Surgeon
Bohyan
Tigran Surenovich
Experience 37 years
Surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, member of the International Association of Surgeons, Gastroenterologists and Oncologists
Make an appointment
A purulent lesion of the soft tissues of the foot, which is diffuse in nature, that is, does not have clearly defined boundaries, and can spread to bone tissue or tendons over time, is called phlegmon of the foot. This is a fairly common purulent process, moreover, often occurring with various complications. The disease affects people at any age, but the most common cases occur in the most active age group of 35-45 years. Men are injured more often than women. This is explained by the nature of the injuries leading to infection, which in most cases patients receive during their work activities.
General information
The ICD-10 code for phlegmon of the foot is L03.0, and its immediate cause is infection of the foot tissue with bacteria that cause purulent inflammation. They penetrate into tissues:
- in case of damage to the skin in the form of an abrasion, scratch, crack, puncture or cut of the skin, abrasion caused by uncomfortable shoes;
- if the nail plate is damaged during a pedicure without observing proper aseptic requirements;
- when a foreign body enters soft tissue;
- from a ruptured abscess located elsewhere on the foot or leg;
- from a subcallosal abscess formed due to the appearance of a callus on the skin;
- through blood or lymph from a source of chronic infection in the body, which can be a carious tooth, boil, inflammation of the tonsils, etc.
In addition, the inflammatory process can be triggered by the penetration of certain chemicals into soft tissues, but such cases occur extremely rarely.
A number of pathogenic bacteria act as the causative agent of inflammation - staphylococci, streptococci, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, etc. When infected with an anaerobic bacterium, the most severe gangrenous form of the pathology develops. Among the microorganisms that can cause inflammation, the most common are peptococci and clostridia.
All of these microorganisms cause acute purulent inflammation. There is also chronic phlegmon of the foot, which develops due to infection of soft tissues with pneumococci, diphtheria or paratyphoid bacillus.
A characteristic feature of the development of a purulent process is its spread: when the plantar part is affected, the inflammation often spreads to the phalanges of the toes or to the lower leg. Quite often the process is complicated by osteomyelitis. The infection spreads through the blood and lymphatic tracts, muscles, and tendons. All this makes phlegmon of the foot a pathology that creates an immediate danger to the patient’s life.
Reception is strictly by appointment only!!!
Doctor Plus LLC License No. LO-77-01-004801
Registration at the clinic by phone
Make an appointment at the clinic
- +7 (495) 125-49-50
- Addresses of clinics in Moscow
- Daily
- call me back
Abscess of the leg
occurs when a purulent bacterium enters the soft tissue. This could be Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus and other bacteria. Treatment is possible at home.
But unqualified treatment can provoke a chronic form of the disease and lead to undesirable consequences. In this regard, the best option when an abscess appears is to visit our clinic, where the patient can be treated by an experienced doctor.
You can make an appointment with a surgeon from our consultants by calling +7 (495) 125-49-50
Prices for services Addresses of clinics Consultation with a gastroenterologist Hirudotherapist Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity Call a surgeon to your home
Factors that provoke the development of inflammation
Injuries to the skin of the feet are quite common, but they do not always lead to the development of purulent inflammation. As a rule, phlegmon of the ankle or foot most often develops against the background of weakened immunity caused by:
- diabetes mellitus or other endocrine disease leading to the development of diabetic angiopathy - deterioration of blood circulation in the foot;
- vascular pathology, which leads to disruption of blood microcirculation and thereby impairs tissue nutrition;
- depletion of the body due to prolonged malnutrition, previous serious illness, recovery from injury, surgery, radiation or chemical therapy.
A weakened immune system cannot cope with the infection, and the penetration of the pathogen leads to the development of a purulent process. Infection of soft tissues poses the greatest danger to diabetics, in whom, due to deterioration of blood circulation, resistance to pathogenic microorganisms decreases and the sensitivity of nerve endings deteriorates. At the same time, while walking, prerequisites arise for the spread of infection into bone tissue, tendons, etc.
