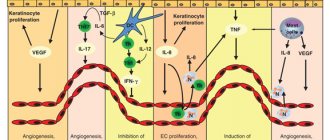
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-infectious skin disease that affects the skin, nails and joints. There are several theories of the origin of the disease - viral, psychoneurogenic, autoimmune, hereditary, etc., but none of them is generally accepted. Scientists have come to the conclusion that psoriasis has a multifactorial nature.
According to some data, more than 3% of the world's population suffer from psoriasis on the face and body, and the disease can appear for the first time at almost any age.
Until now, the disease was considered incurable, but techniques have emerged that will not only bring noticeable relief to the patient, but also ensure stable remission of psoriasis. Treatment is based on the use of innovative technologies.
Psoriasis is successfully treated in our clinic. Treatment of this and other dermatological diseases (vitiligo, atopic dermatitis, eczema) is carried out using the latest high-tech equipment. We know how to significantly reduce the manifestations of psoriasis and achieve stable remission even in the most difficult cases.
In addition, treatment with the Excilite µ excimer system allows the patient to stop taking steroid (hormonal) drugs.
1 Excilite µ system
2 Excilite µ system
3 Excilite µ system
Psoriasis: clinical picture and symptoms
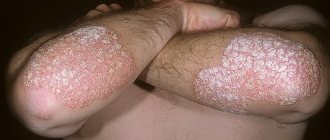
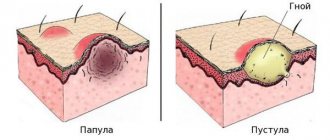
The classic manifestation of psoriasis on the face and body is the presence of a rash in the form of papules and plaques covered with silvery-white scales.
Scraping papules leads to the following manifestations:
- the phenomenon of “stearin stain” - with slight scraping, peeling intensifies, the surface of the papules becomes similar to a crushed drop of stearin (hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis);
- the phenomenon of “terminal film” - after removing the scales, a wet, thin, shiny film appears: this is the mucous layer of the epidermis exposed;
- “blood dew ” phenomenon - scraping the film leads to the appearance of pinpoint droplets of blood (injury to the plethoric papillae of the dermis as a result of papillomatosis).
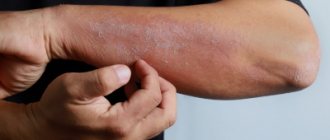
The disease is also characterized by an isomorphic reaction: rashes appear on areas of the skin that have been subjected to mechanical or chemical stress (scratching, cuts, exposure to acids, alkalis, etc.).
The most typical places for the formation of psoriatic rashes are the scalp, elbows, and knees (the so-called “duty” or “sentinel” plaques). Psoriasis often occurs on the face, psoriasis of the nails, and joints, genitals, skin folds, feet (plantar psoriasis), palms and other areas can also be affected.
There are two forms of the disease: winter (characterized by exacerbations in the autumn-winter period) and summer (a rarer form, relapses occur in the summer).
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is one of the pressing problems of dermatovenereology, given the widespread prevalence of dermatosis in people of working age, the constant increase in incidence, chronic relapsing course, the lack of effective methods of therapy, and the study of development mechanisms.
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is a chronic recurrent skin disease associated with increased secretion of sebum, changes in its qualitative composition and characterized by localization in areas of accumulation of sebaceous glands - on the scalp, face, upper body, folds.
The cause of diabetes is unclear. The development of diabetes is facilitated by the activation of the lipophilic yeast fungus Malassezia spp., increased secretion of sebum and changes in its qualitative composition against the background of psycho-emotional overstrain, stressful situations, hormonal, immune and neuroendocrine disorders, and the use of certain medications. There is evidence indicating the appearance of rashes that mimic seborrheic dermatitis with a deficiency of zinc and nicotinic acid, vitamin D.
