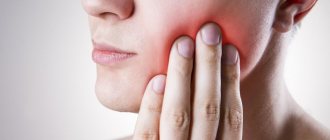
Atheroma on the face is not just a cosmetic defect. It occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. If infection penetrates inside, purulent inflammation may develop. Inflammation of atheroma on the face is very dangerous, especially if the process is located above the line of the mouth. This is due to the peculiarities of the blood supply to the head. The veins of the face drain into the venous sinuses of the skull, which leads to the rapid progression of the disease and the development of abscesses in the brain. The degree of danger of atheroma depends on other factors, including the size of the formation and the presence of underlying chronic diseases, such as diabetes. Therefore, when facial atheroma appears, treatment should only be carried out by a doctor.
Rice. 1 Facial atheroma occurs due to blockage of the sebaceous glands
Diagnosis of atheroma on the face
Atheroma looks like a small subcutaneous ball. The tumor itself does not resolve and gradually increases. With long-term existence, atheroma on the face can reach 7 cm in diameter. On its surface you can always see a black dot that blocks the sebaceous duct. Atheroma has clear boundaries and a spherical shape. The patient does not feel pain upon palpation. Visually, atheroma is similar to lipoma, hygroma, fibroma, hemangioma, so a doctor must make an accurate diagnosis. If there are difficulties in diagnosis, an MRI may be prescribed to determine the nature of the tumor. After removal of any formation, including atheroma, a histological examination is carried out.
Rice. 2 Atheroma looks like a small ball under the skin of the face
Could the lump be a herniated disc?
Lumps localized along the spine may well be a large intervertebral hernia or protrusion. These are protrusions and protrusions of the jelly-like core, which fills the intervertebral disc and is held in place by a fibrous membrane in the form of a ring. The pathogenetic factor in the formation of a hernia is dehydration and degeneration of the intervertebral disc, which develop against the background of impaired blood circulation, a sedentary lifestyle, chronic diseases of the spine and musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis, osteosclerosis, osteoporosis, etc.).
Formation of intervertebral hernia
Clinically, the hernia may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, but if the size of the protrusion exceeds 5-7 mm, the patient begins to notice pronounced pain and neurological disorders. With large hernias, the clinical picture usually consists of the following symptoms:
- stiffness in the muscles and joints of the spine, which does not go away within 10-15 minutes and usually occurs after prolonged rest (usually after sleep);
- back pain that can radiate to the arm, shoulder, lower limbs and buttocks (radiculopathy, radicular syndrome, lumbago, lumboischialgia);
- paresis, paralysis, tics, tremors and other neurological disorders in the lumbar region and limbs;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs (fecal and urinary incontinence).
Herniated disc
If the hernia has formed in the upper back (cervical and thoracic spine), specific symptoms associated with compression of the basilar and vertebral arteries also appear: dizziness, migraine, headaches, arterial instability. Hernias in the thoracic spine can cause pain in the chest area (thoracalgia) as well as difficulty breathing.
Note! You can visually notice a hernia in the form of a protruding subcutaneous lump on the back in cases where its size exceeds 10-20 mm. Of great importance in the ability to identify a formation as a result of a visual and physical examination is the constitution of the body and the localization of the hernia: in slender patients, as well as patients with hernias and protrusions in the cervical spine, a volumetric protrusion on the back is detected almost 4 times more often than in obese patients.
Microsurgical treatment of intervertebral hernia
The danger of atheroma on the face
Sebum and keratin masses accumulated in the atheroma capsule have a cheesy consistency. This is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria. An attempt to squeeze out the atheroma can lead to infection getting inside the capsule and causing suppuration. The main symptoms of its onset are:
- redness of the skin around the atheroma;
- pain in the affected area;
- Migraine-like headaches;
- temperature increase.
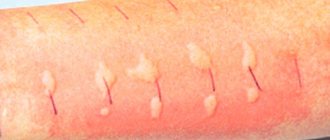
Inflamed atheroma can lead to phlegmon - inflammation of adjacent tissues without precise boundaries.
Rice. 3 Self-squeezing of atheroma usually leads to inflammation of facial tissues
Rheumatic bumps
Painless bumps in the form of subcutaneous nodules can be a manifestation of erythema nodosum, characteristic not only of rheumatism, but also of some severe infectious diseases, for example, erysipelas or tick-borne borreliosis. Rheumatism is a connective tissue disease in which mainly the membranes of the heart become inflamed, as well as large joints, such as the joints of the legs, knees or hip joints. Rheumatism of the back is diagnosed quite rarely and accounts for no more than 8.4% of the total number of patients with this diagnosis.
