What are they and how do they manifest themselves?
- Thermal: flame, hot liquid and steam, heating radiators, hot water pipes and other hot objects.
- Chemical: acids and alkalis - often included in household chemicals.
- Electrical: lightning, current.
- Radiation: ultraviolet, radiation.
- Mixed: several factors from the above.
Almost all burns are thermal: damage to the skin, and sometimes mucous membranes, muscles and bones, as a result of exposure to high temperatures. They most often affect children, and in 95% of cases the cause is a flame.
According to Russian clinical guidelines, there are three degrees of depth of skin damage for thermal burns:
- Only the epidermis is the topmost layer. The skin turns red and swells. The pain is usually minor because the nerve endings are deeper. After 2-4 days, the dead epithelium sloughs off. There are no scars left.
- The epidermis and upper dermis is a layer rich in blood vessels and nerve endings between the epidermis and subcutaneous fat. In addition to redness and swelling, small blisters with cloudy or bloody contents appear - this is when the epidermis peels off and the void between it and the dermis is filled with blood and lymph. Second degree burns are very painful because the nerve endings are left without their protection - the epidermis. In 1-2 weeks, the lower layer of the dermis, closest to the subcutaneous fat, is renewed and the wound heals. Scars may remain if a large area of skin is affected.
- Full thickness skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones. A dense brown or black crust forms over the burn, which “sticks together” with the tissues below. The blisters merge with each other, and ulcers then appear in their place. Pain occurs only at the time of injury. Then pressure or slight discomfort is felt, and there is no pain even when touching the wound - because all the receptors have died. When the dead tissue begins to be replaced by new tissue, pain appears again. Amputation of the burned limb and plastic surgery of defects may be required. Scars always remain.
Types of oral burns
A burn is a very common injury. Along with the oral cavity, the larynx and esophagus may be affected. There are four main forms of burns:
- Thermal burn. Occurs through contact of the oral cavity with hot liquid or steam.
- Electrical injury. The most common case of such an injury is a violation of the rules for conducting physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Chemical burn. This injury occurs as a result of contact of the oral mucosa with acids, alkalis or chlorine.
- Radiation burn. You can get such a burn during radiation therapy in the complex treatment of malignant neoplasms of the larynx.
Why does it hurt so much
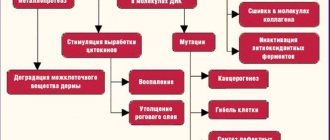
The skin is the largest organ: 4−6% of the total body weight. It contains up to 82% water and a third of the total blood volume. There are 2 million nerve endings in the skin, 1.5 million of them are pain receptors.
Temperatures above 44 °C destroy skin proteins - the integrity of the cell membranes is disrupted and water from the cells goes into the space between them. This can be illustrated using an egg as an example. It contains approximately 73% water, 13% protein, 12% fat and minerals. When cooked, the proteins in the cell membrane are destroyed and folded - water comes out. The same thing happens to the skin, only the water goes into other tissues. Therefore, swelling occurs.
Then platelets stick together in the vessels of the dermis and clog the lumen. The blood supply to the burned area is reduced, which can lead to complete tissue death if help is not provided in time. A burn also leads to the release of substances into the blood that provoke inflammation.
Causes of chemical burns
Chemical burns can occur at work, at home, or during suicide attempts. They occur when exposed to the following substances:
- acids (sulfuric, hydrofluoric, hydrochloric, acetic, nitric, etc.);
- alkalis (caustic soda, etc.);
- petrol;
- phosphorus;
- kerosene;
- bitumen;
- salts of heavy metals (zinc chloride, silver nitrate), etc.
The insidiousness of chemical burns lies in the fact that tissue damage occurs before the substance is completely neutralized and eliminated. In this case, acid burns are more favorable, since upon their contact with tissue proteins, a scab is formed, preventing further penetration of acids. Alkalis, unfortunately, have a fat-dissolving effect, so they cause deep burns. Phosphorus causes not only serious local tissue damage, but also severe general poisoning.
