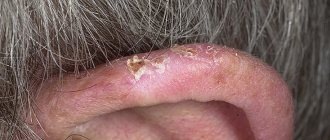
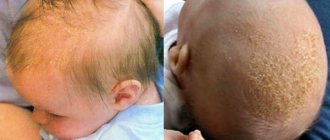
Usually, an adult is not in a big hurry to go to a medical facility if any health problems arise, especially if we are talking about rashes. As a rule, everything is attributed to poor ecology or severe fatigue, poor nutrition. If crusts, cracks or redness appear behind the ears, then the person tries to monitor hygiene more carefully. But cracks behind the auricle can appear against the background of serious pathological processes. Therefore, if a crack appears behind the ear, you should immediately contact a dermatologist, who will conduct the necessary tests and make a diagnosis, because there are many reasons for this condition.
Possible and fairly quickly eliminated causes
First of all, we should not forget about personal hygiene in any area of the body. It is necessary to clean not only the area behind the ears, but also regularly remove wax from the ear.
Another common cause is a lack of vitamins. The lack of vitamins and nutrients is especially acute in winter; the skin becomes dry and may crack over time. In light of this, it is necessary to adjust your diet and take vitamin and mineral complexes.
Dry skin is another cause of cracks behind the ears. The only problem in such cases is that the body lacks moisture. This may be due to an excessively dry climate in the place where a person lives or poor nutrition or insufficient water intake into the body. Depending on the suspected cause of dry skin, treatment is prescribed; you may only need to drink more water and moisturize the area around the ears.
For the same reason, or after suffering an infectious disease, the body’s immune forces may weaken, which often leads to problems with the skin.
Stress is also a fairly common cause. As you know, all problems are caused by nerves, and the skin is no exception.
Cracks behind the ear can appear due to hormonal imbalance, and most often this occurs during gestation. Although such failures can occur in people of any gender and age, for example, while taking certain medications.
Another cause is heat urticaria. Inflammation behind the ear occurs due to blockage of the sweat glands. In parallel with this, severe itching, redness appears, peeling begins and a crust appears behind the sink. Most likely, no special treatment will be required, you will simply have to learn how to properly use moisturizers and control the process of sweating.
However, the reasons can be much more serious and require immediate attention and qualified medical care.
Prognosis and prevention
Patients who comply with the treatment regimen quickly get rid of the problem. Medicines relieve inflammation, relieve itching, eliminate flaking, and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues. After treatment with appropriate medications, the skin behind the ear acquires a natural color and healthy appearance.
Dermatological disorders will not appear if you follow preventive measures:
- carry out hygiene procedures in a timely manner,
- eat rationally,
- consume sweets in limited quantities,
- do therapeutic exercises,
- do not be stressed.
Healthy skin has an intact surface layer, there are no cracks, keratinized particles, rashes, or crusts. If the epithelial tissues in the parotid zone are flaky, wet and itchy, these are alarming signals. If these negative signs appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Eczema
This pathology can appear at any age and in any person, on any part of the body. Contact dermatitis is just a type of eczema that appears upon contact with an allergen or a specific irritant. In this case, cracks behind the ear may occur after using shampoos, dyes or other cosmetics for skin and hair care. Blisters or rashes may appear first, and then cracks. This condition is characterized by a strong tooth and redness in the area of irritation.
Ointments for irritation in these types of dermatitis are prescribed, usually with an antihistamine effect and salicylic acid. The doctor may also recommend using shampoos and hair care products containing zinc pyrithione and selenium. In severe cases of dermatitis, antibacterial agents may be prescribed for oral administration.
Therapy
Treatment of the patient begins by determining the cause and type of disease. The treatment regimen includes the necessary medications and procedures.
If a man, woman or child has skin damage behind the ear caused by allergies, use the following algorithm:
- eliminate the irritant (jewelry, cosmetics, medicines),
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet,
- Antihistamines are prescribed: Fenistil, Loratadine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Zyrtec.
For eczema or dermatitis, treatment is carried out as follows:
- They use drugs that can relieve inflammation and itching: Sofradex, Otipax.
- They use ointments and creams to eliminate swelling, dry out, soften the skin, and regenerate cells: Radevit, Dexpanthenol, Fenistil-gel, Ichthyol and Zinc ointment.
- In severe forms, the lesions should be smeared with external agents containing corticosteroids: Hydrocortisone, Pimafucort, Afloderm, Elokom.
- If a secondary infection occurs, antibiotics are used: Erythromycin, Doxycycline, Ciprofloxacin.
Idiopathic form
There is also such a thing as weeping eczema behind the ears and on other parts of the body. Although this is not a scientific name at all, this rash is actually called idiopathic eczema. A characteristic feature of the disease is blisters that burst over time, and serous fluid appears in these places.
