A thermal burn is a specific injury to the skin and (sometimes) underlying tissue due to exposure to high temperatures. Sources of thermal effects can be both solids and liquids, as well as steam or gas. As a rule, contact with a carrier of excess heat occurs as a result of a violation of safety standards for working with its sources or as a result of an accident. Sunburns should also be partially classified as thermal. They arise due to the combined effect on the skin and mucous membranes of both ultraviolet rays, which themselves have a destructive effect on the body, and the thermal energy of solar radiation.
When exposed to thermal energy, the body primarily injures the skin (or mucous membranes). If the intensity of the thermal effect is high, then the injury can affect not only all layers of the skin, but also the tissues located underneath it. Depending on the depth of tissue damage, in clinical practice there are 4 degrees of burns, each of which has its own symptoms and clinical features, on the basis of which the treatment program is based. Therefore, before moving on to considering the treatment of thermal burns, you should familiarize yourself with them.
LEATHER. SKIN STRUCTURE. SKIN FUNCTION
SKIN is one of the most complex organs of our body, subject to the strongest physical and physiological stress. Skin is the largest organ of our body. The complex structure of the skin with its numerous vessels, nerves, sebaceous and sweat glands is necessary to perform certain functions.
Skin is: -Preventing fluid loss by the body; -Protection of internal organs from the negative influence of external influences; -Ability to evaluate pressure, touch and vibration. Nerve endings and receptors inform the body about temperature and pain effects; -Barrier functions. This is protection against bacteria and microorganisms; -Protection from ultraviolet radiation; -Maintaining optimal body temperature.
The skin consists of two layers: EPIDERMIS and DERMI
. Under these layers is subcutaneous fatty tissue.
EPIDERMIS
- avascular upper thin layer of skin (does not have its own blood supply). The epidermis receives nutrition from the capillary bed of the dermis due to the diffusion of nutrients. The epidermis consists of numerous layers of living cells, on top of which are dead cells.
The layers of the Epidermis can be represented as follows:
- Basal (germ layer).
The lower layer of the Epidermis. Consists of cells capable of regeneration (cell division) - cylindrical keratinocytes. The basal layer ensures constant regeneration of the Epidermis, however, cell division is regulated by certain factors: hormones, vitamins, kelons. Keylons are simple substances that suppress growth and regulate the functioning of the basal layer. Thanks to keylons, basal cells have limited growth (proliferation). Beneath the stratum basale is the basement membrane, which separates the stratum basale from the dermis. - Spiny.
Contains up to 6 layers of irregularly shaped cells. They have little activity for cell division (limited mitotic activity). - Grainy.
The death of Epidermal cells begins in this layer. Contains up to 3 layers of cells. - Brilliant.
The stratum pellucida consists of anucleated cells in which intense enzymatic activity is observed. Eleidine is formed in the stratum lucidum. Eleidin is a substance rich in fats and proteins with a high refractive index of light, looks like a homogeneous dense shiny layer, which gives its name to this layer of cells. The shiny layer protects the body from the effects of various aqueous solutions. - Horny.
The stratum corneum consists of anucleated keratinized cells (keratin is a protein that has high mechanical strength and performs protective functions), which are called corneocytes. The cells of the stratum corneum lie with some overlap, like brickwork, and are firmly connected to each other by the finest fibers (tonofibrils). The stratum corneum has 15 to 20 layers of cells, with the outer layer continually being shed as detached flakes of skin.
So, in general, the Epidermis works like this: in the lower, basal layer, cells are constantly dividing. After division, one of the newly formed cells passes into the next layers of the Epidermis. From layer to layer, cells lose contact with nutrients coming from the Dermis and lose the ability to divide. The closer a cell approaches the surface of the skin, the more strongly external environmental factors begin to act on it, keratinization of the cell occurs, the cell loses its nucleus and turns into a scale of the stratum corneum.
The stratum corneum, the upper layer of the epidermis, easily allows low-molecular substances such as oxygen from the environment to pass through. Bacteria, which are significantly larger in size, are not able to overcome the upper layer of the Epidermis, therefore the Epidermis is the skin protection that is optimal for the body. In the Epidermis, the processes of cell division of the lower Basal layer, regulated by keylons, the gradual transition of cells to the upper layers, transformation into keratin scales and, finally, exfoliation of the outer scales in the stratum corneum occur in a balanced manner. Complete renewal of the Epidermis lasts from 10 to 30 days.
The high strength of the Epidermis serves as a good barrier to various substances and does not allow them to penetrate the body. This also applies to most cosmetics.
DERMIS
- the frame, the skin itself, which provides its mechanical properties: elasticity, strength and extensibility. These properties are provided by connective tissue that has elastic fibers, Elastin, which allows the Dermis to stretch, and collagen fibers, which strengthen the Dermis.
The following structures are located in the Dermis: blood vessels, sweat glands, nerve endings, hair roots with sebaceous glands. Deeper is the subcutaneous fatty tissue - the hypodermis. It absorbs the effect of mechanical factors on the skin and participates in the thermoregulation of the skin. In this part of the skin there are clusters of fat cells separated by bundles of collagen fibers.
Treatment
To choose the right course of rehabilitation, you first need to correctly diagnose the problem. For this purpose, various classifications of burn marks have been invented, the most popular of which is the Vancouver Scar Rating Scale. In Russia it is slightly changed, in accordance with national characteristics:
| Points | Description |
| by color | |
| 0 | the color does not stand out from the overall skin tone |
| 1 | hyper- or hypo-pigmented (the color is either brighter than the base tone or paler) |
| 2 | immature scars - shades of red |
| in relation to the level of surrounding healthy skin | |
| 0 | at the level |
| 1 | below level |
| 2 | above level |
| by relief and surface quality | |
| 0 | flat |
| 1 | uneven, bumpy |
| 2 | with hyperkeratosis and ulcerations |
| according to form | |
| 0 | scar cord or fold (length greater than width) |
| 1 | scar mass (length and width are equal) |
The scores shown in the table indicate the degree of burn. So “0” corresponds to the first degree, “1” to a superficial burn, “2” to a deep or third degree burn.
How to treat which degree
Since the scale of the problem at 3 degrees is different, the treatment will be different:
- To treat a 1st degree burn, homemade applications with a special cream are sufficient, and within a week the damaged area should recover.
- If in grade 1 there is only redness, then in grade 2 there is a burning sensation and blisters. This is still not scary, and the burn can be cured with the same cream, but the course of applications will last 30-40 days. Under no circumstances should you puncture the blisters, as this will inevitably lead to infection of the wound.
- With a 3rd degree burn, swelling, dead skin, scabs, blisters and hyperemia around the wound are observed. In this case, a doctor’s supervision is required, as well as complex treatment with ointment or cream, as well as cosmetic procedures, physiotherapy, and even surgery with skin grafting. The body will recover for at least 2 months.
