Contact dermatitis in children occurs where the skin comes into contact with irritating substances. Obligate irritants cause damage and inflammatory reactions to the skin in all people. In this case, simple contact dermatitis develops. Examples: contact with detergents, cosmetics, rubber, metals.
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs to a specific substance in a specific person due to the fact that his body has developed an intolerance, or a delayed immune reaction. The first contact occurs without any symptoms, but then, over the course of two weeks to several years, T-cells of the immune system accumulate in the body, which remember this allergen. Every time they encounter it, the cells will produce cytokines - biological substances that cause an inflammatory reaction in the skin.
The peculiarity of dermatitis in children is that a reaction in the form of itching, swelling, redness, rashes and other signs of an allergic disease can develop to a host of provoking factors:
- overheating, hypothermia;
- excess nutrition;
- New Product;
- synthetic materials, low-quality toys, diapers.
Only a doctor can recognize allergic dermatitis in children and prescribe treatment that will be effective. Therefore, it is better to immediately contact the clinic with all complaints, and not experiment with the child’s health.
Causes
The main causes of contact dermatitis:
- Physical factors - sun, high or low temperatures, ultraviolet radiation, electric current.
- Chemical – soap, shampoos, skin care creams, sunscreens, toothpaste, household chemicals (washing powder, dishwashing detergent).
- Biological - plant juice (hogweed, buttercup, primrose), secretions of jellyfish, insects.
The causes of allergic dermatitis in children most often lie in diet. Allergic inflammation in the skin can be caused by:
- chemicals - dyes in fabrics, detergents.
- food allergens - chocolate, citrus fruits, strawberries, cheeses, mushrooms, dyes and preservatives in any product.
- biological allergens - mites, house dust, hair and epidermis of pets, dust in animal food, indoor plants.
- medications - antibiotics.
General abnormalities in the body will contribute to the appearance of symptoms of atopic contact dermatitis:
- Pathology of the endocrine system.
- Bright skin.
- Malfunctions of the immune system. Often the signs of atopic dermatitis are combined with allergic rhinitis, sometimes with bronchial asthma, and other allergic diseases. Close relatives in the family may suffer from allergies.
- Artificial feeding - in this case, children are more likely to overeat, since eating from a bottle is faster and easier than from the breast.
- Excess body weight.
- Diathesis is a feature of the immune system due to which the body reacts to ordinary substances with skin rashes.
- Dysbacteriosis and chronic diseases of the digestive system, frequent unreasonable prescription of antibiotics.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases affect the immune system.
- Weakened body – frequent stress, severe concomitant illnesses, childhood.
Incorrect treatment of atopic dermatitis. 5 main mistakes
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that causes itchy red patches, rashes, peeling and dryness. This disease is diagnosed in 30% of children and 10% of adults. However, atopic dermatitis is often not given due attention, and incorrect treatment of this disease can slow down the onset of remission and worsen the overall level of health. Dermatologist Anna Trushina talks about the 5 most common mistakes in treatment tactics.
Mistake #1. Excessive diagnostics aimed at identifying “non-skin” causes.
The reasons for the development of atopic dermatitis lie in genetically determined features:
1. From the skin - associated with a violation of the barrier function.
2. From the immune system. In response to the penetration of irritants and allergens through a broken skin barrier, inflammation forms.
Therefore, it is not advisable to look for the cause in helminths, disturbances of intestinal microflora, intoxication, etc. The entire range of examinations prescribed in this regard only because of atopic dermatitis is not justified. Efforts aimed at finding the “root cause” outside the skin are better directed towards competent treatment of the skin itself.
Mistake #2. Search for the causative allergen.
Atopic dermatitis is not an allergic disease in nature. However, allergic reactions can be combined with atopic dermatitis as a concomitant disease. This happens in approximately 20-30% of patients.
Therefore, atopic dermatitis itself is not a reason to undergo expensive panels for specific allergens, and the test should only be taken if a specific allergic reaction is suspected in some patients.
Mistake #3. Following an unreasonable diet.
Often atopic dermatitis becomes the reason for prescribing a strict “hypoallergenic” diet. Children's diet becomes monotonous and boring. However, such dietary restrictions are not scientifically justified and do not bring the desired result, even if there is an allergy at the same time.
In addition to the lack of effect, a strict diet can harm the body. It leads to deficiencies of important nutrients, minerals and vitamins, which can negatively affect the overall health of the child. Therefore, children with atopic dermatitis need to eat a varied and balanced diet. Only those foods whose role has been clearly proven to aggravate the pathological process are excluded from the diet. Similar rules apply to the mother’s diet if the baby is breastfed.
