Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the groin area is called inguinal lymphadenitis.
This process almost always signals acute inflammation in the area of the external and internal genital organs.
The presence of clinical signs of such inflammation (dense, painful nodes in the lower abdomen in the area of the inguinal ligaments) requires an in-depth examination, identification of the causes of lymphadenitis and their treatment.
In most cases, it is a consequence of a pathological process in the area of the external and internal genital organs.
The presence of clinical signs of such inflammation (dense, painful nodes in the lower abdomen in the area of the inguinal ligaments) requires an in-depth examination, identification of the causes of lymphadenitis and their treatment.
In order to identify the causes and subsequent effective treatment aimed at eliminating the impact of the main etiological factor.
The main causes of inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are represented by lymphoid tissue, which contains cells of the immune system.
They perform a protective function by collecting and purifying lymph, which flows through lymphatic vessels from certain areas of the body.
That is, these important organs of the lymphatic system serve as something like filters that prevent pathogenic agents from spreading throughout the organs and systems of the body.
Inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes develops due to the presence of foreign agents (bacteria, viruses, protozoan unicellular microorganisms, cancer cells) or toxins in the lymph, the outflow of which occurs from:
- pelvic organs, primarily the internal genital organs
- rectum
- tissues of the groin area (external genitalia, skin, subcutaneous tissue and connective tissue)
A common cause of the inflammatory pathological process of tissues and organs of this localization is an infection with sexual transmission.
The source of infection can be located in any part of the genital organs, in the rectum, in the groin area, or thighs.
Inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes can be caused by several groups of pathogens of sexually transmitted infections:
- Specific bacteria - chlamydia, Treponema pallidum, mycoplasma, ureaplasma.
- Herpes simplex virus, human papillomavirus.
- The simplest unicellular microorganisms are Trichomonas .
- Fungi, in particular yeast, candida.
A peculiarity of these pathogens is their localization in the structures of the urogenital tract.
In addition to such microbes, inflammation in the groin is also caused by nonspecific flora - strepto and staphylococci, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella, Proteus and others.
During their life, toxins, as well as the microorganisms themselves, can enter the inguinal lymph nodes with the lymph flow, causing their inflammation.
Inguinal lymphadenitis can be the result of an infectious process caused by a nonspecific bacterial infection (staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli).
Which does not have strict specificity for the organs of the genitourinary system.
Sometimes inflammation of the lymph nodes develops as a result of an oncological process (the formation of a malignant neoplasm) in the organs of the urogenital tract.
Lymphadenitis - a lump in the groin area
11.11.2021
There are many unusual inflammatory tumors, malignant and benign neoplasms on the human body. Neutralizing each of them requires its own special approach. A lump in the groin area can be represented by either a small swelling or a massive formation.
In any case, such an anomaly should be shown to an experienced doctor . During the examination, the latter will probably prescribe a number of medical procedures. Well, then everything will depend on the type of growth that appears. Most likely, the formation will disappear on its own after a few days, but there are situations when surgical removal is clearly unavoidable.
Lump in the groin in men - causes and treatment
A lump in the groin in men is the very first symptom of inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes. And in this case, it clearly smells like hernia Diagnosis of such a disease is carried out through self-examination or medical examination. This will only give a superficial idea of the severity of the disease. Next you need to undergo a more serious examination.
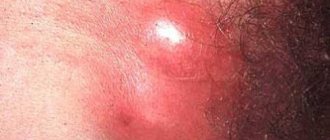
This type of formation appears in men in the upper part of the inguinal fold. The size of their healthy lymph nodes can be compared to a bean, but when it becomes inflamed, the size increases, literally, to a walnut. When a lump appears in the groin, males feel a sharp or dull pain in this area. In addition to the above symptoms of the inflammatory process, there is also a significant increase in body temperature.
Lymphadenitis in the groin area can occur due to infection with a variety of genital infections. Among the latter, viruses are often observed. In this case, treatment will be more predictable than in the presence of malignant or benign tumors. Lymph nodes can become inflamed during prostatitis . And during the course of various types testicular A male lump in the groin is more rarely observed as a consequence of swelling of the scrotum. But for children (boys), this disease is explained by the fact that the testicle does not descend from the abdominal cavity.
Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the male inguinal lymph nodes), which appears between the groin and also the leg, can be removed by modern doctors not only through surgery. There are many medications on sale, the use of which promotes complete resorption of inflammatory formations.
A lump on the pubis in representatives of the stronger sex may also appear after a sudden weakening of the muscles that are located in the wall of the abdominal cavity. Moreover, such a nuisance can provoke not only enormous physical exertion, but even a severe cough. Because of all this, intestinal loops often protrude directly under the skin. Thus, a hernial sac is literally instantly formed and unprecedented pain appears in the groin, which is unbearable. When a hernia is subjected to excessive stress under the influence of physical stress, the skin that is located above it swells very quickly, acquiring a red tint. If a hernia is strangulated, you obviously cannot avoid surgical medical intervention.
