The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
Eczema on the legs is a chronic disease that has a neuro-allergic nature, manifests itself in rashes, itching, burning of the lower extremities, and is prone to frequent relapses.
Eczema is widespread, accounting for up to 40% of all dermatitis. The disease affects both women and men with equal frequency. Although some types of dermatological pathology, for example, varicose eczema, are more common in women.
Trophic venous eczema - what is it?
Trophic venous eczema is a pathological condition that occurs in the form of autoimmune dermatitis, that is, serous non-infectious inflammation of the skin (mostly the papillary layer of the dermis and epidermis), accompanied by symptoms of swelling, redness, itching and pain.
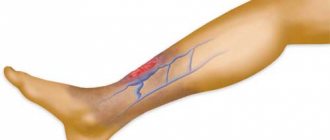
Trophic venous eczema
Venous eczema is a type and common form of eczema, which is caused by congestion in the skin due to impaired venous outflow. Venous eczema is also called varicose, congestive or gravitational. It most often has a chronic (recurrent) course. The pathology affects one or both lower extremities in combination with venous insufficiency. In the modern European, and most popular among leading experts, classification of chronic venous diseases - CEAP, this pathology is designated as C4a. This means quite severe tissue damage due to chronic venous edema.
Types of eczema on the legs
Depending on the etiology, several types of the disease are distinguished.
- True. It has symmetrical lesions, weeping and swelling of the skin.
- Microbial. Develops near wounds, burns, cracks and other damage. It is characterized by weeping, a large number of crusts, and peeling of the epidermis. Subtypes of microbial eczema are nummular, varicose, intertriginous, mycotic.
- Seborrheic. It occurs where there are most sebaceous glands. It appears as oily plaques, which are covered with yellowish crusts.
- Professional. It occurs upon contact with an irritant and quickly disappears if the provoking factor is eliminated.
In addition, when classifying the disease, doctors pay attention to the location of the rash.
- Inner thigh: coin-shaped formations that are difficult to treat.
- Lower leg: varicose eczema. Its complications are sclerotic formations.
- Inguinal folds: seborrheic as well as intertriginous eczema, which causes skin hyperemia, weeping, cracks, itching.
- Between the toes: as a rule, this is a dyshidrotic type of the disease.
Eczema of the feet manifests itself as compactions, which over time form calluses with painful borders. If you do not consult a doctor, the patient begins to have problems with walking. The greatest discomfort is caused by heel eczema, which makes movement very difficult.
The disease cannot be left without treatment. It not only dramatically reduces the quality of life, but can also cause secondary infection and serious complications, such as asthma and massive skin lesions.
If you have eczema on your feet or other parts of your legs, you should not use medications that you read about on the Internet or heard from friends. Therapy must be comprehensive, prescribed by an experienced doctor, and carried out under his constant supervision.
Why does trophic venous eczema occur?
Venous eczema is most often observed in middle-aged and elderly patients - according to leading European dermatologists, it affects up to 20% of patients over 70 years of age. This is due to the following reasons:
- Phlebeurysm.
- Previous deep vein thrombosis of the affected limb.
- The presence of venous trophic ulcers.
- Previous cellulitis on the affected limb.
- Chronic swelling of the lower leg, aggravated by hot weather and prolonged static position (standing).
The main cause of the pathology is varicose veins, which is why you can sometimes come across the term “Varicose eczema”.
Venous eczema of atypical localization
Quite often, signs of eczema can be found in young patients with a long history of varicose veins. There is no doctor, both in public and private clinics, who would not observe venous eczema in patients under 40 years of age.
Trophic venous eczema is very bad
Varicose eczema has a chronic, relapsing course and a tendency to progress. Quite often you can encounter a situation, especially in public hospitals, when only dermatologists treat venous eczema. Considering the main etiological component of the pathology, impaired venous outflow, treatment of such patients takes years.
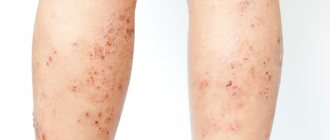
Chronic recurrent eczema on the right lower limb
The disease slowly recedes, but invariably appears again. Moreover, trophic changes in the lower extremities progress, lipodermatosclerosis occurs, and then an ulcer appears.