Clinical signs of erythema nodosum
Cones with rheumatic inflammation of the spine are painless, have a dark red, purple or burgundy color and clear contours. The structure of the formations is dense, motionless (less often, inactive). The size of the nodules can range from a few millimeters to a chicken egg, and their occurrence is preceded by high fever and other symptoms, which may include:
- intense aching pain in the back (mainly in the area where the nodules are located);
- progressive curvature of the spine;
- numbness, trembling in the limbs;
- pale pink rash;
- minor hemorrhages against the background of increased pallor of the skin;
- increased sweating.
Nodules on the skin
The disease is caused by an infectious pathogen - group A β-hemolytic streptococcus - and often develops after illnesses of the oropharynx (sore throat, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, pharyngitis).
Treatment of facial atheroma
Getting rid of atheroma using traditional methods of treatment, drugs of different release forms, or self-dissection is ineffective and dangerous . Atheroma can only be removed surgically along with the capsule. The smaller the formation, the easier the procedure will be and the greater the likelihood of being left without a scar on your face. Several methods of operating on atheroma on the face are practiced.
- Laser destruction of atheroma is the most effective and painless treatment method, after which there is no scar. Used to remove formations with a diameter of up to 5 mm.
- Laser excision of atheroma is an innovative treatment method that does not require a recovery period.
- The classic operation with a scalpel is the removal of atheroma. It is performed under local anesthesia.
During the inflammatory process, the doctor cleans out the contents and disinfects the atheroma cavity, then performs an operation to remove the capsule and, if necessary, the affected tissue. Even if the atheroma does not bother you and “does not spoil the beauty,” it still needs to be removed. Pressure on nearby tissues causes them to become deformed, and the possibility of inflammation puts your health at risk.
Inflammatory processes
Pus-filled, painful bumps on the back can also be boils or carbuncles. These are purulent-necrotic inflammatory processes in the hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands, which often involve the surrounding connective tissue. One of the main reasons for the occurrence of boils and carbuncles is lack of personal hygiene (irregular showering) and microtrauma of the skin, through which microbes and bacteria enter the hair follicle. In 60-70% of cases of furunculosis, the causative agent of the inflammatory process is Staphylococcus aureus, so treatment of boils and carbuncles may include antibiotic therapy.
What does a boil look like?
You can understand that a purulent lump on the back is the result of an inflammatory process by the following signs:
- the presence of red erythema around the formation and a purulent core in its center;
- severe pain even with mild exposure to external irritants (for example, upon contact with clothing);
- Predominant localization - on the back, back of the head and neck;
- rejection of necrotic tissue with subsequent scarring.
"Flemoxin"
Boils are treated comprehensively. To eradicate the infectious pathogen, penicillin antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Flemoxin) are used. If the abscess has opened, a bandage with a hypertonic solution is applied on top. This is the name of a solution with a higher concentration of dissolved substances and a higher osmotic pressure. After draining the wound, dressings with tetracycline or erythromycin ointment are used topically. If the boil has just appeared, the use of physiotherapeutic methods (dry heat, ultra-high frequency therapy) and ichthyol ointment, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effect, is indicated.
Erythromycin ointment
If you want to know in more detail what types of pain-relieving ointments for the back there are, and also consider the composition and application, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Features of the Lakhta Milon laser
Modern science has long appreciated all the advantages of using lasers in medicine. Therefore, today new, more advanced devices are constantly appearing, one of which is the domestically produced Lakhta Milon device.
With its help, you can perform minimally invasive operations in the shortest possible time, differing in:
- high degree of security,
- efficiency,
- speed,
- short recovery period,
- no need for general anesthesia.
How common are cutaneous and subcutaneous cancer metastases?
In visceral (located in internal organs) malignant tumors, subcutaneous metastases are found in 5.3% of all cases of metastatic lesions of various locations. Secondary skin lesions account for even less - about 0.7–0.8%. Although, in some scientific studies, the authors indicate figures of up to 9%. In 2003, a meta-analysis looked at 1,080 cases of cutaneous cancer metastases in 20,380 patients. The authors suggested an incidence of 5.3%.
In general, at the moment there is no exact unambiguous data on how common skin metastases of cancer are. More recent scientific papers provide higher figures. But scientists do not believe that skin metastases have begun to occur more often in cancer patients - they are simply being diagnosed better now.