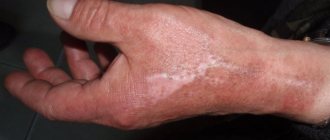
In any case, scars remain after the injury. How to remove a burn scar depends on how serious it was. The first and second degrees do not leave deep damage, so you can cope with them on your own with the help of physiotherapy and cosmetics. With the third degree it is more difficult - damage can reach the bones, therefore the recovery period will be very long and difficult, it involves surgery and skin grafts.
Find out which scar correction method is optimal for you!
doctor Svetlana Viktorovna Ogorodnikova.
doctor
Cosmetic procedures
According to dermatologists, treatment of scars and marks after a burn should begin only when the wound has completely healed and a scar has formed. Starting earlier can only make the problem worse. What solutions will be offered in the beauty salon:
- Chemical peeling . A substance enriched with fruit acids is applied to the scar. It corrodes the “wrong” stratum corneum of the epidermis, due to which the scar softens and evens out relative to the overall skin texture.
- Laser peeling. Popular against facial scars. As cosmetologists assure, the process is safe and effective. The rough scar is carefully “cut off” by the laser beam, leaving new soft skin underneath.
- Silicone sheets and gels prevent the growth of scar tissue due to pressure. This method is effective at the beginning of scar tissue formation.
- Diamond grinding. A type of peeling - microcrystals are placed in a special device, which during operation exfoliate the stratum corneum of the epidermis with sharp edges (let us explain: it consists of dead cells and prevents harmful substances from entering the body). This way you can remove burn marks that are quite large in area.
- Glucocorticoid injections. They are mainly used against keloid scars, but there is a high probability of side effects. The drug is injected directly into the scar.
In addition to the listed procedures, physiotherapy helps get rid of scars - courses based on physical influence: with the help of ultrasound or electrophoresis, drug particles penetrate much deeper than they could with a conventional application.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is effective for correcting both fresh scars and old ones. To achieve visible results, it is very important to choose the right medication.
What procedures are classified as physiotherapy?
- Magnetotherapy. Improves blood supply to the scar and the mental state of the victim after injury.
- Phonophoresis. Resolves scar tissue, increases the elasticity of connective tissue, stimulates blood and lymph circulation and metabolic processes, including intracellular metabolism, enhances the production of biologically active substances and the activity of enzyme systems.
- Laser therapy. Accelerates tissue regeneration, calms nerves, and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Electrophoresis. The therapeutic effect consists of a simultaneous positive effect on the body of electric current and active charged molecules of the medicinal substance. A drug depot (reserve) is created in the skin and subcutaneous fat, significantly increasing the exposure time of the drugs.
The speed of recovery depends not only on properly selected rehabilitation, but also on cosmetics and medications used during the course.
KEYLONS. A LITTLE ABOUT THE MECHANISM OF CELL CYCLE REGULATION
Research in the field of skin regeneration and the general mechanisms of the cell cycle has been conducted since the middle of the last century. R. Weiss and J. Kavanau, W. S. Bullough and T. Rytomaa, V. I. Prilutsky and Yu. A. Romanov are the founders of the theory of cell division. P. Nurse, Leland H. Harwell and R. Timothy Hunt are modern researchers of the principles of regulation of the work of individual cells and the body as a whole.
Disruption of the process of cell division (impairment of cell mitosis) is a source of not only cancer. Limited regeneration leads to aging of cells and aging of the body as a whole. In case of injuries and pathologies, low tissue regeneration significantly prolongs the healing process.
Outstanding examples of self-repair are known to everyone: severed tails, damaged hearts, and spinal cords in amphibians are restored (repaired) in a very short time. What signals does the body give to tissues so that they begin to grow, what is the growth factor? But first, about the life path of cells. A cell is the elementary unit of all living organisms. All living things are made up of cells. Regeneration, cell reproduction by mitosis occurs as follows: genetic material is reproduced inside the cell (this ensures the genetic identity of the daughter cells), after which the cell divides.
The process of cell division from the start of the mechanism to the actual division is called proliferation. Proliferation is regulated both by the cell itself and its environment. The main signal for triggering the cell division mechanism is provided by the plasma membrane of the cell. The membrane has special receptors on its surface that evaluate the “environment” around the cell and trigger the process of proliferation. These signals can come from neighboring cells, as well as from the interaction of cells with various compounds that stimulate entry into the cell cycle. These compounds are called growth factors.
But in tissues there are also substances that limit cell division. These are the Kaylons.
Keylons
- substances contained in tissue (simple proteins or glycoproteins) that specifically suppress cell division and DNA synthesis in this tissue. Keylons do not have species specificity. The action of kelons is to suppress or slow down the rate of cell division in the tissues that produce them. For example, keylons of the Basal Layer of the Epidermis act only on the Epidermis.
Cell regeneration is described by a growth regulation model. This model explains how body tissues carry out self-regulation. Any tissue capable of regeneration consists of two types of cells: cells capable of dividing and cells that cannot divide: proliferating and differentiated cells. The behavior of proliferating cells is controlled by differentiated cells: Kaylons are produced in differentiated cells and act on cells capable of dividing - proliferating cells. If for some reason the number of differentiated functioning cells decreases (for example, after injury), the inhibitory effect of the keylons weakens and the population size is restored. This ensures a balance between tissue growth and loss and explains the regeneration process.
WOUNDS. BURNS (BURN WOUNDS). TYPES OF BURNS
A wound is any open injury associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, with possible destruction of underlying tissues.
Wound healing is the wound process of restoring damaged tissue: restoring its integrity and strength.
Depending on the nature of the damaging factor, wounds can be divided into the following types: Mechanical, Burn, Chronic (trophic skin ulcers). In the presence of several types of damaging factors, the wound is usually called combined.
Wounds are dangerous
primarily bleeding, and, as a result, the development of anemia. As a result of the shock received from injury, dysfunction of vital organs can occur. Depending on the cause of the injury (the etiology of the wound) and the size of the wound, the body may become infected.
The problem of intoxication of the body is especially acute with large areas of burn wounds.
BURN - damage to tissue (skin or mucous membranes) under the influence of various factors: high temperature (thermal burns), chemicals (chemical burns), ultraviolet or ionizing radiation (radiation burn), electric current (electrical burn).
BURN. GRADES OF BURN WOUNDS
The severity of injury in a thermal burn is determined primarily by the depth and area of the thermal injury:
First degree burn (epidermal burn): redness (hyperemia) and slight swelling. Only the Epidermis is affected. Treatment under bandages or open method. Hospitalization is indicated for burns of more than 15% of the body surface.
Second degree burn (superficial dermal burn): the appearance of “bubbles” filled with serous contents. Peeling of the epidermis. The epidermis and upper layer of the dermis are affected. Outpatient treatment is allowed if the burn area is less than 10% and anatomically significant areas (face, neck, perineum) are not affected. But hospitalization is possible depending on the area of the burn, its location, and the age of the patient.
