More than 70% of Russians are infected with the herpes virus, but in most cases it does not pose any threat to health. The virus is relatively safe and becomes active only against a background of weakened immunity, especially in the autumn-winter period. It manifests itself in the form of a rash on the lips, genitals and other areas. As a rule, neoplasms go away on their own, but in some cases you may need to get help from a doctor.
Causes of the disease
Herpes is an infectious disease. This is a virus that enters the body in different ways:
- sexual;
- contact (household);
- airborne (sneezing, coughing);
- placental (from a pregnant woman to a child).
In this case, herpes is most often transmitted by contact. The virus lives in saliva, so a person can become infected through a kiss, toys, underwear, dishes and other objects.
There are several factors that provoke the activation of the virus:
- constant stress;
- depressive states;
- prolonged hypothermia of the body, including one-time hypothermia;
- ARVI with and without complications;
- diseases that suppress the human immune system;
- bad habits, especially alcoholism, unhealthy diet;
- severe intoxication;
- Alzheimer's disease.
Herpes is present in the body of almost every person, but most of the time it is in an inactive state. Usually the virus “wakes up” against a background of weakened immunity. This can happen for various reasons, including against the background of severe stress, lack of sleep and other unfavorable factors.
Methods of infection with viruses
Infection with viruses can occur through airborne droplets, household contact, sexual contact and blood contact. Infection is possible both from patients and from carriers of the virus. The infection persists for a long time in a dried state and can be easily transmitted through household items: cups, towels, toys. The virus also spreads through saliva, blood, vesicle contents, semen, vaginal secretions and other body media.
Infection often occurs in the form of autoinoculation, which involves mechanical transfer of viral particles from one site to another. For example, the virus can spread through the skin and mucous membranes when scratching.
Susceptibility upon contact is quite high. It is believed that about 90% of the adult population are carriers of one type or another of herpes and up to 25% suffer from recurrent forms. As a rule, when examining frequently ill children and adults, several herpes viruses are detected at the same time.
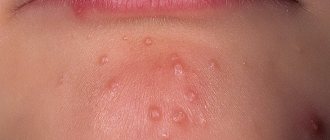
How does herpes on the lips manifest itself: symptoms
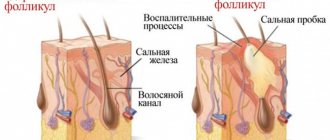
After activation in the first period, which lasts from 2 to 10 days (depending on the individual characteristics of the body), the herpes virus does not manifest itself in any way. After this, characteristic white bubbles (growths) appear on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of the face (including on the lips), which merge with each other. Often the symptoms are accompanied by itching and a slight, barely noticeable tingling sensation.
In some cases, other symptoms are possible, for example:
- headache;
- general weakness;
- fatigue;
- elevated body temperature.
Very rarely, the development of the virus can lead to herpetic meningitis. This is a dangerous condition accompanied by inflammation of the brain. In such cases, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Symptoms of genital herpes
Basically, the symptoms of genital herpes are somewhat similar to the symptoms of common herpes.
This is general swelling, slight redness, minor pain and discomfort in the lower parts of the body.
But as the main symptom, it can be noted that a rash appears on the genitals a few days after the general symptoms.
There is also a feeling of pain when urinating.
In women, the external genitalia, perineal and anal areas are affected.
Damage to the urinary system is also possible.
A rash appears on the inside of the thigh.
In men, a rash should be noted on the tip of the penis and on the foreskin.
It is impossible to determine or know in advance whether a person will become infected with a herpes infection or not.
Even if he can lead a promiscuous intimate life.
The main thing that is necessary is to observe basic rules of personal hygiene, especially intimate hygiene.
And even if a person has already become infected with the herpes virus, then hygiene rules can help avoid secondary infection.
Above we talked about the symptoms and which doctor to contact if genital or genital herpes occurs.
Now let's look at the most common herpes type 1 HSV-1.
Let's start with a cold, when the herpes virus manifests itself on the lips.
In almost 80% of the world's population, this virus is in dormant mode.
Awakens only against the background of colds.
