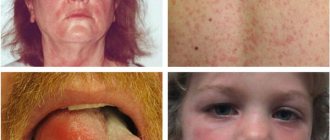
Food allergic reaction
Today, the following types of allergies are distinguished, which are accompanied by various clinical signs on the body.
A food allergy in the body is an immunologically mediated (type I/III) reaction to allergens that enter the body through food.
The most common triggers are cow's milk, fish, nuts, chicken eggs, cocoa, and food coloring added to sweets.
Symptoms of food allergies vary, but most often include rashes, red spots, hives, and itching of the skin (face and body).
In most cases, food allergies are accompanied by the development of urticaria (urticaria).
Urticaria (urticaria) is a skin disease, the main feature of which is itching and the development of rashes on the surface of the skin.
Triggers for aggressive skin reactions can be varied.
All people are susceptible to developing allergic urticaria, regardless of race or age.
In most cases, acute spontaneous urticaria is observed, which occurs completely suddenly and disappears after a few days.
Antihistamines and intestinal sorbents will help speed up the healing process.
If allergy symptoms on the body last longer than six weeks, we should talk about chronic urticaria.
Urticaria can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- It appears in the form of bright pink spots, up to 2 cm in diameter, sometimes more. The spots do not have a clear shape and can merge into larger lesions.
- The localization of spots can change, migrating from one area of the skin to another. Also, allergies can spread throughout the body, both in adults and children.
- It appears suddenly, a few minutes or an hour after contact with the allergen, and can also disappear suddenly.
If we are talking about chronic urticaria, then the skin manifestations of the reaction are complemented by a deterioration in general health, fever, and signs of asthma.
Quite rarely, sudden and painful swelling of the deeper layers of the skin (lower dermis and subcutaneous layer), called angioedema, may occur.
This allergy can cause swelling and itching of the entire body.
Allergy to cosmetic ingredients
Allergies to cosmetics are usually associated with a delayed type IV reaction.
Symptoms include redness, itching, peeling, burning sensation on the skin, and blisters.
Clinical signs usually appear within 24-72 hours.
But there are times when an allergy, for example, to a body scrub or cream, appears after an hour or two.
Typically, an allergic reaction is limited to the area of skin that has been in direct contact with the allergen.
In principle, any cosmetic ingredient can cause allergies or intolerances.
The most common triggers include various herbal additives, preservatives, lanolin, and emulsifiers.
Whether a certain preservative or other additive can cause an allergy depends on various factors.
First of all, it depends on the individual characteristics of the person and on the quality of the products produced.
It should also be taken into account that the manifestation of allergies is partly genetic.
Frequent contact with water and the use of aggressive cleaning agents can also contribute to the development of an allergic reaction.
When using chemicals, allergies often manifest themselves as pimples on the body.
It is a myth that natural cosmetics do not cause allergies.
Many cosmetics, such as natural cosmetics, use plant extracts.
They contain irritating and/or sensitizing substances.
So incompatibility and allergy reactions are also possible here.
Causes
Patients with allergies always have a hereditary predisposition to its occurrence. Among relatives there will definitely be allergy sufferers, and their allergies can manifest themselves in different ways: skin, food, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma - the form does not matter.
To develop the clinical picture, exposure to a sensitizing substance—an allergen—is necessary. They can be dust, pollen, chemicals in detergents, clothing, hazardous industries, some food products, medicines, etc., as well as substances formed in the body itself under the influence of cold or sunlight, metabolic products of parasites.
Cold allergy
Cold urticaria is a rare disease that occurs in approximately 2-3% of cases.
The reaction is caused by cooling of the skin or mucous membranes upon contact with air, water, cold objects or frozen foods.
Cold urticaria appears quickly.
Accompanied by progressive itching, erythema (redness) and swelling of the skin after contact with cooled substances.
Sometimes, the first symptom is a burning sensation of the skin.
Clinical signs occur mainly in areas that have been exposed to cold.
But sometimes they can spread throughout the body.
Symptoms usually go away on their own after a few hours or a few days.
Allergy to cold with typical symptoms on the body manifests itself during exposure to the following factors:
- Low air temperature, cold wind, rain.
