Many of us are familiar with the phenomenon of white spots, spots or small bumps under the eyes. People also call them millet grains because of their resemblance to millet grains. In medical language, their name sounds different - these are milia. They only cause aesthetic inconvenience. What is the reason for their occurrence? Aren't such formations dangerous?
Milia are small white dense balls on the upper and lower eyelids, and in some cases on other areas of the face. Their distribution area depends on the oiliness of the skin. In addition to the eyelids, they can also appear under the lower lip, around the nose, and less commonly on the forehead. The balls do not cause pain, do not change in size, but do not go away, even if you try to squeeze them out. In fact, milia are just a type of acne that can remain on the face for a long time and very rarely disappear on their own. Of course, these formations spoil the appearance and cause aesthetic inconvenience. Why do they arise?
What is a pinguecula of the eye?
A pinguecula is an elastic, compacted yellowish formation that appears in the nasal part of the conjunctival membrane of the eye (in the area of contact with the cornea). It is a mistake to associate this pathology with various types of tumors, since only in rare, especially advanced cases, such a change in the conjunctival membrane can become malignant.
Pinguecula is classified as a benign disease, usually affecting both eyes but not affecting visual acuity.
The worldwide prevalence of this eye pathology is extremely high. Doctors note that with pinguecula of the eye, the causes and treatment may vary. As a rule, the disease manifests itself in the form of a whitish or yellowish growth. If the neoplasm occurs on the protein membrane, it is called a pinguecula, but when it is localized on the cornea, forming a wing-like structure, it is called a pterygium. In fact, pinguecula represents only a slight change in eye tissue due to the increased content of fats and proteins in the body, so often the growth does not affect the cornea and does not cause pain - the disease is asymptomatic. But it cannot be said that the pathology is entirely harmless - it brings aesthetic inconvenience, since it is noticeable to others, and also often causes chronic irritation of the organs of vision.
In general, the disease is not dangerous. It rarely causes dysfunction of the visual apparatus and even less often develops into a malignant tumor, but sometimes it is necessary to treat the pinguecula. In the article we will consider in what cases and what therapy doctors prescribe.
Information about the described pathology first appeared in 1550 BC. It is interesting that from those ancient times, records of the Egyptians have been preserved, who described the pinguecula as “specific fatty deposits in the eye.” Modern doctors believe that the disease can develop due to genetic predisposition or occur in an isolated form. Pathology is diagnosed equally in women and men. People living in countries with hot and dry climates are at particular risk.
Pinguecula: is treatment required?
Depending on the characteristic symptoms, the doctor, after taking an anamnesis, will understand how serious the stage the pinguecula has reached. Treatment is prescribed individually. The frequent lack of indications for removal of the growth is explained by the fact that in the vast majority of cases, the pinguecula is an elastic formation of a benign type.
Often the course of the disease is not accompanied by severe symptoms, other than the formation itself on the conjunctiva. However, sometimes inflammation occurs due to the pinguecula. It is diagnosed in the following cases:
- Dry eye syndrome;
- The presence of a foreign object in the affected eye;
- Scratching and irritation (especially when blinking);
- Redness at the site of damage.
Chalazion of the lower eyelid: symptoms
Inflammation with this disease always appears at the edge of the eyelid, closer to the outlets of the sebaceous glands . With this disease, a dense node forms on the lower eyelid, which can be 5-6 millimeters in diameter (less often – 7 millimeters or more).
Basically, such formations do not protrude outward, but inward, and put pressure on the eyeball.
Due to the possible complications and consequences of such pressure, chalazion inside the eyelid must be treated immediately when the following characteristic symptoms are detected :
- itching and burning in the lower eyelid area;
- involuntary lacrimation;
- swelling and redness of the affected eyelid;
- sometimes – a slight increase in general body temperature;
- in the first days of the development of the disease there is no pain, but after a while, when you press a finger on the formed nodule, the area of pressure will hurt.
Unlike a chalazion of the upper eyelid, in which the nodule is clearly visible, in this case the disease is not so obvious and more closely resembles a typical stye, while due to the structure of the visual organs, the chalazion of the lower eyelid adheres more tightly to the eyeball .
This is fraught not only with the consequences of pressure on the eyeball, but also with the likelihood of infection of the mucous membrane of the eye.
Important! In the absence of treatment, the disease inevitably turns into the form of a cyst filled with mucous contents, but sometimes it does not reach this point, and the swelling nodule opens itself, which also risks the entry of an infected mass onto the mucous membrane.
Causes of the disease
It is quite difficult to talk about the etiology of pinguecula, since it has not been fully studied. The disease in most cases develops against the background of progressive dystrophic or age-related changes occurring in the conjunctiva. Since the body's metabolic processes slow down with age, the rate of metabolism, including proteins and fats, decreases. Together, this leads to unwanted accumulations of these components, which contributes to the development of pinguecula.
Experts identify in the pathogenesis of this eye disease the degeneration of collagen fibers located in the stromal part of the conjunctiva, and the thinning of the epithelium as a consequence. This kind of change can be influenced by ultraviolet radiation, which is known to stimulate the production of fibrillar protein - elastin. It is synthesized by fibroblasts and, in turn, negatively affects the structure of the conjunctiva, leading to dystrophic changes.
Pinguecula often affects people who are exposed to the scorching rays of the sun for a long time.