Mistake #4. Irrational skin care.
The basis of the treatment of atopic dermatitis is the restoration of the skin barrier function and the elimination of inflammation. Therefore, products are prescribed that help HYDRATE and soften the skin and retain moisture inside it, and thereby improve the protective properties of the skin. The complex also uses measures that reduce the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process, i.e. skin contact with potential aggressors from the external environment is limited.
To achieve the goals listed above, careful and careful care of the skin of an atopic child using EMOLENTS is required. These are special products, lotions, creams, balms, which, when applied to the skin, soften and moisturize it, help fill the intercellular spaces in the skin, restoring its barrier properties.
It is important to understand that using simple baby creams 1-2 times a day may not be enough. Proper care requires the application of special emollients in sufficient quantities. They are distributed in a thick (!) layer on both problem and visually unchanged areas of the skin. At the same time, the frequency of application directly depends on the condition of the skin. It is necessary to use emollients so many times during the day that the skin remains smooth, soft and without flaking to the touch all day.
Mistake #5. Refusal of “hormones”.
With atopic dermatitis, an inflammatory process occurs inside the skin (the word “dermatitis” itself, literally translated into Russian, means inflammation of the skin). That is why during an exacerbation, anti-inflammatory external agents are used to stop the inflammation. These drugs include external glucocorticosteroids. However, many parents refuse these “hormones” due to steroidophobia (fear of using steroids).
Topical (i.e., used externally: lotions, emulsions, ointments, creams) corticosteroids have been used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis for decades. During this time, they have demonstrated high efficiency and a high safety profile.
If parents do not use corticosteroids in cases where there are indications for this, or do it irrationally (prescribed independently without taking into account the degree and form of skin inflammation, independently cancel the hormone before the required time without the supervision of a doctor), then this can lead to deterioration of the skin condition , the formation of foci of chronic inflammation and other local complications.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis is a fairly well-studied disease with established mechanisms of development. Regular skin care, timely relief of inflammation and the elimination of unnecessary aggressive manipulations and diagnostic procedures will help cope with this disease as effectively as possible.
Pathogenesis
Simple contact dermatitis in children of the first year of life occurs due to prolonged contact of the skin with diapers, wet diapers, and rough seams on clothes. It is also called diaper dermatitis. Therefore, skin inflammation occurs in the buttocks, groin, abdomen, and inside the thighs. Also, redness and itching often appear in the armpits, under the knees, and on the neck. Here the disease develops due to friction of skin against skin or against clothing.
At an older age, in adults, contact dermatitis is more associated with professional activities, wearing objects made of metal, rubber, and synthetics.
Seborrheic dermatitis develops on the scalp, face, back, and is associated with hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands. It occurs with hormonal disorders, in adolescence, with a genetic predisposition.
Allergic contact dermatitis is an immune inflammation. It is caused by the activation of T cells, which produce a lot of biologically active substances. They are what lead to the appearance of symptoms of the disease.
In children, skin manifestations can appear in response to the penetration of an allergen or hapten (an incomplete allergen, it becomes so only after binding to proteins in the body) into the body by any means - by inhalation, direct contact or through the digestive system. The last way is the most relevant, since the digestive organs are very vulnerable to the penetration of allergens:
- the liver does not produce enzymes actively enough;
- many complex proteins do not break down in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract into simple substances, but are absorbed, becoming allergens;
- When there is a large intake of food, some does not have time to be processed, is absorbed without being completely broken down, and some accumulates in the large intestine, causing intoxication.
That is why many parents are faced with a situation where a child reacts with a severe exacerbation of atopic contact dermatitis to almost any food, and even strict dietary restrictions do not lead to an effect.
Types of dermatitis in children?
The most common type, diaper rash , often occurs in infants due to prolonged contact of the baby’s skin with irritants:
- body secretions (urine, feces, digestive enzymes);
- bacteria, fungi;
- artificial clothing and diapers;
- humidity and ambient temperature.
Manifests itself in the form of a rash and redness , which disappear after some time when using special means and stopping contact with the irritant.
The development of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children is based on a genetic predisposition, when at least one of the parents has a food allergy, asthma, hay fever or atopic dermatitis itself. The first sign of atopic dermatitis in babies may be itching and dry skin. The more weakened the child’s body, the stronger the skin manifestations may be. At risk are children who are bottle-fed, have gastrointestinal problems, and often suffer from colds.