- Staying in cool water or walking barefoot on a cold floor.
- Drinking cold drinks and food.
The diagnosis of cold urticaria is made based on the results of the anamnesis and diagnostics.
To confirm the reaction, a test is carried out using an ice cube.
The test is performed by placing ice wrapped in a plastic bag on the forearm for 5-20 minutes.
The test is considered positive when symptoms develop within 15 minutes after the start or end of testing.
It's worth noting that about 20% of people with cold urticaria have a negative ice cube test.
Rashes on the hands: the most common diseases
In order to choose the right treatment, it is important to distinguish one type of allergic dermatosis from another. Therefore, let’s look at the symptoms of skin diseases in more detail:
- With atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis), a rash often appears on the skin of the fingers and hands. The acute period of the disease is characterized by severe itching, redness and swelling of the skin. Itchy spots can come in different shapes and sizes. Without proper treatment, crusts may form at the site of the rash. In the chronic form, symptoms such as dry skin and flaking are observed.[3]
- Urticaria is divided into several types: immunological, physical, drug and idiopathic. The development of the first two is based on the body’s reaction to external stimuli, including food and household allergens, as well as high or low temperatures, sunlight and other factors. Taking certain medications can trigger drug-induced urticaria. Idiopathic is a rash whose cause cannot be determined.[4] All types of hives present more or less the same way: redness, swelling of the skin and the appearance of itchy blisters.
- Contact dermatitis often affects the skin on the fingers, especially when coming into contact with harmful substances such as rubber and metal products, household chemicals, cosmetics and perfumes, topical medications, certain plants and insects.[5] The disease can occur in both acute and chronic forms. The acute course is characterized by redness of the skin and the appearance of itchy blisters. The chronic form is accompanied by dryness and flaking of the skin, increased skin pattern.
- Eczema is an acute and chronic inflammatory disease that affects both the upper and lower extremities. It may also affect various parts of the body. As a rule, eczema rashes are symmetrical, accompanied by redness and limited swelling of the skin. Small blisters filled with clear liquid often appear on affected surfaces.[6]
Drug allergy
Signs of allergies on the body can range from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
The most common pharmacological substance that causes allergies is penicillin.
Other triggers that may cause reactions (that are not related to IgE antibodies) include the following:
- Sulfate preparations
- Anticonvulsants
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Some types of food coloring (usually red and yellow)
- Chemotherapy drugs
Clinical signs of allergic reactions may be accompanied by mild itching of the skin, redness, and rash.
When identifying allergies to certain medications, it is important not to confuse them with side effects.
They may be accompanied by hives, rashes, and stomach upset.
Particular attention should be paid to cases where drug allergies on the body develop in pregnant women.
It is necessary to stop signs of the reaction as soon as possible.
Allergists often make a diagnosis based only on medical history and associated symptoms.
This is what in practice is called a “clinical diagnosis”.
In many cases, patients may have an allergic reaction when taking multiple medications at the same time.
In these cases, if the doctor cannot identify the true allergen, a comprehensive examination is additionally prescribed.
During the diagnostic process, your doctor will recommend stopping all medications.
Diagnosis of the disease
First of all, the doctor conducts an anamnesis and examination. In a conversation with the patient, the doctor will clarify the time of appearance of the first rashes, the reasons preceding their occurrence, how long it takes for the blisters to resolve, what else worries the patient, what concomitant pathologies are present, which countries the person has visited recently, whether there have been any insect bites.
During the examination, in addition to the type and location of the rash, the doctor will be interested in the condition of the lymph nodes, the presence or absence of swelling in the joint area, and whether the liver and spleen are enlarged.
To identify the allergen, blood tests (general, biochemical), skin or injection allergy tests are prescribed. Source: Clinical and laboratory features of the course of urticaria. Prokofieva N. B. Dermatovenereology. Cosmetology. Sexopathology, 2011. p. 30-35.
If there is a suspicion that urticaria is caused by physical factors, provocative tests are performed. These are mechanical irritation of the skin, physical activity, hot bath, ice cube test, water compress, photo testing, weight hanging test.
Allergy to pets
Animal allergies are the third most common allergy after pollen and house dust intolerance.