How dangerous is the disease?
The course of the pyogenic inflammatory process in the joints depends on the virulence (ability to cause harm to the patient’s body) of the infectious agent, the state of the patient’s immunity, and the presence of chronic diseases. Without treatment, the disease progresses in any case, moving from stage to stage with joint destruction and severe complications.
Stages
Stages of pyogenic arthritis according to the Research Institute named after. Vishnevsky:
- Early
– pus accumulates in the joint cavity without destroying its tissues (on x-rays, an expansion of the joint space appears due to the accumulation of purulent exudate):- 1a
- tissues adjacent to the joint are not changed; - 1b
– purulent inflammation around the joint. - Explicit
– intra-articular tissues (synovium, cartilage, ligaments) are destroyed (on x-ray - destruction of the articular surfaces of bones):- 2a
- without damage to periarticular tissues; - 2b
– suppuration spreads to surrounding tissues. - Progressive
– cartilage and subchondral bone are destroyed (on x-ray – focal bone destruction, narrowing of the joint space), joint mobility is impaired:- 3a
- without damage to the skin and subcutaneous tissue surrounding the joint; - 3b
– ulcers around the joint; - 3c
– fistulas (pus breakthrough) on the surface of the skin. - Ultimate
:- if left untreated
, destruction, ankylosis (immobility) of the joint, disability; It is possible to restore joint function only with the help of endoprosthetics; - If treatment is carried out in a timely manner
, a complete recovery is possible.
Possible complications
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
If left untreated, suppurative processes lead to severe complications:
- complete destruction and immobility of the joint;
- spread of suppuration to the skin, subcutaneous tissue, ligaments and tendons with the formation of fistulas, abscesses and phlegmons that are difficult to treat;
- osteomyelitis – purulent inflammation of the bone;
- compression of nerves by swollen tissues, accompanied by severe pain; for example, ankle arthritis may be complicated by tarsal syndrome due to compression of the tibial nerve;
- sepsis – multiple pyogenic lesions of organs and systems.
Pyogenic arthritis is a disease that cannot be cured with home remedies. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the greater his chances of recovery.
What to do if you suspect purulent arthritis
Algorithm of actions:
- call a doctor at home; if you have a high temperature, call an ambulance;
- take any medicine with anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects: Analgin, Pentalgin, Paracetamol, Diclofenac; Apply an external agent with similar properties to the affected joint: Diclofenac ointment, Menovazin solution;
- lie down and take a position that minimizes pain.
Do not refuse hospitalization under any circumstances!
Clinical manifestations of purulent inflammation
A complex of local symptoms of phlegmon of the left or right foot develops within several days from the moment of infection.
- Within two to three days, a tumor appears on the back of the foot in the form of a dense infiltrate, tissue edema forms, and bursting pain appears.
- Over time, the infiltrate softens in the direction from the center to the periphery.
- The skin in the affected area acquires a beet-red color with a local increase in tissue temperature.
- Palpation during examination causes pain; it is difficult for the patient to localize the source of inflammation.
- Attempts to move the leg, much less walk, are met with attacks of acute pain.
- The motor function of the foot is limited.
- The popliteal lymph nodes are enlarged.
In addition, clinical manifestations characteristic of most inflammatory processes develop quite quickly - an increase in body temperature to 39-40°C, decreased performance, weakness, headaches. If the process quickly spreads deeper, the patient’s condition worsens: shortness of breath and palpitations appear, intoxication syndrome develops, and urinary function is impaired. The patient needs immediate hospitalization.
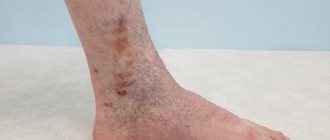
Trophic ulcer - symptoms
Trophic ulcers do not form spontaneously. Initially, swelling appears, accompanied by severe itching. The skin becomes thinner. Pigmentation or cyanosis appears.