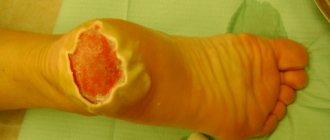
IIIA degree burn: Skin after a burn is diagnosed by a thin mobile scab and large blisters filled with serous contents with an intense yellow coloring. The Epidermis and Dermis up to the reticular layer are affected. But the follicles, sweat glands, and omental bursae remain undamaged by the burn, which will initiate epithelization of the wound. IIIA degree burns are called borderline, because... the lesion is not uniform over the entire surface. The burn can go deeper into the underlying tissues, including due to infection. Victims diagnosed with a IIIA degree burn can be treated on an outpatient basis if the burn surface does not exceed 5% of the body area and no significant anatomical areas are affected.
IIIB degree burn: The entire thickness of the skin is affected: up to the subcutaneous fat. A brown scab forms on the surface. Requires surgical treatment.
IV degree burn: The skin is affected to its full depth and the underlying tissue is destroyed. Subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones are charred. Diagnosed by a dense dark brown or black scab, fused to the underlying tissues. Requires surgical treatment.
THE SKIN WILL NOT BE THE SAME AS IT WAS BEFORE THE BURN – WHAT ELSE IS IMPORTANT FOR PATIENTS TO KNOW
How are patients with burns treated today, why can’t this be done without psychologists, what does a doctor do when a teenager doesn’t want to go to prom because of scars on his neck, and will we stop paying attention to unusual skin? Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Burn Center at Children's Hospital No. 9 named after A. G.N. Speransky Lyudmila Iasonovna Budkevich
A mug of tea on the table, an iron placed on the floor, a hot grill - most burns in children occur due to the carelessness of adults. Forty years ago, pediatric surgeon Lyudmila Budkevich came to work in the burn department and in the first six months wrote a letter of resignation three times, but always stayed. She is known as the head of the burn center of Moscow Hospital No. 9 named after G. Speransky, where children from all over Russia are treated.
– How is it that almost three thousand children come to you every year with burn injuries?
– For some reason, our parents think that trouble can happen to someone else, but not to their child, and most often children under 3 years old get burns at home, due to some kind of carelessness of adults. Just today we discharged a boy who fell face down on a hot grill and received a burn to his face and a cut wound to his lip! Our children are burned by hot liquid - the child curiously reaches for a cup of coffee, throws hot milk or soup over himself, comes into contact with a heated surface - he puts his palm against the burner that is on, against the oven door, against the iron that has just been turned off and for some reason placed on the floor . A child can take any metal object and insert it into an outlet that does not have a plug, or grab a bare wire from a non-functioning household appliance, such as a TV or radio.
– Is there any concern that the house could be so dangerous?
- Exactly! And a small child in the first years of life can get a deep burn, when the skin is damaged to the full depth and sometimes even the underlying tissues, by pouring a glass of water over 45 degrees on himself. Burns up to 30% of the body surface, and irreversible consequences for the skin. Chemical burns occur: for example, a child drinks or spills surface cleaning liquid left open on himself. And it contains alkali, which causes damage to the skin and mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. We notice that burn injuries have a certain seasonality: in winter they are caused by hot liquid, and in summer they are caused by flames. Contrary to instructions, adults pour fire starter fluid onto smoldering coals or firewood, causing an explosion and igniting clothing! There have been cases where a child stands with his feet on hot coals. Summer is characterized by “hookers” - teenagers who run on the roofs of electric trains, getting pleasure and some kind of courage from it, touch the wires, lose consciousness and fall on the platforms, breaking their arms and legs. You see, it only takes a second for a child to get injured, and believe me, in this short time, life is instantly divided into two periods “before” and “after”, problems appear that change the entire subsequent life of not only the child himself, but also his family.
– But if an injury does occur, what would you recommend doing or not doing?
– As a rule, no matter what the thermal burn, with the exception of electrical trauma, you need to pour water over the area at a temperature of 25-27 degrees and keep it there for five to seven minutes to cool the wound surface. This is the very first event that is necessary. At the same time, if clothing catches fire, you should not tear it off the child - thereby we injure the damaged skin. It is necessary to put out the fire and call an ambulance so that, if necessary, the child is hospitalized in a specialized hospital. And the doctors will already figure out what to do next. I do not recommend self-medication. There are a lot of folk remedies, but most often they are harmful. For some reason, grandmothers recommend using sunflower oil, but it only creates a film on the wound surface and prevents the evaporation of heat from the tissue into the environment, and this deepens the burn. For some reason, they use honey or potato cakes, which themselves can cause a burn - mom in a hurry will not feel the temperature of the potatoes. Toothpaste, especially mint, does have a cooling effect, but again you have to wash it off, which is painful. And aerosols with an orange color prevent us from determining the depth of the damage.
Ashina disaster: there were no children with burns of less than 50% area
– Is it true that forty years ago doctors did not want to work in burn departments and often ended up there for some kind of misconduct?
– You know, I found a period in the early 1980s when few surgeons voluntarily went to work in the burn department. Patients are the most difficult and unpredictable in terms of disease outcome of all surgical patients. The treatment used outdated methods known since the Second World War. As a rule, the so-called chemical necrectomy was used to remove necrotic tissue, in which the wounds were cleaned no earlier than the 3rd week of the disease. There was no adequate pain relief. I found myself in such a department, as a sixth-year medical student, I will never forget this smell... And not everyone can withstand the moans and screams of adult patients, not to mention children, so it’s true that most often doctors ended up with burns for some kind of misconduct in of their professional activities. During the first six months of work at the burn center of the children's city hospital No. 9 named after. I wrote a letter of resignation to G.N. Speransky three times, believe me. And although by that time I already had ten years of experience as a pediatric surgeon, for some reason I could not calmly see these suffering children. At that time, there were many children with amputated limbs, with severe burn injuries caused by flames and electric current. And I was a young mother, and I blamed this misfortune on my sons. But life developed in such a way that I stayed for one reason or another.
– Why did you even start working in the burn department?
- That’s how it turned out. People often become combustiologists by pure chance (smiles). I wanted to do science and be an ultrasound diagnostics doctor, but there were free positions for research assistants only in the department of thermal injuries at the Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery. I thought I’d work here temporarily, and two months later the head of the department asks me: “What topic will you write your dissertation on?” And so I became a combustiologist.
– What topic did you choose for your dissertation then?
– My dissertation research was called “Criteria for the readiness of a burn wound for skin grafting.” In 1988 I defended myself and was offered the position of head of the newly opened burn department for young children (the first three years of life). It must be said that such a department is the only one not only in Russia, but also in the world. Just that year, a law was passed that women could take leave to care for children up to 3 years old, and, oddly enough, the number of children with burn injuries increased. And a year later, in 1989, there was a railway accident near Asha (the largest in the history of the USSR and modern Russia. At the moment of the meeting of two passenger trains No. 211 “Novosibirsk - Adler” and No. 212 “Adler - Novosibirsk” due to a gas leak from a gas cloud exploded on the main product pipeline, killing about seven hundred people - ed.), and I and another surgeon from our clinic were delegated to help our colleagues, doctors at children's hospitals in Ufa, where the burned victims were admitted. There were no children with burns of less than 50% area. But the most deplorable impression was made by the trip to the scene of the disaster. The territory within a radius of 500 meters was completely scorched, covered with ashes, children’s shoes and toys were lying under it... In those days, one journalist asked me: “How do you relieve stress?”, and I answered: “The smile of a recovering child is the best medicine,” and for me it still is. Of course, psychologists worked with us, but then there was no time to think about ourselves - there were many sick people, there were cases of death. We took the 28 heaviest children by air to our burn center in Moscow. This tragedy marked the beginning of the creation of the All-Russian Center for Disaster Medicine “Zashchita” and the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
– After the Ashin tragedy, did your attitude towards the profession change?