Features of the course of chronic eczema and differences from acute
We can talk about the process being chronic if the symptoms that first appeared did not go away within 2 months. Chronic eczema, unlike acute eczema, occurs in 2 stages, such as exacerbation and remission, which replace each other. Relapses usually occur in the cold season, but improvement can be noticed in the warm season. In addition to low temperature, exacerbation can be triggered by:
- increased sweating;
- contact with allergens, such as pollen;
- stress and anxiety;
- weakened immunity;
- taking certain medications;
- consumption of allergenic foods.
In the chronic stage of eczema, there is always a rash and itching. Moreover, itching usually precedes the appearance of rashes and can be used to determine that an exacerbation will soon occur. With chronic eczema, there are more dry crusts on the skin than weeping rashes, which is why this form of the disease is sometimes called dry. The crusts crack and itch very much, causing discomfort and even insomnia.
With exacerbation, the signs of chronic eczema intensify. New weeping rashes appear next to the dry crusts, but less exudate comes out of them than in the acute form. Other characteristic symptoms include:
- severe peeling of the skin;
- violation of skin pigmentation, development of pigment spots;
- pronounced linear pattern on the skin;
- excessive compaction and hardening of the rash;
- scratches and cracks in areas of thickening.
Chronic eczema in remission is manifested by constant peeling of the lesions. The skin in these places scars, so it becomes dense, and can acquire a blue-red tint in dark-skinned people and pale pink or beige in light-skinned people.
Why does trophic venous eczema almost always appear on the lower extremities?
The answer to this question lies in the pathogenesis of varicose veins, the dominant cause of venous eczema. Varicose veins affect exclusively the lower extremities, where, according to the gravity gradient, it is in their distal parts that trophic disorders occur. One of which is venous eczema.
Trophic eczema of the lower extremities
Pathological eczematous changes in the skin of the lower extremities are most often caused by varicose veins, since they are the cause of impaired venous outflow (up to 90% according to leading experts in the region).
Trophic venous eczema - diagnosis
Diagnosis of venous eczema in public and private urban medical institutions often begins in a dermatologist’s office, where a specialist evaluates local changes in the skin. It is very important here that the patient is referred to a good phlebologist in a timely manner. If eczematous changes are associated with venous pathology, then treatment of skin manifestations only is likely to be ineffective. Even a visual examination by a phlebologist using all kinds of functional tests often does not reveal the true cause of the pathology. At this stage, the best solution would be a good ultrasound examination of the veins of the lower extremities.
Ultrasound diagnosis of trophic venous eczema
Only competent modern diagnostics of the venous system will help determine the correct treatment tactics.
Trophic eczema, treatment in Moscow
Good treatment of venous eczema in Moscow can be divided into local (topical effect on skin inflammation) and treatment of the venous system. In the first, a dermatologist is often actively involved. Local treatment includes:
- Ointments and creams, steroid drugs, both as part of the latter and as part of systemic treatment.
- The use of antibiotics and antiseptics when an infection occurs.
Often, in the conditions of public medicine, patient care ends at the stage of the above topical treatment. This is not the best solution, since the disease is based on completely different reasons and a relapse of the disease will not take long to occur. Namely, venous stasis, which requires a slightly different approach. It is very important that a patient in Moscow has a timely appointment and diagnosis with a good phlebologist who can determine the correct tactics for managing the patient. The treatment of venous eczema is based on eliminating stasis and improving venous blood flow. Correction of the latter most often involves removing pathologically altered varicose veins. The presence of innovative technologies in modern Moscow centers makes it possible to effectively treat even complicated forms of varicose veins, moreover, on an outpatient basis.
Treatment of trophic eczema in our phlebology center
Leading medical centers in Moscow for the treatment of venous pathology use thermoobliteration techniques for these purposes. In a good city medical phlebology center you can count on safe, effective treatment. Modern vein removal procedures are performed under local anesthesia through skin punctures with minimal surgical trauma.
Bibliography
- Aizikovich, JI.A. Abstracts of scientific works of the VIII All-Russian Congress of Dermatovenerologists / JI.A. Aizikovich, T.V. Sokolova. 4.1. // Dermatology. - 2001.- P.180.
- Glukhenky, B.T. Immune-dependent dermatoses: eczema, atopic dermatitis, true pemphigus, pemphigoids / B.T. Glukhenky, S.A. Grando. Kyiv: Health, 1990 - 435 p.