This type of rash is quite difficult to treat. In this case, the inflammatory process can end on its own, but with an obligatory aggravation in the near future. In fact, this pathology is a chronic disease, but not contagious. In the fight against the rash, the patient must have great patience; he will have to eliminate all irritating factors from his life, reconsider his diet, and never scratch the rash in order to prevent a secondary inflammatory process.
Dermatitis
Problems with the ears can occur due to the development of exudative dermatitis. Dermatitis itself can take two forms: chronic and acute. A rash with this pathology can appear on any part of the body. Clinical picture: ulcers, papules, pimples, plaques, etc. Patients suffer from severe itching, redness and rashes, peeling and exudative discharge.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor first determines the cause of dermatitis. The patient will have to give up all foods that can cause a rash, these usually include: citrus fruits, alcohol, especially sweet ones, chips, baked goods, etc. You will have to rely on foods that contain a huge amount of B vitamins, eat lean meat, dairy products, sardines and others.
For therapeutic purposes, the doctor will prescribe local remedies that have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect and will promote the regeneration of skin cells. To reduce the amount of toxins and allergens, enterosorbents and antihistamines are prescribed. If an allergic reaction is clearly identified, then glucocorticoids are prescribed. As additional therapy, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures: galvanization, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, radon baths and others.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Another inflammatory process on the skin, against which crusts initially appear behind the ears, on which scales (yellow or white) form over time. The provocateur of this type of rash is a fungal infection – Malassezia.
Seborrheic dermatitis often appears in people who are immunocompromised or have been diagnosed with HIV or Parkinson's disease. The disease can be classified as group A, that is, oily dermatitis, and group B, dry. It should be understood that it is completely impossible to cure this type of skin rash; you just need to constantly monitor the condition of the body to prevent relapse.
Causes
There are many factors that can cause peeling of the skin behind the ears. The main reasons include:
- allergic reactions,
- ignoring hygiene procedures,
- fungal infections,
- dermatological pathologies,
- scrofula and gneiss,
- eczema,
- dermatitis,
- purulent-inflammatory diseases (otitis).
The doctor carefully studies the features of the course and symptoms of the process. The signs and causes of inflammation are individual for each patient.
The appearance of weeping and flaky areas behind the ear is associated with the development of pathologies in the body. Foci of inflammation often appear against the background of infections, impaired digestion and imbalance of substances.
Scrofula, gneiss
With exudative diathesis, the skin in the parotid area peels and becomes wet in adults and children. Leads to scrofula:
Scrofula
What kind of disease is this? Many people really don’t know what this disease is, because it most often occurs in children. Although it can also appear in an adult. This is an infectious disease that can be caused by non-tuberculosis and tuberculosis bacteria. Most often, this condition occurs against the background of poor nutrition and metabolic disorders. Heredity plays an important role in this case, and there are also unfavorable living conditions.
What kind of disease is scrofula? It is a rather complex disease, and rashes can appear not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes, lymph nodes, joints, and bones. The main thing is to consult a doctor in time, especially if the causative agent of the disease is Koch’s bacillus, but this can only be determined after a series of examinations, and only after that can adequate treatment be prescribed.
Symptoms and causes
Ears often suffer from excessive hygiene, as cotton swabs and other cleaning items scratch the skin, which greatly increases the risk of developing infections. Insufficient care can also cause peeling.
Other causes of symptoms in adults and children include:
- skin diseases (dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis);
- otitis (damage to the outer ear);
- fungal diseases (mycoses);
- dehydration and lack of nutrients (due to lack of water, the skin behind the ear becomes thin and dry);
- purulent lesions due to mechanical damage to the hearing organ, pimple, boil;
- removal of toxins through the skin (diabetes, liver, kidney or bladder diseases).
If the surface is too dry, use a special moisturizer. Lack of vitamins causes peeling of the area behind the ear or inside. You can compensate for micronutrient deficiencies by taking a multivitamin complex.
Allergies and skin diseases
Allergies occur to personal care products, earrings, metal glasses, headphones or hair dye. If you do not interrupt contact with the irritant, the condition may be complicated by dermatitis or eczema. Often the disease occurs in newborns due to the fact that their immune system is not sufficiently developed.
A similar problem is characterized by the following reactions that appear on the earlobes, inside or in the area behind:
- redness;
- burning;
- itching.
Therapy in this case involves eliminating the allergen and using antihistamine medications - ointments, tablets, creams. The following drugs are popular:
- Suprastin;
- Loratadine;
- Lokoid;
- Advantan;
- Fenistil;
- Zyrtec.