- Undoubtedly! Since then, I have not imagined myself in another branch of medicine. Soon we began working with combustiologists from England and the USA (project “Nadezhda”). The British founded the Friends of Russian Children foundation. The doctors of our burn center and I went abroad for internships, where we became acquainted with modern methods of diagnosing burn injury and its complications, and mastered innovative surgical interventions for victims with deep skin burns. And, of course, thanks to new technologies in all areas - anesthesiology service, antibacterial therapy, and surgical treatment - we began to care for even the most seemingly hopeless patients, who were doomed in the 70-80s.
Treatment of a deep burn is not just a “patch” on the skin
– What does the process of treating children with burns consist of?
– When the wound area is 10% of the body surface or more, children experience burn shock - a process in which not only damage to the skin occurs, but also functional disorders in the victim’s body. And it is urgent to get patients out of this state. Sometimes medical assistance is needed during the evacuation stage.
We had such a case: trouble happened on the river bank, teenagers were riding a motorcycle and a gasoline tank exploded, the guys received deep burns covering an area of 45-50% of the body surface. The burn center is more than an hour and a half away, so it is necessary to carry out resuscitation measures already in an ambulance - place a peripheral catheter in a vein to carry out infusion therapy. It all depends on the severity of the condition. And then the surgeon determines the area of the burn wounds and the depth of the lesion. There is a slightly primitive, but easily accessible “rule of the palm”, that is, each patient’s palm is equal to 1% of the body surface. And to imagine the area of the wounds, you can visually project the victim’s palm onto the wound surface, for example, 30% is thirty child’s palms. This method is good for emergency doctors and nurses. We use formulas for accurate calculations - the volume of infusion therapy depends on it. Next, the doctor performs primary surgical treatment of the wound - treats the surface with an antiseptic solution, and then opens the epidermal blisters. If they are not opened in time, the contents of the blisters from the surface of intact skin will become infected. But again, I don’t recommend doing this yourself. And only then they apply atraumatic mesh coverings to the wound surface. Such meshes do not stick to the wound, making it easier to change dressings. And then, for three days, we observe the picture of changes in the surface of the wound and decide how the skin will be restored: local conservative therapy (independent epithelization of wounds) or surgical treatment (removal of necrotic tissue with skin grafting of the wound defect).
– How is the operation going?
– First, necrotic dead tissue is removed, bleeding is restored, and then a skin graft is taken from the donor site, that is, a piece of healthy skin 0.1-0.2 mm thick, and transferred to the wound. This is a kind of “patch”. If we have a shortage of donor areas of healthy skin, for example, when the burn area is 30-40% of the body surface, and we need to grow cells, then we use foreign skin, xenoskin, taken from animals, in particular from pigs, as a temporary biological covering. And thereby we protect the wound from external mechanical influence and infections, and prevent the loss of fluid and microelements from the body. And after the donor sites are ready to take the split skin graft again, we remove the pig skin - it played its role - and transplant the newly taken skin. But treating a patient is a team effort. This is not only a combustiologist involved in wound management. We need to overcome the period of acute burn injury while maintaining the functions of vital organs. Professionally trained resuscitators and pediatricians help us with this.
Patients may have problems with the gastrointestinal tract - they need a gastroenterologist and nutritionist (medical nutrition doctor). In children of the first three years of life, the central nervous system always suffers due to its underdevelopment - we cannot do this without consulting a neurologist. If the eyelids are damaged, be sure to see an ophthalmologist to rule out eye injury. When the cartilage of the nose or ears burns, an obligatory examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary. Sometimes burn injuries are combined with mechanical ones. The same “hooks”, touching the wires with their heads or hands, lose consciousness from the effects of high voltage current, fall onto platforms, break the bones of their arms and legs, and cases of traumatic brain injury are not uncommon. And here we need traumatologists and neurosurgeons. And when the burn wound is located circularly on the limbs, we invite our fellow traumatologists to install external fixation devices that facilitate wound care. Without an anesthesiologist, we cannot carry out dressings and surgical interventions to close burn wounds. A hematologist is responsible for blood transfusions, clinical pharmacologists are responsible for antibacterial therapy, laboratory assistants are responsible for the accuracy of tests, and rehabilitation specialists are responsible for preventing the formation of severe scars in patients with deep burns. Psychologists - for the emotional state of patients, art therapists - for socialization after recovery and return home. This is truly a team method of treatment; without such a number of medical workers, we cannot make the patient healthier.
– What scientific discoveries are you looking forward to?
– We hope that they will soon print leather on a 3D printer. And such work is already underway. Cell laboratories will be organized in which skin cells are grown, so necessary for our patients with a severe shortage of donor sites in case of extensive burns.
– In your opinion, will it ever be possible not to be afraid of burns?
- Unfortunately no. The course of a burn injury is influenced by various factors - diseases that existed before the injury, age - infants and old people suffer more severely, the area and location of the burn, the state of immunity of the burned. There is a medical term “injury incompatible with life,” and there are cases when doctors are unable to help patients. Sometimes extensive burns of the skin over 50% of the body surface are combined with a burn of the respiratory tract mucosa (thermal inhalation injury). In such a situation, the total area of burn wounds increases by another 15% of the body surface. The patient has been on artificial ventilation for a long time. And, as a rule, severe complications arise in the form of purulent tracheobronchitis or pneumonia. It is difficult to fight a purulent infection when all the patient’s organs and systems are involved in the inflammatory process. Symptoms of central nervous system dysfunction appear in the form of burn encephalopathy, which is manifested by the victim’s excited state, hallucinations, monotonous crying or screaming, sometimes convulsive readiness in the form of tremors of the limbs, turning into convulsions, which requires analgesic, anticonvulsant, sedative therapy against the background of artificial ventilation. At the same time, the liver suffers (toxic hepatitis), the heart suffers from myocarditis, and the kidneys suffer from acute renal failure. Against this background, stress ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract occur (due to oxygen starvation of the tissues of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum); in some cases, bleeding from the vessels of the resulting ulcers is diagnosed. Patients may die from intractable gastric bleeding. In patients with extensive skin burns and, as a consequence, dysfunction of body organs, generalization of infection occurs with the development of sepsis, which is the main cause of death in burn patients. But still, as I already said, we have now learned to care for completely hopeless patients.
Once a boy from Magadan was rescued with a burn on 95% of the surface of his body; he received burns in a house fire. The boy was evacuated to our clinic, since specialized medical care for patients with extensive burns is not always available locally. But these children and their parents have many problems.
No need to constantly look at these scars!
