Today, treatment of burns is a pressing problem. According to state statistics for 2022, at least 30,000 people suffered thermal or chemical injuries. This is one of the most common household injuries. However, you can often get a burn at work, where safety conditions are not met.
If burns occur, you must be able to provide proper first aid in a timely manner. How quickly you help yourself or the injured person will determine his further condition and the speed of treatment.
The human body is able to regenerate itself and remove minor burns without serious consequences for health. More serious burns require immediate medical attention to prevent complications. Such wounds need to be monitored to prevent infection and regularly treated with anti-inflammatory medications or anti-burn wipes.
If you find yourself close to a burnt person, you really need to know how to treat a burn, otherwise you will do more harm than good with your actions.
Causes of burns
A burn can occur due to exposure to:
- fire;
- hot liquid or steam;
- hot metal, glass or other objects;
- electric current;
- radiation (x-rays or radiation therapy);
- ultraviolet radiation (sun or solarium);
- active chemicals.
It is worth noting that the causes of burns may be different, but all types of such injuries are classified depending on the degree of damage caused and symptoms:
- First degree. This burn affects only the outer layer of the skin. The injury is characterized by redness, swelling and pain. The victim is given first aid and a short course of treatment is prescribed.
- Second degree. This burn leads to damage not only to the epidermis, but also to the underlying layer - the dermis. The lesion is characterized by redness, whitening or mottled skin, pain and swelling. It is possible to develop blisters from burns and severe pain.
- Third degree. With this type of damage, the fat layer under the skin is affected. Burnt areas of the body become charred, blackened or white. Third degree burns often disrupt the functioning of the nervous and respiratory systems.
First steps to neutralize thermal burns
- remove the victim as far as possible from the heat source;
- If clothing or equipment is smoldering, you should get rid of it immediately. If clothing is stuck to the skin, you must carefully cut it off or remove it;
- apply dry ice or use cold water to the damaged area;
- treat damaged areas of the body with burn ointment;
- In case of serious injuries, call an ambulance.
Neutralization of chemical burns
- Rinse the affected area with a strong stream of water. Under no circumstances should you treat a wound with oil.
- If a burn is caused by quicklime or sulfuric acid, it should be
- treat with a dry cloth, the use of water is unacceptable;
- apply a sterile antiseptic bandage.
There are situations when people get severe burns. Treating them outside the hospital requires special knowledge and skills. If a person does not have them, it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
KEYLONS. A LITTLE ABOUT THE MECHANISM OF CELL CYCLE REGULATION
Research in the field of skin regeneration and the general mechanisms of the cell cycle has been conducted since the middle of the last century. R. Weiss and J. Kavanau, W. S. Bullough and T. Rytomaa, V. I. Prilutsky and Yu. A. Romanov are the founders of the theory of cell division. P. Nurse, Leland H. Harwell and R. Timothy Hunt are modern researchers of the principles of regulation of the work of individual cells and the body as a whole.
Disruption of the process of cell division (impairment of cell mitosis) is a source of not only cancer. Limited regeneration leads to aging of cells and aging of the body as a whole. In case of injuries and pathologies, low tissue regeneration significantly prolongs the healing process.
Outstanding examples of self-repair are known to everyone: severed tails, damaged hearts, and spinal cords in amphibians are restored (repaired) in a very short time. What signals does the body give to tissues so that they begin to grow, what is the growth factor? But first, about the life path of cells. A cell is the elementary unit of all living organisms. All living things are made up of cells. Regeneration, cell reproduction by mitosis occurs as follows: genetic material is reproduced inside the cell (this ensures the genetic identity of the daughter cells), after which the cell divides.
The process of cell division from the start of the mechanism to the actual division is called proliferation. Proliferation is regulated both by the cell itself and its environment. The main signal for triggering the cell division mechanism is provided by the plasma membrane of the cell. The membrane has special receptors on its surface that evaluate the “environment” around the cell and trigger the process of proliferation. These signals can come from neighboring cells, as well as from the interaction of cells with various compounds that stimulate entry into the cell cycle. These compounds are called growth factors.
But in tissues there are also substances that limit cell division. These are the Kaylons.
Keylons
- substances contained in tissue (simple proteins or glycoproteins) that specifically suppress cell division and DNA synthesis in this tissue. Keylons do not have species specificity. The action of kelons is to suppress or slow down the rate of cell division in the tissues that produce them. For example, keylons of the Basal Layer of the Epidermis act only on the Epidermis.
Cell regeneration is described by a growth regulation model. This model explains how body tissues carry out self-regulation. Any tissue capable of regeneration consists of two types of cells: cells capable of dividing and cells that cannot divide: proliferating and differentiated cells. The behavior of proliferating cells is controlled by differentiated cells: Kaylons are produced in differentiated cells and act on cells capable of dividing - proliferating cells. If for some reason the number of differentiated functioning cells decreases (for example, after injury), the inhibitory effect of the keylons weakens and the population size is restored. This ensures a balance between tissue growth and loss and explains the regeneration process.
Degree of burns
There are three main degrees of burns: first, second and third. The rating of each grade is based on the severity of the skin damage, with grade one being the most minor and grade three being the most severe.