Herpes symptoms:
- General weakness
- Malaise
- Migraine and muscle pain
- High body temperature
- Feeling of discomfort in the mouth
- The appearance of small bubbles with a cloudy whitish liquid in the area of the red border of the lips, near their mucous membrane.
Diagnosis: which doctor to contact
You should consult a doctor in case of complications (for example, headaches), as well as in cases where the rash becomes more and more numerous and does not go away for a long time. For herpes, contact the following specialists:
- gynecologist (for women);
- urologist (for men);
- therapist (if the rash does not appear in intimate areas);
- pediatrician (for treating children).
The doctor examines the patient, asks questions, analyzes complaints. If necessary, several laboratory tests are carried out to study:
- blood;
- sperm;
- urine;
- vaginal discharge;
- urethral discharge;
- biological material from ulcers or other skin lesions.
Along with the cause of the rash, it is equally important to determine the type of virus. To do this, a common PCR analysis is performed, which stands for polymerase chain reaction.
Prevention of herpes
The basic rules that will help reduce the likelihood of infection with viruses of the herpes family are:
- hand washing;
- limiting contact with sick people;
- nasal instillation with saline solutions during the off-season.
There is now a vaccine against chickenpox. Vaccination helps prevent infection and/or development of severe forms of the disease. “SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary medical institution that provides effective treatment to children facing various diseases. Herpetic infection in any of its manifestations is not a problem. The main thing is to schedule a consultation with our specialists on time. Contact us!
Herpes on the lips: treatment
If the immune system is strong enough, rashes on the lips and other places will go away even without treatment in just a few days or weeks. In some cases, special therapy will be required. The course depends on what specific cause led to the development of herpes.
As a rule, treatment is complex and includes the following measures:
- taking antiviral drugs;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamin complexes;
- special diet (increasing the proportion of protein foods, greens, fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as fermented milk products);
- drink: plenty of it.
Principles of treatment
Complex treatment of herpes infection includes the use of antiviral drugs in tablet form and in the form of local agents for treating the skin and mucous membranes. The duration of drug therapy directly depends on the severity of the patient's condition. Typically, treatment with antiviral drugs lasts 1-2 weeks. It is recommended to combine drugs like acyclovir with interferon. Antiviral drugs should not be used for long periods. Otherwise, viral resistance occurs and the effectiveness of therapy decreases. Antiviral drugs do not destroy the herpes virus, but only reduce its amount in the body. If desired, you can vaccinate, which often allows you to transfer the disease to a stage of long-term remission. The vaccination is given during the period when acute signs of infection subside.
The emphasis in treatment is on immunocorrection. Increasing the body's natural defenses can reduce the number of relapses of herpes infection per year and significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
To prevent exacerbations, it is recommended to follow the following rules:
- avoid hypothermia and overheating, especially for women during menstruation if they are prone to relapses of genital herpes;
- use personal protective equipment during intimate contacts;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well;
- do not react to stress and everyday provocations, remain calm;
- start treatment of acute respiratory infections and influenza in a timely manner;
- regularly take multivitamins and, as prescribed by a doctor, immunostimulating drugs;
- promptly identify and treat sexually transmitted diseases;
- avoid injury to mucous membranes and skin.
By following these simple rules and paying attention to the prevention of exacerbations, you can significantly reduce the number of relapses and avoid complications. The patient works in tandem with a doctor or a group of specialists, but does not try to recover only on his own, using dubious methods.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
What to do first if herpes appears
First of all, you need to carefully monitor your personal hygiene - constantly wash your hands with soap or other means. Also, do not put your hands near your eyes, much less touch the cornea. Insert lenses only after first washing your hands or wearing sterile medical gloves. The fact is that the virus can spread to the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Also, you should not touch the swellings themselves or touch them with your fingers. You can use lipstick and other products, but only without sharing them with other people. You should not remove blisters or crusts yourself - then the virus can spread to other areas of the skin. During the period of illness, you should avoid oral sex.
Important! If a young mother has herpes, she should take care of the safety of the child. Before picking him up or feeding him, you must wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
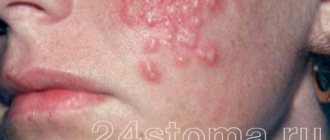
Herpes zoster (shingles)
There are often cases when rashes appear on the human body in the form of small blisters, tightly grouped together.