Characteristic symptoms are sneezing, runny nose and itching.
In the worst case, allergic asthma may develop.
A pet allergy is an intolerance to certain substances found in your pet's saliva, dander, sebum, urine and feces.
In this case, the animal’s fur is not responsible for the manifestation of an allergic reaction.
Therefore, a person can also be allergic to birds.
Triggers of the immunopathological process can be a variety of animals.
Both small ones - cats, dogs, guinea pigs, and large ones - horses, cattle, etc.
Upon contact with an allergen, various reactions may occur on the part of the epidermis - allergic or contact dermatitis.
For example, if you are allergic to a cat, contact rashes may occur on your body after touching the animal.
Direct contact with a pet may cause the following signs and symptoms:
- red spots on the skin (urticaria);
- eczema (inflammation of the upper layers of the dermis);
- itchy skin and small rashes.
Almost always, skin reactions are accompanied by sneezing, itching in the nasal cavity, redness of the mucous membranes of the eyes, and nasal congestion.
Cat and dog allergens are present in epithelial cells.
The main source of cat allergens are the anal glands; In dogs, the trigger is saliva.
Allergy to alcoholic beverages
True alcohol allergy, in which the body produces an IgE antibody in response to alcohol, is very rare.
Alcohol intolerance is more common.
The symptoms of a true alcohol allergy are similar to the symptoms of an immunopathological process that occurs in relation to food (food allergy).
An allergy to alcohol can cause red spots on the body (hives), rashes, itching, tingling in the mouth, swelling of the lips, tongue, and difficulty breathing.
An allergy to alcohol poses a particular danger to humans.
For some patients, drinking 10 ml of ethanol results in anaphylactic shock.
Although true allergies to ethanol are rare, alcoholic beverages can contain a number of different ingredients that can cause allergy or intolerance symptoms.
These can be various herbal additives, dyes, etc.
Alcohol allergy should be differentiated from intolerance.
It is accompanied by headache, nasal congestion, rapid heartbeat, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, abdominal pain, and a small rash on the body (usually on the face).
Those with an alcohol allergy must not only abstain from all alcoholic beverages.
But you should also be aware of other foods that may contain alcohol and avoid them.
For example, liquor in candy can be extremely dangerous for a person with a similarly sensitive immune system.
Sun allergy
Itching, redness, nodules or blisters on the body a few hours after exposure to the sun - an allergy or a manifestation of polymorphic photodermatosis.
The most common form of sun allergy is polymorphic photodermatosis.
More than 20% of the world's population suffers from this problem.
More often, women and children are susceptible to allergies (even more often, people with fair skin types).
The exact causes of sun allergies on the body are not clear.
It is only known that UV is a trigger and is considered as a trigger.
Another theory is that sunlight creates aggressive oxygen compounds (free radicals) in the skin, which cause sun allergies.
They can damage epithelial cells and increase the risk of developing skin cancer.
These same radicals can activate the immune system and lead to symptoms of polymorphic photodermatosis.
However, this assumption has not yet been scientifically proven.
Classic allergy on the body in adults and children is manifested by the following clinical picture and symptoms of solar allergy:
- The skin begins to itch and a burning sensation appears.
- The skin changes color and the formation of red spots (redness of the skin) is observed.
- Blisters, nodules, and papular formations appear. The skin may swell during severe inflammation.
In most cases, sun allergy symptoms occur when the skin is not exposed to sunlight for a long time.
Therefore, in spring, as well as during the beach season, sun allergies are most common.
How is the rash treated at Altimed MC?
The first step in treating allergic rashes is to identify the substance that causes the rash. The team at Altimed MC uses diagnostic equipment: functional screening and autonomic resonance testing.
Once your doctor diagnoses the cause all over the body in an adult or child, he or she will help develop prevention strategies to limit exposure to the substance and provide immunotherapy to desensitize your immune system to the allergen.
In addition, our doctors prescribe topical treatments and other options such as PEMF cell-tissue therapy, antifungal and others. A specialist will tell you in more detail.
If you are concerned about allergies throughout your body , call Altimed MC or make an appointment in Kiev by calling 0-800-600-0-80 (free).
