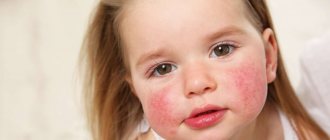
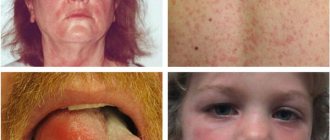
What are allergies in children
Allergy is the body's hypersensitivity to any foreign substance (antigen) followed by an immune response. According to scientific data, this feature itself is not inherited, but the predisposition to it is. Children whose parents have allergies (especially if both of them or just the mother are allergic) may be more likely to develop it.
When we come into contact with an allergen, the body reacts in such a way as to block the access of “dangerous” substances, according to its data, into the blood. This is expressed in inflammatory phenomena that occur due to the release of immunoglobulin E and histamine, a hormone that regulates various functions of the body.
Histamine causes swelling of tissues, stagnation of blood in capillaries, a decrease in pressure, makes the heart beat faster - all these changes should help the body quickly deliver as many leukocytes - protective blood cells - to those areas where their presence is needed.
Excessive sensitivity of the body to a particular allergen leads to the release of excessive amounts of histamine, which is why doctors prescribe antihistamines for allergies.
It is believed that in Russia from 15 to 35% of people suffer from allergies.
What are the symptoms of allergies in children? Common manifestations of this condition include the following:
- runny nose;
- sneezing;
- cough;
- itching;
- watery eyes or dry eyes;
- labored breathing;
- chills;
- rash or redness of the skin, eczema;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes;
- Digestive problems - with food allergies.
In the case of acute allergies, life-threatening anaphylactic shock can develop, when pulmonary edema occurs, breathing is impaired and blood pressure decreases.
What else do parents need to know?
One in five people suffers from allergies at some point in their lives. Hay fever is the most common type of allergy. It is easily treated by avoiding allergens, washing the child in the shower after returning from outside during flowering season, over-the-counter medications, and sometimes additional prescription medications. Most children with hay fever only need allergy medication during seasonal outbreaks.
Allergy symptoms often change with age. Allergy symptoms can worsen during early childhood and often disappear as people get older.
Drug labels list the ingredients of allergy medications. Use the lowest dose possible to treat symptoms, and check with your child's doctor if he is younger than 6 years old before giving him an over-the-counter antihistamine.
What types of allergies are there?
The list of main allergens includes:
- dust - it contains several allergens at once, from plant pollen and dust mites to epithelial scales of pets;
- pollen - allergies can also develop to pollen from domestic plants;
- pet hair and particles of their skin, as well as down and feathers;
- fungal or mold spores;
- Food. Food allergies in children are common. It is very important to take care of its prevention during the mother’s pregnancy;
- Insect bites - usually from wasps, hornets, bees, bumblebees and ants. This allergy occurs in 0.4–0.8% of the population. These and other insects produce a variety of poisons that can cause reactions ranging from hives or swelling to seizures, diarrhea, suffocation and shock. If an allergic reaction occurs, it is important to get to the hospital very quickly or give the child the necessary medications within the first hour, which should be discussed with a pediatrician in advance;
- some medications. It is usually difficult to check in advance which medications cause an allergic reaction. In addition, an allergy to a specific drug can appear at any time in life, even if a person has not previously had one;
- latex - this allergy can manifest itself in very different ways and, as a rule, develops in people who are forced to frequently wear latex gloves, for example, doctors.
Other risk factors include smoking, using a gas stove, dry pet food, household chemicals and industrial pollution. It is believed that a child living in an area where the air is polluted due to proximity to the road can cause allergies.
Symptoms of allergic reactions
- Skin rashes or irritations. Manifest in the form of redness, itching, spots, peeling. Rashes from food or contact allergies often resemble insect bites or nettle stings.
- Difficulty breathing. A runny nose, coughing, and sneezing are the most common allergic reactions to dust, pollen, and animal dander. Allergens cause irritation of the nasal or bronchial mucosa.
- Conjunctivitis. Redness, itching, and watery eyes often occur upon contact with household chemicals, cosmetics, pollen, dust, and wool.
- Difficulty in digestion. Abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting - a reaction to food allergens.
- Anaphylactic shock. The most dangerous manifestation of allergies. Shock can be caused by insect bites, medications, and certain foods (for example, nuts). An allergy sufferer's skin turns red, breathing becomes difficult and the heart rate increases. Loss of consciousness and convulsions are possible. You must call an ambulance immediately!
Symptoms similar to allergies can hide various diseases, so professional diagnosis is indispensable. The presence of allergies is confirmed by skin tests or blood tests. Do not delay your visit to the doctor in order to prescribe a course of treatment as soon as possible and avoid complications.
