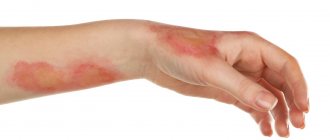
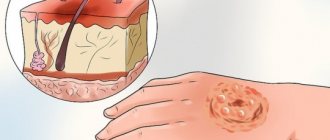
- Current (contact) - occurs directly when a person comes into contact with a live part, when an electric current passes through the body.
- Arc - caused by the thermal effect of an electric arc on the human body: such burns are usually serious and deep.
Voltage is of great importance: for example, at low voltage (up to 240V), alternating electric current is dangerous - it causes muscle contraction, and the person who has come under the electric shock seems to “stick” to the current source and cannot in any way withdraw the limb.
High voltage, on the contrary, usually “throws away” the victim. However, at voltages above 370V, serious damage occurs - burns of 3rd and 4th degree of severity with charring of body parts.
Causes of electrical burn
When a person touches a bare wire, it completes an electrical circuit. Tumors and injuries occur at the site of entry and exit of the discharge. Sometimes there are disturbances in brain function and soft tissue damage.
Experts name several main factors that can cause a burn:
- Contact with a poorly connected socket.
- Contact with the device with a wire on which the insulation is broken.
- Old wiring.
- Contact with high voltage line.
- Lightning strike.
Features of electrical burns
The current penetrates inside the human body and forms a “loop”. The most dangerous are:
- Closed loop - when the current passes through the arms or legs.
- Bottom loop - the charge passes through the feet.
- Full loop - the current enters the body through the legs and exits through the hands.
It is impossible to say exactly what will happen after an electric shock. It all depends on the strength of the discharge and the characteristics of the person. Contact with an object energized by 240 volts is often accompanied by convulsions. It is impossible to unclench your fingers; the cable remains in your hand.
The danger of such interaction lies in the duration. When struck by a high-power electric current, a person is thrown away from the source, but severe burns appear, which are accompanied by charring.
Symptoms
Electrical burns manifest themselves with all the local symptoms inherent in other types of injuries. This:
- pain;
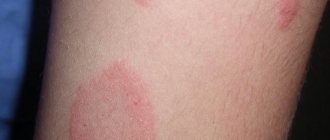
- skin redness;
- swelling;
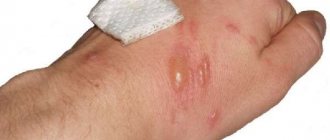
- the appearance of blisters on the damaged surface filled with serous or hemorrhagic fluid;
- in case of severe damage - open wounds on the skin.
A severe electrical burn is indicated by a complete lack of sensation in the area of injury.
In addition to local manifestations, electric shock may be accompanied by:
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- difficulty breathing (becomes shallow);
- increased heart rate;
- convulsions, tics;
- paralysis;
- loss of consciousness.
An electric shock can also cause other functional disorders that cannot be predicted with certainty. It all depends on the strength and location of the damaging factor. With a strong blow, rupture of internal organs (liver, spleen, kidneys), falling into a coma (usually short-term), and cardiac arrest can occur.
What are the types of electrical burns?
Electrical burns can occur at home, at work, or even in the natural environment. Various types of damage are possible:
- Thermal ones manifest themselves in the form of a burn on the skin.
- Biological - muscles contract convulsively, problems with the functioning of the respiratory system, open wounds on the skin, and sometimes fractures occur.
- Electrolytic - damage to lymph and blood flow is dangerous due to disruption of organ functioning.
Based on the type of interaction, there are two types.
Current (contact)
This type occurs when a person comes into contact with an object or wire through which current passes. Current penetrates in the case of direct interaction. The formation of a current burn is a consequence of the conversion of electricity into heat.
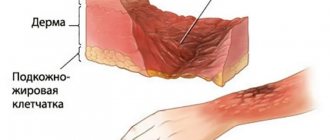
The skin suffers because it has a greater degree of resistance compared to other tissues. More often, grade 1 or 2 is diagnosed. Stronger ones are less common.
Arc
This type of electrical burn is explained by the impact on the body of an electric arc with high temperature (more than 3500 degrees) and high energy.
You can get it when working with high-voltage lines and other high-voltage devices. The injuries are grade 3 and 4. The general condition depends not so much on the force of the blow, but on the area of the affected area.
Types and features
There are 2 types of electrical damage.
- Contact (electric) burns are caused by direct interaction with a current conductor. Such injuries often occur when working with low-voltage electrical equipment, so electrical burns are characterized by a mild degree of injury.