– What are these problems? Aesthetics are understandable...
– I always say that burn injury is a social problem. Unfortunately, deep burns heal by forming a scar, which, yes, can form in aesthetically important areas - on the face, in the collar area, neck, anterior chest, hands and feet, as well as in the area of large joints - and this causes contractures , tightening of the skin, due to which children cannot fully straighten or bend one or another joint. If the injury is on the hand, then the fingers function poorly, and often a large number of corrective surgical interventions are required to straighten these fingers and make them functionally active. If contractures interfere with the development of the skeleton, it is necessary to operate again, otherwise the child will no longer care for himself. Children who have been diagnosed with a disability must have it confirmed annually. And to avoid a relapse, you need to constantly do massages, wear special compression clothing, mud and paraffin therapy is necessary. It happens that deep burns end in amputation, so prosthetics are necessary for such patients. The child grows and the prosthesis needs to be replaced multiple times. And even after surgical interventions, the skin will not be the same as before the burn injury...
– If a child in your center asks for a mirror, with what words do you give it?
– You know, we don’t have mirrors in the burn center - it just happened that way, and as a rule, children don’t ask for mirrors, and if they do, it’s certainly not from doctors. Here they are emotionally stable, because they see boys and girls just like them, and when they find themselves at home alone with trouble, then emotional breakdowns begin.
Psychologists and art therapists have been working at our advisory clinic for many years. They work not only with children who have suffered burn injury, but also with their parents. Patients who have suffered thermal injury are under the supervision of clinic staff until they are 18 years old. These specialists help former patients find their place in life.
Our charitable foundation "Children's Hospital" organizes winter and summer camps for those who have suffered severe burn injury - children go to boarding houses in the Tver and Yaroslavl regions. After spending time together in nature, children and their parents communicate with each other, correspond, and consult with each other on what to do in certain health-related situations. All this has a beneficial effect on the quality of life of our patients.
– What words do you use to discharge children and parents?
– There is no stencil, it all depends on the situation (smiles). We recently treated a young man with a large area of wounds, and he was from a cadet school. And I told him: “You will be an officer! Everything works for you - arms, legs, and you can’t see the scars under your jacket.” And naturally, we also work with parents.
– What is important for them to understand and know?
“I always tell the relatives of our patients not to make their children disabled. “You don’t have to constantly look at these scars, because the child feels like his mother is looking at him! Your child is normal, healthy, he just has different skin. After all, there are people with yellow or black skin.” You see, these children should grow up normal, just like before the injury, and play sports - there are no contraindications to this. Well, let the child wear compression clothing - this is not a hindrance, it is the same clothing that can be taken off and put on again. We always work positively, do not let parents and children become discouraged, and find kind words in any situation. If adults, after discharge from the hospital, do not perceive the child as they did before the injury, then the problems will grow like a snowball. It is parents who become the main teachers in life and show children how to behave and instill confidence in their own abilities. I think we need to develop in a direction where there are social workers who, even before the child returns from the hospital to his usual environment, visit kindergartens or schools where this or that patient will return, and conduct explanatory conversations with the children, teachers and educators about how to behave correctly with children who have suffered burns.
– Can a doctor tell parents that the child’s burn was their fault?
- No, the doctor does not tell mom or dad that they are to blame for what happened. But, unfortunately, not every parent understands this themselves; some come with the words “And this is the second time we’ve visited you!” Sometimes mothers withdraw into themselves, and then we schedule a consultation with a psychologist. If adults do not pull themselves together, thereby not emotionally participating in the treatment process, then it is not always possible to quickly achieve the desired results. I always tell my employees that they need to sympathize with parents and take their place. We treat our patients like our own children, and my sons, when they were younger, repeatedly said: “You love your patients more than us.”
– Did you change anything in the arrangement of your home when you started working with burns? Maybe they also became more attentive?
– I don’t want to praise myself, but... I live by the rules and ask those around me to follow them. Place the pots on the last row of burners. Before putting your baby in the bath, you should test the water with your elbow, where the skin is most sensitive. Children should not be in the kitchen while food is being prepared. You need to iron when the child is sleeping, and remember that the floor is not a place for a hot iron. Anything dangerous must be removed. Electrical sockets must have plugs. Well, I don’t know... I was raised this way and I hope that my sons, one of whom already has their own children, remembered these rules. But even now I often remind them of the dangers that exist in the house.
The most harmful thing is bad manners
– What would you say to a stranger who looks askance at a person with a burn?
“You, too, can end up in this place at any time; no one can guarantee you that you will be a healthy person forever.” After all, a burn patient is exactly the same person, he just has unusual skin. Why turn around and discuss in the back? I think that the most destructive quality in people is bad manners in any of its manifestations. And why doesn’t our employer hire a salesperson with hands that have scars on them? This is exactly the same skin, it is washed with soap in the same way, it is not contagious! But why? You know, I keep in touch with many former patients. Many of them have higher education, are married, and have children. Recently, a former patient Valechka came to our clinic for an open day; she had a burn on her face and scalp, which she received as a newborn child. And now she already has her own child!
And the other day I received a call from the mother of a patient who was about 2 years old when he was hospitalized with us for a burn. Now he is 24 years old, he has become a doctor, he wants to join us as an anesthesiologist, so that he can also help sick children.
– But do those who have extensive burns experience gratitude and joy?
“We immediately warn parents and older children not to expect that they will develop the same skin as before the injury. Teenagers are often capricious, and they have to explain that if this procedure is not done now, they will have certain health problems that will be difficult to solve later. Treatment of a burn injury involves constant monitoring to ensure that complications do not occur. And our job is to treat patients and strive to ensure that the consequences of a burn for them are minimal.
– Has your attitude towards appearance changed in any way over almost forty years of working at the burn center?
– You know, I am very critical of my appearance and always say that “don’t drink water off your face,” and appearance doesn’t matter at all. You communicate with a person, and not with his appearance, and, probably, you are interested in his character, attitude towards others, and not what shape his nose is and whether his eyelids are his own or artificially made. Wisdom comes with age... As a rule, people become wiser after thirty. I think wisdom in terms of attitude towards appearance also comes to our patients. Of course, it’s nice to look at a beautiful person, but you definitely shouldn’t judge him by his appearance.
“Can you tell that to a teenager?”
- Certainly can! Why not say if he’s already big and understands everything? I have a patient - he is now 25 years old. At the age of 3, he received a severe burn injury and was in extremely serious condition for a long time. We managed to save him. But rough post-burn scars formed on the neck and face. How complex he was! He wore turtlenecks all the time or tied a scarf around his neck, regardless of the time of year, to hide the consequences of the injury. The school graduation ceremony has arrived. His mom (she's pure gold!) bought him a suit. And I - a shirt with a turn-down collar that would cover the scars on my neck. I say: “Sasha, on this day you should be the most elegant and beautiful!” And he forced himself to put on this shirt. Over time, the boy grew up, and his opinion about his appearance changed. He is married and works as a successful lawyer. Life is good! Believe me, I can find so many positive qualities in a person, so much positivity that can overshadow all his complexes! It is necessary to draw the child’s attention in time to that “zest” in his character, which will become important and life-affirming for him.
