Fisenko Karina Olegovna
Specialty: Adult gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist Work experience: more than 25 years Cost of appointment: 1600 rubles Cost of online appointment: 1200 rubles
Make an appointment
- Clinical picture of the disease
- The main causes of inflammation of the external genitalia and vagina in children
- Types of vulvovaginitis in girls
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Treatment of the disease
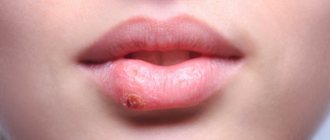
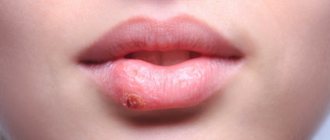
When pimples on the genitals are not dangerous
The first sign that indicates that pimples on the labia are not dangerous is the absence of purulent discharge and signs of inflammation along the edge of the neoplasm. As a rule, white pimples on the labia, which are slightly lighter in color than the surrounding integument, occur due to blockage of the enlarged sebaceous gland with too thick secretion - a so-called wen is formed in their place.
In most cases, wen on the labia does not cause concern to doctors; there is no specific treatment for this problem. However, if the tumor becomes larger than a bean, interferes with sexual activity and causes discomfort, the doctor may decide to surgically remove it.
Another type of non-hazardous formation on the genitals is white pimples on the labia after depilation at home. They appear especially often due to lack of treatment with antiseptics before and after the procedure. The fact is that when a hair is pulled out, the mouth of the follicle remains open for some time.
The ingress of water, cosmetics, or fabric fibers into such micro-wounds can result in irritation and inflammation of the follicles. In this case, small white pimples form on the labia with slight redness along the rim. Antibacterial soap and products with antiseptic properties (hydrogen peroxide, alcohol solution and chlorhexidine) will help to cope with them.
Clinical picture of the disease
Vulvovaginitis in girls is accompanied by complaints of severe itching, pain, burning and discomfort in the external genitalia and perineum. Additionally, pathological vaginal discharge of a reddish, yellow or green color, leucorrhoea or curdled discharge may appear. The girl’s genitals were hyperemic and very red, and a rash and scratches appeared on the skin.
The baby constantly pulls her hands to the crotch area and scratches. Vulvovaginitis may not seriously affect the general health, except for the deterioration of the child’s mental state - tearfulness, irritability, anxiety, etc. As the disease progresses, when the inflammatory process affects other organs, additional symptoms may appear - difficulty urinating, pain in the lower abdomen, fever, etc.
Symptoms
Acute vulvitis in girls occurs in the same way as in adult women. The first sign is pronounced redness of the labia minora and majora, the clitoris and the surrounding soft tissues. There is swelling that can spread to the pubic area, groin and even thighs. The most common complaints are:
- itching and burning in the genital area, intensifying during urination, physical activity, and touching;
- discomfort and slight pain in the perineum;
- discharge of leucorrhoea of various types.
Vulvitis in babies under one year of age can be suspected by obsessive attempts to touch and scratch the affected area; older girls also complain of an unpleasant odor, abdominal pain, and weakness. In some cases, the disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes in the groin, increased temperature, excitability, tearfulness, and decreased appetite.
In the chronic course of the pathology, swelling and redness subside slightly, itching and discomfort increase. The recurrent form of vulvitis often leads to complications such as fusion of the labia minora or vagina, cystitis, and discoloration of the genitals.
The main causes of inflammation of the external genitalia and vagina in children
Inflammation can occur for many reasons, the most common cause of vulvovaginitis is:
- Allergic reaction. The cause of the pathology is the abuse of certain foods (strong allergens are chocolate, citrus fruits, foods high in dyes, honey). Allergies can also be caused by medications, household chemicals, and synthetic underwear.
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics. It is no secret that antibiotics destroy not only pathogenic bacteria, but also beneficial microflora, which “populate” the vagina in large quantities. In this case, it is important, along with antibiotics, to take drugs to restore the microflora.
- Visiting public or private baths, saunas, swimming pools, swimming in polluted bodies of water. This is the most common cause of infection in young children. In addition, the child may be allergic to chlorine, which is used to disinfect pool water.
- Foreign body in the vagina. In learning about their bodies, babies often try to insert small objects into natural openings - the nose, ears, mouth and, sometimes, the vagina.
- Viral and infectious diseases. Vulvovaginitis can appear against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, measles, rubella, chicken pox and other diseases. In this case, specific treatment is not required; the disease that caused the pathology is treated.
- Worm infestation.
- General decrease in immunity and endocrine disorders.
An important role is played by the features of the anatomical and morphological structure of the vagina in pre-pubertal girls - the neutral environment of the vagina, the thinness of the mucous membrane, the proximity of the anus to the entrance to the vagina, which also contributes to the development of inflammation.