Zyrtec oral drops have antipruritic properties and are suitable for infants.
Skin diseases can be of an allergic nature or occur due to mechanical irritation (reaction to dust); they can also form under the influence of inflammatory processes or be a consequence of a weakened human immune system.
Read also: What is snoring and how can you get rid of it?
Signs of dermatitis are:
- itching on the scalp, ears, or sink;
- redness of the skin on which a bubble of sulfur appears;
- after opening the formation, peeling is observed with the formation of weeping or dry crusts.
Anti-allergenic drugs help with this condition. Anti-inflammatory drops (Sofradex, Otipax) are also prescribed. Emollient creams can be used.
Otipax ear drops eliminate inflammation.
Eczema is a disease that, like dermatitis, is characterized by redness, itching and the subsequent appearance of rashes. The soft tissue becomes denser. In the area of the blisters, crusts form that peel off when combed, and the skin begins to crack. Sometimes eczema can be confused with a fungal infection. When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor, since pathology increases the likelihood of developing otitis, penetration of purulent infection, and inflammation.
For this disease, oil solutions against crusts, anti-inflammatory ointments that have antifungal and antibacterial effects, rinsing with Furacilin, corticosteroid-based creams, and antihistamines are used.
Inflammatory processes, purulent lesions
Otitis media occurs due to water getting into the ear canal, hypothermia, or mechanical damage. Manifestations of the inflammatory process are:
- itching in the very depths of the ear;
- congestion and hearing loss;
- feeling of a “traffic jam”.
If left untreated, the condition will be complicated by pain, purulent lesions, which can lead to dermatitis. For otitis media, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets and suspensions (Amoxiclav, Nitrofural) or anti-inflammatory and antibacterial ointments, gels, creams. In case of mild disease, a solution of boric acid is used. If drug treatment does not help, physical therapy may be prescribed.
The antibiotic is effective for otitis media.
If infection occurs, a pimple or boil will form. In this case, the hair follicle, subcutaneous cells or sebaceous glands become inflamed. Primary symptoms are:
- itching and redness in areas of inflammation;
- swelling and pain, aggravated by touching the affected skin, chewing, or pulling on the ear.
The boil is treated with surgery and drug therapy with antibiotics.
Fungal diseases
Fungi thrive in water, so their appearance is often caused by excessive hygiene. You can also become infected through other people's products, in contact with the ears, in dirty ponds, etc. The skin, colonized by pathogenic agents, itches and turns red.
Fungal infections are characterized by:
Read also: Adenoids in children: degrees of lymphoid tissue hypertrophy, symptoms, treatment
- headache;
- tinnitus;
- itching and peeling of the skin;
- sensation of a foreign body and the formation of sulfur plugs;
- discharge from the ears.
Treatment is carried out using antibiotics that are active against a specific microorganism. Therapy is carried out using ointments, creams, and symptomatic treatment is carried out using vegetable oil, alcohol solution, and petroleum jelly.
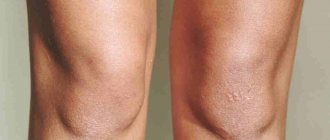
Psoriasis
This is an inflammatory dermatological pathology that does not select age and gender. Psoriasis often appears in the knees, elbows and head. The exact cause of this problem is still unknown. It is characterized by a very thick and red rash that becomes covered with scales and crusts. If the rash appears on the head, it often spreads to the ear area. All therapeutic measures in this case are aimed at stopping the further development of the skin rash. Most often, cortisone-containing ointments are used for treatment; herbal remedies may be prescribed and injection therapy may be performed.
Ear mycosis
Another reason that can lead to a crack behind the ear. This pathology is associated with the introduction of a fungal infection in the ear area. Mycosis does not always appear due to poor hygiene; it is possible that wax has accumulated in the ear canals, where it is impossible for the person to reach it. Sulfur and desquamated epithelium are an excellent environment for the development of fungal spores.
A crack behind the ear in an adult with a fungal infection can appear due to the use of someone else's headphones or earplugs, as well as other devices for the ears. The patient may be bothered by a headache, constant itching in the ear area, and noise. It may seem to a person that there is some kind of foreign object in the ear canal, or that a wax plug has appeared. In some cases, purulent discharge, clear or serous, may be observed from the ear.
Inflammation behind the ear is treated depending on the type of fungus that has affected the auricle. If we are talking about mold fungi, then Nitrofungin, Itraconazole, Naftifine or Terbinafine are prescribed. If the cause is yeast, then mycosis is treated with the following drugs: Clotrimazole, Econazole, Fluconazole or Pimafucin. In this case, the cleanliness of the ears comes first for the patient.
