Home » Departments » Phlebology - appointment with a phlebologist » Causes and treatment of spider veins on the chest in women
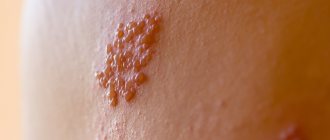
Spider veins (telangiectasias) are small skin formations that look like small dots, lines, and branches, usually red-violet in color. Such formations appear due to local expansion of the walls of the microvasculature structures with the formation of a protrusion. Spider veins on the chest of women not only bring psychological discomfort, but can also be a manifestation of the development of various pathological processes.
1. Benign breast tumors, types of tumors
If you notice any lumps, lumps or changes in your breasts during self-examination, which is recommended for all women to do periodically, you should immediately consult a good doctor. But there is no need to panic in advance. 80% of all breast lumps are benign breast tumors
. This means that the tumor is not breast cancer. Benign breast tumors usually have clear, even borders and may move slightly if you press lightly on them. Often such tumors form simultaneously in both mammary glands.
There are several common causes of benign breast tumors, including normal physiological processes, infections, breast trauma, and certain medications.
Types of Benign Breast Tumors
- Fibrocystic changes.
In some women, normal hormonal changes in the body can cause fibrocystic tumors. Typically, these tumors appear as lumps in both breasts and cause breast enlargement and tenderness before menstrual bleeding begins. Sometimes discharge from the mammary glands appears. Lumps and lumps in the breast may be hard or soft. Fibrocystic changes most often appear in women around 40 years of age, and overall they are the most common type of benign tumor in women aged 35-50 years. - Simple cysts.
Simple breast cysts are fluid-filled “sacs,” or cavities, that form in both breasts. Cysts can be single or multiple, and can vary in size, which often changes during the menstrual cycle. - Fibroadenomas.
Fibroadenoma is another very common type of benign breast tumor in women. It consists of hard, round lumps that move freely in the chest. When pressed, as a rule, there is no pain. Fibroadenoma appears as a result of excessive formation of lobules of the mammary glands and surrounding tissues. Most often occurs in women aged 20-30 years. - Intraductal papillomas.
These are small warts, or growths, in the milk ducts near the nipple. As a rule, they appear in women aged 45-50 years and can cause bleeding from the nipple. - Traumatic necrosis of fat cells.
This condition occurs after a sudden injury to the breast, although often women cannot remember the specific incident when the injury occurred. As a result, fatty lumps form in the breasts, usually round in shape, hard, solitary and painless.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Spider veins during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special physiological state of a woman, in which the course of most processes changes. First of all, this concerns hormonal levels, as well as metabolism (metabolism). Spider veins during pregnancy are a consequence of the influence of certain hormones, the level of which increases, on the functional state of the walls of the microcirculatory structures. After childbirth and normalization of hormone levels, telangiectasias do not disappear on their own, but require treatment.
2.Can breast lumps occur in men?
Yes. In men, breast enlargement may occur, often with the formation of a lump under the nipple. Sometimes it occurs in only one breast, but most often the disease affects both. This benign breast tumor in men
is called
gynecomastia
. Gynecomastia can appear, including after taking certain medications.
What to do if lumps or lumps are found in the breast?
In any case, if you notice any changes in your breasts, you should consult a doctor. A good specialist should examine you if you notice:
- An area that is visually different from any other area in both glands;
- A lump in or near the breasts that persists through the menstrual cycle;
- Changes in the size, shape or contour of the breast;
- Small, pea-sized lumps in the breast;
- Marble-like areas under the skin of the breast;
- Change in the sensitivity or appearance of the skin on the breast or nipple - wrinkled, scaly, flaky, or inflamed;
- Discharge from the nipples, including bloody ones;
- Redness of the skin of the breast or nipple.
Visit our Gynecology page
Causes of spots and additional signs: table of symptoms
If you find yourself with a spot, check the symptom chart. Some spots are not dangerous and do not even need to be treated. Others are a beacon of serious illness. A spot in the bust area may appear:
- due to allergies (food, care products, synthetic underwear);
- traumatic injury;
- insect bite;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- as a result of dyschromia (pigmentation disorders due to stress, metabolic disorders, ovarian dysfunction), for example, vitiligo;
- parasitic diseases;
- fungal infections.