Rash on butt
Small red, goose bump-like rashes on the butt often appear in children in the first 12 months of life. It is impossible to determine on your own the true cause of the spots. Based on the clinical picture and shape of the rash, parents may suspect one of the conditions.
- Allergic reaction to tangerines, sweets or other foods. The buttock area can also turn red from medications that are often prescribed to children (Nurofen, Viferon, Sub-Simplex, penicillin antibiotics and other drugs).
- Diapers can cause a maculopapular rash on the butt. This often happens when changing hygiene products. You should give preference to hypoallergenic brands of diapers and change them promptly.
- Homemade diapers often cause irritation on the butt. Visually, it resembles a miliaria - small reddish pimples with whitish nodules in the center. With this condition, the baby may be diagnosed with diaper dermatitis.
- Prolonged exposure to high ambient temperatures causes a rash on the butt. Subsequently, the spots spread throughout the body.
- Childhood diseases can begin with a rash on the butt. Fever often precedes the appearance of redness. Differential diagnosis allows you to make one of the diagnoses: scarlet fever, chickenpox, rubella, measles, Epstein-Barr virus, Coxsackie disease, molluscum contagiosum and others.
- Parasitic infections appear as a rash near the anus. If left untreated, the spots spread to the liver area, lower and upper limbs, and areas of the face. Such signs are characteristic of Giardia and yersiniosis.
- Autoimmune diseases cause skin manifestations with a predominant localization in the gluteal region and lower extremities. When diagnosed, a child may be diagnosed with diabetes, pemphigus, and lupus. The reaction occurs due to inappropriate behavior of the body's defense systems.
Types of vulvovaginitis in girls
- Specific infectious vulvovaginitis occurs when contaminated with pathogenic microflora - Trichomonas, chlamydia, gonococci, etc.
- Nonspecific infectious vulvovaginitis is caused by excessive growth of opportunistic microflora - staphylococci, streptococci, etc.
- Primary vulvovaginitis can be caused by infection due to the penetration of a foreign body, as a result of helminthic infestation, or infection with nonspecific microorganisms.
- Secondary inflammation occurs against the background of other diseases - endocrine disorders, pathologies of the genitourinary system, viral diseases, atopic dermatitis, etc.
Vulvovaginitis varies depending on the pathological agent that caused the inflammation. Among the pathogens are Trichomonas, chlamydia, Koch's bacillus, as well as viruses, fungi, etc.
The most common pathologies:
- Trichomonas vulvovaginitis. Caused by Trichomonas. It can be transmitted to a newborn girl from the mother during childbirth, as well as in girls over 12 years of age. It is characterized by foamy discharge with an unpleasant odor, severe itching and swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Mycotic vulvovaginitis. The cause is yeast-like fungi. Diagnosed in newborns and girls over 12 years of age. It is characterized by severe itching and the appearance of white, curd-like discharge.
- Viral vulvovaginitis. The cause of inflammation is viral infections - measles, rubella, ARVI, characterized by mild redness and swelling of the mucous membranes.
In terms of duration, the disease can be acute (lasting up to 3–4 weeks), subacute (lasting from 1 to 3 months) and chronic, lasting from 3 months or more.
Relationship with lactation
For allergic rashes on the butt, breastfeeding has a positive effect. With the help of mother's milk, the baby recovers faster. This process is associated with the continuous transfer of immunity from mother to infant. Innate antibodies disappear in the first 5-7-9 months of a baby’s life. Subsequently, the mother passes on the so-called additive immunity to the baby, protecting it from various pathologies accompanied by a rash.
In rare cases, breastfeeding can cause a groin rash. If certain infectious diseases are detected in a woman, it is necessary to take care in advance about temporary or complete cessation of lactation. The list of transmitted pathologies includes: syphilis, HIV, hepatitis, candidiasis.
Treatment of the disease
Therapeutic therapy is prescribed based on the results of the examination, depending on the cause of the inflammation and is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, reducing itching and relieving swelling. The following drugs are used for this.
- Local antiseptics for the sanitation of the external genitalia and vagina.
- Bacterial preparations based on bacterial culture results.
- Antibiotics locally and systemically.
- Antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antiviral or antimycotic agents.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a pediatric gynecologist. With a long course of the disease without the necessary therapy, vulvovaginitis is fraught with various complications - narrowing of the vagina, necrosis of the walls of the vagina and cervix. In addition, inflammation can affect the organs of the urinary system or internal genital organs - the uterus and appendages.
For any gynecological pathologies in children, contact medical specialists. Pediatric gynecologists will conduct the appointment as tactfully and carefully as possible, without pain or discomfort for the child. You can sign up for a consultation by calling the numbers listed on the website.
Preventive actions
The basis for the prevention of vulvitis and other genitourinary diseases in girls is teaching children the rules of intimate safety and hygiene. Parents of children need to monitor:
- daily washing before bed and after defecation with warm, clean water using soap or other products no more than 3-4 times a week;
- timely change of diapers;
- wearing loose, non-tight clothing and underwear made from natural fabrics;
- providing girls with personal care products: towel, soap, washcloth;
- wearing panties or swimwear on the beach.
