At the burn site, the victim experiences pain of varying intensity. A finger burn refers to an injury that occurs at home, at work or in everyday life. Damage to the skin can be superficial, or deeper layers are affected. At the burn site, the victim experiences pain of varying intensity. It is not always possible to eliminate injuries sustained at home on your own. Deep lesions require qualified treatment.
- 1 Types of burns 1.1 Finger burns are classified by degree
- 3.1 Traditional medicine
Classification of burns
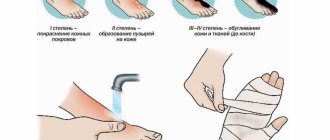
Based on the depth of tissue damage, doctors distinguish four degrees of burns.
The first one is easy. The top layer of skin is damaged. The epithelium turns red and swells. The wound is accompanied by a strong burning sensation. Heals in 3-4 days even without treatment.
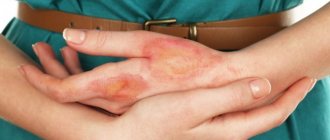
The second is of medium severity. The epithelium and dermis suffer. At the same time, blood vessels and nerve fibers remain in order. The person experiences acute pain and burning. Small blisters appear at the site of damage. They are filled with clear liquid. Heals within 2 weeks.
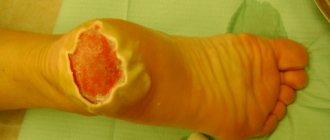
The third one is hard. The skin is damaged to its full depth. Blood vessels. Partially subcutaneous tissue. Large blisters form. Some of them burst. Pain sensitivity in the injured area decreases.
The fourth is extremely difficult. Skin, muscles, tendons, and bones are severely damaged. Necrosis of the injured area occurs.
The first two degrees cause burning and pain. The third and fourth are accompanied by pain only at the time of injury. Then pain sensitivity decreases. The reason is the destruction of nerve fibers.
Symptoms and severity
There are four types of damage received:
- The first is that the upper outer layers of the skin are damaged. Redness forms on the fingers, accompanied by minor pain.
- Second, the burned area becomes covered with a blister, and acute pain is felt.
- The third is caused by damage to the deep layers of the skin. After recovery, scars and scars may remain.
- The fourth is the most dangerous type. All tissues of the finger are affected, affecting ligaments and bones, even to the point of charring. Recovery in this case is problematic; there is a high risk of amputation of the phalanx.
I burned my finger - how to relieve the pain?
- The first thing is to eliminate the source of injury. Move the pan or hot item away. Turn off the electrical appliance.
- Then cool the affected area of skin. For some time it itself remains a source of heat. As a result, it damages healthy tissue. Don't skip this point! Otherwise, in an hour the burn will expand its borders.
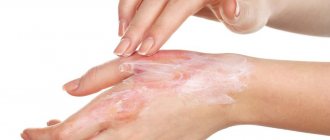
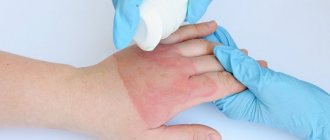
- If you have anti-burn gel in your first aid kit, apply it to the affected finger. It will not only cool. Pain relief. Neutralizes the wound.
- When there are no special preparations, ordinary water can be used for cooling. She should have a temperature of 15-20 degrees.
- Remove the rings. Later, due to swelling, this will be difficult to do.
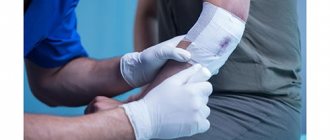
- After cooling, apply a sterile bandage to the burn site. In places where the blisters have burst, you can place pieces of clean cling film. It will not stick to the wound. This will make it easier for you to remove the bandage later. You don't have to tear it off with the meat.
- Need to numb the pain and burning sensation? Take any analgesic. Apply a pain-relieving compress. It's easy to prepare. Soak the bandage in the novocaine solution. Apply to the sore spot.
Causes
The most common ways to burn your fingers:
- Chemically - prolonged contact of the skin with an aggressive chemical environment or alkalis. A highly concentrated solution damages the area of the fingers in the first seconds of contact with the epidermis. The phalanx pad wrinkles and becomes covered with a hard crust.
- Thermal - injury occurs as a result of contact with heat sources (stove, fireplace), heated objects (frying pan, cup, etc.), the influence of steam or hot water. Household burns are most common (iron, oil).
Types of burns
If you burn a finger on your hand, first aid is required. But initially they determine what type of injury was received.
- Thermal. The victim burns his finger with fire, steam, boiling water or a heating element. One of the deepest lesions is considered to be damage to the skin by hot objects. After its exposure, clear boundaries remain on the skin. Exposure time, temperature and thermal conductivity play a big role.
- Chemical. Skin damage on the fingers occurs after contact with aggressive acids and alkalis. Their degree is critical if the substance has a high concentration. If the epidermis is damaged, a strong scar subsequently remains.
- Radial. Occurs when exposed to ultraviolet, infrared rays and other types of radiation. Such injuries are often recorded at work, where appropriate equipment is used.
Finger burns are classified by degree
Degree of injury.
- the superficial lesion is accompanied by redness, stinging pain and slight swelling.
- Painful blisters or blisters containing lymph appear on the skin.
- a painful necrotic process of tissue begins with the formation of a scab.
- complete death of soft tissues affecting bone and muscle tissue.
Rules for first aid for burns
In the vast majority of cases, people receive such injuries at home, in hazardous work, or during outdoor recreation. To save the life of the victim, it is important to know the procedure for providing first aid for each type of burn.
For thermal burns
- Remove exposure to source of damage (eg fire, steam, boiling water).
