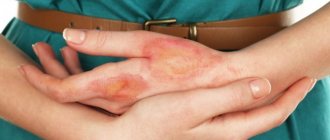
Types of chemical burns
Taking into account the characteristics of the damaging substance, the following types of damage are distinguished:
- Acidic.
When it comes into contact with the skin, the acid causes the protein to coagulate. As the protein breaks down, it forms a dense crust that prevents the substance from penetrating deep into the tissue. Therefore, such burns are usually shallow. - Alkaline.
Improper handling of caustic soda, quicklime, and ammonia leads to serious consequences. The aggressive substance corrodes tissue, causing deep damage. Such wounds heal more slowly than other burns. - Burns from heavy metal salts.
Less dangerous compared to previous species. Damage is limited to the outer layer of the skin. - Phosphoric.
Upon contact with the skin, the substance ignites, leaving behind a deep wound.
In the absence of first medical aid, the substance continues to destroy the integrity of the integument. Removing the chemical from the skin is not enough to stop the reaction; only inactivation will help.
Consequences
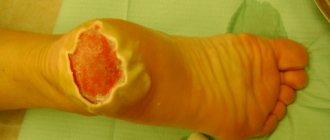
If the burn was caused by an acid or alkali, a crust forms in its place, which has its own name - a scab.
Alkalies in contact with skin are much more dangerous than acids, because... they quickly penetrate into the deep layers of tissue, causing serious damage.
- If the burn was caused by alkali, the color of the scab is whitish, without clear boundaries, with an imperceptible transition to adjacent healthy tissue. The texture of the scab is soft and loose; it hardens much later.
- When exposed to acid, the scab looks different - from dense, hard and dry. The border is clearly defined, the transition to healthy areas of the skin is visible to the naked eye. Typically, such injuries are superficial, which speeds up recovery.
The color of the tissue in the affected area depends on the type of chemical:
- When sulfuric acid comes into contact with the skin, the burn is initially white, then turns gray or brown.
- When exposed to nitrogen acid, the burn will be light yellow, with a greenish or brown tint.
- When skin comes into contact with hydrochloric acid, a yellow burn is formed;
- Acetic acid leaves off-white burns when it comes into contact with the skin;
- After carbolic acid, white traces remain, which subsequently become brown;
- Concentrated hydrogen peroxide leaves dirty-gray burns.
It is useful to study and remember the differences in burns by color so that in a critical situation you can quickly determine the type of composition that burned the skin. This will help minimize harm or even save lives.
When chemicals get on the skin, their effect continues for some time after contact has been stopped (the wound is washed, a bandage is applied).
This is due to the peculiarities of the functioning of our tissues - the absorption of the substance does not stop instantly, which makes it much more difficult to determine the degree of the burn.
Sometimes the substance continues to act for several hours or even days - so it is very difficult to immediately draw conclusions about the depth of the damage. As a rule, it is possible to accurately determine the extent of the burn only 1-1.5 weeks after the injury - by this time the scab begins to suppurate, which is one of the parameters when determining the depth of the damage.
The severity of a burn from contact with chemicals depends on two key characteristics - depth and area. Chemical burns themselves are usually deep, and if they are also large, this aggravates the situation.
Classification by severity
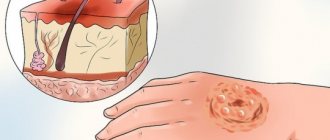
Depending on the severity of the injury, there are three degrees of burns. The first is diagnosed with superficial damage to the skin.
Such burns are formed by short-term or weak contact of the substance with the cover. Accompanied by mild swelling, redness and burning. The wound heals in 3-5 days. There is no scar left.
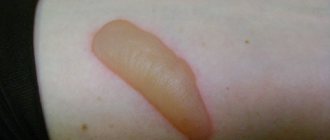
Blisters filled with clear liquid indicate a second-degree burn.
Pain and redness are more pronounced. It takes about two weeks for tissue recovery after such a lesion. The threat of infection increases.
The third degree is the most severe.
Characterized by damage to the lower layers of the skin. The wound heals after 1-2 months, leaving behind a rough scar.
Burns of mucous membranes are classified in a similar way. In such cases, diagnosing the severity of the lesion becomes more difficult and requires medical assistance.
Treatment
To choose the right course of rehabilitation, you first need to correctly diagnose the problem. For this purpose, various classifications of burn marks have been invented, the most popular of which is the Vancouver Scar Rating Scale. In Russia it is slightly changed, in accordance with national characteristics:
| Points | Description |
| by color | |
| 0 | the color does not stand out from the overall skin tone |
| 1 | hyper- or hypo-pigmented (the color is either brighter than the base tone or paler) |
| 2 | immature scars - shades of red |
| in relation to the level of surrounding healthy skin | |
| 0 | at the level |
| 1 | below level |
| 2 | above level |
| by relief and surface quality | |
| 0 | flat |
| 1 | uneven, bumpy |
| 2 | with hyperkeratosis and ulcerations |
| according to form | |
| 0 | scar cord or fold (length greater than width) |
| 1 | scar mass (length and width are equal) |
The scores shown in the table indicate the degree of burn. So “0” corresponds to the first degree, “1” to a superficial burn, “2” to a deep or third degree burn.