Adolescent girls also need to be told in a timely manner about the dangers of unprotected sexual relations.
If your daughter has symptoms of vulvitis, the pediatric gynecologists of the SM-Doctor clinic will conduct the most delicate examination and prescribe the necessary diagnostic procedures and treatment measures. Remember, the lack of timely treatment can cause the process to become chronic and cause ascending infection of the vagina, uterus, and bladder.
Depending on the nature of the pathology, the following are used:
- medications that act on infectious agents;
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory ointments that relieve swelling, burning and itching;
- sitz baths with medicinal ingredients;
- hygienic washing with antiseptic solutions;
- physiotherapeutic techniques.
In the case of allergic vulvitis, a thorough analysis of the child’s environment is carried out, possible allergens are identified and eliminated: diapers, clothes, detergents, food. To relieve symptoms and relieve itching, general and local antihistamines are prescribed.
When to ask for help
If rashes, redness of the perineum or genitals occur, you can initially cope with it on your own. Key signs that a boy will need medical attention include:
- The penis is swollen or very red.
- Blood or purulent discharge from the penis is detected.
- The child cries or is fussy when urinating (especially if he or she also has a fever).
- The foreskin pinched the head of the penis.
- There is redness, blisters or erosions on the skin of the perineum.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
9,354 total views, 13 views today
( 44 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)
Types of fistulas in urology: causes, symptoms and signs, diagnosis, treatment
Types of radiation therapy for prostate cancer, consequences, rehabilitation
Related Posts
Damage to the foreskin (phimosis)
The foreskin is a layer of skin covering the head of the penis, attached at the frenulum to the penis. If not circumcised, the foreskin covers the head of the penis and may be pulled back and down the shaft of the penis.
Important
Until the age of three, the head of the penis usually does not appear; gradually the skin stretches, allowing it to be exposed.
In some boys, the removal of the head is difficult due to pathological phimosis, a narrowing of the foreskin. Time usually resolves the problem, however, if the baby is particularly in pain or discomfort and the foreskin is red and swollen, doctors may recommend cutting the flesh or circumcision.
Sometimes, when the foreskin narrows pathologically, it can pinch the head of the penis with the development of acute pain, redness, and swelling. This is very painful and requires immediate medical attention, cutting or cutting the foreskin. Without help, paraphimosis, as doctors call the pathology, is dangerous with complications.
Diaper rash care
How to treat diaper rash in newborns?
Doctors recommend purchasing special products that will help soothe the skin and relieve irritation. The product must be safe for children's skin, without fragrances or dyes. Typically, special creams are applied several times a day until the redness completely disappears. If you notice slight redness on your baby's skin, it is important to review his skin care and make the necessary adjustments. Usually it is enough to be more attentive during daily hygiene, change diapers in a timely manner, and make sure that the child does not overheat.
During this period, it is especially important to pay attention to the fact that skin care products are hypoallergenic, do not contain harmful additives, and are approved by pediatricians.
Anti-inflammatory powder “My Sunshine®” is included in this category. It will help prevent and eliminate irritation, redness and diaper rash. The composition includes zinc oxide, which perfectly dries out inflammation. Powder-cream “My Sunshine®” differs from regular powder in that it does not roll off on the skin and provides more comfortable and safe use. It prevents powdered talc from entering the baby's respiratory tract. You just need to apply powder-cream for diaper rash in newborns on the baby’s skin in places of redness and watch how they gradually disappear.
Also pay attention to the cream with panthenol “My Sunshine®”. It contains 5% D-panthenol, a concentration considered optimal in clinical studies. Cream Children's panthenol “My Sunshine®” promotes:
- restoration of healthy baby skin;
- improving the protective functions of the epidermis;
- protecting children's skin from moisture loss.
The cream is suitable both for getting rid of diaper rash and for preventing its occurrence.
Both products from the “Moyo Solnyshko®” brand can be used for babies from the moment of birth.
If you experience grade 2 or 3 diaper rash, you should visit your doctor. He will conduct the necessary tests and make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, all you have to do is follow his recommendations, follow the instructions in a timely manner and monitor the progress of treatment.
Trauma and wounds on the skin of the penis in a child
Most little boys are a bundle of energy; they constantly run, jump, ride scooters and bicycles, jump from trees, and can often get injured. While this is normal, it is a reason for parents to be vigilant about perineal and genital injuries. When it comes to the penis and perineum, there is often just bruising, superficial damage to the skin, and the area may be a little sore for a while. However, if genital tissue is crushed, cut, or has lacerations, medical attention is required immediately (the same applies to the testicles and scrotum). You must first treat the skin with hydrogen peroxide or miramistin, apply a sterile bandage and immediately show the baby to a urologist or surgeon.