WHAT WORRIES YOU? PAIN during intercourse HOW TO GET YOUR VIRGINITY BACK YOU DO NOT like the labia CYSTITIS after sex DARK perineum SIZE of the vagina INTIMATE life after childbirth LACK OF ORGASM WHAT IS YOUR INTEREST? Plastic surgery of the labia Restoration of virginity Surgical defloration Vaginal reduction Clitoral plastic surgery Intimate muscle training How to achieve orgasm HOW TO DO IT? Get intimate plastic surgery... Get contour plastic surgery... Intimate cosmetology... Take tests for a fee... See a gynecologist
In addition to being concerned about the appearance of their genitals, many women experience soreness or other problems related to the health of their labia. Inflammation, pain, swollen or irritated tissue and itching are common problems in this intimate area. Additional complaints include stretching after childbirth, pimples, increased thickness, and unusual or tender lumps on the inner surface of the labia minora.
The female reproductive system is divided into external and internal. When a process occurs in one organ, there is a risk of it occurring in the other. Infections often begin in the folds of skin of the external genitalia, primarily because they are moist due to their proximity to the urethra and vagina. For many women, the initial symptoms of genital diseases, especially itching, burning, swelling, discomfort, begin with minor irritation and can then progress and spread to the rest of the vulva and vagina.
Other symptoms that may occur with inflammation of the labia may include pain in the lower abdomen, burning when urinating, and increased vaginal discharge. They are usually thick, yellow, green, and have a persistent unusual odor. The most common causes of vulvar and vaginal discomfort are thrush and bacterial vaginosis, and these can be successfully treated with medication. Sexually transmitted diseases are a concern both in terms of correct diagnosis and rational, effective treatment.
Inflammation of the labia minora and majora can often be accompanied by the formation of erosions and ulcers on their surface. As a result of scratching, the ulcers can merge and form confluent erosive surfaces that are prone to bleeding. Ulcers are most often the result of the spread of a virus or infection that leads to inflammation. Itching of the external genitalia in women is present in almost any type of infectious process. Inflammation of the labia is almost always accompanied by itching, which aggravates the severity of the process. The fact is that constant trauma when scratching an intimate area contributes to the spread of the inflammatory infiltrate and an increase in the number of ulcers. The addition of secondary microbial flora is also possible.
But inflammation of the genital organs is not always a consequence of infection. It may be a manifestation of an allergic reaction to the substance. Most often these are remnants of washing powder, lubricant on a condom or intimate hygiene gel. Sometimes inflammation can be a response to lack of hygiene in partners. This fact must also be taken into account during intimacy.
Inflammation of the labia may be a consequence of recent hypothermia (for example, after a swimming pool or simply in cold weather). As a result, dense formations the size of a pea are palpated in the area of the external genitalia - this is an inflamed lymph node.
Why do the labia become swollen after sex?
Some girls are frightened by the situation when, after sex, the labia is swollen - one or two at once. In fact, nothing terrible happened, because they are equipped with a large number of venous and arterial vessels and nerve endings. Since one of the erogenous zones of the female body is located in this place, any caress or simple touch causes swelling of the lips of the genital area. The quantitative increase in their size depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the level of hormonal levels. By the way, according to the observations of gynecologists and reviews from the patients themselves, rubbing, itching and swelling occur in girls and women who have enlarged, stretched labia of complex shape.
If the change in the size of the labia, their swelling and the desire to scratch them lightly are associated only with intimate contact, then there is no need to worry. But if swelling does not go away after 8-10 hours after sexual intercourse, you should think about visiting a gynecologist, as the cause may be a disease.
If any discomfort occurs in the intimate area, including when the labia minora are swollen, it is worth determining the cause and a good gynecologist will help with this. Reception of a specialist in our clinic daily, from 10-00; pre-registration by phone 8(495)761-1085 or online on the website.
Symptoms of inflammation of the labia
The inflammatory process in the area of a woman’s external genitalia (vulva) is referred to in gynecology as “vulvitis.” This condition has characteristic symptoms, such as redness, itching, swelling of the labia, painful symptoms when urinating, and copious natural female discharge. A woman may also experience a number of additional symptoms:
- the appearance of roughness of the labia minora, which is nodules of enlarged sebaceous glands;
- the appearance of a whitish coating, plaques reminiscent of psoriasis rashes;
- feeling of general malaise and fever.