The treatment process involves the selection of suitable drugs that will strengthen the immune system, which will make the body less susceptible to external irritants. The equipment used is guaranteed to determine the cause of an allergic reaction - the main task that must be performed.
Dangerous symptoms of an allergic reaction on the body
The most dangerous symptoms and complications of an allergic reaction are Quincke's edema and Lyell's syndrome.
Quincke's edema is a skin reaction characterized by rapid swelling of the skin involving the mucous membrane.
Edema is often accompanied by swelling of the tongue and larynx, which can be life-threatening.
Quincke's edema got its name thanks to the doctor who first described this clinical sign in 1882.
In allergology, the symptom is found under the medical term angioedema or angioedema.
Doctors distinguish two forms of angioedema:
- Histamine-mediated angioedema. This form includes allergic angioedema and drug-induced angioedema.
- Angioedema due to hereditary C1 inhibitor deficiency (HAE). The C1 inhibitor is a protein in the blood that aims to protect the body from angioedema. In addition, there is also angioedema due to acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency (AAE).
In most cases, angioedema is a symptom of a severe allergic reaction.
Requires immediate medical attention.
Allergic angioedema can be treated with anti-inflammatory drugs.
For example, a doctor may give intravenous cortisone, epinephrine, antihistamines (anti-allergy medications), sodium thiosulfate, and calcium gluconate to quickly relieve symptoms.
As a result of swelling of the tongue, eyelids, lips and larynx, various complications can occur.
The root of a swollen tongue, expanding, narrows the airways, which threatens asphyxia.
Lyell's syndrome is the most severe form of allergic dermatitis and is also known as toxic epidermal necrolysis.
They are characterized by the appearance of blisters, followed by their opening and the formation of erosive lesions of the skin epithelium. More than 30% of the body surface area may be affected.
As a rule, it is a consequence of exposure to certain groups of medications, most often antibiotics and NSAIDs.
If such a symptom develops, patients should be hospitalized in the intensive care unit or burn department.
The mortality rate for Leila syndrome reaches 20-25%, sometimes reaching 50%.
Treatment of an allergic reaction on the body
Most cases of allergic reactions can be successfully treated with antihistamines.
Antihistamines are the first choice for mild to moderate symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Drugs are prescribed if the patient has the following symptoms:
- Allergic rhinitis (runny nose), hay fever, lacrimation, redness of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
- Hives, which is accompanied by itching and the formation of bright spots on the skin.
- Angioedema (swelling of the dermis and/or swelling of the mucous membrane).
- Drug allergies that appear within an hour.
- With severe itching, a sign of eczema, dermatitis and other inflammatory skin reactions.
Antihistamines can be used locally (nasal spray, eye drops, ointments) and orally in tablet form.
Separately, antihistamines for intravenous administration, as well as hormonal creams and ointments, can be prescribed.
Dermatologists usually recommend using antihistamines in tablet form.
Because they are more effective than topical creams or cooling gels.
As a rule, one dose of the drug is enough to relieve signs of allergies on the body in the form of urticaria or dermatitis.
However, in the case of tablets (and other systemic forms of administration, such as injections or infusions), side effects such as fatigue and drowsiness cannot be ruled out.
Nowadays they more often resort to the use of non-selective second generation antihistamines.
They are better tolerated and have a smaller range of adverse reactions.
Glucocorticoid hormones from the adrenal cortex (cortisone) may also be prescribed.
Medicines containing cortisone are primarily prescribed and used when antihistamines do not satisfactorily relieve the symptoms of an allergic reaction.
For example, with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and bronchi.
Therapeutic effectiveness from cortisol medications is usually observed within 24-48 hours.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies conducted by specialists have proven the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products, including for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients.
Many remedies are recommended by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Sources:
- Reken Martin, Schaller Martin, Sattler Elke, Burgdorf Walter, Atlas of Dermatology, MEDpress-inform, 2022.
- Andropova T.V., Gudina M.V., Odintsova I.N., Hygiene of children and adolescents, Siberian State Medical University Publishing House, 2022.
- Cohen Bernard A. Pediatric dermatology, MEDpress-inform, 2015.
Photos of allergies in children
Photo album on the disease