Burns from boiling water, hot oil or any other hot liquids require an adequate and timely response, and if this happens, first aid should be provided immediately. Both the depth of tissue damage and the area of damage, as well as the healing period, will depend on this.
If this is a minor injury, you can provide first aid for a hand burn with boiling water yourself, but for serious injuries (3rd-4th degree burns), you should trust the doctors. Under no circumstances should the resulting blisters be opened, as this can lead to tissue infection. It is forbidden to sprinkle starch on burns, treat the wound with vegetable oil, iodine and other alcohol-containing liquids. All this can only increase pain and slow down healing. In case of particularly deep burns, when dirt and fragments of clothing have entered the wound, you should not try to clean the wound yourself, but rather wait for the doctors to arrive.
What to do if you get an oil burn?
First of all, you need to understand the extent of the damage. In domestic conditions, there is a possibility of receiving thermal burns of three degrees:
- 1st degree - the skin turns red, swelling forms at the burn site. Such damage occurs as a result of short-term exposure and heals on its own after a few days.
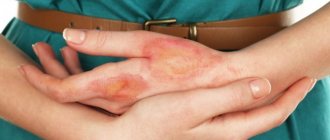
- 2nd degree - blisters containing clear liquid appear at the site of the oil burn. Such burns occur when oil comes in direct contact with the skin and are accompanied by swelling and redness. They are quite painful and healing can take up to several weeks.
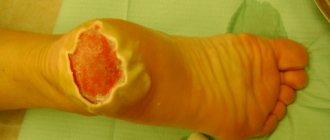
- 3rd degree - deep burns, in which tissue necrosis and the appearance of a wet gray or dry brown scab are observed.
There is another 4th degree of burns with damage to bones, muscles, and organs. The likelihood of such serious injury from a hot oil burn at home is fortunately minimal.
How to relieve pain?
To eliminate pain from a burn, you can use any analgesic that is in the first aid kit and is suitable for the victim’s age. It is better to give preference to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, nimesulide or ibuprofen. You can take analgin tablet, but it is better to refrain from using aspirin.
Pain medications should be taken only as directed and without exceeding the recommended dosage. Larger amounts of the drug will not relieve pain more effectively, but may cause a number of unpleasant side effects.
First aid
Regardless of the degree of burn received, it is necessary in any case to provide assistance to the victim. And the sooner the better.
The most important thing for a burn is to cool the damaged skin and remove hot oil from the surface so that it does not aggravate the condition.
Keep the burned part of your body under running cool water for 20 minutes. Cold will stop the spread of the burn, slow down tissue destruction and relieve inflammation.
When cooling, adhere to the following rules:
- The water temperature must be at least 150C, otherwise hypothermia may occur. This is especially true for children who quickly lose heat. Wrap the victim in a blanket while they cool the burn.
- If the victim is unconscious, a basin of water in which the injured limb can be immersed, or wrapping in a wet sheet will do.
- You can try to remove the clothes remaining at the burn site after soaking. This can only be done if it is not “welded” to the skin. Otherwise, it’s better to leave this to the doctors: otherwise you risk damaging the wound.
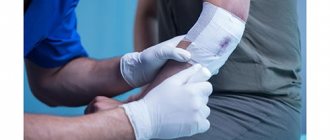
After cooling, cover the burn site with a sterile, damp bandage to prevent infection.
Peculiarities
The danger of burns from hot oil is due to its physical properties. Oils:
- boil at high temperatures (olive oil - at 180° C, and peeled sunflower oil - at 260° C);
- characterized by high heat transfer due to the high density of the liquid;
- getting on the skin, they form a film on its surface that prevents the natural cooling of burned tissues.
Contact of even a small amount of boiling oily substance on the skin can cause severe burns with damage to the deep layers of the dermis.
What kind of oil burn is strong and serious?
It is necessary to assess the extent of the damage: a victim with 2nd and 3rd degree burns needs medical care. Minor 1st degree burns and small 2nd degree oil burns can be treated at home.
A burn is considered significant if it occupies more than 10% of the total body area. You can determine the size using the “rule of the palm” or the “rule of nines”.
In the first case, the unit of measurement is the palm, the size of which is equal to 1% of the total body area. So, a burn that takes up 10 palms, or several scattered burns the size of a palm, is serious.
According to the “rule of nines,” different parts of our body occupy an area that is a multiple of nine (as a percentage of the total area of the body). If any limb is injured, for example, a hand was burned with oil, then it is easier to determine the severity of the injury in this way:
- Chest and back – 18% each;
- Legs – 36% (18% each);
- Head and neck – 9%;
- Hands – 18% (9% each).
Symptoms of the lesion
In most cases, the injury occurs on the arms or legs, less often on the chest, abdomen or mucous membranes. Such injuries are considered serious and require medical intervention and hospitalization. Getting gasoline into the eyes causes serious complications, including loss of vision, so you should not hesitate if you have the first symptoms.
Signs depend on the degree of damage and the extent of the wound. The following stages with different manifestations are distinguished:
- in the first degree, no significant tissue damage is formed. The injury is localized in the upper layers of the skin. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and burning. Sometimes patients complain of minor pain;
- the second degree is characterized by more extensive damage. At this stage, victims are faced not only with redness, but also with the formation of blisters, most often filled with transparent contents;
- The third degree is characterized by severe damage to all skin. Deeper tissues suffer. Patients complain of blisters with purulent contents and severe pain. Tissue necrosis begins;
- at the fourth degree, irreversible processes occur. The reagent penetrates into muscles, tendons, and bones. Victims report severe pain.
