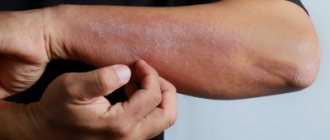
Bacterial skin infections are a large group of diseases initiated by pathogenic bacteria and characterized by damage to the skin and soft tissues. They are considered one of the most common in dermatology and can be localized either on a small or large area of skin (within several hours). In terms of severity, such infections are very diverse and range from small nodules to conditions that pose a threat to the patient’s life.
The dermatovenereology department of CELT offers diagnostics and treatment for bacterial skin infections in Moscow. We have been conducting professional activities in the capital's paid medical services market for almost three decades and enjoy a good reputation. Diagnostics are carried out using modern equipment, which makes it possible to detect diseases even at the initial stages of development, and their treatment is carried out in accordance with international standards.
At CELT you can consult a dermatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Etiology of bacterial skin infections
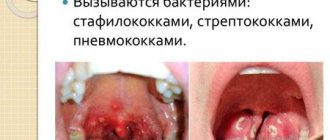
The most common causative agents of skin infections are staphylococci and streptococci:
| Bacterium | Description of provoked infections |
| Staphylococcus | One of the representatives of the Staphylococcaceae family, which is a gram-positive coccus. Distributed in soil and air, it can be part of the normal skin microflora of humans and animals. Pathogenic and opportunistic staphylococci, which can cause diseases, affect not only the skin, but also the nasal or oral pharynx. These species include Staphylococcus aureus, epidermal and hemolytic staphylococci, which cause eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, and purulent lesions of the skin. They enter the body through damaged skin and hair follicles. Risk groups - patients:
|
| Streptococci | They represent a genus of ovoid or spherical gram-positive anaerobic bacteria of the Streptococcaceae family. They are parasites of humans and animals that live in the oral and nasal cavities, digestive tract and large intestine. Despite the fact that today 21 groups of streptococci have been identified, the most common are considered to be groups “A”, “D”, “F”, which parasitize the skin, neck, and nasal cavity. They enter the body through the respiratory tract and mouth. The following skin infections are caused by:
|
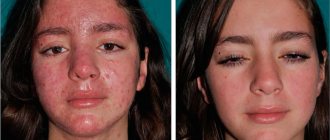
Symptoms of contagious skin diseases
At the first appearance of the following symptoms, you should urgently make an appointment with a dermatologist:
- itching;
- redness;
- rashes of different nature and localization;
- irritation;
- peeling of the skin.
Associated symptoms include insomnia, deterioration in quality of life, nervousness, lack of self-confidence, and the development of psychological problems and complexes.
With mycoses, there is separation of a certain amount of skin, a change in the appearance of the nail or affected areas.
Due to frequent mechanical stress (scratching), inflammation may occur.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure
Types of bacterial skin infections
| View | Skin infection and its features |
| Staphylococcal infections | Superficial folliculitis - characterized by inflammatory processes on the skin with a white purulent center. Most often, the infection affects the hair areas on the arms, legs and thighs, usually after hair removal carried out without observing hygiene standards. May become chronic. |
| Boils are a type of deep folliculitis, characterized by an acute purulent-necrotic inflammatory process of the follicles, sebaceous glands, and connective tissue around them. Most often, the infection is found in the cervical, occipital, femoral areas, on the back and even on the face. In the latter case, it can cause serious complications such as sepsis or meningitis. | |
| Anthrax is another type of deep folliculitis. It is a particularly dangerous infection, characterized by very rapid development and acute course. It is manifested by intoxication, inflammatory processes of the skin, lymph nodes, and internal organs. | |
| Panaritium is an infection characterized by an acute purulent process that affects the fingers of the upper and, less commonly, lower extremities. It manifests itself as pain, swelling, redness, and fever. In later stages of development, surgical intervention is required. | |
| Streptococcal infections | Erysipelas is an infection caused by group A streptococcus. It is characterized by the development of inflammatory processes of a serous or serous-hemorrhagic nature, manifesting themselves as focal lesions of bright red skin with swelling, general intoxication of the body and an increase in temperature. It is one of the most common bacterial infections. |
| Streptoderma is an infection characterized by the development of serous inflammatory processes without suppuration, severe swelling of the affected area, and the rapid formation of blisters or spots prone to peeling. | |
| Abscess - characterized by the formation of a cavity in the subcutaneous fatty tissue or muscles filled with pus. The infection manifests itself with swelling, hyperemia, and pain symptoms. |
How contagious skin diseases spread
No one is immune from dermatological diseases. Regardless of belonging to a particular social group, everyone can become infected with a skin disease.