Atopic dermatitis is caused by internal processes in the body, when dryness, redness and inflammation on the skin symbolize digestive problems, so the simple absence of suspected allergens in the diet may not be enough. If you suspect atopic dermatitis in a child, you need to contact a pediatrician and allergist for a comprehensive analysis of the problem and treatment, since it can be difficult to determine the extent of the disease at home. Skin manifestations that have been ignored for a long time can develop into full-fledged allergic rhinitis or even asthma, so you should not delay going to the doctor.
Seborrhea is a common problem in infants. It is caused by a fungus that is part of the microflora of healthy human skin, Malassezia furfu. With seborrheic dermatitis in infants, mainly on the head (in the hair area), less often in the armpits, groin, ears, yellow-gray scales appear, greasy to the touch.
Contact dermatitis is usually a one-time inflammation of the skin caused by an external irritant. The level of skin inflammation depends on the general state of the baby’s immunity, the strength and duration of exposure to the irritant. This could be temperature changes, exposure to sunlight, X-rays, too much disinfectant, unsuitable cream or toothpaste, burning plants, insect bites.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis
Acute contact dermatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Redness where the skin comes into contact with an irritating object.
- Skin itching.
- Edema.
- There may be rashes resembling bumps and blisters. If you comb them, there will be erosions on the skin with a weeping surface. As they heal, crusts form.
If contact with the causative factor is not eliminated, the process may develop into chronic inflammation. The following is more typical for him:
- Thickening of the skin, its pattern becomes more pronounced.
- You may notice traces of scratching on the body, dry skin.
- Due to dryness, cracks often form. If bacteria penetrate inside, an acute inflammatory reaction develops with redness, swelling, various rashes, pustules, and fever.
- The chronic inflammatory response occurs in the form of alternating periods of improvement and exacerbation. Deterioration may occur due to stress, hypothermia, acute respiratory viral infections, or vitamin deficiency.
Symptoms of dermatitis
Dermatitis, like any other inflammatory disease, is accompanied by a classic pentad - redness, pain, swelling, local increase in body temperature, decreased function of the affected organ. It is worth noting that in children the severity of the clinical picture can vary significantly, which is due to the anatomical and physiological individual characteristics of a particular child and his skin. In addition to the classic ones, there are additional signs:
- rash, crusts on the baby’s skin;
- itching in pathological areas;
- irritability, emotional lability;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.3 ° C. With the parallel addition of bacterial flora with the development of purulent lesions of the epidermis, fever can reach values of 38°C and higher.
Infants with dermatitis may refuse to feed; Normal sleep is disrupted, the child is constantly capricious. These symptoms are a signal for parents to force them to show their baby to a doctor.
Where is contact dermatitis most common?
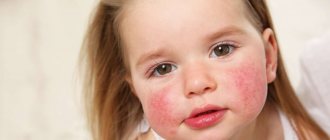
In children, skin symptoms of atopic dermatitis are most often localized:
- on the face – cheeks, chin, around the mouth;
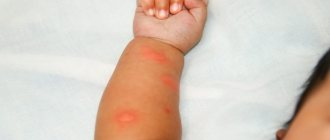
- on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs;
- on the torso, buttocks.
The peculiarity of contact dermatitis in children and adults is its localization in the place where the body comes into contact with an unwanted object:
- In case of photosensitivity – face, open areas of the body.
- Occupational contact dermatitis - hands when working with paints, lubricants, oils, insecticides, acids, alkalis, cement, solvents, food products. Contact with rubber occurs when working with gloves.
- In contact with metal - on the wrist, neck, décolleté, earlobes, that is, where jewelry is worn.
- The area around the eyes reacts to eye drops, glasses, the skin near the lips - to lipstick, the mucous membrane in the mouth - to dentures, braces, toothpaste, the cheek - to the phone, fingers - to nail polish, feet - to shoes with low-quality rubber, armpits - for deodorants, buttocks and back - for furniture upholstery, head - for curlers, shampoos, hats.
Classification and stages of development of contact dermatitis
Depending on the cause that caused the skin lesions, there are:
- Simple contact dermatitis.
- Allergic contact dermatitis.
- Seborrheic dermatitis.
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Unexplained etiology.
Depending on the severity, the disease can be classified into mild, moderate and severe.
Contact dermatitis occurs:
- thermal – burn, frostbite;
- radiation – against the background of treatment with ionizing radiation;
- traumatic – when rubbed by clothes, shoes, plaster cast;
- medicinal – reaction to ointments, care products;
- parasitic – tissue reaction to the presence of ticks, fleas;
- photodermatitis - some drugs increase skin sensitivity to sunlight, for example, antibiotics, retinoids;
- periwound dermatitis develops due to skin irritation with tissue fluid, purulent and bloody discharge.