Like any other inflammatory process, vaginitis is divided into acute and chronic. The acute form is characterized by pronounced symptoms, while the chronic process is more sluggish and unnoticeable.
Expert opinion
You should be especially careful about the development of vulvitis in little girls, since children tend to hush up problems associated with discomfort in the intimate area. For this reason, it is necessary to make it clear to the child that if he experiences any unpleasant sensations, he must inform his elders about their occurrence.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Gynecologist appointment
Acne in pregnant women: is this normal?
During pregnancy, a woman experiences enormous stress, and the change in hormones alone is worth it. Acne forms on the face, décolleté, back, and genital area. If you maintain daily hygiene, everything will go away on its own. The threat of miscarriage and taking strong medications increases the risk of strange lumps appearing in the delicate area.
The 2nd and 3rd trimester also provokes rashes on the genitals, this is due to the rapidly growing tummy, which prevents the penetration of air to the genitals. It is recommended to choose loose cotton clothing. During gestation, the work of the sweat and sebaceous glands is overloaded several times, so you should rinse more than once so that the pores do not become clogged with dirt. Continue taking vitamins to avoid the risk of vitamin deficiency, and as a result, a decrease in the protective functions of female microflora. By following all these tricks for 9 months, be sure that pimples will not affect the happy course of bearing a child.
You can ask your question to our author:
Causes of vulvitis
In order to clearly understand the causes of vulvitis, it is worth dividing this disease into 2 types: primary and secondary. Primary vulvitis develops in the case of:
- Failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene (irregular washing, rarely changing tampons and pads during menstruation, rarely changing underwear, wearing tight and synthetic underwear).
- Sudden hypothermia or overheating of the body.
- Mechanical damage to the vulvar mucosa during sexual intercourse, constant use of tight clothing made of coarse fabrics, removal of hair, and combing.
- Chemical exposure to various drugs.
- Hormonal imbalance and metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes, insufficient ovarian function, lack of vitamins and minerals in the body);
- Allergic reactions.
Secondary vulvitis, vulvovaginitis (Vulvovaginitis) occurs due to infection of the external genitalia by pathogenic microorganisms contained in vaginal discharge.
Vulvitis - causes
Irritation of the labia can be caused by thrush, colpitis (Vaginitis), endometritis (Endometritis) and other diseases of various organs, not necessarily directly related to the mucous membranes and skin of the genitals. It is worth noting that long-term or frequent use of antibiotics can cause disruption of the vaginal microflora and subsequent vulvitis.
Inflammation of the labia - vulvitis
As medical statistics show, secondary vulvitis most often occurs in women of reproductive age, while primary inflammation is more often diagnosed in childhood. This is facilitated by the tendency of children to diathesis, helminthiasis (Helminthosis) (pinworms with improper hygiene can get into the labia area, causing an inflammatory process).
In this case, vulvitis in girls can be complicated by the appearance of synechiae, which are adhesions connecting the labia minora.
Vulvitis can occur during pregnancy, especially if a woman does not follow the rules of intimate hygiene or wears inappropriate underwear. Vulvitis can occur after childbirth. As the fetus passes, the vagina and labia are injured, which can cause subsequent inflammation.
White coating on the penis: when is this normal?
Why might a white coating on the penis be normal? Due to the increased production of a special male secretion - smegma. It is produced by tyson (preputial) glands under the foreskin - a type of exocrine sebaceous glands. Smegma facilitates the sliding of the foreskin when exposing the head of the penis. The secretion mixes with exfoliated epithelial cells, forming a white coating on the head of the penis. The problem is more common in men who have not undergone circumcision. Increased secretion of the preputial glands does not require special treatment. But if the rules of hygiene of the genital organs are not followed, it can lead to inflammation (balanitis, balanoposthitis) and oncopathology.
Diagnosis of vulvitis
To diagnose vulvitis, in most cases, a simple manual examination by a doctor is sufficient, as well as taking a smear for bacteriological, bacterioscopic and cytological examination. The results obtained allow us not only to determine the presence of inflammation, but also to exclude malignant tumors and identify the causative agent of the infection. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a stool test to detect helminthiasis.
