it colonizes and begins to actively reproduce only under certain conditions:
- increased skin oiliness;
- weakened immune system;
- metabolic disorders;
- violations of lifestyle, hygiene;
- chronic diseases that reduce the protective properties of the skin;
- constant stress factors.
Demodex folliculorum parasite
It has an oblong shape, it is almost transparent, the size of an adult is 0.1 - 0.4 mm.
It is impossible to distinguish it without special equipment. The mite feeds on skin cells and sebum. The parasite lives only a few days. The individual is designed in such a way that it does not have excretory organs. During its life, the tick only feeds and produces offspring. Then he dies. The development of the larva from the egg also takes 2-3 days. Thus, it can be assumed that intensive treatment destroys all adult parasites and the larvae they lay within a week. However, in practice everything is not so simple. The chronic course of demodicosis is caused by constant reinfection of a person
from his own household objects. There are especially many skin mite larvae on towels, pillowcases, combs and massage hair brushes, and cosmetics.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Causes of the disease
So, we know that the source of pathology lives inside each of us. But people behave differently. Some try to be treated for demodicosis, others are not even interested in their problem. In its usual form, the harmless Demodexfolliculorum lives inside us and calmly removes toxins. But as soon as the environment familiar to it changes, the tick causes trouble.
In ophthalmology, there are two stages of this disease - primary lesion and secondary. At the first stage, healthy areas of the eyelids are affected; at the second, the disease develops against the background of existing skin problems (papillomas, neoplasms, etc.) and eye diseases.
Several conditions can lead to the development of the disease:
- hot weather;
- long exposure to the sun without eye protection;
- excess or lack of water procedures;
- problems with immunity;
- high acidity of the epidermis;
- poor vision (farsightedness, myopia).
There are many more reasons contributing to the appearance of the disease. As a rule, doctors refer to the general condition of the body: typical acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, disruptions in the endocrine system, neurological problems, postoperative recovery period during eye surgery (for example, after cataracts).