Everyone is familiar with such an injury as a burn. It is the timely and correct provision of pre-medical care that determines a person’s further condition. In order to quickly navigate and help the victim properly, it is important to know what types of burns there are, how the methods of providing assistance differ depending on the severity of the injury. Pay special attention to actions that are prohibited and priority measures.
Degrees and treatment of burns
Features of treatment and further regeneration of the skin will depend on the degree of the burn, its depth and size.
There are four degrees of burn:
- 1st degree burn. The outer layer of skin is damaged. As a result, there is slight redness of the epidermis and swelling, which may be accompanied by pain. Typically, burn marks disappear after 2-3 days;
- 2nd degree burn. The upper, stratum corneum layer of the skin is affected, and sometimes the next layer is damaged. Blistering, redness and pain are quite common. If you choose the right treatment method and use appropriate therapy, after 10-12 days there will be no trace of the burn;
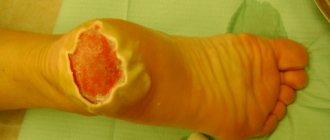
- 3rd degree burn. It is one of the most serious skin injuries. It spreads to the deep layers of the skin, affecting the upper subcutaneous tissue. Blisters and scabs appear. The wound takes a long time to heal;
- 4th degree burn. The skin becomes charred and the subcutaneous bones are damaged. All skin layers and tissues located underneath die. In this case, immediate hospitalization will be required.
In order to properly provide the necessary assistance and not harm the victim, it is worth understanding the cause of the injury. This will not cause any difficulties if you have an idea of the types of burns:
- thermal burns can be obtained when the skin interacts with boiling water, fire, or a hot object;
- a chemical burn is caused by a chemical or alkaline agent;
- radiation burn occurs as a result of ultraviolet radiation;
- A radiation or electrical burn occurs when in contact with an electric current or a voltaic arc.
For quick healing when receiving a first-degree burn, it is important to provide first aid in a timely manner. To do this, it is necessary to urgently eliminate the cause of the burn. Cool the affected skin area with ice or cold water.
It is not recommended to immediately apply anti-burn cream or ointment to the wound. Initially, you need to clean the intact skin located in close proximity to the burn with ether, then wipe with alcohol. Sodium chloride can be used to remove dead tissue from a wound.
A victim with a severe burn, before the ambulance arrives, should be given an anesthetic, analgin, ketanal or pentalgin, and an antihistamine in the form of claritin, tavegil or suprastin. Dexpanthenol is effective for burns.
If there is no vomiting, you can drink mineral water or liquid with dissolved salt and soda with a dosage of 0.5 tsp. per liter of water.
If you receive severe burns, you should not self-medicate; you should immediately seek medical help.
Types and severity
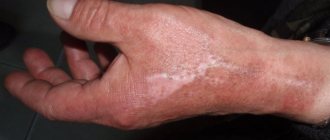
The palm can be burned by boiling water, steam, oil, chemicals, iron, etc. Depending on the area of the damaged skin surface and the duration of its contact with the damaging factor, the burn refers to one of the following degrees:
- Minor injury, in which the skin turns slightly red and there is slight swelling;
- At this degree, the pain becomes stronger, most often blisters appear on the integument;
- The burn is accompanied by a scab, deep tissue damage occurs;
- The most severe and profound degree is characterized by damage not only to the skin, but also to muscles and bones. There is a high probability of death.
Skin restoration
After a burn, a blister containing a colorless liquid may form on the skin. Its proper treatment will help avoid an inflammatory and purulent reaction. Under the neoplasm there will be a renewed skin layer; after 8-10 days, the damaged part will dry out and fall off.
In place of the blister, new skin will appear in the form of a pink spot. The renewed skin area is usually very sensitive, so it is recommended to treat it with special creams and ointments that promote effective and safe recovery.
Failure to provide first aid in a timely manner can lead to disappointing consequences. An infection will appear at the burn site, the resulting blister will become inflamed and begin to fester. The phenomenon usually entails fever, poor health, chills and weakness. The wound will heal slowly and recovery may take too long. In order to avoid serious complications, you should not hesitate, you need to urgently contact a specialist, who, in turn, will conduct tests and prescribe the correct treatment.
Prohibited actions
If you are treating at home, take precautions. The following actions cannot be taken:
- Apply oil to the affected area (at the initial stage). It will only increase the destructive effects of high temperature;
- use alcohol or iodine to treat the surface;
- try to open the formed bubbles yourself;
- tear off pieces of clothing that are stuck to the skin.
In case of hand injuries, assistance must be provided even before the ambulance arrives. Determine the damaging factor and eliminate it, then cool the limb under running water. However, for some types of chemical injuries, you should not wash the wound as this will cause the condition to worsen. Mild injuries can be treated at home, but severe injuries require mandatory hospitalization and hospital treatment.