Appointment with a doctor for the treatment of vulvitis
A detailed description of the symptoms and the initial stage of the disease will also have diagnostic value for the doctor. This will simplify the diagnosis and make it possible to exclude any concomitant infections. After all, the itching that vulvitis causes leads (especially often in girls) to the appearance of scratching in the area of the external genitalia, which may also indicate the presence of diseases such as pediculosis, dermatitis or lichen. Also, the cause of itching in the labia area can be any sexually transmitted disease, which sometimes may require consultation with a dermatovenerologist or additional diagnostics.
Arteriovenous compression
- Aorto-mesenteric compression of the left renal vein
Aorto-mesenteric compression of the left renal vein (aorto-mesenteric “tweezers”, nutcracker syndrome, mesoaortic compression syndrome of the left renal vein) is a situation in which the left renal vein is compressed between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. This leads to disturbances in the outflow of blood in the left renal vein, expansion and formation of “reverse” blood flow through the left gonadal vein with the formation of symptoms of varicose veins of the female genital organs.
- May-Turner syndrome
May-Turner syndrome is a situation in which the left common iliac vein is compressed by the right common iliac artery, leading to expansion of the common iliac vein below the site of compression and overflow of the pelvic vessels with venous blood. We also often observe the development of varicose veins - expansion of the left lower limb, the formation of persistent swelling of the soft tissues of the left lower limb and even trophic disorders (pigmentation). Most often, with May-Turner syndrome, varicose veins on the outer labia develop during pregnancy and remain forever after pregnancy (photo).
- Postthrombotic disease
Quite often one can observe the development of pelvic varicose veins in patients who have previously suffered deep vein thrombosis (especially proximal thrombosis) when there is a residual narrowing of the lumen or complete occlusion of the lumen of the common iliac vein. In this case, the outflow of blood from the pelvic organs is sharply hampered and, as a consequence, the expansion of the lumen of blood vessels and the development of pelvic varicose veins.
- Venous dysplasia
This is a malformation of the superficial or deep veins that occurs in the early phases of the formation of the vascular system of the embryo in the period from 4 to 8 weeks of intrauterine development. Venous dysplasia leads to the appearance of varicose veins of the minor lips. The diagnosis of dysplasia can be established provided that other causes of dilation of the genital vessels are excluded. Dysplasias look like dense vascular spots that are difficult to empty when squeezed. They resemble tumor-like formations more than dilated varicose veins.
Treatment of vulvitis
If you notice any alarming symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a specialist can diagnose the cause and prescribe correct and quick treatment, including a set of measures: relieving inflammation, eliminating factors that are catalysts for the process.
The basis of treatment for vulvitis is the elimination of the causes of the inflammatory process and treatment of concomitant diseases, which may include diabetes mellitus (Diabetes mellītus), gonorrhea (Gonorrhoea), diphtheria (Diphtheria), helminthiasis. After receiving smear test data and checking the sensitivity of the infectious agent, the doctor can prescribe medication, most often antibacterial drugs. Vulvitis responds well to treatment with local remedies, which include all kinds of ointments, gels and suppositories.
In parallel, in the course of treatment of vaginitis, vitamin complexes can be prescribed, including vitamin A to effectively protect the epithelial layer, as well as vitamins E and C, known for their antioxidant properties.
To combat severe symptoms, other drugs may be prescribed:
- Antihistamines that help relieve itching.
- Hormonal, occurring in atrophic vulvitis in the postmenopausal period.
- Anesthetics that relieve pain.
In addition to the medications prescribed by your doctor, you can use Gynocomfort Restoring Gel. This product was created by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and underwent clinical trials at the Department of Dermatovenerology with the clinic of the St. Petersburg State Medical University. During testing of the gel, it was proven that it is a very effective additional agent as part of the complex therapy of inflammatory processes of the female genital tract.
As additional therapeutic measures that can be used at home, it is worth mentioning warm baths with herbal infusion.
Chamomile, calendula, string, and comfrey have excellent anti-inflammatory properties.
Baths will help not only reduce inflammation, but also relieve symptoms such as itching, burning and pain.