This is the so-called “shingles” in common parlance.
This is also a herpes infection.
When it occurs, small nerve endings or their clusters are damaged, which are affected by the herpes virus.
The most dangerous type of herpes infection, as it can cause paralysis of joints and limbs.
In more dangerous cases, half the body.
The symptoms of herpes zoster still include: general weakness, malaise, increased body temperature, itching in the affected area and the appearance of a rash.
The places where the rash appears can be the side of the face, the back (scapula area, kidney area).
The doctor directly involved in the treatment of herpes zoster is a dermatologist, and you should contact him.
But this infection can also be dealt with by a general practitioner, who can also prescribe appropriate treatment for you.
Another type of herpes infection is gluteal herpes.
As the name suggests, this is the appearance of the same small bubbles on the buttocks area.
It is not uncommon for rashes to occur between the buttocks.
This type of herpes can be attributed directly to type 2 herpes HSV-2.
Symptoms of gluteal herpes appear 1-3 days after infection.
After a person has become weak or caught a cold, and then the “sleeping” mode of the herpes virus is “activated”:
- Itching
- Swelling in the affected area
- Body aches
- Pain and feeling of heaviness in the lumbar region or hips
- Weakness
- Malaise
Small clusters of vesicles appear on the affected area (buttocks or between them).
The vesicles contain a pale yellowish liquid.
They are saturated with the herpes virus.
When they burst, the liquid flows onto a healthy area of the body, where new vesicles are formed.
During this period, a person is most dangerous to others, as he carries a high risk of infecting healthy people.
It should be remembered that the herpes virus has very negative consequences if it is not treated in a timely manner.
This is most dangerous for pregnant women.
Since the virus carries a great risk for the intrauterine development of the fetus, including miscarriage.
Our first encounter with the herpes virus occurs at an early age.
When we are kissed by parents or relatives, when hugging, when licking a spoon, a baby's nipple, without observing basic rules of personal hygiene.
Herpes 6, 7, 8 types
6 is involved in the formation of multiple sclerosis. For treatment, individual therapy is selected, which includes a large number of drugs. 7 in quite a number of cases is transmitted in conjunction with the 6th. It is considered the culprit of chronic fatigue syndrome. Requires antiviral treatment with drugs. The 8th can cause a number of cancers in people with immunodeficiencies. It is not dangerous for a healthy person, but it settles in the body for life, and will manifest itself when immunity decreases.
Epstein-Barr virus
This subtype of herpes provokes the development of mononucleosis, which affects the lymph nodes and mucous membranes of the mouth.
The most common symptoms of the disease:
- a sudden increase in temperature to very high levels, although there seems to be no reason for this;
- pain in the body, in particular in the muscles, throat, head, joints;
- symptoms on the oral mucosa - swelling and swelling, small rashes;
- fatigue and drowsiness;
- significant growth of lymph nodes.
Diagnostics consists of searching for viral DNA in the patient’s biomaterial. In addition to mononucleosis, the development of Burkitt's lymphoma (oncology) is possible. Treatment is carried out in a hospital.
2. Causes of stomatitis
We have already talked above about why irritation of the oral mucosa may begin. Now let's dwell on the question of why ulcers and herpes appear. Ulcers.
In fact, the exact causes of stomatitis in the form of ulcers are not known. But many things can contribute to their development. These include certain medications, oral injuries, poor diet, stress, bacteria and viruses, sudden weight loss and the consumption of certain foods - potatoes, citrus fruits, coffee, chocolate, cheese and nuts.
Stomatitis may be associated with a weakened immune system due to colds, flu, changes in the body's hormonal levels, as well as a lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid. Even accidentally biting the inside of your cheek or chewing on a sharp piece of food can cause an oral ulcer.
Ulcers can occur as a result of a genetic predisposition. In this case, it is considered an autoimmune disease. In general, ulcers appear in about 20% of people, but the disease is not contagious.