How to treat which degree
Since the scale of the problem at 3 degrees is different, the treatment will be different:
- To treat a 1st degree burn, homemade applications with a special cream are sufficient, and within a week the damaged area should recover.
- If in grade 1 there is only redness, then in grade 2 there is a burning sensation and blisters. This is still not scary, and the burn can be cured with the same cream, but the course of applications will last 30-40 days. Under no circumstances should you puncture the blisters, as this will inevitably lead to infection of the wound.
- With a 3rd degree burn, swelling, dead skin, scabs, blisters and hyperemia around the wound are observed. In this case, a doctor’s supervision is required, as well as complex treatment with ointment or cream, as well as cosmetic procedures, physiotherapy, and even surgery with skin grafting. The body will recover for at least 2 months.
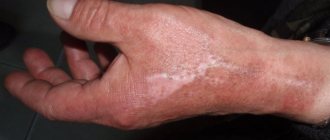
In any case, scars remain after the injury. How to remove a burn scar depends on how serious it was. The first and second degrees do not leave deep damage, so you can cope with them on your own with the help of physiotherapy and cosmetics. With the third degree it is more difficult - damage can reach the bones, therefore the recovery period will be very long and difficult, it involves surgery and skin grafts.
Find out which scar correction method is optimal for you!
doctor Svetlana Viktorovna Ogorodnikova.
doctor
Cosmetic procedures
According to dermatologists, treatment of scars and marks after a burn should begin only when the wound has completely healed and a scar has formed. Starting earlier can only make the problem worse. What solutions will be offered in the beauty salon:
- Chemical peeling . A substance enriched with fruit acids is applied to the scar. It corrodes the “wrong” stratum corneum of the epidermis, due to which the scar softens and evens out relative to the overall skin texture.
- Laser peeling. Popular against facial scars. As cosmetologists assure, the process is safe and effective. The rough scar is carefully “cut off” by the laser beam, leaving new soft skin underneath.
- Silicone sheets and gels prevent the growth of scar tissue due to pressure. This method is effective at the beginning of scar tissue formation.
- Diamond grinding. A type of peeling - microcrystals are placed in a special device, which during operation exfoliate the stratum corneum of the epidermis with sharp edges (let us explain: it consists of dead cells and prevents harmful substances from entering the body). This way you can remove burn marks that are quite large in area.
- Glucocorticoid injections. They are mainly used against keloid scars, but there is a high probability of side effects. The drug is injected directly into the scar.
In addition to the listed procedures, physiotherapy helps get rid of scars - courses based on physical influence: with the help of ultrasound or electrophoresis, drug particles penetrate much deeper than they could with a conventional application.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is effective for correcting both fresh scars and old ones. To achieve visible results, it is very important to choose the right medication.
What procedures are classified as physiotherapy?
- Magnetotherapy. Improves blood supply to the scar and the mental state of the victim after injury.
- Phonophoresis. Resolves scar tissue, increases the elasticity of connective tissue, stimulates blood and lymph circulation and metabolic processes, including intracellular metabolism, enhances the production of biologically active substances and the activity of enzyme systems.
- Laser therapy. Accelerates tissue regeneration, calms nerves, and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Electrophoresis. The therapeutic effect consists of a simultaneous positive effect on the body of electric current and active charged molecules of the medicinal substance. A drug depot (reserve) is created in the skin and subcutaneous fat, significantly increasing the exposure time of the drugs.
The speed of recovery depends not only on properly selected rehabilitation, but also on cosmetics and medications used during the course.
How to provide first aid for a chemical burn
In case of a burn, you need to act immediately, on the spot.
First of all, it is necessary to remove the substance from the skin as quickly as possible. Do not use a napkin, sponge or other materials - even light pressure can cause the agent to penetrate deeper into the tissue. It is better to shake off the powder. Residues should be washed off with water, the duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. If the wound is shallow, it is enough to apply a sterile bandage or bandage. In case of serious burns, the victim must be wrapped in a clean sheet, given painkillers and called an ambulance. To reduce the risk of poisoning, you should open the windows and, if possible, take the victim to fresh air.
In some cases, contact with water will only worsen the situation; for example, aluminum compounds may ignite. Therefore, it is initially necessary to find out the details of the incident from the victim.
The extent of the wound depends on how timely first aid was provided for chemical burns.
Precautions and prevention measures
To protect yourself from chemical burns, you should follow simple rules.
When working with aggressive substances, you must wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles and a respirator. Chemicals should be stored in tightly closed containers (labeled) away from food and places where children can reach them. After use, ventilate the room. It is dangerous to mix substances if you are not sure of the consequences of their combination.
Added: 10/19/2021