Signs of damage look like this:
- first degree burns: the epidermal layer is damaged, the skin is red, slightly swollen;
- Second degree burns: blisters appear and skin peels off;
- third degree burns: tissue necrosis is observed, the skin becomes white, a crust forms;
There are also fourth degree burns. This degree includes all the symptoms of a third degree burn. The damage penetrates beyond the skin and spreads to the tendons and bones. It is in this case that scars remain after a burn.
Chemical and electrical burns require immediate medical attention because they can affect internal organs, even if external damage is barely visible.
The type of burn does not depend on the cause of its occurrence. A scald, for example, can cause all three types of burns—thermal, chemical, and physical—depending on how hot the liquid is and how long it remains in contact with the skin.
BURN DISEASE. CLINICAL SYNDROMES
In burn disease, four clinical syndromes can be distinguished: Burn shock, Intoxication, Infection, Convalescence. There are no sharp boundaries between these syndromes.
BURN SHOCK. It occurs as a result of a neuro-reflex and neuro-endocrine reaction of the body. As a result of a strong inflammatory process in a burn victim, the central and peripheral blood supply is disrupted, the permeability of vascular and cellular membranes increases, the volume of circulating blood decreases with a violation of the ratio of its formed elements and plasma (hypovolemia), plasma escapes from the vascular bed and plasma loss through burn wounds. Plasma loss during burn shock depends on the depth and area of the burn.
Thus, with superficial burns, predominantly external loss of plasma is observed, and with deep burns, plasma enters the surrounding tissues and swelling occurs.
During a burn, the evaporation of fluid through damaged skin increases significantly, leading to a large loss of fluid from the victim’s body. Loss of fluid reduces the mass of circulating blood, resulting in a sharp deterioration in glomerular filtration of urine. Burn shock usually occurs within 2-3 days. Signs of burn shock include: an excited or inhibited state, in severe cases, consciousness is confused or absent; decreased pulse blood pressure, decreased amount of urine excreted by the kidneys (oliguria), vomiting, thirst, chills, muscle tremors.
INTOXICATION. As a result of the appearance in the victim’s body of toxic products, under-oxidized compounds, and bacterial tissue, a period of acute burn toxemia begins. Body temperature rises, loss of appetite occurs with the development of signs of toxic damage to internal organs (toxic myocarditis, hepatitis). During this period, it is necessary to carry out active detoxification measures (forced diuresis, plasmaphoresis, hemosorption).
INFECTION. At the third stage of burn disease, infection begins to progress. Metabolic disorders and weakened immunity give rise to infection of the body. Infection significantly complicates the course of the wound process - it maintains intoxication, suppresses restoration processes in tissues, and can affect various organs.
RECONVALESCENCE (recovery). It occurs from the moment of complete closure of granulating wounds. An important factor in recovery is prompt closure of burn wounds.
Treatment after burns
If you receive minor injuries, you can try to neutralize them on your own. If you have knowledge of how to treat superficial wounds, you can handle this yourself.
Ointment or gel for burns from boiling water helps well with kitchen problems. If second or third degree burns have been sustained, hospital treatment is required. It should be done in a clinic under the supervision of doctors. The therapist will recommend how to treat the burn or how to treat a burn with blisters.
What else can you do at home?
To speed up the healing of superficial burns, preparations with dexpanthenol are recommended - preferably in the form of sprays, so as not to create a film over the affected area. It is applied to the wound 2-4 hours after the burn and only in the first degree. Sometimes it is allowed to treat a child at home and for burns with small blisters. In this case, it is necessary to promptly change clean bandages and, if the doctor prescribes, treat the wound with chlorhexidine.
In 2008, WHO issued a report on the prevention of childhood injuries. Pediatricians have developed a brochure for children, “Live an interesting and safe life”: it is written in simple language that children can understand and is presented in the form of stories and entertaining quizzes, and the advice from it is still relevant today.
Skin restoration after a burn
What helps with burns is careful hygiene and regular wound care.
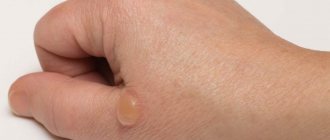
After injury, a blister immediately forms on the skin, filled with clear plasma, which can seep through the burned tissue. With proper treatment, inflammation and suppuration can be avoided, and regeneration will occur faster.
Within a few days, the blisters from the burns will begin to subside and peel off, and new skin will begin to form under the blister. At this time, the wounds may itch, but you should not touch the affected area - by the end of the first week the itching will go away on its own.
If the wound is neglected, a process of suppuration may develop. It may be accompanied by fever, sudden weakness and chills. With such a history, regeneration of the skin may take weeks. In this case, compacted growths and ridges are likely to appear.
Associated symptoms
With a 2nd degree burn, hyperthermia, swelling, and redness of the affected area most often occur. Liquid bubbles may form. When the blisters break, sores form. They will take about 2 weeks to heal. The listed symptoms may include pain and increased sensitivity at the site of the lesion. If the area of damage is extensive, vomiting, weakness, dizziness, and fever may occur. Particularly severe symptoms of 2nd degree burns occur in children.