- An arc burn results from the thermal effects (temperatures that can exceed 350°C) of an electric arc without current passing through the body. An electric arc burn often leads to very serious damage that extends into the deep structures of the skin.
In case of electric shock, in addition to burns, phenomena occur that are uncharacteristic of other types of damage (thermal, chemical).
- Many patients have characteristic marks in the area of contact with the current - oval, round, or in the form of stripes (in case of lightning) yellowish or brown areas. These marks have clear boundaries and are about 5-10 mm in size. Over time, they disappear, but the speed of restoration of skin sensitivity and its properties depends both on the degree of damage and on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- When an electric shock occurs, the current travels through the body in a path called a loop. As a result, burn damage occurs not only in the area of contact with the current source, but also at the point of its exit from the body (usually this is the area of the body in contact with the surface of the earth or metal). A full loop, characterized by the passage of current through both arms and legs, is the most dangerous. A more favorable prognosis for the victim is when the current passes only through the lower limbs (lower loop).
Electric shock causes various types of damage:
- thermal - often a current discharge is accompanied by a high-temperature effect, as a result of which the victim’s clothing catches fire, and a thermal burn is added to the electric shock;
- electrolytic – the composition of the blood changes, internal tissues are destroyed;
- mechanical - due to convulsive involuntary contraction of muscles caused by the influence of current, tissues are torn, deep (sometimes right up to the bone) wounds are formed on the skin, dislocations and even bone fractures often occur;
- biological - the functioning of the nervous system and the function of thermoregulation, cardiac activity are disrupted (myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest may occur), blood pressure increases, arrosive bleeding, pulmonary edema, glomerulonephritis, functional liver failure may develop;
- electroophthalmia - inflammation of the eyes caused by radiation burns of the cornea, retina (with a short circuit and the formation of an electric arc, in addition to a visible bright flash, intense ultraviolet radiation occurs, affecting the structures of the eyeball);
- metallization of the skin - tiny particles of molten metal are absorbed into the skin, the skin becomes hard and rough, and the victim has a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the area of damage.
Types of burns
To properly provide first aid to a victim, you need to know the characteristics and types of electrical burns. Based on the method of production, they are divided into 3 groups.
Household
This kind of burn is often caused at home when safety precautions are ignored. This happens when working with a faulty electrical appliance, breaking the insulation of wires, repairing sockets, replacing light bulbs when the power is not turned off. These burns are the most harmless, but history has known cases of death.
Natural
This type can be obtained in the event of a natural disaster - a lightning strike. The survival rate is negligible, since the effect on the body is too strong.
Production
Electricians most often experience this type of burn while performing their job duties. They are constantly in contact with electrical appliances.
A person whose work involves electricity exposes himself to prolonged exposure to low voltage. However, short-term interaction is no less dangerous.
The child has
According to statistics, electrical injury is diagnosed in every 10th child admitted to the burn department, and in 25% of cases the injury leads to death. At risk are children from one to 5 years of age (injured when they come into contact with a faulty electrical device connected to the network, when playing with sockets) and teenagers (they receive an electric shock when entering electrical substations, train cars, power line supports). And very rarely the cause of injury is a lightning strike.
Providing first aid to a child and treating an electrical injury is carried out in the same way as for adults. But a child’s body needs much more time to fully recover. And even after a long period of time, children can develop serious complications:
- damage to the nervous system - asthenia (a disorder accompanied by a decrease in physical and mental performance), encephalopathy (brain damage), neuritis (inflammation of peripheral nerves), paresis (partial paralysis);
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system - cardiac muscle conduction disturbances, microcardiodystrophy;
- autonomic disorders - hair loss, hyperhidrosis (increased sweating throughout the body or in certain areas);
- hearing impairment, hearing loss;
- cataract (clouding of the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision or complete blindness).
Electrical burns are the most dangerous injuries, often leading to disability or death. It is extremely important to observe safety precautions when working with industrial electrical installations and household appliances. To prevent injury to a child, it is necessary to block access to sockets, monitor the serviceability of electrical equipment and the integrity of the insulation of electrical wires, and conduct explanatory conversations about the inadmissibility of playing with electrical appliances and near energy facilities.
Degrees
In total, there are 4 degrees of electric shock strength. Each of them has its own differences, the nature of the damage to the body.