The main reasons for the spread are the following factors:
- population migration;
- use of personal belongings of a sick person;
- visiting public places such as: sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool, changing rooms, shower, toilet.
You can also become a victim of the infection simply by moving on public transport, shaking hands, hugging or having close contact with an infected person. You can catch the disease in a camp, on a hike, in a hotel, on the beach, on a train. In a word, where there are people.
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Skin scraping
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
Unfortunately, contagious skin diseases are always present in human society and can affect people living even in favorable conditions. These diseases are completely curable; it is only necessary to promptly consult a dermatologist when the first signs of the disease appear.
The most common contagious skin diseases are lice, scabies and mycoses (fungal skin infections).
Pediculosis
- a common parasitic disease of humans, the causative agent of which is blood-sucking insects - lice.
There are 3 types: head lice, body lice and pubic lice.
Infection occurs through close household and sexual contact, or through the use of the patient’s belongings.
The first sign of this disease is itching, which is the result of an allergic reaction to the saliva of lice introduced into the skin during blood sucking. With head lice, itching is most often in the back of the head, temples, and behind the ears. Body lice is accompanied by almost unbearable itching all over the body, worsening at night. Moderate itching and burning with pediculosis pubis occurs in the anus and genital area, less often in the eyelid area.
Skin manifestations: Traces of scratching, hemorrhagic crusts, redness (with lice pubis, bluish tint) and papules in places where lice suck blood. Complications are possible in the form of a secondary infection (pyoderma), dermatitis and eczematization of the skin.
Recommendations for the prevention of head lice:
- Regular and careful personal hygiene;
- It is important to use only your personal items and hats;
- Perform a weekly change of bed linen and a daily change of underwear;
- To reduce contact with objects and other people, avoid having your hair down;
- Use a rubber cap in the pool;
- In case of lice infestation, you must immediately seek medical help to prescribe adequate treatment.
- Do not allow children to play with stray animals, pick them up and carry them into the house;
- Do not allow animals into playgrounds;
- When walking your pets, do not allow them to come into contact with stray animals;
- Keep pets in specially designated areas, do not take them to bed, have animals checked regularly by a veterinarian;
- Do not throw sick animals outside, take them to a veterinary hospital;
- After handling animals, wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- After getting a haircut at the hairdresser, immediately wash your hair with warm water and soap;
- Do not use other people's hats, clothes, combs, or towels.
Microsporia, trichophytosis
– common fungal diseases caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum and Trichophyton.
Infection occurs through contact with a sick animal (cats, dogs, hamsters), in rare cases with a sick person, through infected household items, environmental objects: for example, dust on staircases, hairdressing equipment: combs, hair clippers, brushes for shaving, etc.
Signs of the disease:
In sick animals, areas of hair loss (bald patches) are noticeable in the form of round or oval spots, most often in the head area (on the muzzle, the inner surface of the ear), neck, and limbs. Sometimes an animal may look healthy, but be a carrier of microsporia.
A person's smooth skin and scalp may be affected, and rarely, nails. When smooth skin is affected, round or oval lesions of pinkish-red color appear, their surface is covered with scales, blisters and thin crusts along the periphery. Single lesions of round or oval shape usually develop on the scalp. The affected hair breaks off and protrudes 4-8 mm above the skin level, and is covered with whitish scales at the base.
If the scalp is affected, treatment is carried out in a skin clinic, since long-term systemic antifungal therapy requires regular monitoring, and daily hair removal and treatment of hair in the area is also necessary.
In case of fungal diseases, timely consultation with a dermatologist is very important. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate; you risk not only blurring the picture of the disease, but also prolonging the treatment time.
Recommendations for the prevention of fungal infections:
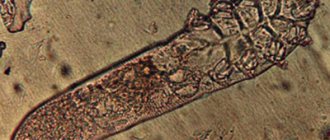
Scabies
– a contagious parasitic skin disease caused by the scabies mite. Scabies can be contracted through underwear, bedding, and clothing. During the day, ticks are dormant, and in the evening and at night they become active. Scabies becomes most widespread when people are overcrowded and standards of public and personal hygiene are violated.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- skin itching, worse at night;
- the appearance of scabies on the hands, wrists, elbows, feet, mammary glands of women, genitals of men;
- the appearance of nodular and vesicular rashes, scratching, bloody crusts on the body (abdomen, buttocks, chest), thighs.
