Folliculitis - symptoms, causes and treatments
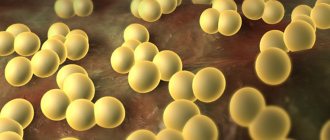
Folliculitis means “inflammation of the hair follicle.” This process accompanies a group of skin diseases caused by staphylococcal infection. Folliculitis belongs to pyodermatitis - pustular skin diseases, the most common of dermatoses.
Pyoderma accounts for half of the cases of temporary disability due to skin diseases. A considerable proportion of them belong to folliculitis. They can occur in different people, but most often they affect representatives of certain professions - miners, builders, metallurgists, and transport workers. In this regard, pyodermatitis and folliculitis in particular are socially significant diseases, in the fight against which both the state and employers in the most dangerous industries from the point of view of dermatological morbidity should participate.
Reasons for development
Inflammation of the hair follicles is initiated by pathogenic microorganisms: fungi, mites, viruses and bacteria. It becomes a place of residence for these organisms due to external factors or due to human health problems.
Thus, the causes of folliculitis are conventionally divided into:
- exogenous (external circumstances);
- endogenous (diseases that create optimal conditions for the life of pathogenic organisms).
Among the endogenous factors are:
- liver diseases;
- obesity;
- low hemoglobin;
- diabetes;
- malnutrition, due to which the body experiences a deficiency of certain substances.
Exogenous causes include:
- high ambient temperatures;
- hypothermia of the body;
- skin injuries (cracks or microcracks);
- incorrectly selected clothing (made from “non-breathable” and (or) synthetic materials, tight);
- skin contamination caused by poor hygiene or specific human work (work on the ground, activities requiring contact with certain reagents, chemicals (locksmith, car service employee, etc.).
Sometimes folliculitis is initiated by strange, not at first glance, reasons: caries, tonsillitis, gingivitis, pharyngitis, periodontal disease.
It would seem, how can a hair follicle on the arm become inflamed due to a sore mouth or throat? The point here is pathogenic microorganisms localized in the mouth and throat. They are carried by the blood throughout the body, without even passing through the hands. A weakened immune system is unable to put up a reliable barrier around healthy organs: bacteria (viruses) reach the hair follicles and settle there.
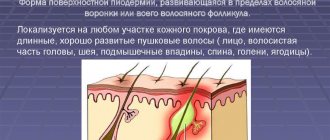
Hair follicles - what are they?
Hair follicles are hollows
in the skin in the form of tubules in which the hair roots are located.
They also serve as an outlet for the sebaceous glands that produce secretions. Their function is to protect the epidermis. Irritation or damage
to the opening of the hair follicle causes germs to enter the hair follicle, leading to infection.
The infection causes inflammation of the hair follicle, which results in painful
and itchy patches in the growing hair area.
Folliculitis symptoms
The symptoms of folliculitis will depend on the type of folliculitis you develop. For example, with the superficial type, pustules can reach sizes up to 0.5 mm in diameter and be painless to the touch. As a rule, there is a pink inflammatory area around them, sometimes with a reddish tint to the skin. Approximately on the third day, the ulcers dry out and become covered with a brownish crust, leaving a slight peeling behind. The appearance of pigmentation on the skin may also be present.
The deep form of folliculitis is manifested by more severe damage to the hair follicle. Reddish nodules up to 1 cm in diameter may appear on the skin and are painful. On their surface there is an abscess, which is penetrated by a hair. The abscess can usually open within a few days, become covered with a crust, and the inflammatory nodule disappears over time.
The main complaints of a patient with folliculitis are pain and itching. In some cases, there may be enlargement of the lymph nodes that are located near the area of inflammation. The patient may also be concerned about a cosmetic defect on the skin that remains after folliculitis. This could be excess pigmentation or scars.
Staphylococcal folliculitis manifests itself in the initial period as a process of inflammation around the hair, beginning the development of ostiofolliculitis, or staphylococcal impetigo. These are small-shaped and sized pustules with dense walls, which are pierced in the center by a hair. After a few days, the pustule dries out, forming a cone-shaped yellow crust, which is quickly rejected.
If conditions are not good for the patient, painful sensations occur in the affected area, which especially bothers the patient if there is a large number of folliculitis; in this case, a pronounced infiltrate appears. Due to the involvement of the tissue surrounding the follicle in the inflammatory process and the fusion of specific elements of the rash, deeper, long-lasting varieties of staphyloderma, carbuncle, furuncle, etc. appear.