Pinguecula can be the result of recurrent irritation of the conjunctiva by exhaust gases, smoke, ordinary wind, all kinds of toxic emissions (in particular industrial emissions), as well as chemicals. Some ophthalmologists believe that prolonged wearing of contact lenses also provokes the formation of tumors on the eye. But a number of studies have been conducted on this topic, the conclusions of which did not confirm the reliability of this theory. In addition, the pinguecula is formed against the background of injuries and scar changes in the membrane of the eye, as well as chronic inflammation (conjunctivitis). In approximately 50% of cases, the disease develops in the same form in both eyes, but it is characterized by relatively weak progression abilities (i.e., the growth barely noticeably increases in diameter), as well as a benign nature. With a small size, the pinguecula does not in any way affect the patient’s life.
At the initial stage of development, this pathology is characterized by a latent (asymptomatic) course, while the clinical manifestation is noted already with an increase in the volume of the tumor. Patients may also complain of some discomfort, manifested by a feeling of excessive dryness in the eye. In cases where the growth grows and causes discomfort to the patient, the ophthalmologist may recommend surgical removal of the pinguecula of the eye.
With periodic irritation of the growth, conjunctival hyperemia may appear - the person complains of a constant sensation of a foreign object in the eye, which leads to increased lacrimation. Rarely, this pathology provokes clouding of the cornea.
How to treat pinguecula on the eyes?
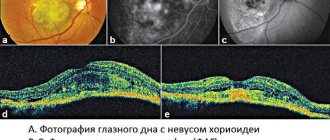
The disease is diagnosed based on anamnestic data, the results of an external examination of the visual apparatus and the Ferning test, as well as data obtained during biomicroscopy, fluorescein angiography or OCT (optical coherence tomography). After conducting an initial external examination, the doctor discovers a rounded formation with a yellowish tint. With biomicroscopy, a specialist can identify a translucent formation at an early stage, when it is practically devoid of trophism. OCT involves determining the degree of penetration of the growth into the internal structures of the affected eye, as well as the shape, diameter and size of the formation. The Ferning test will help the doctor examine the visual system for the presence of uncharacteristic, abnormal components in the tear film. The fluorescein angiography method will allow you to visually determine possible disturbances in microcirculation processes in the medial part of the conjunctiva.
There are several stages of this pathology, distinguished by the nature and severity of the course.
Depending on the cause of its appearance, treatment of this disease can be carried out in different ways - conservative or surgical. The choice in favor of one method or another is determined both by the attending physician and based on the special wishes of the patient.
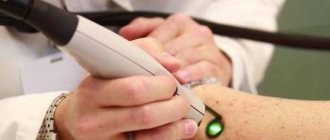
Conservative therapy helps alleviate the symptoms of the disease (it is mainly aimed at reducing the severity of irritation of the eyeball). For this purpose, special eye drops or gel-like substances are often prescribed - artificial tear preparations, which provide hydration of the mucous membrane at the proper level, reducing the severity of the corresponding symptoms. Hormonal medications can alleviate the condition. Less often, the ophthalmologist prescribes antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to the patient. Refusal to wear contact vision correction devices during the course of the disease will help eliminate feelings of discomfort. When pathology develops, experts do not recommend using traditional methods. If the patient wants to completely get rid of the tumor in the eye, then treatment can be offered to him in the form of surgical intervention. A safer and almost painless method of therapy against the background of standard surgery is laser removal, in which:
- No bleeding;
- There is a rapid rehabilitation period;
- No scars.
Is it possible to remove whiteheads at home?
Never try to get rid of acne on your own by piercing or squeezing it. Firstly, this way you won’t be able to remove them anyway, and secondly, a very painful redness will form at the site of the squeezed pimple, and the appearance will become even worse. In addition, there is a high probability of infection under the skin. Scars may also remain at this location.
Is there an effective prevention of pinguecula?
To reduce the risk of pinguecula formation, experts advise remembering to wear high-quality sunglasses in open spaces and free exposure to UV rays. A proper diet helps normalize metabolic processes in the body, which will also reduce the likelihood of developing pathology. If a person lives in hot and dry climates, it is necessary to take care of additional eye hydration using special drops, ointments or other preparations.
As for the prognosis of working capacity and life activity with pinguecula, they are very favorable - the neoplasm often does not affect the quality of life and does not provoke a decrease in visual acuity.
The Ochkov.Net website offers a wide selection of contact lenses. We recommend choosing models with a UV filter, such as Acuvue Oasys with Hydraclear Plus or 1-Day Acuvue TruEye.
How are whiteheads removed?
The cosmetologist will carefully study your skin type and suggest one of the existing methods for removing acne. Their effectiveness is the same, but there is a difference in the cost and duration of the procedure:
- Mechanical removal - the doctor makes a puncture with a thin sterile needle and squeezes out the contents of the eel. The procedure takes quite a long time (no more than 10 blackheads at a time) and is not suitable for people with thin or overly sensitive skin. Currently it is hardly used.
- Electrical coagulation - the balls are destroyed by cauterization with high-frequency electric current. The procedure is suitable for removing blackheads that are too deep. All milia can be removed in one or two sessions. As a result of cauterization, a small crust forms, which must be wiped with an antiseptic for 10 days; it will then fall off on its own.
- Laser coagulation is the most modern method of removing whiteheads. It is especially advisable if there is a large accumulation of them or if they are located in sensitive areas (for example, on the eyelids, very close to the eyeball). The laser will allow layer-by-layer removal of formations without thermal or mechanical effects on surrounding healthy areas. With this method there is no risk of relapse, as with mechanical removal.
To prevent the formation of milia in oily skin, you need to carefully select facial care products, and also limit the consumption of too spicy, smoked, and sweet foods. If whiteheads appear, do not try to remove them yourself, so as not to cause even more harm to the skin. Modern cosmetology will help solve this problem.