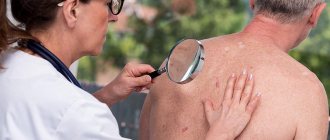
Severe itching of the toes is an uncomfortable sensation and requires identification of the causes. They can be different, from an individual reaction to a fungal disease. You should not ignore the symptoms, because the itching itself rarely goes away; it is eliminated in accordance with the cause of the problem. Constant skin irritation between the toes can develop into a serious illness, including eczema, which is not easy to get rid of. At the first sign of itching, consult a dermatologist and get the appropriate tests.
Medicines that may cause a reaction
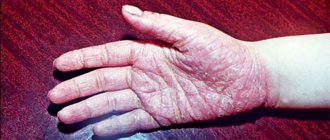
Hand-foot syndrome
The following medications may cause hand-foot syndrome.
- capecitabine (Xeloda®);
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin®)
- Fluorouracil (5-FU®)
- Liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil®)
- Cytarabine (Cytosar-U®)
Palmoplantar skin reaction
The following medications may cause hand-foot reaction.
- Sorafenib (Nexavar®)
- Sunitinib (Sutent®)
- Cabozantinib (Cometriq®)
- Regorafenib (Stivarga®)
- Axitinib (Inlyta®)
- Pazopanib (Votrient®)
- Vandetanib (Caprelsa®)
- Vemurafenib (Zelboraf®)
- Dabrafenib (Tafinlar®)
to come back to the beginning
Causes of allergic arthritis
The cause of allergic arthritis is the body's increased sensitivity to various environmental factors - allergens. Allergens can be various particles that enter the body - food, particles of skin or animal hair, fish scales, medications, infectious agents, etc. The disease can also develop in response to the introduction of a vaccine or serum.
The introduction of an allergen into the body causes sensitization - increased sensitivity of the body to a certain substance - antigen. In response to the introduction of this substance, the body produces antibodies that neutralize it. When this allergen enters the body again, antigen (allergen)-antibody complexes are formed, deposited on the walls of target organs and causing an inflammatory process. In case of allergic inflammation of the joints, the target organ is the internal synovial membrane lining its cavity.
Allergic arthritis in children in most cases is of an infectious-allergic nature. Its onset is associated with a bacterial or viral infection. Most often it is a streptococcal, staphylococcal, intestinal or chlamydial infection. The disease is acute, benign in nature and with proper treatment of arthritis ends in complete recovery.
In some cases, in the presence of a hereditary burden (close relatives suffering from allergic diseases), an allergy to the infection first develops, and then an allergy to the patient’s own tissues joins it. In arthritis, it is an allergy to intra-articular tissue. As a result, a long-term, recurrent autoimmune inflammatory process develops that destroys the affected joint - rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to children, persons suffering from diabetes mellitus, cancer, AIDS, sexually transmitted infections, other allergic diseases and chronic arthritis of various etiologies are prone to the development of infectious-inflammatory arthritis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hand-foot syndrome and hand-foot skin reaction may appear 3 to 6 weeks after starting chemotherapy. Depending on the medicine you are taking, any of the following symptoms may appear on your palms and soles of your feet:
- sharp tingling or burning-like pain, especially in the tips of the fingers and toes;
- dry, cracked, scaly or flaky skin;
- thickened skin that looks like a callus;
- mild or pronounced redness;
- edema;
- blisters;
Symptoms of palmoplantar skin reaction usually appear on parts of the body that are subject to a lot of pressure, such as the balls of the toes, between the toes, and the sides of the feet.
Symptoms of hand-foot syndrome and hand-foot skin reaction can range from mild discomfort to a painful sensation that can prevent you from doing normal activities. You may have difficulty grasping small objects such as a pen or fork. It may be difficult to fasten buttons on clothes. Some people have difficulty walking.
Symptoms usually go away when the dose of chemotherapy is reduced or when the course of treatment is completed. The skin begins to recover after a few weeks.
to come back to the beginning
Why do my toes itch?
Itching between the toes occurs for several reasons. They are divided into alarming and not causing any particular concern. The latter include:
- Thermal irritation. Hypothermia, like high temperatures, makes you want to scratch the affected areas of the skin.
- Allergies to foods, medications, household chemicals, cosmetics or water with added chlorine.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Feet should be washed with warm water every evening. You can make salt or soda baths.
- Stagnation of blood. In this case, the thumb may become red and a desire to scratch it may occur.
Internal factors that cause itching are more serious and more difficult to eliminate. These reasons are:
- Psychosomatic factors. Itching occurs due to constant stress.