In diagnosing a disease such as folliculitis, an important role is played by examining the patient. Rashes with folliculitis are very characteristic and allow a correct diagnosis. Additional examination measures will help to accurately identify the cause that could lead to the development of the disease.
Folliculitis on the penis due to rubbing
One of the main factors predisposing to the development of pathology.
Chafing on the penis can occur due to a number of accompanying factors:
- while walking or running
- due to wearing uncomfortable underwear or tight clothing
- with rough or too frequent sex
- due to scratching (due to itching, sweating)
- commitment to masturbation
In each of the mentioned cases, folliculitis of the penis due to chafing occurs due to abrasion of the skin.
In this case, the hair follicles may be injured, which will allow access to pathogenic pathogens inside.
Features of different types of folliculitis
There are many types of folliculitis, and therefore, from a practical point of view, it is advisable to consider separately the characteristics of each of them.
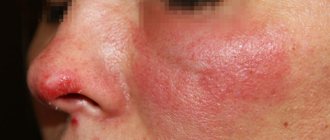
- Herpetic. Just like staphylococcal, it is more common in men who shave in the area of the nasolabial triangle and on the chin.
- Kleshchevoy. It develops after a tick bite, lasts longer than other varieties, and requires specific treatment of the underlying disease (if the tick poses an epidemiological danger).
- Eosinophilic. It is observed only in an isolated group of patients (HIV-infected).
- Candida. This type of folliculitis usually occurs under occlusive dressings. The risk of developing folliculitis increases with local use of drugs from the group of corticosteroids under a bandage. Also, the risk of the disease is higher in bedridden patients and long-term feverish patients.
- Staphylococcal. Characteristic of areas where bristly hair grows (nasolabial triangle, chin). It occurs mainly in men who shave. In severe cases, when the death of hair follicles occurs, after the end of the inflammatory process, connective tissue scars are formed.
- Acne. This type of folliculitis is a consequence of syphilis. It is characterized by the fact that the inflamed follicles acquire a faded red color and, in some cases, are located in groups. Elimination of this pathology is possible only by treating the underlying disease with specific agents.
- Gram negative. Develops in patients with weakened immune systems who have been taking antibacterial medications for a long time due to acne. It is characterized by the fact that the patient’s condition worsens sharply, which manifests itself in increased acne. Abscesses may form.
- Pseudomonas. Caused by the pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This type of folliculitis is also known by another name - “hot bath” folliculitis, because it usually occurs after taking a bath in hot water that has not been sufficiently chlorinated.
- Folliculitis, caused by fungi belonging to the genus Pityrosporum, is characteristic of tropical and subtropical climates. It is characterized by an itchy rash of a monomorphic nature (papules and pustules), which is located at the mouths of the follicles. In such patients, scratching is found localized in the shoulders, back, face and neck.
- Folliculitis caused by dermatophytes. This infection typically begins with the upper layer of the epidermis, after which the inflammatory process seizes the mouths of the follicles, and then the hair shafts. A complication in this case is dermatophytosis of the scalp.
- Gonorrheal. It is most rare compared to other types of this disease. Its location is the foreskin in men and the perineal area in women. Occurs with long-term and untreated gonorrhea. When examining the contents of pustules in such patients, gonococci are found in large quantities.
- Professional. It develops in people of certain professions and is associated with exposure to irritating chemicals on the skin. With this type of disease, rashes are usually localized on the back of the hands, as well as on the extensor surfaces of the forearms.
- Impetigo Bockhardt, despite its name, nevertheless belongs to the group of folliculitis. In this case, hemispherical, superficial pustules appear, which can range in size from a poppy seed to a lentil. The pustules are permeated with vellus hair and are arranged in groups. The reason for the development of this folliculitis is increased sweating and maceration of the skin, which is a consequence of the use of warm compresses.
- Depilatory folliculitis of smooth skin is another type of disease that occurs mainly in hot countries. Middle-aged men are more susceptible to the disease. Also, this type of folliculitis is characterized by symmetry of the lesion. Inflamed follicles appear evenly on the skin of the lower extremities. After eliminating folliculitis, characteristic follicular scars remain on the skin.
Folliculitis on the penis after sexual intercourse
The development of penis folliculitis after sex is possible in two scenarios, in each of which sexual intercourse takes place:
- During friction (during vaginal, anal or oral sex), swellings may form on the penis, which will allow pathogenic pathogens access to the follicle cavity. This probability increases significantly if there is insufficient production of pre-ejaculate (lubricant produced during sexual arousal) or the use of low-quality condoms.