When to call an ambulance
- A child, an elderly person, a pregnant woman or a seriously ill person was burned.
- 3rd degree burn
- A 2nd degree burn covering an area of more than 1 palm of the victim.
- 1st degree burn over 10% of the body surface.
- Received an oil burn on the face, head, groin area, joints, hands, and feet.
- The victim feels very unwell or is unconscious.
While waiting for an ambulance, you should stay close to the victim at all times and give him something to drink. In case of severe pain, the victim can take a painkiller if he does not have allergies.
If you notice that the burn site begins to swell, try to place the burned part of the body above the level of the heart and check the bandage. A bandage that is too tight should be loosened to improve blood circulation.
What is not recommended to do
- Remove stuck clothes.
- Pop the bubbles that appear from the oil burn yourself.
- Bandage the burn tightly.
- Apply oil, sour cream, kefir to the burn site: you have just cleaned the burn from the oily environment, so you should not introduce microorganisms into it that can cause the development of infection.
How to treat a burn from boiling oil
The healing time depends on how timely and correctly first aid was provided, as well as on the further actions of doctors and the victim.
- 1st degree burns can be treated at home. If you quickly cool the damage and immediately apply Panthenol or Olazol, the recovery time will be reduced to 3-4 days. However, it makes sense to use these anti-burn agents only before blisters form. For 2nd degree burns this is no longer effective.
- Small 2nd degree oil burns can also be treated independently with outpatient medical supervision. The fact is that the blisters that appear from an oil burn contain liquid (exudate), which means an inflammatory process. Blisters will not resolve on their own; they need to burst for the burn to heal.
Only a physician can do this under sterile conditions, leaving the skin to protect the burn site from infection. The burn can then be treated at home.
Healing may take several weeks and, with proper care, will not leave scars.
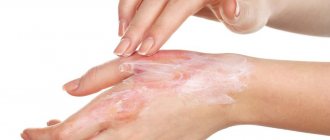
It is important to remember that the skin formed at the burn site is especially thin and needs additional protection. Therefore, during and after healing, it is recommended to lubricate it with emollients and moisturizers. La-Cri cream is perfect for these purposes.
La-Cri cosmetics are sold only in pharmacies. It does not contain preservatives, hormones or fragrances. The cream contains only natural ingredients that have a truly miraculous effect:
- Seed and licorice extracts relieve inflammation;
- Violet extract and bisabolol (the active ingredient of chamomile) soothe delicate skin;
- Panthenol and avocado oil have a regenerating and softening effect, nourish and moisturize the skin;
- Walnut extract fights germs and promotes rapid healing.
If you are looking for something to anoint an oil burn, La Cree Revitalizing Cream is perfect for this purpose.
Alarming symptoms
If you have come into contact with a chemical or vapor, you should immediately contact a clinic. Otherwise, the condition will only get worse. There is a high probability of internal damage if:
- Severe, persistent pain appeared in the mouth, throat, and along the esophagus.
- When you swallow, the discomfort intensifies, and you can’t even drink the liquid.
- There is vomiting, especially with blood.
- Profuse salivation began.
- It became difficult to breathe.
- The temperature has risen (due to intoxication).
- Swelling of the mucous membrane.
- The victim is either drowsy or, on the contrary, restless.
- Severe burns of external tissues, blisters.
Folk remedies for oil burns
SOS tools
Can be used immediately after cooling the burn to relieve symptoms. Suitable only for 1st degree burns without blisters or wounds!
- Fresh potatoes: grate, place on gauze or bandage and apply as a compress to the burn. Instead of potatoes, you can use carrots or add cabbage leaves.
- Tea brewing: brew a bag and cool to 13-150C. Dip gauze into the tea leaves and apply to the burn site. Excellent for relieving swelling.
- Aloe leaves: wash the aloe leaf thoroughly, cut lengthwise and apply to the burn site. You can also rub aloe and squeeze the juice out of the leaves to make a compress.
Treatments for healed burns
Used to treat 2nd degree burns after the blisters have healed.
- Fir and sea buckthorn oils: mix in equal parts and smear the burn area until completely healed. Perfectly soften the skin and prevent the formation of scars.
- St. John's wort herb: pour half a glass of St. John's wort herb into 1 glass of vegetable oil and leave for 21 days in a cool place without access to light. Then strain and lubricate the burn site several times a day.
- Dairy products: 1 tbsp. mix a spoonful of vegetable oil with 2 tbsp. spoons of sour cream and 1 egg yolk. Apply the mixture to damaged skin and cover with a bandage. Change 5 times a day.
Sources:
- Yukhtina N.V., Modern ideas about atopic dermatitis in children
- Kamasheva G.R., Khakimova R.F. Valiullina S.A., Methods for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in young children, Dermatology journal, 2010
- Kovyazina N.A., Fedosimova N.A., Illek Ya. Yu. Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in young children, Vyatka Medical Bulletin, 2007
Security measures
In everyday life, when working with vegetable oil, you should follow some safety rules to avoid injury. When cooking, it is not recommended to use a lot of oil and fry over high heat. It is also recommended to use special oven mitts when cooking and keep the oil away from the heat.
Thus, if you follow the rules and work with oil carefully, you can avoid consequences. Treatment must be comprehensive and timely - health and rapid recovery depend on this.