– Is this also a doctor’s task?
- A doctor is also a person. Sometimes I really want to compliment a stranger on the street. And sometimes I restrain myself, and sometimes I speak. Why not say if a person, for example, has a very beautiful dress or hat? We say so few kind words to each other!
- And how do they react?
– They smile more often. Maybe they think: “Crazy” (laughs). And you know, sometimes I see a person with burns, and I just want to come up and advise where they can help correct the scars. If I know, why not tell me? But again they will say that... But since I recently started praising those around me, maybe I’ll start giving advice.
BURN DISEASE. CLINICAL SYNDROMES
In burn disease, four clinical syndromes can be distinguished: Burn shock, Intoxication, Infection, Convalescence. There are no sharp boundaries between these syndromes.
BURN SHOCK. It occurs as a result of a neuro-reflex and neuro-endocrine reaction of the body. As a result of a strong inflammatory process in a burn victim, the central and peripheral blood supply is disrupted, the permeability of vascular and cellular membranes increases, the volume of circulating blood decreases with a violation of the ratio of its formed elements and plasma (hypovolemia), plasma escapes from the vascular bed and plasma loss through burn wounds. Plasma loss during burn shock depends on the depth and area of the burn.
Thus, with superficial burns, predominantly external loss of plasma is observed, and with deep burns, plasma enters the surrounding tissues and swelling occurs.
During a burn, the evaporation of fluid through damaged skin increases significantly, leading to a large loss of fluid from the victim’s body. Loss of fluid reduces the mass of circulating blood, resulting in a sharp deterioration in glomerular filtration of urine. Burn shock usually occurs within 2-3 days. Signs of burn shock include: an excited or inhibited state, in severe cases, consciousness is confused or absent; decreased pulse blood pressure, decreased amount of urine excreted by the kidneys (oliguria), vomiting, thirst, chills, muscle tremors.
INTOXICATION. As a result of the appearance in the victim’s body of toxic products, under-oxidized compounds, and bacterial tissue, a period of acute burn toxemia begins. Body temperature rises, loss of appetite occurs with the development of signs of toxic damage to internal organs (toxic myocarditis, hepatitis). During this period, it is necessary to carry out active detoxification measures (forced diuresis, plasmaphoresis, hemosorption).
INFECTION. At the third stage of burn disease, infection begins to progress. Metabolic disorders and weakened immunity give rise to infection of the body. Infection significantly complicates the course of the wound process - it maintains intoxication, suppresses restoration processes in tissues, and can affect various organs.
RECONVALESCENCE (recovery). It occurs from the moment of complete closure of granulating wounds. An important factor in recovery is prompt closure of burn wounds.
Treatment methods
There are two approaches to the treatment of 3rd degree burns: conservative, or closed, and surgical.
How to treat a 3rd degree burn is determined by the doctor. The choice of technique depends on the scale of the lesion. Grade IIIA burns require long-term conservative therapy in combination with surgical treatment. Deep burns are treated only with surgical methods in a hospital.
Conservative treatment
First of all, the doctor will assess the severity of the harm and take measures to prevent wound infection. For this purpose, bandages with antiseptic and iodine-containing preparations are used. Daily dressings with drugs that help drain purulent discharge and reject scabs prevent intoxication of the body.
At the regeneration stage, balsamic dressings are used to stimulate the growth of granulation tissue. In the postoperative period, sponge dressings with anti-inflammatory drugs are used.
Surgery
There are several methods, each of which requires a specific sequence of actions:
- surgical removal of necrotic tissue from the wound;
- necrotomy - dissection of the scab to viable tissue to improve blood supply;
- necrectomy - excision of necrotic tissue in order to create conditions for epithelization or in preparation for skin transplantation;
- amputation of a limb or part thereof on an arm or leg;
- excision of granulations;
- skin plastic surgery in areas of high functionality and aesthetically important areas.
Physiotherapy
At the initial stage of treatment, physical therapy is used to relieve pain and prevent infection. At the granulation stage - to accelerate the rejection of necrotic tissue and stimulate epithelization. In the postoperative period - in order to accelerate the survival of implants and prevent the formation of scars and contractures.
As the burn site heals, the following methods are used: ultraviolet irradiation, ultrasound, laser irradiation, phototherapy, cryotherapy, ozone therapy, magnetic therapy in accordance with the algorithm prescribed by the doctor.
OBJECTIVES OF TREATMENT OF BURNS
FIRST AID FOR BURNS
The goal of treating burns is to preserve the life of the victim and restore the skin. In this regard, it becomes important to provide first aid:
- Stop the victim's contact with the damaging factor.
- Prevent microbial contamination.
ACTIVE TREATMENT OF A BURN
During further treatment, the doctor prescribes the following measures:
- Restoration of microcirculation to preserve the paranecrotic zone.
- Protection against infection and suppression of bacterial growth in the affected area.
- Excision of necrotic tissue.
- Stimulation of regeneration processes (granulation and epitilization).
- For dermal burns - surgical restoration of the skin.
Frostbite
Frostbite is damage to the skin under the influence of low temperatures, both from local freezing and from general hypothermia of the body. Low temperatures impair metabolism in cells and lead to their death.
1 Treatment of frostbite
2 First aid for frostbite
3 First aid for frostbite
Nature and degree of frostbite
A person can get frostbite in different situations:
- frostbite of the cheeks, nose, ears, fingers and toes in frosty weather;
- wearing tight and wet shoes at sub-zero temperatures;
- hypothermia of the body as a result of prolonged exposure to water or snow;
- prolonged exposure to the cold while intoxicated.
Watch for the following signs of frostbite. At first, a person will feel cold, then a burning sensation, first the skin turns red, and then turns white. Skin sensitivity is impaired and numbness occurs. Usually a hypothermic person does not feel his condition, and this makes diagnosis difficult.
Degrees of frostbite
Just like with burns, frostbite is divided into 4 degrees.
- 1st degree of frostbite : redness and numbness of the skin area and loss of sensitivity of the affected area of the skin, burning and itching occur. When warmed and rubbed, frostbitten skin begins to turn red. Stage 1 frostbite goes away within a week.
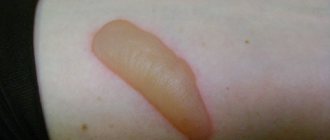
- Stage 2 frostbite is characterized by deeper damage to the layers of the skin and the appearance of blisters with clear liquid on the skin.
- 3rd degree of frostbite : tissue necrosis appears, healing takes place within a month with the formation of scars.
- 4th degree frostbite : not only the skin is affected, but also the bones and joints. The affected tissues are bluish in color and blisters appear.
EPLAN: PROTECTION, FIRST AID, TREATMENT OF BURNS
EPLAN - SKIN PROTECTOR
Eplan is able to penetrate the upper layers of the Epidermis, completely fill the free intercellular space of the Epidermis and create an additional barrier layer, which provides skin protection for a long time. Skin protection after treatment with Eplan lasts up to 8 hours.