Allergic contact dermatitis, in turn, is divided into types depending on the allergen with which the skin comes into contact:
- rubber;
- metals (primarily nickel);
- plastic;
- dyes;
- medications (lanolin, antibiotics);
- cosmetics (formaldehyde);
- plants;
- food products;
- unknown etiology.
Differential diagnosis and treatment of diaper dermatitis in newborns
Diaper dermatitis is very common in young children due to the characteristics of their delicate skin and risk factors that exist at an early age. Preventing and treating diaper rash is quite simple, but sometimes you don't see the effect of what you do. Why does this happen? The fact is that very similar changes are caused not only by diaper dermatitis, but also by candidal, allergic contact, atopic, seborrheic and other dermatitis, which, although they have similar symptoms, are treated differently .
How to distinguish and properly treat various dermatitis in young children?
Video: Diaper dermatitis in newborns - differential diagnosis and treatment
Causes of diaper dermatitis in children
On the one hand, these are age-related characteristics of the child’s very delicate and not yet perfect skin , on the other hand, this may be the effect of irritating factors , not very good care, metabolic disorders of the child, his immune functions or heredity . Most often, due to improper skin care in young children, usually at the age of 2 months , diaper or irritative dermatitis occurs, or as it is sometimes called, diaper rash , diaper rash , in which inflammation of the skin appears in areas of contact with the diaper or diapers.
This is usually facilitated by prolonged contact of the skin with the wet surface of the diaper , which leads to maceration and disruption of the protective function of the skin.
Irritant effect:
- urine, feces,
- digestive enzymes,
- change in the acidity of the skin under the diaper,
- bacterial and fungal infection
All these irritants play an important role in the development and maintenance of the inflammatory process. Such a child develops redness, erythema , slight peeling erosions may appear, epithelial defects healing without scar formation on the convex surfaces of the genitals and buttocks, where there is good contact with the diaper. The child usually becomes restless and cries when changing diapers or when cleaning the skin of the buttocks and genital area. In this case, at first there is no redness in the folds of the skin, but the convex surface of the buttocks, thighs, lower abdomen and groin area almost always suffer.
In children under 4 months of age, the first manifestation of the disease is mild erythema in the perianal area. There are three degrees of severity of diaper dermatitis : mild, which is characterized by the appearance of hyperemia and single small papules, skin rashes, in the form of cavityless formations, rising above the skin level, localized in the groin or buttock area.
With moderate and severe diaper rash, redness of the skin and papular rash are more pronounced, erosions and even pustules : cavitary elements that contain clear liquid or pus . In more severe cases, the process spreads to other parts of the body, and a secondary infection, most often of the genitourinary system, may occur.
In some cases, a severe but fortunately rare variant of diaper dermatitis called Sevestra-Jacques erosive dermatitis , which causes ulcers with sharp edges and erosions with raised edges.
Diaper dermatitis treatment and prevention methods
The main method of preventing and treating diaper dermatitis is the use of products that enhance the skin’s natural defenses, improve its regeneration and create a protective barrier between the skin and external irritants. One of the best remedies today for the prevention and treatment of diaper dermatitis are ointments and creams that contain dexpanthenol and lanolin .
It was the combination of dexapanthenol and lanolin that showed an excellent preventive effect, creating an ideal long-lasting barrier between the skin and the diaper or diapers, and has a regenerating, healing, soothing and anti-inflammatory effect, which is confirmed by clinical practice.
Diaper dermatitis differential diagnosis
What should be differentiated from ordinary diaper dermatitis? To begin with, with its complicated forms. Diaper dermatitis can be complicated by the development of fungal, cadidal skin lesions.
Fungal candidal dermatitis in children
Clinical signs of the disease are erythematous spots with typical peeling along the periphery, collar-like peeling plaques appear on the erythematous base , as well as small pink papules that can spread to the genitals, perianal area and folds. Involvement of skin folds, the appearance of similar lesions, they are called satellite lesions, in the thighs and abdomen is an important criterion for the differential diagnosis of candidiasis from primary diaper dermatitis.
Candidal dermatitis should also be suspected when conventional preventive and treatment measures are ineffective . You are doing everything correctly, but you don’t see much effect. The diagnosis can be confirmed skin scraping for fungi from the periphery of erythema, papules or pustules.
Fungal candidal dermatitis treatment
If you suspect a candida complication in your child, it is highly advisable to contact your doctor. He will prescribe the antifungal agents nistatin, clotrimazole, miconazole, both topically and in some cases orally. In persistent cases , a course of fluconazole is prescribed at a dose of 5 mg/kg of masa per day , always under the supervision of a doctor. If there is erosion , it is good to take a sitz bath with a weak solution of potassium permanganate , after which dry the diaper area by blotting the skin and apply an aqueous solution of methylene blue .