- Infection with pathogenic microorganisms in public places (bathhouse, swimming pool).
- Scabies mite. During the warm season, this parasite often affects exposed legs.
- Diseases of internal organs. Since a large number of nerve endings are concentrated on the soles of the feet, itching in areas corresponding to specific organs may signal problems in their functioning.
- Fungus. With this disease, the skin of the fingers itches and the nail plate becomes deformed.
Skin peels off and itches
Peeling skin and burning between the toes indicate health problems . This condition is caused by the following factors:
- Peeling and itching often become symptoms of diabetes, heart problems, and malignant neoplasms.
- Individual reaction to external stimuli.
- Dust and sweat contribute to skin irritation.
- Lack of vitamins in the autumn-spring periods causes peeling and itching.
- Scabies, athlete's foot or eczema often appear on the toes.
- Mechanical or chemical damage to the epidermis can cause itching.
Thumb
Skin irritation on the big toe occurs for the same reasons as in other cases. If symptoms persist for more than 3 days, you can be sure of the fungal origin of the uncomfortable condition . There are several factors that influence the desire to constantly scratch your thumb:
- pregnancy;
- heredity;
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- phlebeurysm;
- pathologies of the kidneys, liver, bile ducts.
Article on the topic: Remantadine - instructions for use and reviews of the drug
Eliminating symptoms
Tell your healthcare provider as soon as you develop symptoms. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have diabetes, vascular disease, or peripheral neuropathy. These diseases cause destruction of the skin, prevent wound healing and can cause infection.
Follow the tips below to help you manage these symptoms.
It is forbidden:
- Pop blisters. Apply a petroleum-based ointment, such as Vaseline®, and cover it with a bandage (Band-Aid®).
- Immerse your hands and feet in hot water or a hot bath.
- Take hot baths.
- Wearing socks, tights or shoes that are too tight.
- Doing anything that requires rubbing your palms or soles, other than lightly applying lotion or cream.
Need to:
- Wear thick, soft cotton socks with all shoes. We also recommend using wicking foam insoles and shock-absorbing inserts to ease the pressure of shoes on your feet.
- Wear heavy cotton gloves when doing chores around the house or outside the home, such as cleaning the house, gardening, or grocery shopping.
- Keep your hands and feet well moisturized. To do this, soak them in cool water for 20 to 30 minutes, pat them dry with a towel, and then apply a fragrance-free moisturizer such as Eucerin®. This should be done at least once a day.
- Use unscented lotion or cream containing petroleum products, for example: Urea cream;
- Kerasal® One Step Exfoliating Foot Moisturizer Therapy™;
- Udderly Smooth®;
- if you are over 18 years of age, you can also use the tools below; do not use these if you are under 18 years of age: salicylic acid;
- moisturizer CeraVe® SA.
- steroids;
to come back to the beginning
Preventative techniques
To prevent a fungal infection or its recurrence, it is recommended to use preventative methods.
- Using quality shoes
. It should be made from genuine leather, suede, nubuck and other natural components. It is important to prevent your feet from sweating or developing calluses. - Use of antifungal ointments
. They can be used in a short course for the purpose of prevention. - Disinfecting shoes
. To do this, use a spray previously purchased at the store. It is not recommended to use someone else's shoes and socks. - If the patient visits the bathhouse
, after it it is necessary to thoroughly wipe the feet with a towel. The pores are open, and infection easily spreads into them. - Immunostimulation
. To do this, eat foods high in vitamins, trace elements and minerals. Hardening procedures are carried out. They take multivitamins and go for walks often.
Fungal infections are easy to treat at the initial stage, so you need to pay attention to peeling, itching, layering and changes in the color of the nails. If you use fungicidal drugs in time, recovery will come much faster.
When should you contact your healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following.
- temperature 100.4°F (38°C) or higher;
- chills;
- symptoms do not go away or get worse;
- any of the following symptoms appear on the skin of your palms or soles: skin that is hard, warm, or hot to the touch;
- bright yellow or green discharge;
- bleeding.
- unpleasant odor from the palms and feet;
- increasing redness or swelling;
- increasing pain or discomfort;
to come back to the beginning
What is allergic arthritis
Allergic arthritis is an inflammation of the joints caused by an allergy to various particles entering the body. This disease develops especially often in children. Minor disruptions in the process of formation of the immune system lead, as a rule, to the development of an acute inflammatory process, which is easily treatable and ends without any consequences.