Among all malignant skin tumors, 98% are primary tumors and only 2% are metastatic lesions.
Anatomy of the wrist joint
The anatomy of the wrist joint and carpal bones is extremely complex, probably the most complex of all joints in the human body. The joints and bones of the wrist allow us to perform a variety of movements in all planes. At the same time, the wrist ligaments must provide strength to the joints.
The wrist is made up of eight individual small bones called carpal bones. The bones of the wrist are connected on one side to the radius, on the other they are connected to the metacarpal bones.
Ligaments hold all the bones of the wrist together and allow the hand to move in all directions. These ligaments fuse together to form the wrist joint capsule. The joint contains a fluid called synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint surfaces as they move against each other. Almost all movements of the hand are transmitted by the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles. Hygroma, increasing in size, usually pushes apart the surrounding tissues, tendons, and ligaments. Like a ball containing intra-articular fluid (hyaluronic acid).
70 percent of carpal hygromas form on the back of the wrist.
Hygroma of the palmar surface of the wrist or wrist joint is much less common and is usually localized in the projection of the radial artery - where the pulse is checked.
A ball-shaped seal under the skin - how to get rid of it: reviews
Reviews:
- Olga: “I recently discovered a small ball on my neck. It was tight. I went to the doctor, he said that it was an ordinary wen, and advised me to remove the formation. The operation lasted no more than 10 minutes. Everything went well".
- Svetlana: “A small ball appeared on my knee. The doctor who examined me said that there was nothing wrong. He recommended doing compresses and prescribed taking anti-inflammatory medications. The ball disappeared a month later.”
- Oleg: “When I was a child, I was diagnosed with a lump on my neck. Mom was very worried, the doctor said that it was an inflamed lymph node. He prescribed me a treatment that gave excellent results. After a couple of weeks I completely forgot about the bump.”
What to do if there is a ball under the skin?
- If the doctor discovers a lipoma , he prescribes surgery. The seal can be removed using laser, ultrasound, radio waves, cryogenic destruction. In addition, the patient is prescribed vitamins, immune and anti-inflammatory drugs. Plus the doctor prescribes a hormonal drug. The patient also adheres to a special diet.
- Hygroma is treated with paraffin heating, mud compresses, and electrophoresis. If the case is advanced, a glucocorticoid is injected into the affected area and the pus is sucked out.
Treatment
- A bandage with a special ointment to the area where atheroma , and the area is treated with an antibacterial agent. You can remove peeling and itching with hormonal medication. If intoxication begins, the doctor prescribes an antipyretic drug.
- A small ball is removed with a resolving injection. It could be a hormonal medication. It is introduced precisely into the area where the seal is located. Small balls are not always eliminated. In some cases, the contents of the ball are simply pumped out, and the patient undergoes a course of therapy.
- Folliculitis , as a rule, is treated very simply - just follow the rules of hygiene and eat right. If the disease is advanced, the area is treated with an antibacterial agent.
How dangerous is metastasis to the skin?
Skin metastases in cancer are rare, and their appearance always indicates an aggressive malignant tumor, advanced disease and worsening prognosis. Thus, in one study involving 4020 cancer patients, it was found that from the moment of detection of skin metastases, the average life expectancy of patients ranged from 1 to 34 months, depending on the type and characteristics of the primary tumor.
In another study of 228 patients, the median survival for cutaneous metastases was 6.5 months. The indicators for individual types of cancer were:
- squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (except skin) - 8.8 months;
- squamous cell skin cancer - 6.5 months;
- esophageal cancer - 4.7 months;
- colon and rectal cancer - 4.4 months;
- pancreatic cancer - 3.3 months;
- stomach cancer - 1.2 months;
- liver and gall bladder cancer - less than 1 month.
Survival rates for breast cancer turned out to be the highest - 13.8 months after the start of observation, 50% of patients were alive. For melanoma, this figure was 13.5 months, and for lung cancer - 2.9 months. Some patients with breast, simplex, larynx, squamous cell skin cancer and melanoma were able to live more than 10 years. The worst survival rates were observed for lung cancer.
As you can see from these data, everything is individual. In general, the best prognosis for skin metastases is observed in patients with malignant breast tumors. In recent decades, survival rates have been improved with the use of more modern chemotherapy drugs. The clinics of the federal network "Evroonko" use the most modern treatment methods, original antitumor drugs of the latest generations. This allows for the best survival rates among patients with metastatic cancer.