Otomycosis: when fungi grow in the ears
When mentioning fungal diseases in humans, most of us will probably only remember nail fungus or thrush. But it turns out that there are also mushrooms that grow in the ears and cause a lot of trouble to a person. The pathological process caused by fungi in the ears is called otomycosis.
What is fungal otitis and how does it happen?
Otomycosis is a disease of various parts of the ear, which is caused by certain types of mold and yeast-like fungi. Most often, the causative agent of the pathological process is fungi from the genus Aspergillus
and
Candida
.
Otomycosis is a kind of collective concept that indicates the fungal nature of ear pathology. The specific name of the disease depends on which part of the ear is affected: if the auricle and skin of the external auditory canal are involved in the pathological process, this is fungal external otitis; if the process spreads to the eardrum, they speak of fungal myringitis; if the tympanic cavity (middle ear) is affected, then it is fungal otitis media.
What causes otomycosis?
As a rule, those fungi that cause otomycosis are classified as opportunistic, i.e. they cause the disease only if there are predisposing factors. Factors that increase the risk of otomycosis include:
- injuries to the skin of the auricle and auditory tube (most often due to improper hygiene of the outer ear, the use of cotton swabs, as well as allergic diseases accompanied by itching and scratching), which increase the risk of the fungus penetrating the skin and opening the gates of infection;
- existing inflammatory diseases of the ear, since local immunity is significantly reduced;
- fungal infection of other localizations, for example, fungus of the nail plate, foot, thrush, etc. Most often, a fungal infection manifests itself against the background of decreased immunity and changes in the composition of the skin microflora. Disturbances occur throughout the body, so if a fungal infection appears in one place, there is a chance that it will manifest itself somewhere else;
- diabetes mellitus - sugar, the content of which in earwax increases significantly during this disease, is a good nutrient medium for fungi and promotes their growth;
- concomitant chronic diseases that lead to a decrease in the body’s overall resistance;
- taking antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics - long-term and irrational use of these drugs leads to changes in the normal composition of the skin microflora and the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, otomycosis affects the ear on only one side. Manifestations of the disease depend on which part of the ear is affected. The common feature is the gradual onset of the disease and the progression of symptoms as the mycelium of the fungus grows into the thickness of the skin.
For external otomycosis
The disease begins with swelling of the external auditory canal, gradually accompanied by itching, pain, and a feeling of ear congestion. Later, discharge from the external auditory canal appears. The nature of the discharge depends on the type of fungus: with candidiasis, it is a liquid, cheesy discharge, often white or yellowish in color; with aspergillosis, it is a thick discharge, ranging in color from green to gray-black.
Hormonal imbalance
If the level of certain hormones changes, problems with the skin may occur, including the area behind the ear. In particular, these are androgens, which are responsible for the production of sebum in the skin. If the hormone level decreases, the skin dries out, cracks, crusts and scabs appear. At risk are women during pregnancy and menopause; persons who use contraceptives, some other drugs. In such cases, hormone replacement therapy is most often used.
Childhood
A crack behind the ear in a child is a fairly common problem, but it requires the direct involvement of a doctor. This is primarily due to the fact that in babies the dermis is still quite loose, the connective fibers are poorly developed, and the veins are intensely filled with blood. It is clear that these factors are not enough for the development of inflammatory processes; damage occurs against the background of general changes in the body or under the influence of local causes. Most often, cracks appear due to diaper rash or fungal infection. But the cause of the appearance may be dermatitis, diathesis or eczema.
Parents should monitor the diet and gradually introduce new foods into it. The temperature regime is very important, that is, the room where the child sleeps should be warm, but not hot, and the air should not be dry. It is also recommended to carefully select washing powders so that they do not cause irritation to the skin.
Diagnostics
The doctor diagnoses the disease after a visual examination of the foci of inflammation and laboratory tests. The following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- In case of purulent-inflammatory processes, the patient's ear is examined using an otoscope.
- If the disease is allergic, the patient is prescribed blood tests. Tests allow you to identify the irritant that led to a negative reaction.
- In case of eczema, damage to the epithelium is carefully examined.
- Patients suffering from diabetes undergo hormone tests.
The doctor selects diagnostic methods, taking into account the specifics of the disease.
Folliculitis
Another skin condition that can cause cracking of the skin. This is an infectious pathology of the hair follicles, resulting in blisters, redness, irritation and cracks. Depending on the severity of the disease, antifungal or antibacterial agents may be prescribed.
An anti-irritation ointment called retinoic ointment is often used. Despite its high effectiveness, it often causes irritation. If within 2-3 days from the start of use severe redness of the skin, peeling and new pimples begin, then you will have to stop using the drug.