Factors contributing to the development of Seborrheic Dermatitis include:
- heredity,
- immune and endocrine factors,
- infectious agents,
- HIV infection and other immunodeficiencies (every third HIV-infected person has seborrheic dermatitis; among AIDS patients, four out of five suffer from it, and their dermatitis is very severe).
- damage to the nervous system, stress,
- diseases of the digestive tract,
- medications,
- environmental influence, etc.
The prevalence of seborrheic dermatitis in the world is 70% among children in the first 3 months of life and 3-5% among adults. Although dandruff as a form of diabetes is observed much more often - in 15-20% of the population.
CLINICAL PICTURE
Rashes with seborrheic dermatitis are located on the skin of the scalp, face, ears, upper body, mainly in the area of the sternum and shoulder blades, and in large folds. In adults, one of the earliest signs of the disease on the scalp may be dandruff, later redness appears and flaking increases. Subsequently, clearly demarcated plaques form, often merging and occupying a large area, spreading to the skin of the forehead. Sometimes serous-purulent crusts may be observed, after removal of which a weeping surface is revealed. Modern knowledge about the nature of dandruff suggests that it is a mild form of diabetes and can transform into dermatitis under three conditions:
- increased sensitivity of the skin to the formation of inflammatory reactions to the action of oleic acid (a waste product of Malassezia spp.) as a result of an innate tendency;
- the presence of sebum as a nutrient medium for fungi;
- the presence of Malassezia globosa in the microflora of the scalp.
On the face, rashes are localized in the area of the cheekbones, wings of the nose, forehead, nasolabial folds, glabella, eyebrows and are usually combined with damage to the scalp. The rashes are represented by round or ring-shaped foci of erythema; infiltration, peeling and crusting are possible. The skin in the affected area acquires a grayish-white or yellowish-red tint, and the follicular openings are clearly visible. Blepharitis may develop with the appearance of crusts along the edge of the eyelid and the accumulation of masses of horny cells around the eyelashes. On the trunk and extremities, the rashes are represented by oval, round or irregular yellowish-pink spots, plaques with peeling and clear boundaries; there may be small nodular elements in the center. Erythema, swelling, weeping, painful cracks, and scaly crusts often occur in the folds of the skin. Secondary infection and spread of secondary pyoderma beyond the initial lesions of the skin are possible. Seborrheic dermatitis in infants appears at 1-2 weeks of life, sometimes at the end of 1 month, and under the influence of rational therapy resolves no later than 3 months of life. In children, the skin process is localized in the scalp, forehead, postauricular areas, in skin folds and is represented by erythema, plaques, greasy scales and crusts; hair loss is not observed. Redness and peeling spread to the trunk and limbs, and on apparently healthy skin, screenings of maculopapular scaly elements appear along the periphery of the main lesions. On the scalp there is hyperemia, infiltration, and accumulation of dense, fatty crusty scales. Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are bothered by itching of varying intensity. Seborrheic dermatitis must be differentiated from psoriasis, dermatophytosis of the scalp, face, trunk, allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, plaque parapsoriasis, rosacea; It is also necessary to exclude demodicosis.
TREATMENT
The choice of treatment tactics for diabetes depends on the severity of clinical manifestations, duration of the disease, and information about the effectiveness of previously administered therapy. The disease requires regular treatment using systemic and topical therapy over a long period of time. For external treatment, agents are used that have anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antifungal, and in case of secondary infection, antibacterial and antiseptic effects. In the acute stage of the process, with severe itching and sleep disturbances, it is advisable to use antihistamines and sedatives.
Drug therapy is selected by the doctor and may include the following drugs: External treatment 1. Topical glucocorticosteroid drugs 2. Possible use of zinc pyrithione or topical calcineurin inhibitors 3. Anti-inflammatory drugs for topical use 4. 1–2% alcohol solutions of aniline dyes (brilliant green, fucorcin) 5. Topical antifungal drugs 6. When a secondary infection occurs, ointments or, if indicated, aerosols containing antibacterial drugs are used. Systemic treatment 1. In case of severe itching - antihistamines 2. In the presence of exudation, the use of calcium gluconate intramuscularly is recommended
Non-drug therapy Laser treatment from 3-4 procedures every 10 days.