Visit our Therapy page
Herpes in children
Children are susceptible to infection with all types of the virus, just like adults. It is difficult for a child to simply wait out the symptoms, especially when it comes to severe itching. For this reason, it is important to immediately consult a dermatologist and receive a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The herpes simplex virus manifests itself according to the standard pattern - on the lips in the form of bubbles (less often - directly in the mouth).
Genital - the baby receives the disease from the mother at the time of birth, when it passes through the vagina. The manifestations are more complex than in adults; a child may suffer from sore throat and stomatitis.
Almost all preschool children have to survive the chickenpox virus. The child has difficulty tolerating the symptoms, so it is important to choose the right local and internal treatment.
Herpes type 6 provokes roseola infantile. Children under 2 years of age are the most common patients with this diagnosis. The rash caused by this particular type of herpes is easy to distinguish from others (especially from the rash caused by rubella, since they are very similar) - when pressed, the pink spots with a rash of blisters turn pale. The process begins with a sharp jump in temperature, which returns to normal within 3-6 days. Then an exanthema appears, which lasts from several hours to several days.
Cytomegalovirus is widespread among children. They often get it in kindergarten through contact with each other. If the child’s immunity is not weakened, the disease may be asymptomatic or with mild symptoms of mononucleosis.
Infectious mononucleosis, provoked by viruses of types 4, 5, 6, can also occur in a complex form with fever, sore throat, enlarged spleen and liver, lymphocytosis, etc. In any case, it is very important to consult a doctor as soon as possible in order to start therapy in a timely manner and avoid infecting other children.
Diagnosis of the disease
Herpetic blisters look so characteristic that they cannot be confused with the morphological signs of other diseases - neither with an abscess, nor with specific ulcerations, nor with an allergic rash. In the vast majority of cases, the diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical manifestations.
A blood test for antibodies to the herpes simplex virus is an indirect method of identifying the pathogen in the body. It can be used if the body’s reactivity (the intensity of the response to external harmful agents) is low, and the infiltrate does not develop into characteristic blisters, which raises the question among clinicians: is it herpes?
Herpes simplex, which is manifested purely by a rash on the face, should be distinguished from herpes type 6, which is characterized not only by a rash, but also by a sharp increase in temperature.
Pediatrician Mikhail Nikolsky: Herpes - to treat or not to treat
Alexandra Petrovskaya: Good afternoon. This is a program for the biggest ones. With us in the studio is pediatrician and candidate of medical sciences Mikhail Nikolsky. Mikhail Andreevich, hello.
Mikhail Nikolsky: Good afternoon.
A.P.: We have gathered here today about your scientific work on herpes types 6 and 7. Let's try to explain to the listeners what it is, and, most importantly, where these types come from, and what other types - the first, second, third and so on - go up to 6 and 7.
M.N.: In total, there are 8 or 9 types of herpes, depending on how you count. The first and second types are common herpes, which causes cold sores on the lips. The third type is the herpes zoster virus, which causes chickenpox or shingles in adults.
A.P.: So what we call chickenpox is, in fact, the same herpes?
M.N.: Not the same, it’s a completely different herpes, but also herpes.
A.P.: By what principle are they all united under this name?
M.N.: It's difficult. When scientists studied the DNA of these viruses, it turned out that they all had similar related features. The fourth type, Epstein-Barr virus, causes infectious mononucleosis. The fifth type is what everyone knows as cytomegalovirus. These are also often infections, mostly for children.
And finally, type 6 and 7 are what I do. Most often they cause roseola in children - a three-day fever or sudden exanthema. Next comes the eighth type of herpes, it occurs in Kaposi's sarcoma. This is a serious disease that predominantly occurs in HIV-infected patients.
A.P.: Besides the common name and some similarities in DNA, what else unites them? Maybe there are common methods of therapy or similar effects of the virus on the body?
M.N.: Firstly, unlike many other viruses, there is a medicine against herpes. This is what makes these viruses different from others in many ways because there are no cures for a huge number of viruses.
A.P.: What about all these fashionable antiviral drugs that are advertised everywhere?
M.N.: Everything that is advertised on TV is, unfortunately, most likely fake.
A.P.: Fakes are prohibited.
M.N.: Fakes are prohibited, but, apparently, advertising of drugs without proven effectiveness is allowed.