- The first degree is characterized by damage to the upper layers of the skin, slight swelling, and a burning sensation. The burn area is small. This kind of damage is the most harmless, so after a visit to the doctor you can continue treatment at home.
- In the second degree, deeper wounds appear, right down to the germ layer. The formation of blisters with exudate is typical at the entry and exit sites. The person feels severe pain and burning. If a small area is affected, you can treat it at home.
- The third degree is characterized by the death of the inner layer of skin. The skin turns red, and with more severe injuries, it may even turn black and blisters appear. Blood clots can be observed in the clear exudate in the blisters. The skin on the affected area dies and cannot regenerate.
- The fourth degree is considered the most dangerous. The injury is accompanied by damage to the skin, muscle tissue, and bones. Only a doctor can provide first aid. The skin does not regenerate, and restoration will require a transplant.
It is important to correctly determine the degree and area of the burn in order to provide first aid without causing harm. In case of incorrect identification, death is possible.
Possible complications
Pulmonary paralysis.
- Scars and scars on the skin.
- Destruction of the spine and bones.
- Cramps.
- Brain damage.
- Changes in vital organs.
- To avoid electric shock, follow workplace safety regulations and work only with protective equipment. Work is carried out only after confirmation that the facility is de-energized and safe.
To protect your home, turn off the power before starting any repair work. You should also make sure that your home's electrical system is in good working order. Only in such cases can the risk of burns be reduced to zero.
How to understand that a person has suffered from an electric shock
You can find out about an electrical burn by looking at the marks from the electric arc. The skin of the affected area changes color. It turns red or purple-gray. With severe injuries, blackening or even charring may occur. There is no clear location of the pain; it spreads throughout the body. Electric shock is indicated by muscle spasms and convulsions.
The main signs of electrical injuries include:
- Weak breathing, shallow. Sometimes asphyxia may occur.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Muscle cramps.
- Impaired consciousness, memory loss.
- Disorientation in space.
- Loss of sensation in a limb.
- Unstable vision, inability to focus.
- A clear outline of the burn on the skin.
- Unintelligible speech.
- The victim may complain of nausea and dizziness.
The victim needs to be attentive to the victim. If the current is exposed for a long time, then characteristic marks will remain on the skin. Possible swelling and numbness.
First aid
First of all, it is necessary to stop human contact with the current source. In this case, you need to be vigilant and take precautions. Rubber gloves are put on your hands, and shoes that do not have rubber or metal inserts are put on your feet.
Note! It is acceptable to use a wooden plank to push the person away from the source. In this case, you should stay at a safe distance from it. After the contact is suspended, it is important to turn off the switch and completely turn off the power supply.
If you notice that the victim’s skin color has changed at the site of contact with electricity, and he is suffering from severe pain, then you need to call an ambulance. To choose a treatment method, it is necessary to determine the duration of exposure to the electric discharge and the degree of damage.
First of all, it is necessary to stop human contact with the current source.
If after the cessation of contact the victim is unconscious, then his breathing and heartbeat are checked. If necessary, take emergency resuscitation measures - artificial respiration, cardiac massage.
Note! Your feet should be slightly higher than your head to restore your heart rate.
If the victim is conscious, but complains of pain, then an anesthetic can be given.
Examine the victim's body. The area of the burn is indicated by special marking points. If entry and entry points are clearly identified, a sterile bandage is applied to the affected area to prevent infection of the open wound. Small wounds can be washed under running water.
Providing first aid for electrical burns to a child
If a child has been injured, then calling an ambulance should not be neglected, even if it seems to you that the child’s burn is not severe.
If a child has lost consciousness, he must be kept warm. If there is no breathing, it is necessary to hold your nose and perform artificial respiration until it is restored.
Keeping electrical appliances away from small children and away from electrical outlets and components can reduce the risk of electric shock.
Burns in children, as in adults, are accompanied by severe pain. While waiting for an ambulance, you can give your child an approved painkiller.
Attention! It is forbidden to leave the victim alone, as emergency assistance may be needed.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms depend on the extent of the damage. However, there are also the main symptoms that occur with injuries of this type:
- Appearance of weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Strong pain.
- Vomit.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Rapid breathing.
- Change in skin color.
Other symptoms may occur depending on what part of the body is affected by the electrical current. If electrolyte enters through soft tissue or skin, it should be treated in the same way as a regular thermal burn.
Treatment
If the injury occurs at home, it is most likely minor. Small areas of skin can be treated independently. The wound heals within a couple of weeks.