HOME CARE for seborrheic dermatitis of the face should include: • Gentle, gentle cleansing • Intense moisturizing + soothing effect • exfoliation • anti-inflammatory cosmetics • Protection from UV irradiation For seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, you must choose: • medicated shampoo with exfoliating and antifungal properties • means of additional more thorough cleansing: peeling mask for the scalp • soft basic shampoo for constant use, and for alternation with medicinal shampoo • if necessary, moisturizing care for the scalp: mask, emulsion, cream
A prerequisite for treatment is DIET. The diet should pursue several goals: normalization of digestion, removal of waste and toxins from the body, exclusion of allergenic foods, saturation with nutrients, vitamins and minerals, as well as strengthening the immune system. A diet for seborrheic dermatitis must be followed for a long time, even after the signs of the disease have disappeared. What foods should be excluded from the diet? Since seborrheic dermatitis causes increased sebum production, it is necessary first of all to eliminate products that enhance this process. These products include all food with: • preservatives, • dyes, • flavor enhancers, • spices, herbs, • anything spicy, • pickled foods, • salty dishes. The same list should include confectionery, sweets, semi-finished products and, of course, fast food, all kinds of snacks (chips, crackers, snacks, etc.). You will have to give up fatty foods and alcohol. Such products can not only affect the production of sebum by the glands, but also negatively affect the digestion process and “clog” the body, so avoiding them will help solve several problems at once. Foods that are considered potential allergens should also be limited in the diet, or better yet completely removed from the diet. These include: • citrus fruits, • strawberries, • honey, • chocolate, • cocoa, • nuts, • caviar, • mushrooms, • coffee. You should limit, especially for obese people, carbohydrate foods (pasta, fresh bread, baked goods, baked goods, sugar).
What can you eat if you have seborrheic dermatitis? Many people think that everything tasty (although not healthy) will have to be removed from the diet, and the menu will become monotonous, but in reality this is not the case. If you wish, you can eat not only healthy, but also tasty. Fermented milk products must be included in the diet of people suffering from skin diseases. They will help improve digestion and enrich the body with nutrients and microelements. It is recommended to choose products with a reduced fat content, enriched with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, and without sweet additives, dyes or preservatives. Typically, such products do not have a very long shelf life. Vegetables, herbs, fruits are an irreplaceable source of vitamins, microelements, fiber and other substances necessary for every person. Vitamins help improve regenerative processes in tissues and strengthen the immune system, which is very important for seborrheic dermatitis. A sufficient amount of vegetables in the diet also has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the digestive system. To normalize metabolic processes, as well as as a “building material” for the body, protein is needed, and more than half of the proteins coming from food must be of animal origin. It is recommended to eat lean meat, fish, and eggs (no more than 1-2 per day). We should not forget about seafood (provided that you are not allergic to them), such as squid, shrimp, mussels, oysters, and seaweed. These products contain a large number of microelements, including zinc, which is necessary to normalize the functioning of the skin glands. To improve digestion processes, it is useful to introduce bran, grains, and cereals into the diet, oatmeal and buckwheat are especially useful. Also, we should not forget about vegetable oils containing polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamins A and E, which have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin. You shouldn’t overuse them because of their high fat content, but 1-2 tablespoons of olive, flaxseed or grape oil added to a vegetable salad will only bring benefits. People suffering from seborrheic dermatitis should pay special attention not only to the volume of fluid they drink, but also to its quality. Every day you should consume at least 1.5–2 liters of liquid, the bulk of this volume should be water; It is recommended to drink purified, unboiled water; you can add lemon juice to it. Also useful are freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices, which should be diluted with water, green tea, compotes, and rosehip decoction. You should avoid fried foods (fried foods can be replaced by baked ones in the oven, and it is better to bake foods in foil or a special bag for preparing dietary dishes; this way you can cook meat, fish, vegetables) Another preferred culinary method is steaming food: foods retain the greatest amount of vitamins, and no harmful substances are released during cooking.