A.P.: This is a topic for a separate program.
M.N.: This is a problem for our country, because in our country fakes have even found their way into clinical recommendations. And we treat people with all these “bullshit drugs.” Moreover, we are obliged to treat them, because we have appropriate clinical recommendations.
A.P.: Is someone lobbying for this?
M.N.: Of course, this is lobbied for, it is paid for. And what to take if, excuse me, we have one of the members of the Russian Academy of Sciences - a homeopath.
A.P.: In these words you can feel your contempt for homeopathy.
M.N.: From the point of view of a clinical physician, to some extent, yes, contempt, this is true.
Let's return to herpes. They have a unique feature. After a person becomes ill with a primary herpes infection, these viruses do not leave the human body. All herpes that a person encounters in life remain with him forever.
A.P.: I came across the statement that it is difficult to meet a person on Earth over 10 years old who does not have antibodies to one or another type of herpes.
M.N.: And not only antibodies, but even the herpes themselves. In almost all people after a certain age, one or another herpes can be found in saliva, blood or other tissues. This is the problem with diagnosing them - doctors very often get confused. Colleagues, out of ignorance, but with the best intentions, prescribe, for example, saliva tests for frequently ill patients for the Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, herpes type 6, type 7, and find them in the saliva. And this is the norm.
A.P.: Are they starting to treat?
M.N.: Yes, absolutely right. The patient does not know that this is the norm. He sees that he has a “terrible” test, that such and such a number of these herpes have been found, and the doctor, most likely, out of ignorance and lack of understanding of this problem, begins to treat normal carriers of herpes. And what does he treat? He treats with the same fuflomycins. And nothing happens.
A.P.: Bottom line – there is no need to treat herpes?
M.N.: It is necessary if it caused a serious illness - and all herpes in certain cases can cause serious illnesses. For example, herpes type 6 is a common cause of severe conditions in patients after a bone marrow transplant. If herpes after a bone marrow transplant has worsened against the background of a decrease, the actual destruction of one’s own immunity, then therapy necessarily requires powerful antiviral agents.
Well, take chickenpox – it would seem a harmless disease. But after 11 years it is difficult and can have consequences. Therefore, it is believed that if the patient is under 11 years of age, it often goes away on its own. And if you are over 11 years old, then it is better not to risk it, but to prescribe acyclovir.
A.P.: Is this a drug with proven effectiveness?
M.N.: Yes, it acts specifically on the chickenpox virus.
A.P.: It turns out that herpes, which is always in the body, at some point gets worse. For example, I heard about herpes type 6, that this is a typical disease for children under 2-3 years of age. It turns out that no.
M.N.: The fact is that herpes type 6 is the most common infection that always causes sudden exanthema or three-day fever or roseola. In principle, it is a very understandable infection: the child has a high fever for three days, then a typical maculopapular rash appears. Within two days it disappears on its own and the person recovers.
The infection itself can occur even through an ordinary kiss, as happens with many herpes. That is, the virus can enter the child’s body through contact with the saliva of the mother, grandmother, or any adult, who are usually the carrier of all herpes. And so the child suffers this primary infection through the human herpes virus type 6, and after that the human herpes type 6 remains in this child forever. And it won’t go anywhere, and there’s no way to get rid of it.
But it needs to be treated only in one situation - if it has caused some kind of serious illness, which almost never occurs in healthy people. Only for severe immunodeficiencies, which usually occur during organ and tissue transplantation. There are situations when intensive treatment of herpes type 6 is required.
In all other cases, there is no need to shock-treat it. And we must keep in mind that herpes is a very fashionable topic now. Herpes virus type 6 is easy to find, which means it can be presented for almost any disease as a possible diagnosis. And many doctors use this. For example: “I don’t know what’s wrong with you. Let’s look for what you definitely have.” And here is herpes type 6 - it definitely exists, and it is there.
A.P.: Another such moment. What other diseases can be associated with herpes viruses that are present in the body?
M.N.: As I already said, herpes types 6 and 7 “classically” cause roseola in children. Herpes type 6 and sometimes, but rarely, type 7 are also associated with febrile seizures in children. There are studies that show a connection between certain types of epilepsy and human herpes virus type 6. So it turns out that herpes type 6 actually causes a type of epilepsy.