Treatment of post-burn scars and scars
The scar that appears at the burn site can sometimes become inflamed and form a keloid scar, which is accompanied by severe
itching. Large scars left after a burn injury are treated with surgery. It is possible to get rid of a post-burn scar by excision of the scar, onto which a cosmetic suture is subsequently applied. After its removal, the resulting scar is treated with medications to promote rapid healing.
Scars that occupy a small area can be removed by laser resurfacing; chemical peeling based on fruit acids can also be used. For a quick regeneration process, it is additionally advisable to use special ointments and gels.
Ultraviolet eye burn: first aid rules
A burn of the cornea by ultraviolet light is called electroophthalmia. It often occurs in people who work with welding or are exposed to ultraviolet sun for a long time (for example, when skiing without a protective mask).
The peculiarity of an ultraviolet burn is that the first symptoms may appear only 6-10 hours after the injury.
First aid for ultraviolet eye burns is thorough rinsing with water or saline, instilling moisturizing drops and moving the victim to dark or low light conditions. You can also use sunglasses for this.
Anesthetics can be used briefly to relieve pain. But it is better to first consult with an emergency doctor, since such drugs slow down the healing process of the cornea. Cold compresses can help relieve pain without the use of medications.
To protect against infection, it is recommended to use antibacterial ophthalmic ointments.
An ultraviolet eye burn, if first aid is provided on time, is often a reversible condition and goes away without a trace within a few days. Moreover, electroophthalmia is easily prevented with preventive measures. For example, welders must use special protective masks when working, and skiers must wear ski goggles with high UV protection before skiing.
Remedies for burns
Today, there are many types of medications for burns in the form of gels, ointments, sprays, creams and dressings.
For example, Levomekol helps well with thermal burns. The drug has bactericidal properties, thanks to which the injury heals much faster. Moreover, the constituent components are substances that help relieve pain.
Povidone-iodine ointment contains iodine. The chemical element disinfects the site of damage and promotes the rapid restoration of skin tissue. Balm Rescuer, made from natural ingredients, can restore damaged skin to a healthy appearance in the shortest possible time.
The creams have also actively proven themselves in the treatment of burns, which are used at the recovery stage of damaged tissue areas. They can be used for preventive purposes against the formation of scars. Panthenol cream helps well with thermal and sunburn.
First aid for a chemical burn to the eyes: what to do before the ambulance arrives?
In case of a chemical burn to the eyes, it is important to provide assistance immediately, without waiting for an ambulance to arrive. If the damage occurs as a result of exposure to an alkali, acid or other chemical, the first step is to clean the eye of any remaining substance. To do this, you should start rinsing as quickly as possible. In such a situation, speed plays a decisive role and can determine the degree of burn and the prognosis of recovery.
Rinsing the eye should be done under running water, generously moistening a piece of cotton wool and wiping the eyeball towards the nose with it. If the burn occurs as a result of exposure to alkali, a two percent solution of boric acid can be used for rinsing. If the eye tissues are affected by acid, a soda solution is suitable for rinsing. However, ophthalmologists do not recommend using these solutions without first consulting a doctor, because unexpected reactions of damaged tissues may occur. Therefore, until the ambulance arrives, you can limit yourself to clean water. In case of a chemical burn, you need to rinse your eyes for at least 10-15 minutes.
Ophthalmologists note that if a powdered chemical gets into the eyes, it is necessary to remove its remnants from the eyes with a dry cotton swab before rinsing.
After removing the remaining chemical substance from the eyes, you can drip a 4-5% solution of novocaine, lidocaine or another anesthetic into the eyes, and give the victim a drug with an analgesic effect.
Also, first aid for a chemical burn to the eyes includes instillation of drugs to prevent infections. The emergency doctor will tell you which remedy is best to use.
Treatment of thermal burns
Of course, the main task and goal of treating a thermal burn is to restore the integrity of the skin. For superficial burns that do not involve the germ layer of the skin, regeneration occurs independently. If the burn damages the germ layer, healing is only possible through scarring, so with extensive deep burns there is a need for skin grafts.
In addition to measures aimed at restoring tissue integrity, treatment of burns has a number of other goals:
- pain relief;
- normalization of hemodynamics;
- restoration of water and electrolyte balance;
- normalization of blood pH;
- restoration of protein metabolism;
- prevention of liver, heart, lung, and kidney failure;
- detoxification of the body.
The first step in treating deep thermal burns is to thoroughly clean the burn wound. Foreign bodies, pieces of tissue, and exfoliated epidermis are removed from its surface under aseptic conditions and under local anesthesia. The wound is washed with hydrogen peroxide, after which the doctor decides on the method of further therapy. With the open method, a bandage is not applied to the area of burned skin. The closed method of therapy involves applying anti-burn ointment and subsequent dressing.