Course of allergy
- Allergies in children can develop instantly - for example, in the case of an ant bite - or over several months, as happens when it is caused by cat fur or pollen. It all depends on how often the child comes into contact with the allergen.
- Seasonal allergies occur every year in the spring, summer and fall, and mold allergies can develop if there is prolonged rain outside and humidity levels in the home have increased, leading to the growth of microorganisms.
- It is important to understand that allergies in children can come and go, and there is no exact explanation for this.
Cross-reactions with other foods
Children with allergies to the following foods may react to other foods:
Cow's milk allergy: 90% also react to goat's milk and 40% to soy milk.
Egg: in 5% there is a reaction to chicken meat
Peanuts: In 5% of cases there is a reaction to other legumes (such as peas or beans). In 30% there is hypersensitivity to tree nuts.
Fish: in 10% a reaction to seafood is also observed.
Melon: 90% reacts to bananas and avocados
Ragweed pollen allergies can cause a cross-reaction with all melons, bananas and tomatoes.
Birch pollen allergies can cross-react with raw potatoes, carrots, celery and apples.
Grass pollen allergies may cross-react with tomatoes and kiwis.
How to distinguish a cold from an allergy in a child
A cold goes away within 10 days at the latest, but allergies appear constantly.
Here are the obvious signs of an allergy:
- the child constantly sniffles, especially if the nasal discharge is clear and liquid, and not yellow or green and thick;
- the baby constantly sneezes, his eyes are red, wet and itchy;
- the child has dark circles under his eyes, his nose is constantly stuffy, and he breathes through his mouth;
- dry cough;
- the skin is inflamed, red and itchy.
How to recognize a food allergy and not confuse it with other diseases?
Most often, in order to diagnose a food allergy, a doctor only needs an examination and a detailed interview with the mother. Mom can point out that she herself has a food allergy or point the doctor to a specific food. Sometimes it is difficult to make such a diagnosis right away. Then the doctor may order an examination. First, a general blood test. And then, if necessary, specific allergy tests: examination for immunoglobulins, and at a later age, provocative tests. It is these tests that were chosen as the most informative in the latest clinical recommendations. In addition, your baby may need to consult an allergist, dermatologist or gastroenterologist, depending on the symptoms that are bothering him. And also, additional examination from the gastrointestinal tract.
Allergy prevention
It has been proven that hypersensitivity to a particular allergen can occur in a baby when he is still in the mother’s belly, in the second trimester of pregnancy. This means that even before its birth, the expectant mother must take precautions.
Precautionary measures:
- if she is allergic to a particular substance, she must avoid contact with it during pregnancy;
- you need to stop smoking, take medications not approved by a doctor, carefully ensure that there is no contact with allergens at work - these may include platinum salts, formaldehyde, nickel or chromium compounds, pigments, pesticides, epoxy and other phenol-formaldehyde resins, organic compounds, which include chlorine, fluorine and phosphorus;
- unbalanced diet, the presence of allergenic foods in the diet, products with chemical additives. It is best to formulate a preventive diet that does not contain potential allergens;
- minimize the number of stressful situations.
After the birth of the child you must:
1. Try to establish breastfeeding (we write about how important this is for immunity in a separate article;
2. Follow a diet (which foods can be included in it and which cannot, we tell you here;
3. Temper the baby, monitor his health, give him a strengthening massage and do gymnastics with him;
4. If the child’s parents had bronchial asthma or atopic dermatitis, as well as other allergic reactions, the baby should be examined by an allergist: the sooner the problem is identified, the more effective the treatment will be.
However, it is important to understand that the best way to treat and prevent allergies is to eliminate the factors that trigger them.
If a child is allergic to dust and feathers, in addition to treatment, hygiene rules must be followed:
- mattresses and pillows must be in special plastic covers;
- special bedding should be used;
- if the laundry is ordinary, it needs to be washed and boiled 1 – 2 times a week;
- it is important to choose pillows and blankets with synthetic filling;
- the apartment should have a minimum of upholstered furniture;
- Carpets or rugs with a strong odor should not be used;
- clean using special vacuum cleaners and carry out wet cleaning.
If your baby is sensitive to mold and mildew, you need to:
- wipe surfaces in the bathroom dry after bathing;
- wash the bathroom with special solutions once a month;
- remove steam in the kitchen using a hood;
- dry clothes in a special room, not in the room.
If your child is allergic to wool, you should:
- exclude clothing made from wool and fur;
- do not go to the zoo, circus or houses where there are animals;
- If a cat or dog previously lived in your apartment, the room must be thoroughly cleaned.