Allergic contact dermatitis
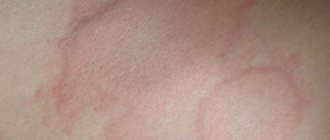
The next thing to differentiate diaper dermatitis from is allergic contact dermatitis , which can be either a separate disease or a complication of pre-existing dermatitis. It manifests as mild erythema and skin irritation, and blisters and papules may be present.
Allergic contact dermatitis rare in children under 2 years . It is suspected in cases where an adequate response to various treatment options cannot be obtained. The most common causes of allergic contact dermatitis are:
- Skin contact with certain specific chemical allergens, such as parabens
- Mercury compounds
- Neomycin
- Latex, incl. used in diapers, pacifiers
- Detergents, cosmetic perfumes
- Medicines
- Dyes
Diagnosis is made based on clinical symptoms and patch tests . Clinically, the diagnosis is relatively easy. With this form of dermatitis there will always be quite intense itching, and the child will immediately show this to you, as soon as you undress him, he will reach out with his hands to the affected areas of the skin.
Allergic dermatitis rare in children under one year of age ; its favorite localization sites are the elbows, popliteal fossae, the anterior surface of the ankles, neck, face, while the edges of the hyperemia are quite clearly limited. Parents or relatives of such a child can often find allergic diseases: asthma, rhinitis, polynosis and other similar problems. The skin of such a child is quite often dry.
Allergic contact dermatitis treatment
Treatment of allergic dermatitis consists of stopping skin contact with the active allergen , limiting the use of synthetic detergents, the doctor may prescribe ointments with weak or medium-strength corticosteroid hormones ointments containing a glucocorticoid, antibiotic, or antifungal drug can be used In more severe cases, calcineurin inhibitors: tacrolimus or pimecrolimus may be prescribed Antihistamines may be prescribed . But please do not treat with these ointments and medications yourself, this is the doctor’s job. If there is no effect, you need to consult an allergist or dermatologist.
Atopic dermatitis
The next, unfortunately, quite common dermatitis in young children is atopic dermatitis. This is a multifactorial inflammatory skin disease, which usually begins in early childhood, characterized by itching, a chronic recurrent course and quite clear age-related localization features and the nature of skin changes. Usually in relatives , such as bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, food allergies. What are the features of atopic dermatitis? It depends on age. From 2 months to 2 years, this is the infant stage of atopic dermatitis. On the face, legs, thighs , extensor surfaces of the extremities, behind the ears, dry skin, symmetrical redness, erythema, exudation, infiltration and swelling of skin areas appear; small vesicles , such bubbles with transparent or cloudy contents, flaccid tire, quickly opening with formation of eczematous wells.
Eczematous papules may appear in the form of small rounded nodules up to 1 mm, which rise slightly above the skin, thickening and peeling of the skin. And all this can be accompanied by itching and burning. Therefore, the child becomes restless, he cries, scratches the skin, leaving characteristic marks on it, and when an infection occurs, serous-bloody-purulent crusts appear.
The diagnosis of atopic dermatitis is a clinical diagnosis and is made on the basis of anamnesis, i.e. questioning , thorough examination of the child, allergy examination , skin tests, determination of specific IgE in the blood . In a limited form, the rash is localized on the face in the area of the cheeks, forehead and chin and symmetrically on the hands. With a widespread form on the skin of the trunk and limbs. Erythema is often worse in the evening and lessens in the morning.
Atopic dermatitis treatment
It should be said that it is at an early age, unlike older children, that food allergies , therefore a strict elimination diet is recommended for at least 4 weeks , first of all dairy products from the diet of a breastfeeding mother, if the effect is not observed, then There's no point in continuing this diet.
Formula-fed children should receive formulas with deep, extensive protein hydrolysis . Very important is thorough and long-term skin care , using emulents, moisturizers, special creams and ointments under the supervision of an allergist or dermatologist.
Seborrheic dermatitis
The next dermatitis that can be found in young children is seborrheic dermatitis, or milky crusts, gneiss. This is a skin disease associated with increased secretion of sebum, in areas with a large number of sebaceous glands - on the scalp, ears, face, chest, upper third of the back.