EPLAN does not disrupt the intercellular connections of the stratum corneum of the skin, so the skin does not lose its strength and natural protective functions.
When EPLAN is applied to intact skin: EPLAN does not penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis (Basal layer) and does not affect the natural proliferation of Epidermal cells, does not change the water-lipid balance of the skin.
EPLAN IS EFFECTIVE AT ALL STAGES OF BURN DISEASE.
EPLAN reduces pain in the burn site by blocking irritation of damaged nerve endings in the affected area, protects the skin after a burn from environmental influences and infection, and does not allow the body to lose fluid through the burn wound.
EPLAN reduces the flow of decay products of dead tissue into the victim’s blood and prevents intoxication. When treating large areas of burns, such as the treatment of burns with boiling water, steam, sunburn, the use of the drug does not lead to toxic damage due to the formulation itself - EPLAN is not toxic and does not contain hormonal components.
When treating burnt skin, EPLAN acts as an antiseptic, preventing infection of the burn wound (both for first aid for a burn and for protection against secondary infection), and eliminates skin itching.
FIRST AID AND TREATMENT OF BURN WOUNDS: EPLAN TASKS TO PREVENT INFECTION
EPLAN has high antimicrobial activity. The reason for this is the lanthanides that make up Eplan.
Phagocytosis is a process in which special blood cells and body tissues (phagocytes) capture and digest pathogens of infectious diseases and dead cells.
The phagocytic activity of blood leukocytes leads to rapid cleansing of the wound from pathogenic microorganisms: leukocytes begin to more actively destroy bacteria, and EPLAN does not interfere with the access of oxygen to the wound area. Thus, the use of EPLAN in the treatment of burn wounds can be considered as a drug for local enhancement of the patient’s immune status.
EPLAN is non-toxic, made without the use of antibiotics or hormonals. The use of the drug EPLAN becomes especially important in first aid for burns with boiling water and treatment of infected wounds with a large affected area. EPLAN is effective in treating the following injuries: treatment of burns with boiling water, steam, treatment of sunburn, thermal burn.
EPLAN IS A CATALYST FOR SKIN REGENERATION.
The effect of EPLAN as a drug for skin regeneration, skin restoration, rapid healing of wounds and burns is due to the presence of lanthanides in its composition. Lanthanides influence the process of cell proliferation. Application of EPLAN to damaged skin, a burn or a wound, triggers the process of lanthanide exposure to the membranes of proliferating skin cells, which leads to stimulation of their cell division. EPLAN cannot be considered as an inhibitor of kylon tissue activity, therefore its effect is local and has no aftereffect after use.
EPLAN WITH BANDAGE
Eplan-cream and Eplan-solution for the treatment of wounds and burns EPLAN WITH BANDAGE: maintains a moist environment and temperature of the wound, prevents the formation of a scab, provides access of oxygen to the wound, does not create obstacles to the removal of exudate from the wound into a dressing, prevents infection of the wound. EPLAN does not contain toxic components, antibiotics, hormonal or analgesic agents, and wound dressings with EPLAN allow the bandage to easily come off the wound without damaging injured healing tissue.
Sea buckthorn oil
Sea buckthorn oil is an excellent natural, inexpensive remedy for burns. Sea buckthorn oil is practically harmless and has no contraindications (except perhaps allergic reactions or individual intolerance). Sea buckthorn oil for burns contains biologically active substances that restore skin cells and heal wounds; the oil also acts as an antiseptic. Sea buckthorn oil is used undiluted to treat burns.
Sea buckthorn oil is universal and is used for many problems (bedsores, trophic ulcers, thermal burns, vitamin deficiencies, etc.).
It is not very convenient, of course, to apply the oil, because it is in liquid form, but this is compensated by its 100% naturalness and effectiveness in treating burns and wounds.
Sea buckthorn oil
OJSC "Nizhpharm", Russia
Sea buckthorn oil is a herbal product, a source of vitamins A, E, K, stimulates reparative processes in the skin and mucous membranes, accelerates their epithelization, inhibits the activity of gastric proteases, has anti-inflammatory, restorative, antioxidant and cytoprotective effects.
Due to the presence of fat-soluble bioantioxidants, it reduces free radical processes and protects cell membranes from damage; lowers cholesterol and lipid levels in the blood. Of all the known vegetable oils, only sea buckthorn contains vitamin A in the most active form in the form of beta-carotenoids and in maximum quantities. In the last decade, scientists around the world have unanimously recognized the outstanding healing properties of this provitamin. from 24
4.0 1 review
941
- Like
- Write a review
Read also: Top 5 best sorbents for poisoning Rating of the most effective and safe sorbents that help with poisoning and hangover syndrome.
BEST WOUND-HEALING OINTMENT FOR BURNS EPLAN CREAM: TREATMENT METHOD
When the skin is locally exposed to temperatures above 55-60 degrees Celsius, aggressive chemicals, electric current or ionizing radiation, a BURN occurs. In assessing the severity of a burn, the area of the body surface affected by the burn is of great importance; there are 4 degrees of burns.
Degree I is characterized by damage to the most superficial layer of the skin (epidermis), consisting of epithelial cells. In this case, redness of the skin appears, a slight swelling accompanied by pain. After two to three days, these phenomena disappear on their own, and no traces remain after the burn, except for minor itching and flaking of the skin.
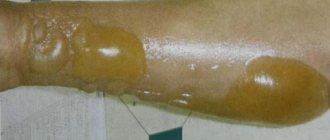
Stage II is characterized by the formation of blisters with a yellowish liquid against the background of redness of the skin. Blisters can form immediately after a burn or after some time. If the blisters burst, bright red erosion is revealed. Healing at this stage usually occurs by 10-12 days without scarring.
III degree burns are characterized by greater depth of damage with tissue necrosis (necrosis) and the formation of a burn scab. The scab is a dry, light brown to almost black crust; When scalded, the scab is soft, moist, and whitish-gray in color. There is a IIIA degree, in which the epithelial elements of the skin are preserved, which are the starting material for independent wound healing, and a IIIB degree, in which all layers of the skin completely die and the resulting burn wound heals through scarring.
IV degree burns are accompanied by charring of the skin and damage to deeper tissues - subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones.
Burns of I-IIIA degrees are considered superficial, and burns of IIIB-IV degrees are considered deep. It is possible to accurately determine the degree of burn (especially to distinguish IIIA from IIIB degrees) only in a medical institution using special diagnostic tests. In domestic conditions, thermal burns most often include: burns with boiling water, steam, iron, sunburn, etc. Burns and scalding with boiling water account for almost 40% of all deaths of children under 15 years of age. In a milder form, this is the most common type of injury for people of all ages.
How to treat burns with a burn remedy - EPLAN?