Lump in the groin in women - causes and treatment
A lump in the groin in women can also occur due to a variety of factors. There are a lot of variations in the process of treating a lump near the groin. Most often, representatives of the fairer sex discover such formations on their own. Well, then, it’s up to the doctors . Most likely, they will diagnose you with harmful enlarged lymph nodes. In this case, it is necessary to identify the causes of damage to these natural protective barriers of the body. Viral infections are considered the most common of them.
In case of inflammatory processes in the organs of the female reproductive system, a lump under the skin in the groin can be treated faster and more productively than in the case of cancer. The most trouble awaits you when malignant processes appear in the body. Even the use of high-precision instrumental examination, including computed tomography or biopsy, does not always help to identify all the nuances regarding tumors.
And finally, remember that it is better to show the above abnormal formations that appear on the body to a doctor , since only medical professionals can promptly save you from the serious consequences of illnesses. And it doesn’t matter whether the lump is in the groin on the right, left or in the center - the main thing is that such an anomaly needs to be eliminated.
Published in Lymphology Premium Clinic
Clinical manifestations
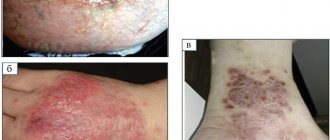
Inguinal lymphadenitis, as a rule, is acute. The process can be one-way or two-way.
In this case, inflammation of the lymph nodes is accompanied by the following symptoms:
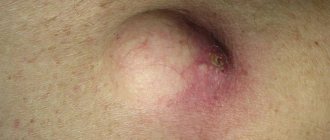
- The appearance of enlarged formations under the skin in the groin area.
- The size varies - from a large bean to a pigeon egg.
- Pain when moving the hips or palpating the lymph nodes.
- Redness of the skin over enlarged lymph nodes.
- The general condition may change - the temperature rises, weakness appears.
In severe cases, inflammation leads to the fact that these immune filters are soldered together into large conglomerates.
This is followed by their abscess formation and the formation of cavities filled with pus.
Sometimes inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes is noted earlier than signs of the infection itself appear; this is typical for syphilis and herpes.
But more often, everything happens the other way around - in the groin , perineum or thighs, which then leads to the development of inguinal lymphadenitis.
Treatment
The course of treatment is selected strictly individually and is aimed at eliminating the cause of the lump in the perineum. If a patient has a bacterial infection, the doctor needs to determine the causative agent. For this purpose, bacteriological culture .
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Depending on the type and properties of the pathogen, the appropriate antibiotic is selected. It is important to know that while taking antibiotics, it is also important to take drugs that restore intestinal microflora. Such drugs are also prescribed by a doctor.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Treatment of perineal hernias is usually surgical, that is, surgery is necessary. This operation is performed under general anesthesia using a combined method.
Most often, perineal hernias occur repeatedly, so patients with a removed hernia still need to undergo examinations from time to time.
Removing fatty tissue is the task of cosmetic surgery. Depending on the size of the wen, it can be removed in different ways, such as:
- liposuction
- laser removal
- radio wave surgery
- simple surgery _
The situation is much more complicated with the elimination of tumors and cysts of the perineum. Comprehensive treatment is very important here; before and after surgery to remove the tumor (if possible), a course of radiation therapy and chemotherapy is carried out.
The likelihood of recovery depends on the stage of the tumor and the presence of metastases. The sooner the patient turned to the doctor for help, the greater the likelihood of recovery.
Nonspecific infections
The groin area is far from sterile.
Therefore, inflammation of the lymph nodes in this area can be caused by “ordinary” pyogenic flora.
Inguinal lymphadenitis accompanies:
- Purulent skin infections (streptoderma and pyoderma) of the groin.
- Boils of the pubis, perineum.
- Carbuncles.
- Ingrown hair.
We must not forget about nonspecific genital infections.
Pyogenic flora in women leads to inflammation of the glands of the vestibule of the vagina (bartholinitis), in men it causes infectious lesions of the foreskin and coronary sulcus.
For nonspecific infections, it is almost always characteristic that symptoms of inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes appear after or simultaneously with the development of an acute process - a wound, ulcer, abscess.
Diagnostics
If lumps appear in the perineum, you should contact dermatologists, surgeons and urologists (gynecologists). When taking a medical history, you should definitely mention all chronic and recent infectious diseases at your doctor’s appointment.
It is important to remember to mention any medications you have taken recently, as well as your living conditions, if necessary. Do not be afraid of questions from doctors, since all information is confidential and may be needed to determine the source of the disease.