Previously, it was associated with the fungus Malassezia furfur, but recent studies deny the role of this fungus in skin lesions at an early age. Therefore, it is not entirely clear here. This is a fairly common pathology; in children, the disease develops in the first 2-3 months of life , and is observed in almost 70% of children of this age. On the skin of the scalp, less often on the forehead, cheeks, in the folds behind the ears, accumulations of fatty, sebaceous scales (gneiss or milk crust) appear, hyperemia is observed, peeling behind the hairline and behind the ears, erythematous lesions, maceration on the skin of the cervical, axillary , inguinal folds, in the folds of the skin of the torso and limbs, a maculopapular rash may occur, which can also become covered with scales on the periphery. The rash can also be in the area of the external auditory canal, on the sternum, on the neck, in the axillary and groin areas.
A characteristic feature of seborrheic dermatitis is the absence of itching , predominantly affecting the scalp and diaper area in children. Allergic diseases are usually not observed in relatives. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical data and visual examination; in the second half of life, the majority of symptoms disappear.
Seborrheic dermatitis treatment
Although seborrheic dermatitis usually goes away on its own at an early age, we want to somehow help the child. The treatment is quite simple - careful systematic skin care . We need to loosen and remove scales and crusts, reduce erythema, redness, and prevent the development of secondary infection. When the scalp keratolytic agents are used: cream with 1–2% salicylic acid , warm compresses with vegetable oil (olive, peach, almond), shea butter, shea butter, glycerin. To suppress possible dissemination of Malassezia fungi on the scalp and body, shampoos containing antifungal components, such as ketoconazole, are used. In the presence of wet elements, aqueous solutions of aniline dyes and zinc-containing pastes are added to the treatment, but in this case, as in the presence of infection, it is better to consult a dermatologist.
Psoriasis
The next type of child dermatitis is psoriasis. Psoriasis in children of the first year of life is rare, but it can begin with a papular rash in the groin area and in the navel area. However, for this disease, lesions in other places are more typical: elbows, knees, face, scalp, torso. Among children, girls are more likely to suffer . In approximately half of the cases there is a family history. In young children, it can be difficult to distinguish between atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
It is worth paying attention to the localization of the lesion: with atopic dermatitis, rashes are rarely found in the perineal area , whereas for psoriasis this area is typical. This is due to the characteristics of the skin of a small child, it is easily vulnerable and prone to the development of macerations even with minor adverse effects, poor hygiene, frequent bathing and use of soap, tight swaddling. In large folds there appears sharply defined hyperemia , edema with maceration and desquamation of the epidermis at the edges; in appearance this may resemble candidiasis, impetigo, streptococcal skin lesions.
This is due to the fact that in newborns the pH of the skin is neutral, and in seborrheic zones and folds, due to caseous lubrication, it is alkaline. Only from the 2-4th week of a child’s life does the skin reaction begin to shift towards the acidic side. In the stationary stage, the plaques seem to sink in the center, and the scaly layers are clearly pronounced.
Therefore, if you have been treating an unclear allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, fungal skin infection, or contact dermatitis for a long time, you should pay attention to the characteristics of the course of the disease, medical history and hereditary predisposition and be sure to consult a dermatologist. to independently diagnose psoriasis , and not every doctor will think about such a diagnosis.
Psoriasis treatment
Treatment methods are selected by a dermatologist for each child individually. In most cases, local treatment with ointments , medicinal creams, and vitamin preparations is prescribed. To treat psoriasis in children, only topical treatment is usually used. The most important thing is to hydrate your skin , especially with moisturizer and baths with emollients. You can use ointments and creams that are already familiar to us, which contain dexpanthenol and lanolin. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe glucocorticoid ointments.
Acrodermatitis enteropathica
Acrodermatitis enteropathica is a rare hereditary disease in which both the mother and father have certain genetic disorders . It is assumed that the disease is caused by a deficiency of zinc in the blood as a result of impaired absorption in the small intestines. The disease begins at an early age, more often in girls, after about 2 weeks when replacing breastfeeding with cow's milk or earlier if the child has received it since birth. Localization of initial manifestations is around natural openings. At the same time, in the perianal region, i.e. Erythematous rashes appear in the diaper area, then symmetrical vesiculobullous and eczematous rashes appear around the mouth, and then on the cheeks, knee and elbow joints. Over time, the erythematous and erosive lesions become dry, thickened, and may resemble psoriasis.
For enteropathic acrodermatitis it is typical: a rash around the mouth and anus, perioral and acral dermatitis, on the extremities, alopecia, baldness and diarrhea.
In the anamnesis of such children, one can note the ineffectiveness of local antifungal therapy , chronic diarrhea, edema due to a reduced amount of protein in the blood serum, eye symptoms (fear of bright light, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, corneal dystrophy), quite often stomatitis, paronychia, lag in growth and bacterial and fungal infections, primarily candidiasis of the skin, mucous membranes, and intestines. The diagnosis of enteropathic acrodermatitis is made based on determining the concentration of zinc in the blood and the level of alkaline phosphatase (an enzyme that is dependent on zinc), as well as the clinical picture of the disease.