Multiple trophic ulcers on the leg
The appearance of a trophic ulcer is often accompanied by chills and night cramps of the calf muscles. Due to stagnation in the lymphatic vessels, droplets of liquid begin to appear on the glassy surface of the skin. Next, the foci of exfoliated epidermis merge, and an ulcer with ragged, compacted edges is formed, causing severe pain at the slightest touch. As a rule, the ulcer surface is quickly colonized by bacteria, and the bleeding ulcer begins to fester.
Diagnostics
A visual examination of the injured limb usually reveals signs of inflammation: swelling and swelling of the tissues, smoothness of the plantar arch, redness, hyperthermia, etc. Most of these signs are characteristic of different types of the inflammatory process, so instrumental diagnosis of phlegmon of the foot is necessary, which includes studies:
- blood - general laboratory analysis;
- punctate of the contents of the inflammatory focus with bacterioscopic examination and identification of the pathogen;
- bacteriological seeding of punctate on laboratory media to identify an infectious agent and determine antibiotic resistance.
In addition, radiography of the foot may be necessary to determine the depth of tissue damage, as well as differential diagnosis to clarify the nature of the purulent process.
Trophic ulcer - treatment without surgery
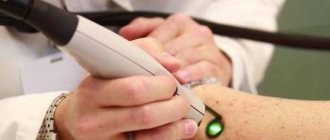
If the cause of the ulcer is not venous pathology, then conservative measures are sufficient. A portable laser device is a great help in home treatment of the initial stages of ulcerative skin lesions up to 50 cm2 in size. A laser injected into a vein helps reduce blood viscosity, significantly reduces the risk of blood clots, and increases blood flow in problem areas. In addition, the laser beam effectively reduces pain and trophic ulcers. Laser treatment (reviews below) in combination with conservative treatment allows you to avoid surgical intervention.
Laser therapy is carried out in courses of 10-15 procedures. With the correct individual selection of treatment parameters, this treatment method does not cause complications, patients note good tolerability of the procedures, and the trophic ulcer is quickly eliminated. Laser treatment, the price of which is not too high, is very popular.
Treatment methods
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the foot, the purulent-inflammatory process quickly spreads throughout the lower limb and progresses. Therefore, immediate hospitalization of the patient is necessary for any form of pathology. Outpatient treatment of foot phlegmon is excluded, since the patient must be under constant medical supervision. Surgery and subsequent conservative therapy are performed in a medical institution.
The surgical operation consists of opening the source of inflammation, removing pus and necrotic tissue, washing and draining the resulting cavities. At the end of the procedure, an aseptic dressing is applied to the wound. Further treatment consists of the use of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers and restoratives. For phlegmon of anaerobic origin, the patient is administered anti-gangrenous serums. In case of severe intoxication, infusion therapy is indicated.
Since purulent tissue inflammation is a severe pathology, measures to prevent foot phlegmon are extremely important, which include:
- preventing foot injuries, even minor ones;
- using strong shoes with durable soles in traumatic situations;
- timely antiseptic treatment of injured areas;
- rapid identification of the inflammatory process and contacting a medical facility;
- timely treatment of any inflammatory foci in the body, including carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis, etc.;
- strengthening the immune system, treating immunodeficiency conditions.
What is a leg abscess
An abscess is an inflammation that can occur in the human body. The peculiarity of this type of inflammation is that purulent bacteria located in the human body, when placed in favorable conditions, begin to actively multiply. This forms abundant purulent masses, around which a capsule is formed. It has a protective function, preventing pus from entering healthy areas.
After some time, the head of the capsule matures and breaks through. This process must be controlled by a surgeon. At best, the abscess breaks out, but the capsule may empty into the tissue, which will cause unwanted complications.
Is a diet necessary when treating a trophic ulcer?