If the disease is based on complicated heredity, then sometimes the disease can become chronic with slow destruction of the joints.
The most common clinical form of this disease is infectious-allergic arthritis, which today is more often called reactive arthritis. According to statistics in our country, among rheumatic diseases, infectious-allergic arthritis in children under 14 years of age is more than 50%.
The code for allergic arthritis according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) is M13.8.
Allergic diseases can also include rheumatoid arthritis, which is based on an allergy to the patient’s own tissues. The ICD code for seropositive rheumatoid arthritis is M05.8; seronegative – M06.0.
How allergic arthritis is treated at the Paramita clinic
Our specialists treat each patient with allergic arthritis very carefully. He is carefully examined to exclude other clinical forms of the disease and to establish the presence or absence of degenerative changes in the joint. Only after this is treatment prescribed, including:
- methods based on the achievements of modern medicine, developed in leading clinics around the world; the latest medications and non-drug treatment methods are used;
- traditional oriental techniques that came to us from China and Tibet; they have been successfully used for centuries to treat various types of allergies; These techniques are based on restoring the patient’s energy potential, which leads to stimulation of the patient’s vitality, normalization of the function of the immune system and elimination of foci of inflammation.
This approach to treating the disease allows us to completely eliminate the threat of chronic inflammation and joint destruction. But even in advanced stages of the disease, we can stop the progression of the disease. Contact us!
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Allergic arthritis is dangerous because it can be complicated by severe allergic reactions or give rise to the development of an autoimmune progressive disease with loss of ability to work. This is why timely treatment of allergic arthritis is so important. All this can be treated, specialists in Moscow are waiting for their patients!
Is it possible to get disability?
Allergic arthritis rarely leads to disability. The exception is rheumatoid arthritis, which is often a cause of disability.
Who should I contact with this disease?
See a rheumatologist. You will also need to consult an allergist.
What is the prognosis of the disease?
Favorable. Most patients make a complete recovery. If left untreated, the process sometimes becomes chronic, in which case joint dysfunction may occur. But even with rheumatoid arthritis, it is possible to stop the progression of the disease.
Bibliography:
- Alieva D.M., Akbarov S.V. Clinical variants of reactive arthritis in children. Scientific and practical rheumatology, 2001, No. 4, p. 74-79.
- Rheumatology. Clinical recommendations, ed. E.L. Nasonova, M., 2005, p. 86-90.
- JT, Petty RE Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology. Noronto, W. B. Saunders Company 2001; 819.
- Kingsly G., Sieper J. Third International Workshop on Reactive Arthritis: an overview. Ann Rheum Dis 1996; 55: 564-570.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 02/25/2021 Date of update: 04/03/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)
Diagnostics
In order to prescribe adequate treatment, it is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and, if possible, find out the cause of the allergy. For this purpose, the following studies are prescribed:
- Laboratory:
- general clinical
- a general blood test reveals signs of inflammation; - biochemical
– metabolic disorders and signs of inflammation are detected (high levels of C-reactive protein); - immunological
– detection of antibodies to certain allergens, including those of infectious origin; They also determine the presence of rheumatoid factor – autoantibodies to the body’s own tissues; - microbiological
– inoculation of biological media (blood, joint fluid) on nutrient media in order to detect infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics. - Instrumental studies of joints:
- Ultrasound
– reveals signs of inflammation; - radiography
- possible changes in bone structures; - arthroscopy
– performed according to indications; this is an examination of the inner surface of the joint with the possible collection of synovial fluid for examination; helps to distinguish an infectious process from a toxic-allergic one.
It is impossible to diagnose and properly treat allergic arthritis at home. This can only be done in a clinic equipped with modern equipment.
Recommendations for those who have been ill
Allergic and infectious-allergic arthritis usually ends in complete recovery. But there is always a risk of relapse upon repeated contact with the allergen that caused the disease. Therefore, it is recommended for a recovering person to:
- avoid contact with allergens;
- follow a hypoallergenic diet, excluding from the diet foods that have an allergenic effect: honey, nuts, chocolate, eggs, as well as sweets and baked goods;
- do therapeutic exercises, swimming and feasible sports, move more;
- eliminate heavy physical activity, monitor your weight, avoiding its excessive increase;
- promptly treat all acute diseases and sanitize foci of infection.
Prevention of allergic arthritis
This should be especially taken care of by persons suffering from allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma) or a tendency to develop allergic reactions (urticaria, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock). Prevention should include: a hypoallergenic diet, elimination of exposure to allergens and timely treatment of all acute and chronic diseases.