How to prevent
GMS Clinic pediatrician Maria Fadeeva recommends:
- Keep matches and lighters out of the reach of children
- keep hot foods and drinks away from the edge of the table
- Place irons and curling irons that are turned on so that the child cannot reach them
- cook on the back burners, turn the handles of pots and pans towards the wall or to the side so that the child cannot accidentally grab them
- use protective devices that block the switching on of stoves
- do not carry the child in your arms while preparing food
The kitchen is no place for a small child, especially when preparing food.
- Do not leave your child unattended in a room with heaters on.
- Check the temperature in the bathroom before bathing children
- Keep children away from bonfires and do not set off fireworks nearby
- Avoid inhalation over hot decoctions and boiled potatoes for ARVI - this is ineffective and creates a high risk of burns to the respiratory tract and face.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component oral skewers ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component skewers - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Consumer Reviews
Natasha (vseotzyvy.ru)
“Mouth rinse Vertex JSC Asepta mouth rinse is sold in pharmacies, that’s why I bought it, it has more medicinal properties than just a cosmetic product, and indeed this rinse perfectly removes bad breath, disinfects gums, menthol gives freshness for almost a day perfectly helps smokers."
Dilya09 (otzovik.com)
“Hello to all readers of my review! I wanted to tell you my story about how I started using the Asepta oral brush.
It all started with the fact that I had an implant installed instead of an extracted tooth and was given strict instructions to rinse my mouth with chlogrexidine and, preferably, an oral scavenger. At the pharmacy, my choice fell on the Asepta drug, despite the price, because after the implantation procedure I had the feeling that now I would brush my teeth after every meal and rinse my mouth (it was just creepy). The price of this skimmer in pharmacies is above 160 rubles.
It doesn’t taste very nasty like some skimmers; after rinsing, it freshens your breath due to the “Lime” and “Mint” flavors. By the way, I don’t use it regularly anymore, I often forget to rinse my mouth, but, nevertheless, it is always present in the bathroom.
Of course, over the years, the memories of implantation have become dull, much has been forgotten, but Asepta and I are now friends. I take not only the skimmer, but also toothpaste. In general, not only is the skipper good, but the whole series is good. I recommend it to everyone who uses oral skewers.”
First aid
The Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations recommends not to panic, cool the burn, cover the affected area with a clean cloth, give painkillers and call an ambulance if necessary.
Maria Fadeeva tells more:
The most important thing is to stop exposure to the damaging factor: remove the child from fire, hot water or hot objects. For shallow burns, rinse the affected area of skin with running water, and if the skin looks purple and/or blisters appear, immerse it in cool water no higher than 15 ºС for no longer than 20 minutes. For extensive burns, cover the skin with a clean, non-stick cloth, such as cotton. Small areas can be kept open. If the pain is severe, you can give your child ibuprofen or paracetamol and, if possible, raise the burned part of the body above the level of the heart - this slows down the blood flow to the area, reduces swelling and pain. If there is itching, you can take antihistamines.
Why are gum burns dangerous?
Despite all the external harmlessness, any gum burn can lead to serious consequences. Firstly, after an injury it is easy to introduce an infection into the soft tissues and cause complications. Secondly, with severe burns and significant lesions, necrosis of the mucous membrane occurs, which requires immediate intervention by a specialist. It is important to remove dead tissue as soon as possible to prevent necrosis from spreading further.
Do not forget that the thin layer of epithelium in the mouth is a huge number of capillaries. It is the gums that ensure the correct and strong fastening of the teeth; it is the gums that keep our smiles beautiful and even for many years.