Disease prognosis
Varicose veins of the uterus and perineum are not a life-threatening disease. But it is important to note that the quality of life of patients is significantly reduced. In addition to aesthetic discomfort, large perineal phleboectasis can cause painful symptoms during menstruation and complicate sexual life. Sometimes varicose veins become inflamed, causing a lot of physical suffering to patients. You should not count on the therapeutic effect of ointments and tablets - such therapy is not effective, but only eliminating the causes of varicose veins and the venous nodes themselves using sclerotherapy or miniphlebectomy allows one to achieve excellent therapeutic and aesthetic results in all patients. At the Innovative Vascular Center, complete treatment of this disease is possible. We successfully perform endovascular correction of deep vein pathology, eliminate varicose veins of the small pelvis and venous vessels on the genitals.
Prevention of inflammation of the labia
To prevent vulvitis, it is necessary, first of all, to maintain intimate hygiene. It is recommended to use products designed specifically for caring for intimate areas. Ginocomfort washing gels for intimate hygiene, which were developed by specialists of the pharmaceutical company VERTEX, taking into account the characteristics of the microflora of the genital organs, are well suited for this purpose. They do not dry out the mucous membrane and do not disturb the acid-base balance. These products have a package of necessary documents and quality certificates.
Other measures to prevent inflammatory processes in the labia area include the following:
- Proper drying of the genitals after hygiene procedures. It should be carried out with a clean towel or napkin in the direction from front to back or with gentle blotting movements.
- Careful selection of underwear. It is optimal if it is underwear made of natural and soft material that will not squeeze or rub the perineum.
- General maintenance of immunity, which will allow the body to independently fight infection and suppress the proliferation of pathogens.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The list of general recommendations for most pathologies accompanied by pain in the labia area involves changing hygiene habits, sexual rest, adjusting the diet and nature of the diet, and refusing to use synthetic underwear, highly allergenic or irritating hygiene products. Therapeutic measures for inflammatory and infectious processes include:
- Antibacterial agents.
For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed for systemic and local (creams, suppositories, vaginal tablets) use, selected taking into account antibiotic sensitivity. - Other etiotropic medications.
For polymicrobial vulvitis and vulvovaginitis, combined drugs with antibacterial, antiprotozoal and antimycotic effects are used. Antifungals are effective for candidiasis, and antiviral drugs are effective for HPV and papillomatosis. - Local events.
For vulvitis, vaginal suppositories, douching with antiseptic solutions and herbal decoctions, and sitz baths are recommended. For acute bartholinitis, SMT, UHF and UV irradiation are effective; for chronic bartholinitis, ozokerite, paraffin, infrared laser, and mud applications are effective. - Treatment of background pathologies.
According to indications, insulin therapy or the dose of hypoglycemic agents for diabetes are adjusted, antiallergic drugs are prescribed, deworming is carried out, and infectious foci are sanitized.
Patients with vulvodynia are advised to avoid eating foods high in calcium oxalate (celery, strawberries, chocolate) to reduce the amount of this compound in the urine. For mild pain, exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles are useful. Balneotherapy and physiotherapy are effective. If there are signs of atrophy, suppositories and creams are used to stimulate regeneration. For ovarian hypofunction, hormonal therapy is prescribed.
Antihistamines and sedatives are recommended for patients with vulvar kraurosis. For persistent itching, a pudendal nerve block is performed. Hormonal ointments with estrogens, androgens, corticosteroids and progesterone are used locally. The type of medication is selected taking into account age and endocrine status. Balneotherapy, reflexology, laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, and x-ray therapy are effective. It is necessary to take biostimulants, immunocorrectors and vitamin preparations.
Surgery
In most cases, pain in the labia area is eliminated using conservative methods. Surgeries may be required if the following pathologies are present:
- Bartholinitis:
marsupialization, removal of the cyst, removal of the Bartholin gland, opening of the abscess. - Kraurosis of the vulva:
cryodestruction, laser ablation or denervation of the vulva, if malignant tissue degeneration is suspected - vulvectomy. - Condylomatosis:
radiofrequency ablation, laser vaporization, cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, vulvar resection, vulvectomy.
Inflammation of the labia in women, video
Gynecologist Irina Vladimirovna Garyaeva about vulvitis in women.