Enteropathic acrodermatitis treatment
Treatment is taking zinc preparations , the recommended initial dosage is usually 5-10 mg/kg/day of elemental zinc, maintenance dose is 1-2 mg/kg/day . Zinc sulfate, acetate, gluconate, or amino acid chelate may be used . Zinc and copper levels should be checked regularly. Such people need to take zinc throughout their lives. Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
It should be said that there is also a milder form of dermatitis associated with a temporary lack of zinc, which can occur in premature babies aged 2.5-3 months who are breastfed. At this age, their need for zinc increases, and its content in mother's milk decreases. And mild symptoms of acrodermatitis arise, which are resistant to conventional treatment, but quickly go away when zinc is prescribed. In the future, such a child will be completely healthy.
Dermatitis, which is rare in young children
Complications of allergic contact dermatitis
The most dangerous acute allergic reaction occurs when a large amount of allergen enters the body. This can lead to shock, anaphylaxis, and angioedema. These reactions involve the B cells of the immune system and are called immediate reactions. They are not directly associated with dermatitis, but they occur more often in people with abnormalities in the immune system than in healthy people.
Contact dermatitis can lead to the following complications:
- The addition of a secondary infection, when fungi and bacteria penetrate the skin when scratching. This can cause chronic inflammation of the skin, hair follicles, and glands. Purulent foci form, which are very painful, itchy, and cause anxiety.
- Weeping erosions, cracks, crusts that are torn off due to itching can leave behind unattractive scars, areas of pigmentation, thickening of the skin or, conversely, atrophy.
Similar complications are observed in atopic disease.
Treatment of dermatitis in a child
Treatment of skin diseases in children requires an integrated approach. First of all, this is the elimination of contact with the irritant - further treatment depends on the diagnosis. The treatment complex necessarily includes care for irritated skin areas, in addition to medications, if necessary.
Skin care for diaper dermatitis
To soothe irritated skin in the diaper area, it is recommended to use special protective creams, including cosmetic ones, which reduce pain and restore the skin.
Diaper cream 1 2 3 is applicable in two directions at once:
- For redness it is effective in 80% of cases after the first applications 1
- When used regularly to prevent the recurrence of diaper rash, it helps reduce the frequency of exacerbations by 74%1
Skin care for very dry skin and atopic dermatitis
At all stages of atopic dermatitis (including its first signs in the form of increased dry skin), experts recommend the use of emollients - special cosmetics. They moisturize the skin for a long time, help eliminate itching and, in mild cases of atopic dermatitis, help reduce inflammation. It is important to remember that the main task of emollients is to launch an independent process of lipid production in the skin , so pay attention to ensure that the emollient is not addictive.
Stelatopia emollient cream promotes effective hydration in a natural way by helping the skin produce its own lipids.
- In 90% of cases, it reduces excessive dry skin and reduces the likelihood of clinical signs of AD by 51% 2
- In 86% of cases it helps restore the protective barrier2
- Reduces inflammation after 32 hours3
Scalp care for Seborrheic dermatitis
Remember the main rule: do not comb out milky crusts. While combing, you can injure your baby's skin, which can lead to a secondary infection. If you want to get rid of milk crusts at home, use special cosmetics labeled 0+. Pay attention to the composition - it is advisable that the products do not contain perfumes and aggressive surfactants (surfactants).
Shampoo - foam from “milk crusts” for newborns will allow you to gently and carefully remove milk crusts, soften the scalp and normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands. Contains 99% ingredients of natural origin and soft surfactants. And if the crusts are dense and are localized not only on the baby’s head, we recommend using Shampoo - foam for “milk crusts” for newborns in combination with Cream for “milk crusts”.
Cream and Foam Shampoo for “milk crusts” help eliminate milk crusts in an average of 7 days 4
Important: if in doubt, if redness appears in your baby, you should consult your doctor. A professional examination and accurate diagnosis will bring peace of mind to both you and your baby.
Diagnostics
A pediatric dermatologist diagnoses contact dermatitis in children. If necessary, he will refer the patient to an allergist or immunologist (for the diagnosis of atopic, allergic dermatitis).
A careful study of complaints, history of allergies, and characteristic clinical manifestations help the doctor make a preliminary diagnosis. You can confirm it in different ways:
- Elimination therapy, that is, avoiding contact with those things that provoke the appearance of skin symptoms. If after this the redness and itching go away, the patient is advised to avoid such contacts in later life.