The affected area should not be treated with iodine or brilliant green, as they will aggravate the burn. It is better to use creams and ointments for healing burns, which include an antibacterial and antiseptic component. Preparations with sodium fusidine help avoid tissue rotting.
In the first week, you need to take especially careful care of the wound:
- daily smear the injury with an antiseptic solution, anti-burn creams, as prescribed by your doctor;
- carry out dressings regularly;
- for pain, use painkillers;
- antihistamines are required.
For treatment in a hospital setting, 2 treatment methods are used: medication and surgery.
Drug treatment
If a person suffers from high voltage, then most likely he will lose consciousness. In this case, a disruption of the heart rhythm and disruption of the cardiovascular system are possible. In this case, doctors send the patient to the intensive care unit. He is prescribed infusion therapy with anti-inflammatory and painkillers. In some cases, a blood transfusion may be required.
After stabilizing the victim’s condition, therapy is supplemented with local treatment for a speedy recovery. All creams and ointments that can be used to treat burns with blisters prescribed by doctors have an antibacterial effect and stimulate regenerative processes.
If the nervous system is disrupted as a result of an electric shock, the patient is prescribed sedatives and sometimes antidepressants. To stabilize the functioning of the cardiovascular system - stimulants. If circulatory disorders or cerebral edema are detected, then taking dehydration medications is recommended.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is necessary only for the 3rd or 4th degree of severity of the injury. Surgeons clean the affected area and transplant healthy skin.
In particularly severe situations, amputation may be required. It is recommended for those patients whose injury is not amenable to conservative treatment methods and skin grafting.
The decision is made individually, based on the patient’s condition. In some cases, surgery is required immediately when there is a real threat to life or health. Sometimes doctors decide to postpone intervention until the patient has partially recovered, that is, they give time to recover from the shock.
Thermal burn - symptoms and treatment
Medical care for burn injuries is currently subject to the order of the Ministry of Health of 1991 No. 54 “On measures for the further development and improvement of medical care for burn victims.”
First aid for thermal burns
For patients with burns, first aid should be provided immediately at the scene of the accident.
- First you need to stop the action of the thermal agent:
- extinguish the flame on clothing;
- remove the victim from the high temperature area;
- remove smoldering clothing or clothing soaked in hot liquid if it is not soldered to the wound surface. If the tissue is stuck, you need to carefully trim it around the wound.
- In the first 10-15 minutes from the moment of injury, you need to cool the burned surface: for 1st and 2nd degree burns - with cold running water for 10-15 minutes; for a 3rd degree burn, apply a cold, damp, sterile bandage or clean cloth. This will significantly reduce the effect of the thermal agent and stop it from spreading deeper into the tissue. This procedure also reduces swelling and pain. All these points have a beneficial effect on further wound healing.
- Before emergency medical services arrive or before you consult a doctor yourself, it is recommended to perform a dressing using sterile gauze pads or clean sheets.
What not to do for burns
In case of burns, you should not:
- Carry out any manipulations on the wounds.
- Prick or try to remove blisters.
- Use ice to cool the burn area, as it can lead to additional injury - frostbite.
- Separate stuck objects.
- Tearing off the stuck tissue will further injure the victim and cause additional pain.
, it is not recommended to use various powders, ointments and sprays as first aid for burns They can make it much more difficult to determine the depth of the lesion and clean the wound.
Treatment of burns with folk remedies
It is not recommended to use traditional medicine methods such as toothpaste, sunflower oil, diluted boric acid, urine, etc.
It is important to remember that only specialist doctors (surgeons, combustiologists, traumatologists) can provide qualified medical care. Self-diagnosis and self-medication can be dangerous to health [5][9].
When to call an ambulance for a burn
An ambulance should be called in the following cases:
- with deep burns or if their size is larger than the victim’s palm;
- the skin in the burn area is charred or whitened;
- blisters appeared;
- there are other injuries;
- the patient is in a state of shock - trembling, sweating profusely, his skin becomes sticky, breathing quickens, weakness or dizziness appears;
- the victim is pregnant;
- patient under 5 or over 60 years of age;
- the person is known to have heart disease, lung disease, liver disease or diabetes, or has a weakened immune system, for example due to HIV, AIDS or chemotherapy for cancer;
- the victim inhaled smoke, which causes a cough, sore throat, difficulty breathing, and noticeable burns on the face [19].