Source - KVD - dermatovenerological dispensary Sources:
- ROLE OF INFECTIONS IN THE GENESIS OF VULVA DISEASES. Reutskaya M.A., Kulinich S.I. // Siberian Medical Journal (Irkutsk). – 2010. – No. 6. – pp. 239-242.
- CLINICAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT OF CHRONIC VULVITIS. Kulinich S.I., Reutskaya M.A., Pokinchereda T.V., Ezhova I.V. // Acta Biomedica Scientifica. – 2013. – No. 5 (93). – P.42-48.
- Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva: Clinical lectures. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. // M.: MEDpress. - 1999. - P. 432.
- Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis: etiology, pathogenesis, treatment. Levonchuk E.A. // Med. news. - 2001. - No. 4. — P. 40-43.
- Dystrophic diseases of the vulva. Diseases of the cervix, vagina and vulva. Ed. V.N. Prilepskaya. // M.: MEDpress. - 1999. - pp. 326-336.
- https://simptom-lechenie.ru/en/vulvit-u-zhenshhin-i-devochek-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
- https://www.thenakedscientists.com/science-articles
- https://woman-centre.com/vlagalische-i-vulva/vulvit/vulvit-u-zhenshhin.html
- https://simptomer.ru/bolezni/zhenskie-zabolevaniya/864-vulvit-simptomy
Infectious causes of white plaque on the penis
They differ according to the type of pathogen:
Candidiasis
This is a fungal infection. Occurs after long-term use of antibiotics or when infected during sexual intercourse. Candida is usually found in a woman's vagina. During intercourse, microtraumas are formed on the skin of the genitals, facilitating the penetration of infection. The plaque looks like white lumps, has a sour smell, and is accompanied by itching. If treatment is not started on time, pain when urinating and ulcers develop.
Bacterial balanoposthitis
Caused by bacteria that normally live on the surface of the skin, most often streptococci and enterococci. White coating on the frenulum of the penis, on the head. It has a creamy density, combined with red spots. Itching and discomfort increase after urination or sexual intercourse. If treatment is delayed, the infection penetrates and affects the bladder, ureters and kidneys.
In the photo: candidiasis balanoposthitis
Gonorrhea
The plaque is concentrated around the head of the penis. In addition, there will be abundant purulent discharge from the urethra, an unpleasant odor, a deterioration in general health, and painful urination. There may be blood in the urine.
Chlamydia
The head of the penis itches, a white coating is located under the head of the genital organ, abundant, translucent. The disease is accompanied by the discharge of yellowish-green mucus from the urethra and pain.
Syphilis
The appearance of a whitish coating on the head is one of the signs of this complex disease. Characteristic rashes and lumps are not necessary and a person may not notice them. Therefore, it is very important to contact a urologist in time and get tested.
Popular questions
I suspect inflammation and cysts.
The doctor prescribed IV thiosulfate, IM ceftriaxone, and Diclovit suppositories. I just didn’t explain, is it necessary to apply everything at the same time or what? Hello! Most often, this complex of treatment is carried out simultaneously, but it is better to check with your doctor.
Hello. My labia and clitoris are swollen, there is a burning sensation and a cheesy discharge with something in it, the color is unclear. What could it be and how to treat it? Before that I had inflammation and treatment, and after that it all started. Hello! This is how vulvovaginitis manifests itself. I recommend that you contact an obstetrician-gynecologist and conduct an examination to find out the cause of the inflammation. This will allow you to correctly prescribe therapy. At this stage, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil, 1 dose once a day, which will limit the spread of inflammation and improve your well-being.
Hello! Severe itching on the labia, irritation. There is nothing to worry about in the vagina itself. What could it be?
Hello! This may result in an allergic reaction or inflammation. I recommend using Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract, applying it once a day to the discomfort zone for 7 days. If you do not notice relief, consult a doctor.
Good morning, I have vulvitis on my labia minora, I don’t know what to do or how to treat it.
Hello!
If inflammation occurs in the labia minora area, you can use Gynocomfort gel with tea tree oil. The gel is applied in a thin layer once a day for 1 week. If complaints persist, you should consult a specialist. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Prevention
To protect yourself from unpleasant seals and suppurations, you must follow simple recommendations:
- Stop wearing thongs.
