June 1, 2020
The issue of visiting a solarium for psoriasis worries many people, since light therapy is widespread for skin diseases. Dermatologists often prescribe ultraviolet light treatments because they have beneficial effects on the skin. But the question of whether it is possible to go to a solarium with psoriasis cannot be answered with certainty that it is, since the form of the disease plays a role. In general, the procedure is really useful, but the final decision on prescribing such treatment should be made by a specialist.
A Guide to Home Phototherapy for Psoriasis
Phototherapy or light therapy may help reduce the symptoms of psoriasis.
Home phototherapy can be safe and effective for people with psoriasis if they follow their doctor's instructions for its use. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system becomes oversensitive and attacks healthy skin cells. The attacking cells multiply faster than normal and form a rash of thick, inflamed plaques on the skin. These plaques usually have a flaky crust on top.
Phototherapy can be done on an outpatient basis in a clinic, or your doctor may prescribe a phototherapy unit for you to use at home. Research shows that home phototherapy can provide the same results as hospital treatment.
This article explains how phototherapy works, the different types of home phototherapy, and possible side effects.
Triggers and problems associated with the disease
Since psoriasis is characterized by clear genetic determination, epidermal cells are subject to hyperproliferation during its development. As a result of complex processes within the body, among which autoimmune factors probably play a major role, an inflammatory process occurs inside the skin.
Frequent triggers of the disease are definitely stress and mental stress. Various infections (frontal sinuses, sinusitis, diseases of the genitourinary system, etc.) can also be provoking factors. Psoriatic plaques are often localized in places where there is mechanical damage to the skin (scratches, injections, cuts). They also occur after taking certain medications: for example, beta-blockers or NSAIDs. Severe climatic conditions also play an important role in the clinical picture of the disease.
Got some free time?
Then use it! Get additional education!
There is a major problem that many patients face regularly. Despite the variety of therapeutic methods, not every form of psoriasis responds to them, so the search for new treatment methods continues to this day. All patients, without exception, talk about the positive effect of heat and sun on the course of psoriasis. That is why ultraviolet spectrum A and B began to be actively used for anti-psoriatic therapy.
What is phototherapy?
Phototherapy uses ultraviolet light to reduce swelling and slow the overproduction of skin cells caused by psoriasis. Ultraviolet light is invisible to the naked eye and penetrates the skin.
There are two types of UV radiation:
UV-A
This type of light can penetrate deeper into the skin than UVB. A person receiving UVA light treatment must sensitize their skin with a plant-based chemical called psoralen in order for the treatment to be effective.
UV-B
UVB light penetrates the outer layers of the skin and can cause sunburn. Phototherapy using UV-B light is effective on its own, without any chemicals.
Galvanization
Galvanization is a technique of electrotherapy, during which the patient’s body is exposed to a constant low-voltage electric current. Galvanization is applied locally to affected areas and reflex segmental areas, and there is also a method of general galvanization.
Dermatologists traditionally use several galvanization methods:
- local - to foci of inflammation;
- intranasal;
- general according to Vermeule;
- galvanization of the collar zone according to Shcherbak;
- four-chamber galvanic bath;
Indications
Galvanization is indicated for patients with:
- neurodermatitis;
- other itchy dermatoses;
- scleroderma or nodular vasculitis;
- psoriasis or lichen planus;
- keloid scars.
Contraindications
Galvanization is not recommended for:
- eczema, dermatitis and pyodermitis;
- stage 3 hypertension;
- feverish condition;
- oncological diseases.
Side effects
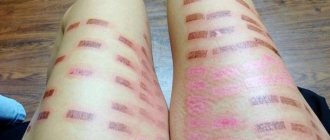
Phototherapy for psoriasis often causes sunburn reactions. In rare cases, this can also lead to blistering.
One 2022 study found that people who used home phototherapy experienced severe erythema, a skin reaction that causes a rash, more often than people treated in a hospital. However, blisters were more common among those treated in hospital.
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation can also increase the risk of skin cancer, so when using phototherapy it is important to follow your doctor's instructions and have your skin examined regularly.
Benefits of PUVA
Therapy using the PUVA technique shows high positive dynamics and has a number of advantages:
- rapid achievement of effect - after two or three procedures, the condition of the affected skin improves significantly;
- comfortable conditions for therapy without interruption from work and personal affairs;
- lack of addiction and prolonged effect;
- the ability to conduct maintenance and preventive sessions without the risk of complications;
- high level of treatment tolerance;
- the possibility of using additional treatment methods;
- long period of remission.
All patients after the course show a significant improvement in the condition of the skin, and in about 80% of people the surface of the epidermis is completely cleansed.
Does phototherapy work?
Phototherapy does not cure psoriasis, but it can reduce symptoms.
According to some data, in special cases, phototherapy can completely clear the skin. In other cases, it may simply reduce the appearance of psoriasis plaques. Doctors recommend phototherapy only if other treatments, such as topical steroid creams, have failed to improve symptoms.