A.P.: This virus is present in almost everyone’s body, but not everyone has epilepsy. That is, this suggests that there is no direct connection; there are other factors influencing the appearance of this disease?
M.N.: Of course, there are many factors here. For example, two people caught the same infection: but one had a runny nose, and the other had meningitis. But the infection is the same. Of course, there are many factors involved.
There was also a study that associated human herpes viruses 6 and 7 with other diseases, suggesting a link with multiple sclerosis. But this has not been proven. This is already a field of science, but we do not have clear indications that herpes is exactly what causes multiple sclerosis.
A.P.: During the program, we talked briefly about all herpes and outlined all the important points. And, concluding the conversation, I want to return to the beginning. What questions does science face today in this area?
M.N.: By the way, I forgot to say that a special form of human herpes type 6 is the chromosomal integrated form of this virus, when herpes type 6 is introduced into the human chromosome and begins to be inherited by all generations.
Now we have received a grant in St. Petersburg. We conduct free examinations of everyone for certain indications for the presence of chromosomally integrated human herpes type 6. It is precisely the presence of chromosomally integrated human herpes type 6 that may provide links with certain diseases. It turns out that almost 1% of the world's population has a chromosomally integrated virus built into its genome.
A.P.: Okay. Remembering my student years, what hypothesis do you have in this scientific research? If something, then what?
M.N.: We are currently recruiting a reference group, we are looking for people, we are examining them. I personally am now most interested in whether there are clinical manifestations of chromosomal integration of human herpes type 6 in newborns. In my opinion, this is the most interesting concept; no one in the world has yet developed this direction. So far there are preliminary results, but I’m not ready to announce them yet.
A.P.: Our guest was Mikhail Nikolsky, a pediatrician and candidate of medical sciences. Thank you and have a nice day everyone!
Herpes simplex
The official name is herpes simplex virus type 1 or HSV-1.
In some sources it is called labial or oral. Infection in most cases occurs in the first year of life, affecting the lips, skin on the nostrils and the area around it. With suppressed immunity, it acts more actively and is especially unpleasant for people diagnosed with HIV. Patients with immunodeficiency suffer from skin lesions on the fingers, mucous membranes in the mouth, nasopharynx, eyelids and eyes. Herpes can lead to nerve damage and suppression of the body's immune defenses. The majority of citizens in the world have the virus; almost every person has at least once experienced manifestations of infection in the form of a rash on the lips. Their development occurs as follows. Small bubbles appear in groups on the lip, nose, or surrounding area. First, the bubbles filled with liquid grow, and then either burst or deflate. A crust appears on the surface of the formation, over time it dries out and falls off.
Additionally, the patient may experience:
- pain throughout the body, which is characterized as muscle pain;
- an irresistible desire to sleep;
- general weakness, inability to work;
- temperature increase;
- a headache that goes away as quickly as it starts.
A doctor can determine the type of virus based on symptoms, but to make a diagnosis it is necessary to carry out a number of procedures:
- identify the pathogen and differentiate it from other varieties;
- determine the stage at which the disease is in the body.
Definitive treatment of herpes type 1 is impossible - it is insensitive to antibiotics, and there are no preventive procedures. All that can be done is to eliminate the symptoms that appear as quickly as possible. One of the most effective treatments is acyclovir and similar new generation drugs. Sold without a prescription in the form of tablets, ointments, solutions.
It is important to use the drug as directed and stick to the treatment plan, even if visible symptoms begin to subside. This will reduce the number of relapses and treatment time in the future. If there are rashes, it is necessary to avoid direct contact with other people to avoid infecting a healthy person.
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes of the 5th type manifests itself with blurred symptoms, like other types of the virus, it is active only when the immune response decreases. The first symptoms seem to be a common cold - weakness, drowsiness, sore throat, fever. As it develops, it can affect the central nervous system, spleen, pancreas, and organs of vision.