- Take care of intimate hygiene - wash, use wet bactericidal wipes, especially after being in a public toilet.
- If you have hypersensitive skin and your bikini area gets irritated every time, there are gentle depilation methods and creams.
- Follow the timing of changing pads and tampons, use soap without perfumed fragrances.
- Wash yourself properly, wash the outer part of the genitals, there is no need to clean the vagina, this disrupts the natural microflora, which can cause infection in the genital tract.
- After purchasing new linen, be sure to pre-wash it and change it for new ones every day.
- Do not overheat in a bathhouse, sauna, or in the sun, and dress warmly in winter.
- Get enough sleep, eat the right foods, drink plenty of water, avoid stress.
- Avoid uncontrolled sexual intercourse.
- Take immunomodulators and multivitamins that will strengthen the body's defenses.
- Do not self-medicate, make an appointment with a doctor immediately, only a professional examination will help you understand the severity of the rash and choose the right treatment.
These simple tips can not only improve your well-being, but also save you a lot of money on visiting a gynecologist, venereologist, virologist and dermatologist.
What tests should be taken for a rash on the labia?
To diagnose the cause of a rash on the labia, a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed:
- a general analysis of urine and blood shows the general condition of the patient, identifies inflammatory processes;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR), is prescribed to determine the DNA of the pathogen, the most informative method that can detect diseases at very early stages;
- immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) detects antigens through the use of a special substance;
- cultural method, an effective procedure that allows you to determine the presence and type of pathogen by placing the biomaterial in an environment favorable to the virus;
- vulvocolpocervicoscopy, examination on a gynecological chair using a microscope to study the nature of the rash.
The doctor may also recommend undergoing an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), a serological method, or an immunogram. An ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, tests for hormones, tumor markers and other diagnostic measures that can find the main cause of the unpleasant symptom are often prescribed.
Diagnosis of a rash on the labia
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination, determining the nature of the rash. After this, depending on the primary diagnosis, additional tests are prescribed:
- PCR;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- biopsy;
- vaginal smear examination;
- general blood and urine analysis.
In some cases, samples are taken for different types of allergens.
Answers to frequently asked questions about skin rashes:
- Which doctor should you contact for a skin rash?
- Is the skin rash contagious?
- What diet is necessary for skin rashes?
- What diagnosis is needed for a skin rash?
- Why is a skin rash dangerous?
- Why is it necessary to get tested for a skin rash?
- What diseases does a skin rash indicate?
- What examination is necessary for a skin rash?
- Which skin rash is dangerous?
- How to distinguish an allergic rash from an infectious one
- How to get rid of skin rashes?
- How to get rid of itching skin rash?
- What organs are affected by a skin rash?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a dermatologist?
- How to get checked for skin diseases?
- What diseases does a dermatologist treat?
- What tests should be taken by a dermatologist?
- What diagnostics can a dermatologist perform in the clinic?
- Where to go with a skin disease?
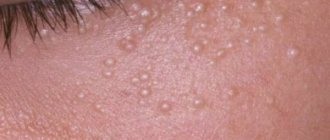
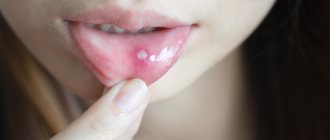
White dots: what types of pathology can we talk about?
The list of diseases that cause rashes in the genital area is quite diverse.
Regardless of whether there are additional symptoms, you should see a gynecologist.
After examining and taking smears, the doctor will be able to determine what caused the rash.
- If white pimples appear on the skin, then most likely their formation is caused by a bacterial or fungal infection. In this case, therapy will be carried out with drugs whose action is aimed at suppressing the pathogen.
- In the case of a viral infection, treatment tactics will depend on the type of pathogen that has infected the genitals. It is possible that therapy will be aimed at removing formations using systemic drugs.
- In the presence of malignant forms, chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy are performed.
Allergic reaction
The appearance of small white dots in the genital area, including the labia, is often a sign of an allergy.
The rash can be single or multiple, the elements can merge with each other.
The patient complains of irritation and itching of the affected area.
When examining the skin and mucous membranes, hyperemia of the affected area is noted.