What not to do
Pediatrician at the Fantasy Children's Clinic, Ph.D. Svetlana Mukhortova does not recommend:
- Lubricate the burn with vegetable oil, cream, sour cream and other fermented milk products. A film forms on the skin, air stops flowing to the wound - it overheats, and the depth of the lesion increases. Lactic acids and fermentation products can introduce microbes into the wound
- treat burned skin with brilliant green, iodine, cosmetic lotions - alcohol dries out the skin and causes burning and pain
- apply bandages with urine to the wound. The effectiveness of urine therapy has not been proven
- puncture blisters - microbes with liquid can enter the wound. The blisters will open on their own - as a rule, this happens when the skin has already been renewed and the wound has “healed”
- remove stuck clothing yourself so as not to injure the burn site
- apply snow and ice longer: burned skin does not feel temperature changes - you can get frostbite
- sprinkle the burn with soda, flour, mustard powder, starch or baby powder - the film prevents cooling, and small particles can fester
- apply tight bandages and seal the wound with adhesive tape - air access is reduced
- rinse with running water if bubbles open - this is painful and can lead to germs penetrating deeper.
When to call an ambulance
“For extensive burns. In the first degree - only redness of the skin - you can seek medical help if the pain and swelling increases,” says Svetlana Mukhortova.
Maria Fadeeva also recommends seeing a doctor if:
- burned skin of the face, fingers and toes, feet, joints, genitals
- The burn area is larger than the child's palm
- the victim is less than 5 years old
- body temperature rises, redness increases, sensitivity disappears at the burn site
- there is a suspicion of a burn to the respiratory tract or eyes - this is possible after fires, falling into a fire, inhalation over hot steam
What else can you do at home?
To speed up the healing of superficial burns, preparations with dexpanthenol are recommended - preferably in the form of sprays, so as not to create a film over the affected area. It is applied to the wound 2-4 hours after the burn and only in the first degree. Sometimes it is allowed to treat a child at home and for burns with small blisters. In this case, it is necessary to promptly change clean bandages and, if the doctor prescribes, treat the wound with chlorhexidine.
In 2008, WHO issued a report on the prevention of childhood injuries. Pediatricians have developed a brochure for children, “Live an interesting and safe life”: it is written in simple language that children can understand and is presented in the form of stories and entertaining quizzes, and the advice from it is still relevant today.
Symptoms and diagnosis of chemical burns
The symptoms of burns are related to the chemical nature, concentration, quantity, duration of the damaging effect of the substance and the location of the injury. The burned person experiences intense pain in the affected area. Burns of the pharynx or esophagus are accompanied by difficulty swallowing. In case of severe chemical burns, general symptoms are observed (fever, disturbances of consciousness, etc.), and burn shock may develop.
The severity of the lesion is determined during a medical examination:
- 1st degree – swelling and redness of the burned area are characteristic;
- 2nd degree - bubbles filled with liquid appear in the affected area. 2nd degree burns are superficial and heal quickly, because epithelization (healing) occurs over the entire wound surface;
- 3rd degree - the appearance of tissue necrosis (necrosis) - refers to deep burns. Such burns can take a long time to heal, because... the wound surface is epithelized only from the edges.
The photo above shows a chemical burn caused by improper use of dimexide. The exfoliated epidermis is partially excised, and the wound surface is visible underneath.
The same burn after treatment 5 days later - the wound has almost healed.
Deep burns are fraught with the subsequent formation of rough, disfiguring scars.
In some cases, the type of damaging agent can be determined by the smell and color of the scab. Thus, when tissue comes into contact with sulfuric acid, a black scab is formed, when interacting with nitric acid it is yellow, and when exposed to acetic acid it is white. It is quite dry, dense and clearly demarcated. In the case of alkali burns, the whitish scab has a soft, friable consistency and blurred boundaries. After a phosphorus burn, a dry scab remains, glowing when darkened. The crust that forms after contact with molten bitumen is difficult to remove.
To clarify the origin of the damaging agent, samples of tissue, vomit, and saliva can be sent for examination within 2 days after the injury.