| Spot color | Description of the spots | Additional signs | Possible cause of the problem |
| Red or pink | Purple spots between the breasts (breasts) | Scratches and pain | Tissue damage from bra underwire |
| Urticular (like tubercles) scarlet under the breasts, on the chest, back, neck | Severe itching, rapid increase in area of rashes | Urticaria (food allergy) | |
| Spots in the bust area, small in size, sometimes looking like small bumps or blisters | Sometimes itchy. Sometimes spots appear asymptomatically or due to insomnia | Excessive excitement. Stress Changes in temperature and humidity conditions | |
| Crimson small formations | Itching | Contact dermatitis | |
| Small spots on the bust and abdomen | Mild itching | Miliaria (appears in summer). Drug allergy. | |
| Spots on the bust, neck and abdomen | Itching, pimples, peeling | Eczema developed due to damage to the gastrointestinal tract, due to genetic predisposition or weak immunity | |
| Education in the field of mammary glands | Increase in local temperature, compaction | Lactostasis | |
| Single scarlet spots similar to herpetic formations | Itching, weeping, small bleeding sores, skin erosion and changes in the shape of the nipple | Paget's cancer | |
| Spots in the mammary glands | Hyperemia of the skin of the bust (redness), increased local temperature, thickening of the skin, swelling and pain | Erysipelas-like cancer, characterized by vascular reaction and rapid proliferation of atypical cells | |
| Protruding formation on the skin, congenital or acquired | No | Mole | |
| Minor rashes | Papules, weeping, itching, scabs (crusts) | Herpes | |
| Extensive lesions on the chest and under the breasts | Redness, itching, peeling | Fungus | |
| Redness in the breast area | Increase in local and general temperature, compaction | Mastitis | |
| Brown | Congenital formation, can be of any shape (usually round) from light brown to black | No | Birthmark (mole) |
| A growth that rises above the surface of the skin, pigmented tissue that is spongy | No | Wart | |
| Light brown formations on the skin are initially isolated, then spreading over the entire surface of the bust and abdomen | The spots are slightly flaky and itchy. | Versicolor/pityriasis versicolor | |
| Light-brown (less often scarlet-reddish) areas on the skin of the gland with a diameter of 10 mm, over time merging into one pigmented area the size of a palm | Reduction in the size of the affected gland, hardening and thickening of the skin | Armored cancer | |
| From light to dark brown spots of different sizes | Flat or slightly raised above the surface | Pigment spots. Age-related hyperkeratosis | |
| Blue | The formation looks like a hematoma, single | The compaction is palpable | Nodular form of cancer |
| Formation of blue, greenish, yellowish color | Pain, swelling. During the healing stage, the breasts are slightly itchy | Hematoma | |
| White | Spots of different sizes | White strand (piebaldism). Spots on the face, abdomen (vetiligo) | Leucoderma (piebaldism, vitiligo) |
| Depends on the cause of pigmentation changes | Consequences of psoriasis, favus, eczema, lichen | ||
| Consequences of stress or inflammation. Pigment cells (melanocytes) die due to acute vascular spasm | |||
| Black | Formations of different sizes, flat or raised above the surface of the skin | Sometimes hair grows from the formation | Melanocytic nevus (mole) |
| Formations of different sizes | Spots during pregnancy on the neck and chest of women | Chloasma (melasma) or melasma | |
| Hyperpigmentation (dark, almost black, coloration of the skin) | Symmetrical hyperpigmentation of the neck, feet, intergluteal fold, in the groin, around the lips and armpits, papillomatosis (extensive growth of papillomas), hyperkeratosis (thickening of the skin). | Acanthosis nigricans (negroid) |
Regardless of whether you have one small dark spot or your chest is covered with a scarlet rash, consult a doctor: a dermatologist, mammologist, allergist.
3.Diagnostics and treatment
Diagnosis of a benign breast tumor
A thorough breast examination by a doctor will help make an accurate diagnosis and rule out breast cancer. If the patient has nipple discharge
, they can be analyzed to help determine the presence or absence of cancer cells.
Imaging examination of the mammary glands - mammography
or ultrasound of the mammary glands - will help determine whether the tumor is a homogeneous solid mass or filled with liquid.
Sometimes a biopsy
– taking a sample of cells or tissue from the breast and further examining it under a microscope.
Treatment of benign breast tumors
The choice of treatment for a benign breast tumor depends on what type of tumor has been diagnosed.
Thus, fibrocystic changes
do not require treatment.
A simple cyst
can be treated with a fine needle, and manipulation is often performed during diagnostic procedures. A breast biopsy uses a small needle. Removing fluid from the cyst using a needle will make the cyst disappear.
Fibroadenomas and intraductal papillomas
can be removed
surgically
.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
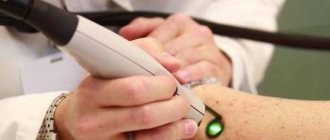
Spider vein removal
The basis of radical therapy for telangiectasias is their removal using various methods of physical or chemical influence, as well as taking measures to prevent re-exposure to the provoking factors of their development. High-quality removal is carried out in our medical center using the following methods:
- Sclerotherapy is the introduction into the lumen of the affected vessel of a special chemical compound (sclerosant), which leads to its gluing.
- Laser therapy is exposure to laser, which leads to “evaporation” of the tissues of the inner surface of blood vessels, followed by gluing.
- Electrocoagulation is the destruction of telangiectasia using local point exposure to electric current of a certain strength and frequency.
- Radio wave surgery – excision of the formation is performed, in which radio wave radiation plays the role of a scalpel.
The choice of method for removing telangiectasia on the chest is carried out individually by a phlebologist-mammologist.
4.Prevention of breast diseases
There are a number of simple rules that, if followed, will help maintain breast health and promptly identify possible problems:
- Women over 40 years of age should have an annual mammogram.
- Women at risk for breast disease should have screening mammography, starting at a younger age, at least once a year. Additionally, it is recommended to do an ultrasound of the mammary glands. In particularly high-risk cases, such as women who have a greater than 20% risk of developing breast cancer, an annual breast MRI may be required. Your doctor will help you decide on a set of specific diagnostic methods after analyzing all the information about your health.
- During an annual preventive examination of the body, women over 20 years of age should visit a mammologist who will examine the mammary glands.
Treatment methods
In medicine, there are three options: surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- The area infected with the tumor is surgically removed. Here, a distinction is made between organ preservation (removal of the site of infection) and mastectomy (removal of the breast).
- Radiation therapy uses radiation.
- Chemotherapy uses special drugs. Depending on the stage of the disease, these methods can be used either separately or together.
It is also important to conduct preventive examinations, both with a doctor and to independently perform self-examination of the mammary glands
Brown and dark spots
First, you can replace one small spot on your chest that is slightly peeling. As a result of the development of the disease, their number and size increase, and peeling intensifies. They begin to itch, hurt and itch. The causes of brownish spots may be:
- Allergy
- Cancer
- Lichen
- A bite of an insect
- Regular stress
If you do not pay attention to the spots from the moment they appear, the brown spots begin to merge into one whole
It is better to pay attention to the disease immediately so as not to cause a worsening of the condition. Brown spots can be birthmarks, in this case there is no reason to worry or need treatment