The doctor can examine the tumor using palpation . Then a series of instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed:
- ultrasound examination of the genital and pelvic organs;
- urethral smear
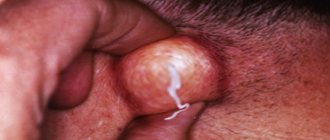
- puncture of the lump (if an atheroma is suspected) or taking a piece of tissue from the lump (if a tumor is suspected).
A number of general tests are required (general and biochemical blood tests, urine tests).
The powers of traditional medicine
For such a disease, home methods will have little effect. It is acceptable to treat furunculosis on your own, being sure that it is he. However, if the cause is any other disease, you should not trust herbs and compresses.
If the “fraction” is accompanied by itching or burning, then you can reduce the discomfort with the help of chamomile infusion. To do this, you need to pour 2 tablespoons of the plant with 2 cups of boiling water and let it brew for 5 - 6 hours.
Then moisten gauze or cotton wool with the broth and apply to the site of irritation. The lump will not change in size, but the itching will become less, probably absent for 2 - 3 hours. In fact, there will be enough time to get to the doctor.
It is possible to use therapeutic exercises. Effective for inguinal hernia, but does not relieve the problem. The real result is that the “sphere” will not increase, but will not dissolve either.
Complications
Complications of lumps in the perineum can be very different depending on the source of their appearance.
If the cause of the lump is an inflamed lymph node, the inflammation, in the absence of adequate treatment, can spread throughout the body. This leads to weakened immunity, as a result of which you can become infected with several more similar infections.
All this is accompanied by a persistent increase in temperature, fever, chills, increased sweating, loss of strength and loss of appetite. The body will desperately try to cope with the infection on its own. Whether this will lead to recovery over time is unknown.
If the hernia is not removed on time, it can also cause a lot of trouble. As the hernia grows, movements will become more constrained, and in order to sit or lie down without pain, it will be necessary to occupy a certain position.
A hernia can compress the nerve trunks, arteries and veins located in the perineal area, which will lead to increased pain.
If the lump turns out to be a wen, then if personal hygiene is not observed, it, although rarely, transforms into a tumor called liposarcoma. This is accompanied by severe discomfort and requires surgical intervention.
An advanced tumor is the most dangerous. It is precisely because any neoplasm can turn out to be a tumor that if lumps appear on the body, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
A tumor is dangerous because of its metastases, which can spread throughout the body at different speeds and unpredictably, killing healthy cells of the body.
Why do the labia swell?
Physiological reasons
Sometimes swelling is caused by wearing underwear that is uncomfortable or irritates the skin. Shaving and various types of hair removal of the intimate area can act as a provoking factor. The labia are abundantly supplied with blood; against the background of arousal, blood rushes to the erogenous zones, so swelling occurs during sexual intercourse, masturbation, and erotic fantasies. The normal appearance of the external genitalia is restored within 1-2 hours; with prolonged stimulation and the presence of certain individual characteristics, changes can last up to 10-12 hours.
Pregnancy and childbirth
Swelling of the labia during gestation is more noticeable in the second and third trimester, due to increased blood circulation in the pelvis. The labia look somewhat swollen, there is no pathological discharge or unpleasant odor. Another possible cause of the symptom is varicose veins of the labia due to pressure from the uterus. Swelling of the perineal area after childbirth is associated with the passage of the fetus through the birth canal and disappears within 2-3 weeks.
Bartholin gland diseases
The first symptoms of Bartholinitis are limited swelling and hyperemia of the labia minora in the area of the exit of the Bartholin gland duct. Then the lower third of the labia majora on the same side swells, and scanty purulent or serous discharge appears. Malaise, fever up to subfebrile levels, and slight discomfort while walking are possible.
When an abscess of the Bartholin gland forms, the swelling quickly increases and becomes diffuse. A woman complains of intense jerking pain that gets worse when sitting and walking. The pain decreases slightly when lying on your back with your legs apart. Body temperature rises to febrile levels. Palpation reveals a sharply painful elastic tumor-like formation, sometimes reaching the size of a chicken egg.
Small Bartholin gland cysts are asymptomatic. As the formation increases, there is a sensation of a foreign body in the perineal area, and the likelihood of injury and the development of an inflammatory process increases. Inflammation of the cyst and surrounding tissues is accompanied by swelling of the labia on the affected side.
Inflammatory diseases
In acute vulvitis, severe swelling and hyperemia of the clitoris and labia are observed. The formation of erosions and ulcers, the spread of inflammation to the area of the inguinal folds and the inner surface of the thighs is possible. Patients complain of burning, itching, pain, which intensifies with movement and touch. Infection with cocci is accompanied by profuse whitish-yellowish leucorrhoea. With candidiasis, the discharge is curdled, white, in the form of loose flakes.