- Infection of the follicle with sexually transmitted sexually transmitted infections. This is possible even when having sex with a regular partner, if the latter is a latent carrier. But the chance of infection is many times higher in cases of promiscuity and neglect of contraception.
Diagnostics
Dermatologists must examine the rash and conduct a dermatoscopy, which will show the depth of the lesion. The specialist can also refer the patient to donate discharge from the pustules, which will be required for:
- microsporia;
- research on fungi;
- bacteriological culture;
- tests for Treponema pallidum.
There is also a need for differential diagnosis. Folliculitis should be distinguished from pathologies such as syphilis and gonorrhea. In this case, the doctor prescribes:
- RPR test.
- PCR diagnostics.
If necessary, the specialist will prescribe blood sugar testing and an immunogram. In addition to gonorrhea and syphilis, the disease should be differentiated from the following:
- phrynoderma;
- streptococcal impetigo;
- Hoffmann's perifolliculitis;
- drug toxicoderma;
- furunculosis;
- pink lichen of Zhiber;
- nodular cystic acne.
The treatment required for hair folliculitis, as well as ailments on the legs, pubis, face, back, and skin, is described below.
Folliculitis on the penis due to poor hygiene
The most common factor contributing to the development of folliculitis on the penis.
Obviously, the likelihood of penile folliculitis due to insufficient intimate hygiene is many times higher than for people who regularly take care of themselves.
Poor hygiene also leads to the development of other pathological processes of infectious origin.
The main factor for folliculitis in this case is irregular washing, bathing or showering.
The skin on the genitals quickly becomes contaminated; this is facilitated by a number of physiological processes:
- urination
- secretory functions
- increased sweating in the intimate area
- having sex and stuff
If a man showers irregularly, the chances of developing folliculitis increase significantly.
Since a favorable environment is created for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
Another factor related to hygiene is wearing underwear for more than 1-2 days, which happens especially often.
In addition, it is important to select suitable personal hygiene products (body gels, soaps, etc.), without neglecting their regular use.
Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene allows you to eliminate pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic bacteria from the surface of the skin, controlling their population.
It also removes sebum, cleanses pores and layers of dead cells that feed bacteria.
The use of hygiene products dries out the skin, creating an unfavorable environment for the life of various microorganisms that love moisture.
Intimate hygiene also includes removing hair from the groin area and directly from the body of the penis, which is increasingly used by men today.
This is a useful procedure from a hygiene point of view, but it is important to carry it out correctly, preferably in a trusted salon.
Otherwise, especially when removing hair on your own, there is a high probability of damage to the follicles, which can cause folliculitis.
Complications
In most cases, this disease does not cause serious consequences for human life and health. But if there is no proper treatment, the infection penetrates deeply and the disease becomes more complicated. The situation is aggravated if the patient neglects the rules of hygiene, and also if he has a significant weakening of the immune system.
Complications of the disease include the following:
- furunculosis and carbuncles;
- dermatophytosis;
- formation of scar tissue;
- rotting of tissues.
Scars and cicatrices are formed as a result of attempts to squeeze out pus from inflammatory elements.
Folliculitis on the penis with diabetes
This pathological process of a systemic type disrupts the functioning of many organs and systems in the body.
Folliculitis on the penis in diabetes mellitus develops due to disruption of blood circulation and tissue innervation.
Such pathological changes in the body negatively affect the state of the immune system.
With a decrease in immunity, an uncontrolled growth of the population of opportunistic microorganisms present on the skin begins.
Under such conditions, the risk of follicular damage increases significantly.
How to treat folliculitis?
Single ostiofolliculitis can go away on its own, without additional treatment. To avoid complications, you can use antiseptic skin hygiene products.
In more severe cases, the following drugs are used:
- Bactericidal ointments and solutions dry the skin and relieve inflammation: Methyluracil, Betadine, Miramistin, zinc ointment. Apply 1-3 times a day;
- Antibiotics topically twice a day - effect on staphylococcus (erythromycin, syntomycin ointments, Levomekol)
- Wiping the skin with alcohol solutions (boric, salicylic, camphor alcohol, brilliant green, methylene blue);
- Antiallergic drugs to reduce itching - Suprastin, Claritin, Lomilan;
- Pure ichthyol is applied in a thin layer to large folliculitis, and an antiseptic bandage is applied on top (change once a day);
- Physiotherapy: UV irradiation, UHF, laser therapy.