- Drynov, G.I. Therapy of allergic diseases / G.I. Drinov. M., 2004. - 398 p.
- Ignatiev, D.V. Local corticosteroids in the practice of a dermatologist. Features of hydrocortisone butyrate (Lokoida) / D.V. Ignatiev, N.G. Kochergin // Consilium medicum. 2007. - T.9, No. 1. -Cl 3-16.
- Kalyuzhnaya, L.D. Modern external therapy for dry senile skin / L.D. Kalyuzhnaya // Veresen (cosmetology). 2005. - No. 3. -WITH. 3335.
- Skin and venereal diseases: a reference book / ed. O.J.I. Ivanova. -M.: Medicine, 1997. P. 315-320.
- Korotky, N.G. Modern external therapy of dermatoses (with elements of physiotherapy) / N.G. Korotky, AB Taganov, AA Tikhomirov; edited by N.G. Short. M., 2001. - P. 194-204.
- Kokhan, M.M. The effectiveness of the combined use of external therapy and skin moisturizing in patients with atopic dermatitis / M.M. Kokhan // Vestn. dermatology and venereology. 2007. - No. 4. -WITH. 55-60.
- Kosheleva, N.V. The effectiveness of complex treatment of patients with eczema using various methods of ozone therapy / N.V. Koshe-leva, A.G. Kulikova // Question. balneology, physiotherapy and exercise therapy. -2001.-No.5.-S. 30-32.
- Wuthrich, B. Definition and diagnosis of instrinsic versus extrinsic atopic dermatitis / B. Wuthrich // Bieber Tal. DYM Atopic dermatitis. Marcel: Dekkerlnc, 2002. - P. 1-20.
Trophic varicose eczema - treatment without surgery
The main factor in the development of congestive eczema is the pathology of the venous system. Therefore, there is no need to talk about any effective treatment without radical intervention. The best solution would be to stop the inflammation and carry out a procedure to remove varicose veins. But is surgery really that scary?
Trophic eczema - laser treatment in our center
Modern European technologies for vein removal are not inferior to advanced manipulations in dentistry in terms of minimal surgical trauma and possible side effects. But today it would not even occur to anyone to refuse caries treatment due to fear of intervention.
Folk remedies
Treatment of eczema is more successful if modern medications are combined with traditional recipes. Not all traditional advice is helpful, and some may be harmful, so you should consult your doctor before following it. And of course, one cannot rely only on folk wisdom, because this can lead to chronicity, further spread of the disease and resistance to therapy.
Celandine
This plant has long been known for its healing properties, which are explained by its complex chemical composition. Celandine alkaloids act as an antiseptic, inhibit cell division (the cytostatic effect explains the effect of celandine in removing warts), and when taken orally, they stimulate peristalsis and salivation; they act on the brain like morphine and can lead to convulsions. A large amount of vitamin C, flavonoids, carotene regulate regeneration, fight oxidation, and promote collagen formation. These properties make celandine useful for eczema, but of course, only externally. Celandine should not be taken internally, it is a strong poison!
Recipe: 10 gr. dry herbs pour 100 ml of boiling water to obtain a concentrated infusion. The warm infusion is used in the form of baths, immersing the affected areas for 15 minutes once a day.
Fish fat
This folk remedy has found application in official dermatology and is actively recommended by doctors. Its effectiveness is explained by the high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D. This useful dietary supplement inhibits the formation of inflammatory mediators responsible for eczema symptoms. Clinical studies have shown its effect. You can meet the body's needs by eating fatty fish (salmon, herring, mackerel, anchovies), or taking fish oil capsules from the pharmacy daily. There are practically no contraindications, however, if fish is chosen as the source, you need to pay attention that some types of fish cannot be eaten more than once a month due to their high mercury content (for example, mackerel).
Dandelion
Recent research confirms folk observations that dandelion juice is an excellent remedy for dyshidrotic eczema on the hands and feet. The juice of this plant regulates liver function and helps cleanse the body. Take it one tablespoon three times a day before meals, mixing with honey to reduce bitterness.
Oil infusions of dandelion herbs and flowers are good to apply to damaged areas to reduce itching and retain moisture on the skin.