Outpatient burn treatment
The frequency of visiting the doctor depends on the severity of the burn. In mild cases, the first visit is scheduled a day after the injury, then you need to visit the doctor about once a week. At the appointment, the doctor treats the wound, assesses the depth of the burn and the need for skin grafting.
If an infection is associated with the burn, then you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible. When a wound becomes infected, adjacent areas of the skin turn red, pus is released intensely, and black or red spots appear in the burn area.
During outpatient treatment, it is important to keep the burn surface clean. The doctor may prescribe ointments that are applied to the wound and then covered with a dry gauze bandage. The dressing should be changed daily. Biosynthetic dressings do not need to be changed if there is no suppuration [20].
Treatment of burns in hospital
Treatment for burn injuries is consistently one of the most expensive. Treatment methods for patients with thermal injuries are now fundamentally different from those generally accepted 10-15 years ago. Modern algorithms for the treatment of burn wounds have been developed largely due to advances in the study of burn disease. The results of treatment of patients with burns have improved significantly due to the development and implementation of active surgical tactics in clinical practice. The basis is early necrectomy followed by skin grafting in order to quickly restore the integrity of the entire skin.
The essence of necrectomy is the excision of non-viable tissue using a scalpel and/or special equipment (hydrosurgical scalpel, dermatome). This is necessary to prepare the wound for closing the defect. If the wound area is small, it is possible to perform autodermoplasty (skin grafting) with local tissue. If the affected area is large, autodermoplasty is performed with a free skin flap, i.e. using one’s own areas of unaffected skin. The skin graft is harvested under general anesthesia using a special instrument - a dermatome. The thickness of the flap is usually 0.3-0.4 mm. Then it is placed on the wound surface, fixing the edges with sutures or metal staples [5].
Innovative methods for diagnosing and treating children with burn injuries include determining the depth of the burn, active debridement (surgical treatment of wounds), and treatment of wounds with negative pressure. The modern approach to the treatment of burn wounds is carried out through the earliest possible preparation for autodermotransplantation [16].
The most effective from a modern point of view is cleansing the wound surface from necrotic masses using hydrosurgical systems . Their main principle is the ability to carry out operations without tools, using a special solution that moves at great speed. The jet in pulsation mode provides cleaning and treatment of wounds, and also makes it possible to excise tissue. The system removes tissue fragments formed during wound cleaning [11]. The hydrosurgical system allows surgeons to set the desired mode and treat even complex wounds as efficiently as possible, with the formation of the desired edge configurations.
Currently, the use of a negative pressure apparatus . The essence of this method is to create a controlled local subatmospheric pressure, i.e., a vacuum, directly in the wound. A constant or variable level of negative pressure is created using a special dressing that isolates the wound surface from the external environment [4]. Vacuum therapy has already received comprehensive scientific substantiation and recognition among specialists in the field of treatment of wounds of various etiologies.
When treating children with burn injury, it is important to pay attention not only to the wound surface itself, but also to the psychological state of the child himself and the relatives caring for him (most often the mother). The mother’s task at the stages of treatment and rehabilitation is to help minimize physical and psychological disorders in the child.
Treatment of deep and/or extensive burns requires long-term hospitalization (about 2-3 months or more). Then comes the rehabilitation period, which can last for years. Typically, recovery, like treatment, includes financial costs [1][6][7]. All this negatively affects the psychological state of the mother.
The longer the victim’s mother experiences physical and mental exhaustion, the worse the prognosis for the child’s long-term adaptation [3][10]. In order to reduce chronic stress and develop adaptive abilities in mothers, individual or group psychotherapy is recommended [8]. Family therapy should be included in the rehabilitation treatment of burned children [2][10].
Rehabilitation after electric burns
At the stage of restoring the integrity of the skin, it is important to constantly disinfect the resulting wound. Very often, a blister with a clear liquid forms at the site of the electrical burn.
Attention! It is forbidden to burst the bubble yourself; it is best to entrust this to a specialist at the emergency room.
If you properly care for the affected area, then within a couple of weeks new skin will form under the fluid, and the blister will gradually dry out and fall off by this time. The new skin will be a little lighter and softer than the rest.
The process usually takes 1–2 weeks for grade 1, about 3–4 weeks for grade 2. For more serious injuries (grade 3–4), the recovery process is individual and depends on factors:
- general health;
- cell regeneration rate;
- presence of surgical intervention;
- individual attitude.
An unfavorable development of events is characterized by suppuration of the wound, which can only prolong the recovery period of the body. In this case, chills, weakness, and increased pain at the site of the injury may be felt.