- Pour cold water over the damaged area for 7-15 minutes (if external signs indicate a 1st or 2nd degree injury). Ice or snow wrapped in a clean cloth is suitable for cooling.
- For a 3rd or 4th degree burn, first apply a moistened bandage to the burn site and cool it in a container of water. Do not direct a stream of running water onto the wound.
- Free the burned area from clothing and accessories. If the tissue is stuck, carefully trim off the excess without touching the wound itself.
- Cover the wound with a clean, damp cloth for grade 3-4 damage.
- Prepare a solution of 0.5 liters of water, ¼ teaspoon of soda and ½ teaspoon of salt, and give it to the victim.
For chemical burns
- Free the damaged area of the body from clothing and accessories.
- Immediately rinse the injured area with cool water for half an hour. If the procedure was not done immediately, then the washing time is increased to 45 minutes.
Attention! If the burn was caused by an organic aluminum compound, you cannot rinse it with water, otherwise it will ignite.
- To avoid worsening the condition, do not dry the burned skin with a towel, even a paper towel.
- If the burn is a result of the action of acid, then wash the wound with a weak solution of baking soda (1 teaspoon per 500 ml of water) or non-contactly treat with soapy water.
- If the cause of the injury is exposure to alkali, then the wound is treated with a non-concentrated solution of acetic or citric acid.
- Cover with a cloth soaked in cool water for 15 minutes.
- Gently cover the wound with a sterile bandage.
If the injuries are extensive and painful, then the victim is given an anesthetic and warm drink, for example, alkaline mineral water. Medicines based on paracetamol, acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen and any NSAIDs relieve pain well.
Calling an emergency medical team is mandatory for 3rd-4th degree burns. And also, if an elderly person or a small child received a thermal injury, a large area of skin, organs of the groin area are affected, the respiratory system, eyes, oral cavity are affected, the victim has concomitant heart disease or diabetes.
Electrical burn
- Turn off the power source to stop the current flowing to the affected person. Or move it to the side with a stick/branch to avoid getting hit yourself.
- Lay the victim on his back and place a bolster under his legs and lower back so that his head is lower than his body.
- Cover any injuries found with a clean cloth to prevent infection.
- Check your breathing and pulse. If they are absent, proceed to artificial respiration and chest compressions.
- Call an ambulance. Only a specialist can determine damage from electrical discharge, diagnose internal organs and remove dead tissue.
For sunburn, it is important to cool and moisturize damaged skin and relieve pain. Take a bath with cool water several times a day, drink more fluids, and use local wound-healing agents.
1st-2nd degree burns can be treated independently. The main pharmaceutical products that have regenerating and antimicrobial properties in this case are Panthenol spray, Dexpanthenol cream, Spasatel or Levomekol ointments, Baneocin powder. Miramistin has proven itself well, preventing infection and helping to reduce pain and itching.
Treatment of 3-4 degree burns is the competence of medical workers; hospitalization and complex treatment are required, surgical intervention is possible.
First aid
Before the ambulance arrives, the following procedures must be completed:
- Neutralize the source that caused the burn. In case of a chemical burn, the damaged area must be washed with plenty of water for 10-15 minutes. Acid burns can be treated with lye and alkaline acids. If you find chemical residues on the skin, be sure to remove them with a sterile cloth (bandage, gauze) before washing.
- To reduce pain symptoms, it is recommended to take painkillers.
- Treat the wound with anti-burn gels or sprays (Panthenol, Levomekol, Oprazol).
- Protect the affected area from exposure to the external environment by applying a dry, sterile bandage. This way you will protect the wound from the penetration of bacteria.
- Try not to disturb the injured fingers with unnecessary movements.
What not to do:
- burst or puncture the resulting bubble;
- use questionable preparations for processing;
- smear the burn wound with honey, alcohol and other products containing irritating components;
- expose your fingers to prolonged hypothermia, as damaged tissue and cellular structure will be destroyed.
Blisters are only punctured in a medical facility by a doctor. The puncture done helps release excess fluid to relieve acute symptoms. If you do this yourself, there is a high risk of the wound becoming infected.
What to do if a child burns his finger
The first thing to do is to calm your baby and divert his attention from the injury. Immediately treat the wound with an analgesic aerosol, apply a dry bandage and go with the child to the nearest medical center. It is recommended to follow the instructions for providing first aid described above.
Traditional recipes for burns
What should you do if you burn your finger with a frying pan and you don’t have any medications at hand? Home-tested folk remedies will help:
- gruel from raw potatoes . A little vegetable is grated into a plate, the “puree” is spread on a cloth or bandage and applied to the burned area;
- sea buckthorn oil . Lubricate the skin or apply a soaked bandage;
- Agave juice (aloe) . Fleshy leaves are applied to the redness (with a cut to the skin) or the tissue is soaked in the juice of the healing plant and a bandage is made.
Cabbage leaf effectively relieves pain and reduces burning sensation . It is applied to the site of injury and secured with a bandage.
Second method: finely chop a cabbage leaf, add raw egg white , mix. Apply the mixture to the burn site and secure with a bandage. It seems like simple means, but they give results, and this has been tested by the experience of many housewives.
Treatment
If you receive a severe burn, you should immediately seek help from a dermatologist. A qualified doctor knows what to do in case of finger burns and how to treat the resulting injuries. The victim is prescribed powerful antibacterial and painkillers. The affected area is treated with special ointments and a loose bandage is applied. The patient is registered and visits the hospital for dressings and further rehabilitation.
It is allowed to treat mild lesions on your own, the main thing is to follow the dosage of medications and ointments for the burn. With proper treatment, no complications are observed; the burned finger recovers after a few days (7-10).