Proven methods and recipes of traditional medicine:
- Compresses, soothing bandages with thorny leaves. Boil 50 g of root in 0.5 liters of water for half an hour. After an hour, strain. Use the decoction daily.
- Chamomile decoction is a valuable remedy for inflammation. Per liter of water - 1 tbsp. l. colors. Steam, let it brew for 30 minutes, strain. Carry out the procedure in the morning, afternoon and before bed.
- Prickly tartar. Excellent relieves inflammation. Grind the leaves, grind them, apply the paste to the rash areas. Keep for 30 minutes.
- Headbands with woodruff. Cover the ulcers with a paste of fresh leaves. Carry out the procedure 2 times a day.
- Dandelion infusion. Wash roots, leaves, chop, 2 tbsp. l. raw materials pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, boil for 10–15 minutes. Strain the infusion after brewing for half an hour. Drink a quarter glass 3 times a day.
- Burdock decoction. Pour a spoonful of crushed root into 0.5 liters of water. Boil for 10 minutes, let sit for an hour, strain. Take the healing infusion twice a day before meals.
- Effective applications. Prepare a decoction: pour 2 tbsp. water 200 g of rose hips, the same amount of viburnum, add 100 g of nettle, 10 g of green walnut shells. Simmer on fire for 10 minutes. The decoction is infused for a day. Mix 50 g of fresh cottage cheese and honey. Dilute the curd-honey mixture with a decoction, apply it 3 times during the day for 15–20 minutes.
If the lesion is large, then oral antimicrobial drugs are prescribed - Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Cephalexin, Amoxicillin. Before using any of these remedies, consult your doctor!
During treatment, avoid contact with water and do not visit the sauna, swimming pool or shower.
Folliculitis on the penis due to allergies
Allergic reactions are not capable of causing the development of folliculitis in any of its manifestations.
However, allergy manifestations on the surface of the skin of the penis are possible.
Such allergic reactions are accompanied by a rash and itching and can be caused by the following factors:
- wearing underwear made of synthetic or low-quality materials
- individual intolerance to personal hygiene products
- allergy to powders and rinse aids used in washing underwear
- individual reaction to the use of certain contraceptives
To combat such forms of allergies, creams and ointments are often used, which are applied to the skin of the penis.
Such topical preparations can clog pores and hair follicles.
This disrupts secretory functions and promotes the development of anaerobic bacteria, provoking the occurrence of folliculitis of the penis due to allergies.
Some local antiallergic drugs contain topical glucocorticoids.
These medicinal substances reduce immunity at the local level, provoking an increase in the population of opportunistic bacteria that can provoke the development of folliculitis.
Nutrition
Diet is not necessary when folliculitis occurs. But there are concomitant diseases for which dietary adjustments are necessary. Patients who are obese or have diabetes should follow a low-carbohydrate diet.
It is important to adhere to the following dietary rules:
- The consumption of animal fats should be limited.
- Eliminate flour products, spices, chocolate, sweets, alcohol, strong coffee and tea from your diet.
- Eat as many fresh vegetables as possible to provide your body with the required amount of fiber. You can also eat bran.
- You should include a sufficient amount of protein in your diet, including animal protein. Preference should be given to lean meats such as veal, chicken and turkey.
- It is worth eating more foods rich in vitamins. Carrots, beets, rose hips, and blueberries will be especially useful.
Folliculitis on the penis due to enlarged sebaceous glands
Anatomically, hair follicles are associated with endocrine glands.
Some representatives of the stronger sex experience an increase in sebaceous glands.
This anatomical feature caused by increased production of sex hormones is called hypertrophy.
Folliculitis of the penis with enlarged sebaceous glands occurs due to the increased secretory function of the latter.
As a result, the follicle becomes clogged with sebaceous secretions and epithelial cells.
An artificially created isolated environment promotes the development of pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the occurrence of folliculitis.
This factor occurs especially often among young men who have increased synthesis of androgens.
They stimulate the function of the sebaceous glands, causing hypertrophy and increasing sebum production.
Principles of treatment of folliculitis on the penis
Treatment of penis folliculitis is conservative, based on drug therapy.
Drugs are selected based on diagnostic results.
The key factor in choosing medications is the etiology of the disease and identification of the pathogen.
So, for fungal infections, antifungal agents are used, for bacterial ones, antibiotics are used.
In the early stages of development of the pathological process, local drugs are prescribed.
How to anoint penis folliculitis, there are different variations:
- Bacterial etiology, for example, common staphylococcal infection - penis folliculitis is treated with antibiotic ointments. One option would be to use Zinerit to treat penis folliculitis.