The virus in the body of a pregnant woman has negative effects on the fetus. Under its influence, the brain and respiratory system are formed incorrectly, development is delayed, and skin rashes develop. Infection during pregnancy leads to the need for termination. If it occurs before pregnancy, treatment with antiviral drugs and immunomodulators may be prescribed.
Symptoms of herpes simplex infection
There are few signs of herpes, but they are all very characteristic. Therefore, difficulties in differential diagnosis almost never arise.
The main symptoms of infection with herpes simplex, which is the most common form of herpetic lesions, are as follows:
- painful tissue swelling appears in the affected area;
- after 1-2 days it transforms into a denser infiltrate;
- the infiltrate turns into a bubble with liquid;
- the blister bursts and a painful ulcer forms in its place;
- the ulceration dries out and is covered with a new layer of epithelium - the wound heals.
The way lips look after herpes is the same as after any other skin disease: the swelling disappears, but the ulcer cannot heal for some time. It is covered with a yellowish film that constantly “peels off” from the wound surface, thereby exposing the wound and delaying the process of epithelial regeneration at the site of the lesion.
How long does the virus live?
Fully formed and ready for subsequent reproduction, “daughter” infectious virions appear inside the infected cell after 10 hours, and their number becomes maximum after 15 hours. During its entire life, the primary (“mother”) viral particle reproduces from 10 to 100 “daughter” ones. viral particles, and 1 ml of the contents of a herpetic vesicle contains from 1000 to 10 million viral particles. Virions are extremely thermostable - they are inactivated (destroyed) at 50-52 degrees for 30 minutes, at 37.5 degrees for 20 hours, stable at 70 degrees, and remain in tissues for a long time. On metal surfaces (coins, door handles, water taps) it survives for 2 hours, on plastic and wood - up to 3 hours, in damp medical cotton wool and gauze during the entire drying time at room temperature (up to 6 hours). A unique biological property of viruses is the lifelong preservation of viruses in a modified form in the nerve cells of the regional (relative to the site of virus introduction) ganglia of sensory nerves. The most active herpes simplex viruses (labial and genital) in this regard, the least active are the Epstein-Barr virus.
All known varieties of viruses are capable of recurrence . For example, recurrence of infections caused by the herpes simplex virus is often observed against the background of stress, nonspecific endocrine disorders, changes in the geographic area of residence, increased solar radiation, etc. Asymptomatic relapses of cytomegalovirus infection are most often observed in pregnant women and patients receiving immunosuppressive and hormonal therapy . In general, herpetic infections take a recurrent course in no more than 8-20% of patients with obvious malfunctions of the immune system.
Herpes viruses can lead to infection of the fetus during pregnancy. Pregnancy is very often a physiological immunosuppressive factor (there is a natural decrease in immunity). In the cervical canal of pregnant women, the risk of intrauterine infection of the fetus, as well as infection of the child during childbirth, significantly increases. The virus is the most common sexually transmitted infection in pregnant women. Therefore, before an expected pregnancy, we recommend that expectant mothers be examined for the presence of herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus infection on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, determine the presence and level of antibodies to these viruses, and, if necessary, receive a course of preventive treatment.
Organs and systems of the body that can be affected by the herpes simplex virus and the diseases it causes:
- Optic tract (keratitis, iridocyclitis, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis, phlebothrombosis)
- ENT organs (pharyngitis, “herpetic sore throat”, laryngitis, external ear, sudden deafness, vestibular disorders)
- Oral organs (stomatitis, gingivitis)
- Skin and mucous membranes (face, lips, genital herpes, etc.)
- Lungs (bronchopneumonia)
- Cardiovascular system (myocarditis, myocardiopathy, participation of HSV in the processes underlying atherosclerosis)
- Gastrointestinal tract (hepatitis, ileo-colitis, proctitis)
- Female genital organs (colpitis, intrauterine HSV infection: endometritis, amnionitis, chorionitis, metroendometritis, reproductive dysfunction)
- Male genital organs (prostatitis, urethritis, sperm damage)
- CNS (encephalitis, sympathoglioneuritis, nerve plexus damage)
- Psycho-emotional sphere (depression, aggravating influence of HSV on the course of hydrocyanic dementia and nuclear schizophrenia)
- Lymphatic system (HSV lymphadenopathy)