Drug treatment prescribed by a doctor and following a diet for seborrheic dermatitis will help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of this disease as soon as possible.
Types of psoriasis
Depending on the nature and localization of the process, several types of psoriasis are distinguished:
- Seborrheic psoriasis is a lesion of the scalp and adjacent areas (forehead, skin behind the ears). Scalp psoriasis is a form that occurs in 80% of patients with psoriasis. Patients with scalp psoriasis often urgently need the help of a psychotherapist.
- Exudative psoriasis is the formation of yellowish lamellar scales on the surface of the papules, when removed from the surface of the papules a weeping, bleeding surface is exposed.
- Intertriginous psoriasis is a lesion of large folds, characteristic of children and the elderly (often patients with diabetes). Peeling is not typical for this form; the lesions are sharply defined, have a smooth surface of a rich red color, often moist.
- Plantar and palmar psoriasis is a thickening, roughening of the upper layer of skin (hyperkeratosis), which leads to the appearance of callous-like seals that are reddish in color and often covered with cracks. Outwardly it may resemble mycosis, eczema, or secondary syphilis.
- Inveterate psoriasis is the formation of large, long-lasting plaques, which are often localized on the lower back, thighs, buttocks and can be characterized by papillomatous growths. One of the varieties of this form of psoriasis is rupoid psoriasis ( formation of multilayered crusts of a conical, rupoid shape).
- Guttate psoriasis is the formation of abundant papules throughout the skin against the background of acute infectious diseases (with this form of the disease, Streptococcus pyogenes is sown from the pharynx and skin folds).
- Psoriasis of the nail plates (nail psoriasis, psoriatic onychia). Psoriasis of the nails on the hands is more common. There are the “thimble” symptom, the “sand waves” symptom, the “bird’s claw” symptom, the “oil stain” symptom (a brown spot under the nail) and other types of deformation of the nail plates.
- Psoriasis of the mucous membranes - damage to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity (cheeks, lips, tongue), the formation of flat grayish papules on them, with clear boundaries and a pink peripheral rim.
The most severe forms of psoriasis are psoriatic erythroderma, pustular and arthropathic psoriasis.
- Psoriatic erythroderma is an acute process in which the skin becomes like one giant infiltrated plaque with a characteristic silvery-white peeling. The patient’s general well-being worsens (fever, swollen lymph nodes, joint pain). With the allergotoxic form of psoriatic erythroderma, signs of general intoxication also appear (headache, swelling of the skin, itching, skin tightness, as well as hair loss and pain in the limbs when moving).
- Pustular psoriasis is the formation of small superficial pustules against a background of bright erythema. The process is accompanied by pain and burning. The lesions quickly grow so that psoriatic plaques are no longer distinguishable, and the superficial layers of the epidermis peel off in the form of the so-called. "purulent lakes" Against this background, erythroderma may develop.
- Arthropathic psoriasis - in addition to typical skin rashes, joints (usually small ones) are affected. Characterized by pain, swelling, limited mobility of the joints, and subsequently their dislocations, ankylosis, and deformation. This form often leads to disability of the patient.
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis
The first signs of the disease are small papules with small scales, which over time turn into plaques. During development, slight flaking and itching occurs, which constantly intensify. As a result of scratching, wounds, abrasions, and cracks appear that become inflamed, the skin becomes rough, and papules turn into plaques. Further development of the pathology occurs according to the following scenario:
- The formation of dandruff due to exfoliation of epithelial cells.
- The appearance of whitish flakes as a result of thickening of the scales.
- Red plaques, the skin is easily injured, which leads to microcracks and wounds. At this stage, the development of psoriasis can stop in 80-90% of patients (seborrheic psoriasis).