- Fungal infection - drugs with a wide spectrum of antifungal activity are prescribed (Terbinafine, Fluconazole).
- Herpetic form - acyclovir-based products are used.
- Demodicosis - the best option is to use Parmethrin cream.
Examples can be given for a long time; it is important that each medication is prescribed by the attending physician.
In severe cases of the disease, with deep damage to the follicle, systemic therapy is added to local therapy.
The doctor will answer what antibiotics to take for penis folliculitis.
Most often these are drugs of the erythromycin or tetracycline series.
In order to reduce the spread of infectious lesions to nearby tissues, doctors recommend the auxiliary use of boric alcohol.
The solution is used to treat the affected and surrounding areas of the skin.
In some cases, physiotherapy using ultraviolet radiation is performed.
Folliculitis on the penis – which doctor should I contact?
The disease is characterized by pathological damage to various layers of the skin; accordingly, diagnosis and treatment are carried out by specialists associated with dermatology.
If the disease is caused by poor hygiene, chafing and other everyday causes, even a dermatologist can help.
If we are talking about factors related to sexual activity and STDs, you should contact a venereologist.
However, the best solution to receive complete treatment would be a visit to a dermatovenerologist.
In some cases, it is possible to prescribe treatment after the initial examination.
If a severe form of the disease is suspected, for example, provoked by a syphilitic infection, a full diagnosis is required, on the basis of which drugs are selected.
Preventive measures against folliculitis and boils
It is impossible to completely insure against boils and folliculitis, but there are a number of measures that will reduce the risk.
Preventive measures include a set of measures:
- Using individual towels and personal hygiene items to avoid spreading the infection to other family members.
- Refusal of uncomfortable tight clothing made from synthetic fabrics to avoid skin irritation.
- Daily change of bed and underwear.
- Washing towels, bed linen and underwear in hot water to kill pathogenic microbes, mandatory ironing after drying.
- The use of dressing materials is for one-time use only. Dispose of used dressings using paper bags.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Regular body hygiene using mild antibacterial soap will help prevent the development of boils and folliculitis.
- Timely treatment of cuts, abrasions and other even the smallest wounds.
- Eating healthy foods that support a healthy nutrient balance and immune system.
- Avoid shaving and other cosmetic procedures on the affected areas.
- Refusal to swim in open reservoirs, swimming pools, visit public baths, locker rooms in sports sections, etc.
See also methods for preventing candidal folliculitis.
Clinical picture of folliculitis on the penis
The clinical picture of the development of the pathological process is clear and characterized by rapidity.
Most of the symptoms cannot be missed, as they cause significant discomfort, especially when folliculitis is localized in the groin area.
In dermatology, the symptoms of penis folliculitis develop in the following sequence:
- In the area of the affected follicle, a distinct hyperemia of the skin occurs with noticeable traces of infiltration. At this stage, most patients experience severe itching; scratching can aggravate the pathological process and provoke complications.
- The area of hyperemia increases in diameter; in place of the follicle (at the base of the hair), a pustule is formed, filled with serous or whitish purulent contents. This formation also itches, but when touched it responds with strong painful sensations.
- After spontaneous, accidental (when scratching, rubbing on clothes) or intentional (it is recommended to do this only at a doctor’s appointment) opening of the pustule, pus flows out of it (or is cleaned out by a doctor). At the site of the pathological formation, an ulceration remains, covered with a purulent-bloody crust.
Subsequently, upon receiving adequate treatment, the crust comes off, and a scar remains at the site of ulceration.
When the entire body of the follicle is affected, the scar is more pronounced, and traces of hyperpigmentation may be present.
Before any signs of the disease appear, patients often experience itching and soreness at the site of future development of folliculitis.
It is noteworthy that even in the area of the penis, on the body of which there is a small number of hairs, folliculitis has a multiple course (in most cases).
Prevention of penile folliculitis
To prevent the development of a pathological process or prevent its relapse, prevention is important.
Following a number of simple recommendations can reduce the likelihood of follicle infection:
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene, regular washing with hygiene products;
- wear comfortable underwear made from natural materials, change your underwear regularly;
- dress according to the weather - overheating in the groin area leads to increased sweating, provoking the occurrence of folliculitis;
- lead a healthy lifestyle to maintain immunity (healthy eating, exercise, etc.);
- avoid promiscuous sex or regularly use condoms;
- in case of relapse due to depilation, refuse to remove hair in the groin area.
If folliculitis appears on the penis, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.