- Patch skin allergy tests - patches with the most common allergens applied to them are glued to the body. After 2–4 days, the skin reaction under each patch is assessed and conclusions are drawn about intolerance to a specific element, confirming the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis.
- Immunological tests allow you to analyze the functioning of the immune system, the number of T and B cells, circulating immune complexes, and antibodies.
What should be the diet of the baby and mother with atopic dermatitis?
If atopic dermatitis is detected, the diet of a nursing mother involves avoiding the consumption of spicy, salty, sour, spicy foods and dishes. Additionally, you should refrain from including chocolate, strawberries, coffee, beans, nuts, cocoa, honey, citrus fruits, fatty broths and smoked meats in your diet. Undesirable products - confectionery, snacks and all fast food, factory juices, semi-finished products; hard cheeses, products rich in flavors and thickeners. Optimal nutrition for a nursing woman:
- Potatoes, cabbage, zucchini (boil or bake).
- Dairy products.
- Apples, pears - raw, boiled.
- Porridge made from barley, pearl barley, and corn.
- Beef.
- Rye bread, crackers.
- Compote made from natural fruits.
During lactation, it is not advisable for a woman to introduce new foods into her diet (exotic fruits, meat, drinks) if the reaction to them cannot be foreseen. Nutrition for atopic dermatitis in children involves switching to the use of hypoallergenic mixtures. Their presence on the menu helps strengthen the immune system and normalize the digestion process. Only a pediatrician can prescribe a certain mixture. The following options are used: 1. With soy protein: Humana SL, Bona soy, Enfamil soy. 2. With protein hydrolysate: Alfare, Damil Pepti, Nutrilon PeptiTSC. 3. With goat milk: Nanny. 4. With amino acids: Alfare Amino. 5. Fermented milk: Gallia Lactofidus, Agusha fermented milk.
If you are intolerant to cow protein, the optimal solution is to use Frisopep nutrition. This mixture can be used by children from the first days of their life. Each new product should be introduced no more than once every 2 weeks. This approach allows you to control the reaction of the child’s body to changes in diet. During the period of exacerbation of the symptoms of skin inflammation, the introduction of new complementary foods is contraindicated.
Differential diagnosis
Many skin diseases are accompanied by itching, hyperemia, and rash. A doctor can distinguish them, after which suitable treatment will be prescribed. Contact dermatitis may resemble:
- atopic dermatitis;
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- lichen planus;
- scabies;
- dermatophytosis.
To differentiate skin pathologies, the body is examined:
- examination of the skin with magnification;
- specific samples;
- scraping and examination under a microscope;
- blood tests, urine tests, biochemistry, hormonal examinations.
There are common diseases in which dermatitis also occurs, but there are also other clinical symptoms:
- phenylketonuria;
- porphyria;
- acrodermatitis against the background of enteropathy.
In this case, you need to treat the underlying disease, then the skin manifestations will go away.
Diagnosis of dermatitis in a child
Only qualified specialists - a pediatrician, an immunologist, a dermatologist - can diagnose one or another type of skin disease in a baby. In addition to a thorough visual examination, the diagnostic process includes collecting information about the diseases of family members, various laboratory examinations and tests. However, while bathing, swaddling and dressing your baby, you should pay attention to his skin, thereby conducting an independent diagnosis. If redness or rash does not go away and raises suspicions, this is a reason to consult a specialist.
Treatment of allergic contact dermatitis
To treat atopic and contact dermatitis, it is important to eliminate exposure to the allergen on the body. Sometimes it cannot be established even after a long examination. In this case, treatment with drugs is indicated:
- Second generation antihistamines - they inhibit the release of histamine by mast cells, reduce skin itching and other manifestations of acute allergic inflammation. Tablets are prescribed internally, and ointments with a soothing effect are prescribed locally.
- Hormonal drugs for severe contact dermatitis. They can also be used internally and externally.
- Specific desensitization is the introduction of an allergen in microdoses, in ever-increasing quantities. This helps the body change its perception of the allergen and correct pathological reactions of the immune system.
- For secondary bacterial or fungal inflammation, antibiotics and antifungal agents are added.
Therapy for atopic dermatitis is often long-term and requires persistence from parents and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations. Healthy:
- follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- monitor the regularity of bowel movements;
- avoid stress;
- use skin softeners (emollients), apply them twice a day without damaging the skin;
- for weeping erosions, ointments with zinc, dye solutions (Castellani liquid, fucorcin) are applied topically, and lotions are made with herbal decoctions (oak bark).