What should be avoided if there is a trophic ulcer? Photos of complications will help you control yourself when dieting. Diet for trophic ulcers excludes salty foods and spices. It is necessary to saturate the body with nutrients, vitamins and Omega-3 acids. Vegetables (carrots, tomatoes, cabbage), fruits, nuts, milk, cheeses, vegetable and butter, and fish are especially useful. You should eat small portions to avoid a sharp increase in blood sugar. A radical change in diet is not required; a small adjustment will have a beneficial effect on the healing process.
Trophic ulcer - treatment. Reviews from our patients.
Patient's review of laser treatment for trophic ulcers in our center.
Victor Petrovich, 65 years old.
I am a pensioner with a whole cartload of all sorts of ailments. My legs had been hurting and swollen for a long time, but I, like many, put off going to the doctor until later. I took some pills on the advice of a neighbor nurse, although I didn’t notice any particular improvement. In general, I lived to the point where I had a huge ulcer on my leg. God bless your doctors, I already thought that I would be left without a leg. They gave me laser treatment. I didn’t particularly delve into the nuances of this case; the doctors guaranteed a good result. Everything went without pain, literally after a few days my trophic ulcer began to disappear before my eyes, and after two weeks only a small scar remained. Of course, various medications were prescribed, then I went to a sanatorium and forgot about this terrible disease. Thanks to all the doctors of the Medical Center for Phlebology, especially Dr. Malakhov Alexey Mikhailovich.
A patient's review of the treatment of trophic ulcers using the EVLO method in our center.
Komissarova L.I.
Our patient with surgeon-phlebologist A.M. Malakhov. after treatment
My leg ached constantly, there was a buzzing sensation in it at the end of the day, and then a trophic ulcer formed, which became larger and larger. I didn’t dare to have surgery using the classical method, because I was afraid after reading reviews online and all sorts of complications. Well, my daughter is in the know, she found me an experienced doctor in Moscow, Alexey Mikhailovich Malakhov. Before the operation, and this is endovasal laser coagulation, at the medical center in Moscow, where I decided to have it, they did an ultrasound, donated blood and that’s it. After the operation, I was forced to get up from the table and walk for about an hour. After 3 weeks I saw my doctor. I didn’t worry about scars, the main thing was that the ulcer healed faster. It's been 3 months since the laser procedure on my leg. Everything is fine, the ulcer has become very small, but I hope it will heal completely soon.
I'm very glad that everything went well. Thanks for all. Komissarova Lyudmila Ivanovna, December 7, 2016
Trophic ulcer - prevention
To prevent the trophic ulcer from returning and the treatment not to be in vain (the cost of which can only be found out after consultation), take care of prevention. Measures to prevent the occurrence of trophic ulcers and relapses:
- early detection and treatment of diseases that provoke the appearance of trophic ulcers;
- moderate physical activity (daily walking 2-3 km);
- use of compression hosiery;
- ignoring baths and saunas, hardening procedures for the legs;
- refusal of flour and sweets, predominance of fruits and vegetables in the diet;
- medical examination 2 times a year.
Trophic ulcer - radiofrequency treatment (RFA, RFO)
The radiofrequency treatment method is considered the most modern and safe if you have a trophic ulcer. RFA treatment in Moscow involves heating the walls of the vein with microwaves, it “closes”, and the trophic ulcer gradually shrinks. RFO treatment - and after a few months the problem vein is a connective tissue cord, and the entire load is transferred to neighboring, healthy vessels. This is how the trophic ulcer gradually heals.
Treatment of trophic ulcers with radiofrequency (RFA, RFO) in our center
RFO treatment in Moscow is carried out quite quickly; the patient goes home 10 minutes after the intervention. The radio frequency method provides the following advantages:
- short duration of the procedure - 30-40 minutes;
- exposure parameters are selected automatically and without the participation of a doctor;
- cosmetic effect - the absence of additional trauma promotes the formation of a less rough scar where there was a trophic ulcer. RFA treatment is very positive in this regard.
- the procedure is completely painless and easily tolerated;
- Hospitalization is not required, the patient can lead a normal life, limiting activity only after the procedure.