By following simple rules of personal hygiene, you will protect yourself from scabies infection:
- Regular hand washing;
- Take a shared shower daily;
- Do not forget about frequent changes of linen and regular sanitization of outerwear;
- New clothes must be washed before wearing;
- Treat outer clothing purchased at markets with steam or put it in a plastic bag and tie it tightly (if left without air, ticks will die in a few days).
- All personal hygiene items must be strictly individual.
If you or your family members experience any of the above symptoms, you should definitely consult a dermatologist. There is no need to self-medicate, as this will blur the clinical picture of the disease and make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Moreover, improper treatment leads to a protracted course of the disease, disrupts the general health of the patient, and most importantly, to infection of loved ones. Timely qualified treatment and compliance with doctor’s recommendations leads to complete recovery. Therefore, seeking professional medical help is necessary not only to get rid of an unpleasant disease yourself, but also to protect your family and friends from contagious skin diseases.
And most importantly, treatment for each specific patient MUST be carried out simultaneously with anti-epidemic measures (disinsection of hats, clothing, bedding and premises, etc.) in order to avoid re-infection.
Treatment of viral skin infections
To choose the right treatment, you first need to determine the type of infection. Diagnostic tests and treatment are performed by a dermatologist. Each individual type of disease has its own treatment regimen.
Herpes and herpes zoster occur when the immune system is weakened, so complex therapy will include, in addition to antiviral agents, immunomodulators, vitamins and physical therapy. For treatment to be effective, it is necessary to examine the blood for the presence of antibodies to the herpes virus - immunoglobulins and assess the general state of the body's immunity.
Condylomas and warts are removed in various ways. The cheapest is electrocoagulation. Modern safe techniques are laser and radio knife. Some clinics still use special solutions - concentrated alkalis or acids that cause necrosis of warts.
But this technique is considered outdated, since it can damage surrounding tissues, causing a burn. Removing molluscum contagiosum involves the use of medications that enhance immunity and the removal of plaques.
For each case, the dermatologist chooses individual treatment, taking into account the location of the tumor and its size. Additionally, immunocorrective agents, restorative treatment and other methods can be used.
List of contagious skin diseases
The main pathologies that are contagious include diseases such as:
- Scabies. The cause is a microscopic mite that settles on the skin. During the daytime it is at rest, and closer to night it begins to become active. The female gnaws special holes in the skin and lays eggs there. Young individuals quickly reach reproductive age and continue to reproduce.
- Pediculosis. People call this pathology lice. Small insects are transmitted through things and through personal contact.
- Microscopy. It is formed by microscopic spores of dermatophytes that can maintain their viability for up to 10 years. They easily tolerate heat and severe frosts and die only under the influence of disinfection and boiling.
In our clinic, we can carry out all the necessary diagnostic measures; after making a diagnosis, a highly qualified doctor will prescribe effective treatment.
How to choose a drug for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections?
When choosing antibacterial therapy, the approach to drug selection is extremely important, which is determined by the level of soft tissue damage, the characteristics of the course of the disease, and the presence of drug resistance.
It should be remembered that any wound, regardless of its location and origin, always contains a certain number of microorganisms (primary microbial contamination). The main purpose of any primary dressing is to stop bleeding and prevent wound infection, regardless of whether it is applied at home, by emergency physicians, clinicians, or hospitals. Subsequently, treatment is carried out in accordance with the phase of the wound process and the species composition of microbes that have entered the wound.
What viral skin infections require treatment?
Viral diseases are provoked by a wide group of pathogens that can remain in the body in an inactive state for a long time. In this case, the symptoms of a skin disease do not appear until the onset of “favorable conditions” in the form of weakened immunity, hormonal disorders or exacerbation of a chronic disease.
The most common viral infections that affect the skin include:
- Herpes simplex -
the disease is also called “cold on the lips”. It is caused by the herpes virus type 1 and is manifested by intense itching, burning and swelling of the skin of the lips or perioral area. Bubbles filled with clear liquid form in the area of redness. - Genital herpes is
similar to a simple virus, but differs in localization. In this case, symptoms appear in the external genitalia and anal area. - Shingles is
a disease caused by the chickenpox virus and manifests itself as skin lesions along the nerve nodes. The pathology causes severe, excruciating pain, itching, burning, and blistering rashes. - Papillomas and condylomas -
these skin neoplasms are benign in nature and are formed as a result of infection of the patient with the human papillomavirus, which has more than a hundred species known today. Separate mention should be made of condylomas, which form on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and can transform into an oncological tumor.
Also worth mentioning are skin diseases such as rubella, erythema infectiosum, measles, roseola, etc. A distinctive feature of viruses of this group is their system-wide manifestations.