Along with nonspecific pathogens, vulvitis in girls can be caused by helminths. With chronic vulvitis in children and adults, all manifestations are smoothed out, swelling is moderate. In women with acute vaginitis, swelling of the labia is caused by intense inflammation and reactive swelling of adjacent anatomical areas.
When the process spreads from the vagina to the external genitalia, vulvovaginitis develops. Leucorrhoea, irritation, a feeling of pressure and fullness, pain during urination and sexual intercourse, characteristic of vaginitis, are complemented by symptoms of vulvitis. Deterioration of general condition is rarely observed.
Specific infections
Vaginitis, vulvitis, vulvovaginitis can be caused by both nonspecific and specific flora. An important sign that helps determine the cause of inflammatory edema is the type of leucorrhoea. Gonorrhea is accompanied by the appearance of a thick, purulent, white-yellow discharge. With trichomoniasis, the discharge is foamy and yellowish-green. Patients with gardnerellosis have transparent leucorrhoea with an unpleasant fishy odor.
With primary syphilis, unlike the diseases listed above, there is no widespread swelling. When a hard chancre is located on the labia in this anatomical zone, a painless or slightly painful rounded red erosion with a dense infiltrate at the base is detected. An atypical variant of chancre is indurative edema - an area of such high density that finger pressure does not cause the appearance of an indentation.
Kraurosis of the vulva
At the initial stage of the disease, swelling, redness of the labia majora and minora, paresthesia, and symptoms of vulvodynia are detected. Subsequently, the swelling disappears, the skin and mucous membranes become rough, dry, and wrinkled. The leading place in the clinical picture of kraurosis is occupied by persistent paroxysmal itching. Dyspareunia, urination and defecation disorders are possible.
Genital allergy
Allergic reactions can occur to medications, vaginal contraceptives, male sperm, cosmetics and hygiene products. The perineal area and perianal area are affected. The most persistent symptoms are itching and erythema. The swelling is combined with a burning sensation in the vagina, which intensifies after sexual intercourse. Symptoms disappear 2-3 days after stopping contact with the allergen.
Toxic shock syndrome
Swollen labia occur in one third of menstruating women with toxic shock syndrome. Chills, weakness, fever, muscle pain, diarrhea, repeated vomiting, and specific skin rashes resembling a sunburn are detected. In severe cases, signs of damage to the respiratory system, liver and kidneys are detected: transient pain in the abdomen and lower back, shortness of breath, cloudy urine, yellowing of the skin.
Tumors of the vulva
For small benign neoplasms, an asymptomatic course is typical. With large neoplasias, there is a sensation of a foreign object in the perineum. Swelling of the vulva is observed during trauma, inflammation, suppuration of tumors, and is accompanied by pain. With a pronounced inflammatory process, weakness, fatigue, and general hyperthermia are possible.
Vulvar cancer in the early stages is manifested by paroxysmal itching and burning, intensifying at night. Swelling, pain, bloody, serous or purulent discharge occur. Weeping is observed and ulcerations form on the skin. In later stages, swelling spreads to the pubic area and lower extremities, accompanied by constipation and urinary disorders.
Other reasons
Swelling of the labia area can be caused by general infectious diseases, pathologies of blood vessels and internal organs. The causes of the symptom are:
- Diphtheria.
The anal-genital form of the disease is rare and affects the vagina, but can spread to the vulva and perineum. Hyperemia, edema, and hemorrhagic discharge are observed. - Varicose veins of the pelvis.
The swelling is accompanied by itching, heaviness, discomfort, and bursting pain in the labia area. Spontaneous or post-traumatic bleeding is possible. - Prolapse of the urethral mucosa.
A sensation of a foreign object, pain and burning in the area of the exit of the urethra are detected. The clitoral frenulum and labia minora become red and swollen. Possible urgency and urinary incontinence. - Kidney adenocarcinoma.
The swelling is caused by the proliferation of venous vessels in the lumbar region, followed by varicose veins in the labia area. - Anasarka.
Develops in severe diseases of the heart, kidneys, liver, malignant tumors, exudative enteropathies. There is total swelling and rapid weight gain. Severe swelling of the genital organs is due to abundant blood supply and loose tissue.
Diagnosis of pain in the leg closer to the groin
Joint pain cannot be ignored. Any unpleasant sensations indicate a violation of the functionality of the body and pathology of the internal organs. Contact KDS Clinic. Experienced specialists will provide assistance at any time. The patient is sent for tests and a comprehensive examination of the body. With such symptoms, the patient should undergo an X-ray of the joints and ultrasound diagnostics. General tests will show details of the body's internal indicators. To get a more accurate result, it is worth doing magnetic resonance imaging. The procedure is prohibited for pregnant women, women during the lactation period and children under sixteen years of age. Consult your doctor before undergoing the examination.
Make an appointment with a specialist by number. In some cases, the patient is left in the hospital to monitor improvements in indicators. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with prices for all services on the official website of the medical institution.