Sometimes it is recommended to simply eat five or six dandelion stalks a day. We must remember that this herb from the Asteraceae family is a common source of contact allergies, and before applying the infusion or oil topically, you need to try how the body reacts by applying it to a small area.
Trophic venous eczema - laser treatment (EVLO, EVLT), radiofrequency treatment (RFA, RFO)
Considering that radical treatment of varicose eczema is the treatment of venous pathology, it is modern methods of removing varicose veins that will be the main way to combat eczema itself. Today, the undisputed leaders at the forefront of innovative treatment of varicose veins are thermal obliteration techniques, laser and radiofrequency. If we compare both technologies, there are simply no fundamental differences for the patient.
Treatment of trophic eczema with radiofrequency
What are the advantages of thermoobliteration technologies:
- Radicality and effectiveness (when used by experienced specialists, the result is practically 100%).
- Low invasiveness, the procedure is carried out through skin punctures.
- Highest cosmetic value.
- Full outpatient, no need for anesthesia or hospitalization.
- Safety and comfort of the procedure for the patient.
The result of laser treatment of trophic eczema after 1 month
After endovascular treatment, the symptoms of eczema quickly resolve on their own.
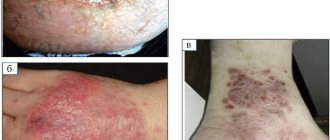
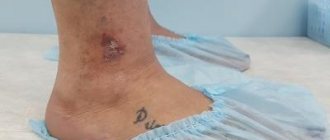
Results of treatment of trophic venous eczema. Photos before and after treatment
The result of treatment of trophic eczema using endovenous laser coagulation (EVLC) using German Biolitec technology in our center
Photos before and after treatment of trophic eczema on the left lower limb
The result of treatment of trophic venous eczema using radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in our patient
Photos before and after treatment of trophic venous eczema on the left lower limb
Frequently asked questions from patients on the Internet about trophic venous eczema
How to treat venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
For good treatment of venous eczema of the lower extremities in Moscow, you need to contact a competent specialist, a phlebologist. The doctor will conduct a detailed diagnosis, including an ultrasound examination. Only after this can we talk about modern treatment. The best solution would be to find a good city phlebological center, where the ultrasound will be performed by the phlebologist himself.
What is the modern treatment for venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
In Moscow, good modern treatment of venous eczema that meets European standards includes innovative technologies for both diagnosis and treatment. Leading city phlebological centers, including our Moscow Innovative Phlebological Center, successfully treat venous eczema. First, a detailed duplex angioscanning of the venous system of the lower extremities is performed. Only then is treatment prescribed, including the fight against local inflammation and modern treatment of the true cause of eczema, varicose veins.
How to treat venous eczema with folk remedies?
Specialists of the Moscow City Phlebological Center have good experience in working with various trophic disorders in venous diseases, including venous eczema. Leading phlebologists at our center do not recommend treating venous eczema with folk remedies. The disease responds well to treatment using modern technologies, but we often encountered serious complications after treatment with folk remedies.
My mother has venous eczema on her legs, which doctor is best to see?
If you suspect that your mother has venous eczema, it is better to first contact a good phlebologist, a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of venous pathology. First you need to understand the cause of inflammation in the lower extremities. You may need the help of a dermatologist. If eczema is of venous origin, then now there are modern European technologies with the help of which curing your mother will not present any special problems.
Questions and answers
Are there differences in the causes of eczema on the hands and eczema on the feet?
The appearance of foci of inflammation on the extremities is in most cases associated with traumatic factors or exposure to aggressive chemicals. The formation of vesicles or weeping on the body is often the result of allergic reactions and systemic pathologies identified in patients.
What are the main clinical recommendations for diagnosed eczema?
A patient with a confirmed diagnosis of eczema should discuss with a dermatologist the advisability of consultations with other doctors: endocrinologist, allergist, gastroenterologist. Their use can reduce the frequency of exacerbations of the disease and reduce the intensity of reactions to factors that provoke the inflammatory process.
Do patients with chronic eczema need to take any medications regularly?
Drug and hardware treatment along with courses of physiotherapy are prescribed during periods of exacerbations. After relief of acute symptoms of the disease, the patient does not need to systematically take medications. A significant role during this period is played by the child or adult’s compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician and preventive measures.