For first and second degree burns, we suggest using the drug EPLAN in ointment and liquid form. The affected area is lubricated with Eplan and, as it absorbs and dries, the treatment is periodically repeated until complete healing. If burn blisters occur, the exfoliated skin should be removed, but you do not need to open the blisters yourself before going to a medical facility, because this can lead to wound infection. Treat the edges of the wound with an antiseptic (hydrogen peroxide, miramistin, chlorhexidine), apply sterile wipes soaked in the drug and secure with a gauze bandage. Change dressings every other day. Epithalization begins on days 7-9, from the moment granulations appear. The treatment process under bandages is continued with EPLAN liquid (12-14 days). At the healing stage, the edges of the wound are treated with dry sterile wipes (without antiseptics).
If EPLAN is immediately applied to damaged areas, redness and inflammation disappear, and blisters with serous fibrous contents do not appear.
Burn: when do you need medical help?
You can treat a burn at home if it is redness of the skin followed by the appearance of small blisters with clear liquid (no more than 1 cm). The burn area should not exceed the patient's palm. A person needs to be urgently taken to hospital if:
- the affected area is larger than the size of the palm;
- burns on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, face, genitals;
- clothing has become stuck to the burn site;
- there is opaque content inside the blister (blood, pus);
- body temperature increased;
- there is nausea, vomiting, confusion;
- the victim is too young or too old;
- the victim is weakened by a recent illness.
Before being examined by a doctor, a person with a burn should be given a lot of water; if the burn site is very painful, it is better to offer a painkiller.
Themes:
Burns Thermal burn Sunburn Wounds Wound treatment Burn ointment Burn spray Panthenol spray Bepanten Plus Olazol Radevit Sea buckthorn oil
SUNBURN. PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
TIPS FOR TREATING SUNBURN
When going on a trip, do not forget that the skin is defenseless against active sunlight, and the desire to quickly get a brown tan is understandable, but not entirely correct. The result of prolonged and uncontrolled exposure to the sun is a sunburn. This is characterized by poor appetite, sometimes vomiting, insomnia, fever, and tachycardia. Against this background, drowsiness may occur. Children suffer especially hard from sunburn.
What should you do to protect yourself and your family from sunburn?
Firstly, you need to actively moisturize your skin and drink as much water as possible, because the very first negative effect that solar ultraviolet radiation has is dehydration. Secondly, in the first hours after getting a sunburn, you can take antihistamines (suprastin, tavegil, etc.) - this will reduce skin inflammation and simple painkillers (ibuprofen, paracetamol) - this will reduce pain. Thirdly, use EPLAN burn ointment (or solution) to treat the affected area. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day. We recommend that you first lubricate the affected area with the solution in order to instantly relieve redness and swelling. EPLAN solution also has a cooling and analgesic effect. To consolidate the effect and soften the skin, we recommend continuing treatment of sunburn in the evening, using EPLAN cream. Fourth, to protect the skin from sunburn, we recommend applying Eplan solution to the skin 10-15 minutes before going out into the sun. Eplan forms a protective film on the skin, which will protect the skin from burns in the future.
Must remember! Changes in the structure of the skin are irreversible after any burn (including sunburn and boiling water burns); in the future, the skin may constantly react in a more severe form to new portions of sunbathing.
Detailed information on the use of EPLAN for the treatment of burns, wounds and skin lesions in the EPLAN section: AREAS OF APPLICATION
Bepanten Plus
The active component of this burn cream is also dexpanthenol, but it also contains an antimicrobial substance. All this together helps to effectively treat sun and thermal burns, as well as prevent infection from entering the wound. "Bepanten" is often prescribed to nursing women for cracked nipples.
A minor disadvantage of this burn cream is that it has to be applied by hand or with a cotton swab, but this in no way affects the effectiveness.
Bepanten Plus
F. Hoffmann-La Roche, France
Prevention and treatment of dry skin when the integrity of its integument is violated;
— care for the mammary glands during breastfeeding (treatment of dry nipples and painful cracks); — treatment and care of the baby’s skin (diaper rash, diaper dermatitis); - activation of the skin healing process for minor injuries, minor burns, abrasions, skin irritations, chronic ulcers, bedsores, cracks and skin grafts. from 308
4.0 1 review
523
- Like
- Write a review
FIRST AID FOR BURNS WITH BOILING WATER AND STEAM
A burn is an open injury or destruction of the skin and mucous membranes. For burns, not only the type of damage factor matters, but also the duration (exposure) of its action.
The skin is the outer covering that protects the body and its connection with the environment, its mass is 4-6%, and together with the subcutaneous layer - 16-17% of the total body weight, its area in average adults is approximately 1.7 m2 . The skin performs a number of important functions: protection from the external environment, thermoregulation, participation in metabolism, water and heat transfer, blood distribution in the body, receptor, secretory, pigment-forming, respiratory, energy-saving (fat depot), immune.
When burned by boiling water or steam, tissue damage occurs quickly; the source of the burn must be removed immediately. Cooling significantly reduces the severity of the burn and relieves severe pain.
Burns from boiling water and steam are a very important problem in adult and child traumatism: burns become especially dangerous for young children and the elderly due to imperfections in the body’s protective functions. Most cases of burn injury occur at home due to negligence.
A superficial burn with boiling water and steam, like a sunburn, should be immediately treated with an anti-burn remedy - EPLAN solution. This will allow injured skin to heal in the shortest possible time. The drug can be used in different age categories. In serious cases, when anatomically significant areas (face, neck, perineum) are affected by the burn, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Detailed information on the use of EPLAN for the treatment of burns, wounds and skin lesions in the EPLAN section: AREAS OF APPLICATION
Complications and consequences
The victim often experiences neuropsychiatric disorders, disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and liver, the formation of scars and contractures, loss of limbs or parts thereof.
The prognosis of how long it takes for a burn site to heal depends on the area and depth of the lesion, as well as the age of the patient. High mortality rates are observed among older people over 60 years of age and children.
Life-threatening burns represent 10% of the surface of the face or perineum and 15% of the surface of other parts of the body.
HOW TO USE BURN OINTMENT IN FIRST AID
There are several stages in providing medical care for burns.
First stage (prehospital)
includes first aid for burns, provided in the form of self- and mutual aid at the scene of the incident. The burn surface for superficial burns is painful, so mechanical cleaning is allowed only in case of severe soil contamination by irrigation with antiseptic solutions. It is necessary to choose the optimal remedy for burns in a particular case. Burn wounds are covered with anti-burn dressings that do not stick to the wounds or sterile dressings with water-soluble ointments (levomekol, levosin, dioxykol, dermazin).
Instead of traditional remedies used in these cases, we recommend the universal, ready-to-use drug EPLAN (ointment and solution). EPLAN has unique properties for providing first aid, especially for sunburn.
EPLAN has the following useful properties: - pronounced absorbent activity (dehydrating activity is 13.5 times higher than that of a hypertonic NaCl solution); -low toxicity; -good permeability in fabric; - no irritating effect; - ease of application on surfaces.
If the ointment (cream) is immediately applied to the damaged areas, redness and inflammation disappear, and blisters with serous fibrous contents do not appear.
For local treatment of burns with EPLAN, two methods can be used: open (without bandages) and closed (with bandages), subsequent dressings are carried out daily or every other day until the wounds are completely healed.