If you need to protect your baby from pollen:
- when plants bloom, windows should be closed;
- do not walk in windy weather;
- You need to be careful with soaps and shampoos containing herbal preparations.
It is also important to avoid:
- stress;
- hypothermia or overheating of the baby;
- too high humidity;
- intense physical activity;
- infectious diseases - they provoke an exacerbation of allergies.
Is it necessary to go to the doctor right away? What examinations can he order?
Considering that the first months of life are critical in the formation of a child’s allergic immune reactions, of course you should consult a pediatrician as soon as possible. You may need to consult an allergist-immunologist, dermatologist, or gastroenterologist. If the doctor suspects a food allergy, a diagnostic elimination diet will initially be prescribed for 2–4 weeks and a food diary will be kept. If a food allergy is confirmed to a specific product, the duration of the elimination diet is determined individually and should be at least 6–12 months.
For a child with food allergies who is bottle-fed, the correct prescription of the medicinal formula is especially important. The doctor has information about the types, composition, indications for therapeutic nutrition (highly hydrolyzed mixture, amino acid mixture). After the symptoms of food allergy have been relieved, the question of the time and rules for the diagnostic administration of a causally significant product is within the competence of a pediatrician, allergist-immunologist.
It is possible that additional laboratory and instrumental research methods will be required to identify the entire spectrum of causally significant allergens. The feasibility and necessity of which will also be determined and explained by a specialist.
A pressing question for parents of a baby with food allergies is which complementary foods can be introduced. Current scientific evidence indicates that strict elimination diets in infancy have no benefits for the child. At the same time, the role of complementary feeding products is still being researched and caution should be exercised when introducing allergenic complementary feeding products to a child with a history of allergic reactions or primary manifestations of food allergies. It is correct to determine the time, type, dose, and schedule of administration of the supplementation product by a doctor with subsequent monitoring of the child’s condition.
For children with clinical manifestations of food allergies, modern industrial complementary feeding products recommended as first choice can be recommended:
- Vegetable puree (zucchini, cauliflower, broccoli)
- Grain complementary foods (dairy-free rice, corn, buckwheat porridge)
- Rabbit and turkey puree
- Fruit puree (apple, pear, plum)
Causes
A child develops a food allergy due to:
- genetic predisposition;
- decreased protective functions of the intestinal mucosa;
- large amounts of food consumed, etc.
In circumstances where tolerance fails, the immune system produces an Ig E antibody response against the specific food. The process begins in the intestines (although it can also affect other areas, such as the respiratory system or skin).
When a patient consumes a “dangerous” product, the antigen associated with Ig E is detected on the surface of basophils and mast cells. At this time, they are activated, and histamine and other inflammatory substances are released.
These products have a number of important qualities
- meet the functional requirements for nutrients, vitamins and minerals;
- made from natural, environmentally friendly raw materials, without the use of GMOs, without dyes, without flavors, without preservatives, without thickeners, without sugar;
- are monocomponent;
- their consistency and homogeneity corresponds to the physiological characteristics of the child’s age;
- have low immunogenicity.
Knowledge of the causes of the development of allergic reactions and the first symptoms of food allergies allows parents to promptly consult a doctor for advice and receive modern scientifically based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of food allergies, and the development of a diet that meets the current needs of the child.
Caring for a child with allergies
Cool air is preferable for allergy sufferers. Children with skin lesions, allergic rhinitis, and asthma live easier at a temperature of 18-22 °C and a humidity of at least 50%.
Children with allergies need to be bathed daily. In this case, the water temperature should be 32-36 °C, and the duration of swimming should not be more than 10 minutes.
With atopic dermatitis, children's skin needs intensive hydration after bathing. For this purpose, special creams and ointments are used. Without sufficient hydration, the skin quickly becomes dry and easily injured.
In children with allergies, it is important to regularly determine the level of vitamin D in the blood. A sufficient content of this substance in the body reduces skin permeability and serves as a barrier to the penetration of allergens.
Vaccinations are not contraindicated for allergy sufferers, but they should be carried out during remission.
Online consultation with a pediatrician
consultation cost: 500 rubles
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
The most common allergens
Products that most often cause food allergies:
- eggs;
- nuts (hazelnuts, almonds, peanuts, etc.);
- fish;
- citrus fruits (oranges, tangerines, etc.);
- berries (strawberries, wild strawberries, etc.);
- chocolate;
- milk;
- legumes (soybeans, beans, peas, etc.).
- nutritional supplements.
Allergens found in some foods may be similar to pollen allergens. This is called cross allergy. For example, wormwood pollen is a cross-allergen for peppers, carrots, mustard, bananas, and citrus fruits. This means that a patient with hay fever may also have food allergies.