An allergic reaction can be triggered by:
- depilation of the intimate area using creams and other products necessary for the procedure;
- use of tampons and pads;
- wearing underwear made of synthetic fabrics;
- intimate hygiene products;
- local use of drugs;
- excessive hygiene of the genital area;
- using a latex condom;
- sexual partner's sperm.
Papillomas
When the body is infected with papillomavirus (HPV), neoplasms (condylomas) may appear on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals.
Favorite places for the formation of white spots: the mucous membrane of the labia minora and majora and under them - in the perineum, the mucous membrane of the vagina, cervix and urethra.
The disease is transmitted by contact.
Symptoms of human papillomavirus infection:
- the presence of burning and itching in the area of the growth;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- swelling and hyperemia of the affected tissue;
- if condylomas are localized in the urethra, then discomfort occurs when urinating;
- the growths are colored from white to pink;
- possible enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes;
- if the growths bleed, then there is a high probability of degeneration into a malignant form.
The development of HPV can be provoked by a decrease in the activity of the immune system and the presence of vitamin deficiency.
Diagnosis is based on the result of a PCR smear analysis.
Fat cysts (Fordyce granules)
They are hormonal in nature.
Formed during the process of blockage of the sebaceous gland.
The pathology is a cosmetic problem and is not contagious.
The defect does not pose a danger to its owner.
In appearance, hormonal nodules look like a scattering of white grains filled with yellowish contents (lipids and cells of dead epidermis).
The size of the dots is about 1-2 mm.
Cysts do not manifest themselves in any way and do not affect the quality of a woman’s sexual life.
Occasionally, ladies may complain of periodic itching.
Cystic formations can be removed at the woman’s request by electrocoagulation, laser or cryodestruction.
Surgical excision is not used as it may leave scars on the skin.
"Retin-A" is a remedy that can have a positive effect in the fight against fatty cysts.
Leukoplakia
The development of pathology occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance.
The causes of the pathology have not been sufficiently studied.
It appears as whitish dots on the mucous membrane of the labia.
Symptoms at the beginning of the disease are accompanied by the appearance of dryness, slight tingling and burning, which appear more often at night.
If you do not consult a specialist in time, then over time the symptoms become more pronounced.
This pathology refers to precancerous diseases.
In the absence of timely treatment, cancer may develop.
Genital herpes virus
The onset of a viral infection begins suddenly.
A small watery rash forms in the intimate area, at the site of which there is acute pain and a burning sensation.
In some cases, there is a rise in temperature.
After some time, the watery dots open and dry out.
In their place, crusts form.
During the opening of the papules, a secondary infection may occur.
There are no scars left in place of the crusts.
The viral infection is chronic, so periods of remission alternate with periods of exacerbation.
The route of infection with the genital herpes virus is sexual.
Molluscum contagiosum
The pathology is of viral origin.
The disease is transmitted through sexual contact.
The duration of the incubation period can reach 2 months.
Localization of white spots during infection with molluscum contagiosum: pubic area, labia, perineum.
The size of the formations ranges from 1 to 1.5 mm.
There is a depression in the center of the formation.
When the element is squeezed out, a white substance is released.
If a secondary infection occurs, itching may occur.
An examination is enough for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis.
White dots: causes of appearance and location of localization
The labia are abundantly supplied with hair follicles and glandular cells.
Sex hormones actively influence the activity of the glands.
The appearance of white spots on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals can be caused by:
- blockage of glandular ducts;
- development of the infectious process;
- cystic formations in the ducts of the glands. The resulting wen (lipomas) in the absence of an inflammatory process in them are considered harmless. They are a benign form. Lipoma on the labia is painless and mobile. There are: fibrolipoma, angiolipoma and liposarcoma. Lymphosarcoma is a malignant form and tends to metastasize. The presence of cysts may indicate a weak immune system;
- infection of the hair follicles (folliculitis).
- White spots that form under the skin or in the thickness of the labia majora require mandatory consultation with a specialist. They can be caused by an infectious process or hormonal changes;
- when the formations are localized inside the labia on one side, it may mean inflammation of the Bartholin gland or be a sign of the formation of a boil;
- degeneration of tissues into a malignant form;
- changes in hormonal balance.
If white dots appear on the labia minora or majora and they cause concern, then we may be talking about a pathological process.
In this case, you will need to undergo additional research and consult specialists.