- Grayish scales over the entire surface, right up to the hairline (pustular psoriasis).
- In the absence of any intervention during the course of the disease, psoriasis may extend beyond the hairline (guttate psoriasis).
The nature of the disease is a disruption of the growth cycle of cells in the upper layer of the epidermis, which begin to divide twice as fast, which leads to layering and the above symptoms.
Psoriasis. Treatment
Such a varied clinical picture of the disease makes diagnosis difficult - it is necessary to differentiate psoriasis from a significant number of diseases (for example, lichen planus, syphilis, seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis , rheumatoid arthritis , etc.).
Remember that the slightest peeling or redness of the skin cannot be ignored - these may be symptoms of psoriasis and other dermatological diseases that will progress without treatment. Experienced dermatologists at our clinic will conduct the necessary research and make the correct diagnosis.
Treatment of psoriasis is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and includes a whole range of therapeutic measures. Today there are many methods and drugs for the treatment of poriasis. When prescribing therapy, it is important to take into account the prevalence of skin lesions, the form and stage of the disease, the characteristics of the process, the presence of concomitant diseases, etc.
The comprehensive treatment program for psoriasis includes general and local therapy, the prescription of antihistamines, physiotherapeutic methods, etc.
Local drug therapy (using products containing sulfur, naphthalan, tar and other components) is aimed at reducing inflammation and peeling of the skin.
In the progressive stage, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed, the use of which has a number of restrictions and should be prescribed exclusively by a specialist. Thus, the use of strong glucocorticosteroids is associated with a high risk of withdrawal syndrome, which is expressed in a sharp exacerbation of the process. Self-medication with such drugs can lead to atrophy, swelling of the skin, etc.
1 Excilite µ system
2 Excilite µ system
3 Excilite µ system
We know how to treat psoriasis! The MedicCity clinic uses the latest Excilite excimer laser system. Unique equipment makes it possible to achieve stable remission of the disease and a significant reduction in the manifestations of psoriasis.
It is very important to start treating psoriasis as early as possible! You can check prices for a course of procedures with the clinic administrator or by phone!
1 Excilite µ system
2 Excilite µ system
3 Excilite µ system
Treatment of psoriasis using the Excilite system is based on exposure of the affected area to monochromatic radiation with a wavelength of 308 nm. There is a targeted phototherapeutic effect on pathological cells. The effectiveness of treatment is 90%! Positive results are noticeable after just a few procedures. Rapid healing of inflammatory foci and removal of plaques occurs. Moreover, the procedures are painless, comfortable, and have no side effects.
1 Excilite µ system
2 Excilite µ system
3 Excilite µ system
In the treatment of psoriasis, it is also important to follow a special diet, special skin care (the use of moisturizing, skin-softening creams, etc.), spa treatment, the use of vitamin therapy, etc.
In addition, it is necessary to correct concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, hormonal sphere, etc.
The material was prepared with the participation of a specialist:
Psoriasis cream
Creams and ointments for psoriasis have different purposes and are used at different stages of the disease. Hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments and creams are used to stop inflammatory processes in the skin. There are several classes of hormonal drugs. They have different absorption abilities and different activities. When used in children, they try to avoid applying hormonal drugs to the face and neck area, the area of skin folds - places where the skin is thinner. Local preparations based on calcipotriol (a derivative of vitamin D) also have an anti-inflammatory effect. This is a later generation of drugs. Currently they are not used during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Salicylic ointment and salicylic acid-based lotion are designed to remove skin flakes with severe peeling. Salicylic acid not only has an exfoliating effect, but also increases the effectiveness of topical hormonal medications. In the stationary and regressing stage, when inflammation has become less active, salicylic acid-based products are used in higher concentrations.
Products for restoring skin structure and eliminating dryness are used throughout the entire treatment period, and also in conjunction with ultraviolet irradiation to reduce skin itching. After the exacerbation has stopped, these products help maintain the protective properties of the skin and reduce the risk of new rashes.