A 2022 study compared the results of phototherapy treatment at home with the results of treatment in hospitals. The researchers used the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), which measures the intensity and extent of an outbreak, as a baseline. Their results showed that 40.7% of those treated at home scored a PASI score of 75 after 46 treatments, compared with 41.7% of people treated in a hospital. A PASI score of 75 corresponds to a 75% reduction in symptoms.
The study also found that people were generally more satisfied with treatment when receiving it at home.
Phototherapy on dark skin
Research into the effectiveness of phototherapy for different skin tones has been limited, but research is currently ongoing. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, phototherapy can be very effective in reducing psoriasis symptoms in people with dark skin, who often have thicker skin lesions.
However, such patients may find that phototherapy may leave spots on their skin. This is because treatment can further accentuate the hyper- or hypopigmentation that psoriasis can cause.
Indications
Using ultraviolet therapy, it is possible to cure almost all forms of psoriasis. In this case, the lesion should not affect more than 30 percent of the body.
The method of physiotherapeutic influence is prescribed when diagnosing plaque, palmoplantar or point psoriasis along with taking psoralens.
Ultraviolet irradiation is also possible for exudative or erythrodermic forms of psoriatic rashes.
UV therapy is also recommended in cases where drug treatment does not bring the desired effect. Physiotherapeutic treatments are also prescribed as the disease progresses. But before starting the course, detoxification therapy is necessary in order to relieve signs of intoxication and prevent the development of complications.
How long does this procedure take?
Phototherapy is usually three sessions per week for 4 weeks to 3 months. Research shows that phototherapy more than three times a week provides little benefit, although it does expose the patient to an increased risk of side effects such as rash.
Some people can only do two classes a week. According to a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, patients who received two phototherapy sessions per week saw their psoriasis symptoms resolve in an average of 88 days, compared with 58 days for those who received three sessions per week.
After the initial treatment period, your doctor may recommend ongoing weekly treatments to keep your skin clear.
At-home phototherapy machines reduce the need to visit a clinic or specialist's office, but doctors still recommend frequent psoriasis screenings.
Types of treatment used
In physiotherapeutic practice, three PUVA treatment protocols are used:
- systemic technique - to influence the patient’s entire body;
- local – for therapy of individual zones;
- combined – a combination of the first two methods.
Photosensitizing drugs are available in different forms - tablets, emulsion, cream, solution. They are used for both internal and external treatment.
One effective way is bath therapy. 50 mg of psoralen is dissolved in water, the patient is immersed for 15 minutes, after which he undergoes a UV irradiation session. Such baths give good results both with a systemic and local approach.
Recommended irradiation parameters (per dose per cm2):
- low threshold: 10 – 20 J;
- medium – 50 – 60 J;
- high – up to 120 J.
To obtain the effect, a therapeutic course of 10–15 procedures is carried out with the selected dose. Then, preventive sessions are recommended twice a year.
How to do phototherapy at home?
Your doctor will explain how to use the phototherapy machine at home. Be sure to follow their instructions as UV rays can damage the skin, causing premature aging, sunburn and skin cancer.
Some doctors begin phototherapy in a hospital setting before recommending that the patient continue treatment at home. Your doctor will explain the importance of protecting sensitive areas of the body, such as the eyes and genitals, and explain when to use moisturizers. He will also explain how to position the device so that it targets the appropriate area and how far away from the device the patient should stand.
The doctor will evaluate the medical history and note any medications the patient is taking, including supplements and herbs. Depending on your skin type, doctors will recommend a starting dose for the first few treatments and gradually increase it.
You should maintain at least a 24-hour interval between sessions and reduce the exposure time if you regularly skip treatment.
Irradiation methods
Ultraviolet rays affect human skin in the summer and their positive effects have been known since ancient times. That is why in dermatology, artificial ultraviolet sources with different wavelengths are used to treat diseases.
Phototherapy for psoriasis promotes the regeneration of epidermal tissue and reduces inflammatory infiltration.
In addition, a full course of ultraviolet treatment reduces the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the blood, normalizes cellular and humoral immunity, which allows for faster remission of the disease.
Cosmetologist, dermatovenerologist, laser therapist
Nachoeva Irina Nasredinovna
7 years experience
The following methods of influence are distinguished:
- Long wave. Wavelength from 315 to 400, range A.
- Medium wave. Also called UVB. This method also includes narrowband phototherapy. The wavelength ranges from 280 to 320 nm.
- Combined. Waves of different ranges are used. The therapy involves the use of UV irradiation and various medications (photosensitizers) that help concentrate energy on the surface of damaged skin. But the use of a combined method of exposure has a number of contraindications.
- PUVA baths. Prescribed in cases where there is no possibility of using furocoumarins internally. The drugs are dissolved in water, after which the patient takes a bath and then undergoes ultraviolet irradiation.
- Selective phototherapy. Indicated for generalized psoriasis in the absence of pronounced soft tissue swelling. The method is based on the selective use of medium-wave irradiation.
Excimer xenon chloride laser irradiation can also be used for psoriatic rashes. The wavelength is 308 nm. This is one of the most modern methods of therapy, in which the beam is delivered by a special device in the form of a beam. This eliminates the negative impact on healthy skin tissue.