Treatment of scars after burns
If you are interested in how to get rid of the external consequences of a burn, you need to know that in case of serious damage to the skin, the scar will remain in any case. Here you will need the help of a cosmetologist who will help restore the normal appearance of the skin.
Typically, for such an operation, a scar excision technique is used, after which several cosmetic sutures are applied to the tissue. When the sutures are removed, the damaged area is treated with ointments that prevent the formation of new scars on the skin.
For particularly difficult cases, for example, burns from boiling water, the laser resurfacing technique is used. Modern equipment allows you to completely remove scars and achieve perfect skin. If the severity of the burn is insignificant, chemical peeling with fruit acids is recommended.
Features of home therapy
After providing first aid for a 2nd degree burn, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to completing the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor. Rules that are recommended to be followed:
- eliminate heavy physical labor, since excessive stress provokes inflammatory processes in the body;
- avoid working in dusty and dirty objects to avoid infection of an open wound;
- Monitor the sterility of the dressings and follow the schedule for their replacement.
New tissues regenerate quickly if there are no complications due to external irritants. Recovery will take about 2 weeks, but may take up to 3 weeks for some. Healing slows down in older patients with chronic diseases. With successful therapy, recovery occurs without scars or scars.
Remedies for burns
How to treat a burn, and what kind of surgical assistance can be provided independently in the field or at home?
The use of creams such as Levomikol or Rescuer is guaranteed to help with minor injuries, such as briefly touching a hot pan. Dexpanthenol works very well for first degree burns. If the degree of damage is more serious, creams can only be used as a preventive measure and there is no point in relying on them.
Anti-burn products such as sprays or gels - for example, Burnshield Anti-burn Hydrogel - are more effective because they are dispersed and are better absorbed by the skin. These drugs combine two functions - anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Buy
Buy
Buy
There is another type of treatment - special anti-burn dressings. They are recommended when the patient needs to be outdoors. Such dressings prevent dirt and dust from entering the wound.
Why does it hurt so much
The skin is the largest organ: 4−6% of the total body weight. It contains up to 82% water and a third of the total blood volume. There are 2 million nerve endings in the skin, 1.5 million of them are pain receptors.
Temperatures above 44 °C destroy skin proteins - the integrity of the cell membranes is disrupted and water from the cells goes into the space between them. This can be illustrated using an egg as an example. It contains approximately 73% water, 13% protein, 12% fat and minerals. When cooked, the proteins in the cell membrane are destroyed and folded - water comes out. The same thing happens to the skin, only the water goes into other tissues. Therefore, swelling occurs.
Then platelets stick together in the vessels of the dermis and clog the lumen. The blood supply to the burned area is reduced, which can lead to complete tissue death if help is not provided in time. A burn also leads to the release of substances into the blood that provoke inflammation.
To reduce the risk of general burns
At home, you can quite simply reduce the risk of burns; you just need to follow a few recommendations:
- Do not leave cooking or already cooked food on the stove unattended;
- frying pans are placed on the stove with handles towards its back;
- any hot liquid must be placed out of the reach of children and animals - boiling water is a common cause of thermal burns;
- Do not store electrical appliances near water;
- Do not cook in flammable clothing;
- You should block your child’s access to electrical and gas appliances;
- Protective caps must be put on sockets that are not in use;
- you should not smoke at home;
- smoke detectors require regular maintenance and battery replacement;
- the house or apartment must be equipped with a fire extinguisher;
- Chemical burns are caused by chemicals - they must be stored in a place inaccessible to children and animals.
Prevention measures
Preventing burns involves careful handling of chemicals, household electrical and heating appliances. If we are talking about a child, he needs to be protected from danger - potentially unsafe objects and liquids should be kept away. If an injury occurs, you must immediately provide assistance and, if necessary, call a doctor.
Prevention of complications is careful adherence to the doctor’s recommendations during the treatment process, timely wound care, and the use of sterile materials. It is better to use specialized ointment dressings that accelerate healing and do not stick to the wound surface. You should also limit mechanical and physical irritation of the injured area, maintain hygiene, establish a drinking regime and eat a balanced diet, and the body will do the rest itself.
Experts' opinion
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Clinical studies have confirmed that bisabolol inhibits the production of anti-inflammatory mediators NO and PGE2 in cells, reduces the expression of iNOS and COX-2 genes by inhibiting the NF-kB and AP-1 signaling pathway. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, tests have also proven the bleaching and lightening activity of the substance.
One of the key components of the cream is violet extract. This plant is widely used in medical practice, due to the richness of its chemical composition. Violets are rich in flavonoids; anthocyanin glycosides and phenolcarboxylic acids are found in their flowers. The plant extract is prescribed by specialists for various skin diseases.
Sources:
- Yukhtina N.V., Modern ideas about atopic dermatitis in children
- Kamasheva G.R., Khakimova R.F. Valiullina S.A., Methods for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in young children, Dermatology journal, 2010
- Kovyazina N.A., Fedosimova N.A., Illek Ya. Yu. Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in young children, Vyatka Medical Bulletin, 2007