Pain and palpable lumps in the chest can be a manifestation of various diseases. In most cases they are benign in nature. Malignant diseases develop much less frequently. In order to determine the exact cause of these symptoms, you need to consult a doctor.
- Why does a lump appear in the breast?
- Lumps and tenderness in the mammary gland during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Self-examination of the mammary glands
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
Breast tumor
If a biopsy of a benign breast tumor reveals proliferation or atypia , this is just an alarming factor: with this process, the risk of cancer is higher than without it (maximum 4 times). Without proliferation and atypical hyperplasia, all benign breast tumors - papilloma, fibroadenoma, cyst, FAM or FCM - have no higher risk of cancer than all other women .
- Operations for fibroadenoma
- Treatment of breast cysts
- Breast papilloma
- Surgeries for gynecomastia
- Plastic surgery for benign breast diseases
- Mastitis or inflammation of the breast
Diseases of the mammary glands as a cause of nipple pain
A dangerous disease that causes pain in the nipples is breast cancer. These can be benign tumors, Paget's disease, carcinoma. Symptoms that should alert a woman include:
- tightening of the nipples, their inversion, flattening;
- yellowish or bloody discharge;
- painful lumbago, colic, itching of the nipples;
- redness of the areola.
Other diseases that cause nipple pain are mastopathy and fibrotic processes in the tissues of the hemispheres. For skin problems - eczema, herpes, impetigo, you should contact a dermatologist.
It is possible to differentiate the benign nature of the course from the malignant one only with examination - ultrasound, mammography, puncture. These services are provided at the clinic at affordable prices. Remember, timely contact with specialists will help avoid dangerous consequences for health and life.
Breast tumor
Facts of the degeneration of a benign tumor into cancer are described only for atypical ductal hyperplasia and for benign processes with proliferation and dysplasia. All of these conditions cannot be determined by examination, ultrasound, mammography or other non-invasive tests. They can only be detected by a biopsy and examination under a microscope of the formation that was found using the above non-invasive diagnostic methods.
Even the detection of atypical hyperplasia, dysplasia or proliferation does not guarantee the development of breast cancer: these conditions only increase the risks by a maximum of 4 times. In most women, these conditions never develop into cancer.
Not every tumor found in the breast is necessarily malignant or will become so!
Self-examination of the mammary glands
The main rule for self-examination and palpation of the breast is regularity. Experts recommend performing a self-examination at least once a month and on the same day of the menstrual cycle. The first step is to examine your breasts. The woman carefully examines the skin for redness, bluish discoloration, rashes, or changes resembling “lemon peel.” You should also check the symmetry of the mammary glands. Slight differences in shape or size are not a symptom of any disease and are considered normal. If the asymmetry appears suddenly, is pronounced or continues to increase, the woman should inform the doctor about it. During further breast examination, the woman stands in front of a mirror and raises her arms up. The presence of retractions may indicate the presence of a malignant tumor.
The next step is to palpate the breast. The hand on the side of the breast being examined is raised behind the head. The fingers are placed flat on the chest. The examination is carried out around the chest - from the nipple to the periphery or vice versa. All areas of the breast should be examined.
You should also pay attention to nipple discharge. They may appear as spots on clothing that touches the breast or appear when pressure is applied to the nipple.
Why is fibrocystic mastopathy dangerous?
Mastopathy is always characterized by the formation of both cysts and fibrosis. When this process is balanced - equal parts of both, and it is distributed throughout the entire gland - then they speak of fibrocystic, diffuse or mixed mastopathy.
Fibrous mastopathy
Fibrous mastopathy is characterized by a predominance of the fibrous component over the cystic component in the development of fibrocystic mastopathy.
Increased formation of connective tissue at the site of former proliferation makes the breast gradually denser and more painful. It becomes difficult to evaluate her with mammography and even place her in a mammograph (due to pain). CESM and MRI are more suitable for diagnosis and screening .
Nodular mastopathy
Sometimes, with fibrocystic mastopathy, denser nodes appear in the breast tissue, often in the upper outer quadrants (where there is initially more glandular tissue). They often look suspicious for cancer upon examination and on mammograms and require MRI (or CESM ) and biopsy for definitive diagnosis.
Mastopathy compaction
Often such patients are even offered surgery—sectoral resection for localized fibroadenomotosis—as cancer is suspected. The operation can be combined with a breast lift, reduction or breast augmentation with implants.
Cystic mastopathy
Cystic mastopathy is characterized by the predominance of the process of cyst formation over fibrosis in the development of fibrocystic mastopathy.
These cysts are always multiple. At first they are small, but over time they can merge, reaching large sizes. puncture brings relief .
If the cysts recur, it is proposed to remove them, which can be combined with lifting, reducing or enlarging the mammary glands with implants.
Regarding mastopathy, monitoring for cysts and for preventive examinations of the mammary glands, we recommend that you consult a doctor:
Subbotina Olga Yurievna , AF-clinic, Spassky lane 11, M. Sadovaya, Sennaya, Spasskaya, tel. 310-00-33 and
Sokolova Valentina Ivanovna , Nova Vita Clinic, intersection of Engels and Thorez Ave., tel. 8(911)007-20-02
Dushina Irina Ilyinichna , SMT Clinic, Moskovsky Ave. 22, tel. 777-9-777
Raevskaya Natalya Aleksandrovna , Polyclinic No. 83, M. Sportivnaya, tel. 498-09-22 and 8(921)944-10-45.
About harmless nipple pain in girls and women
The pain can spread not only to the nipples, but radiate to other areas, as a result, women begin to ache in the area of the shoulder blades, neck, and shoulders. The nature of the pain syndrome is different - shooting, aching, tingling, sharp, muffled. The reaction of a woman and a girl should be the same - an immediate visit to a doctor to determine why the nipples hurt and what to do about it.
The cause of sore nipples in girls is most often a hormonal surge associated with puberty and the growth of the mammary glands. The syndrome is temporary, does not require treatment, and has no consequences. If a girl experiences similar sensations before menstruation, they also have hormonal origins; at the end of menstruation, this goes away. If you experience constant and severe pain, you should consult a doctor.
Female mastodynia is possible during the maturation and ovulation of the egg at any age. This pain is natural, it subsides after the cessation of menstruation.
Other causes of pain in women are changes in the secretion of sex hormones:
- due to the use of inappropriate contraceptives;
- in stressful situations;
- in the absence of sex for a long time:
- during pregnancy.
For nursing mothers, nipple pain is a common occurrence if the woman has not prepared them for feeding.
Symptoms of mastopathy
Pain is the main symptom of mastopathy.
Connective tissue can swell and hold liquid (like white films on meat dipped in water). Completely similar - overformed connective tissue in the mammary glands during mastopathy - swells with excess fluid in the body. The swollen tissue mechanically affects the nerve endings in the mammary gland tissue, causing pain.
This happens physiologically in phase II of the cycle - when progestins (ovarian hormones) promote fluid retention in the body (normally). Therefore, pain in the mammary glands with mastopathy also occurs before menstruation.
In addition to pain with mastopathy, women find vague lumps in the mammary glands, usually painful and during the period of premenstrual tension. Ultrasound, mammography and MRI usually show nothing, or multiple cysts are found.
Lumps and tenderness in the mammary gland during pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the ratio of hormone levels in a woman’s body changes. During pregnancy, the corpus luteum and placenta synthesize progesterone, under the influence of which acini and ducts actively develop in the breast tissue - structures necessary for the production and secretion of milk. In the postpartum period, the mammary gland is already capable of lactation. If this process is disrupted, various diseases can develop, including:
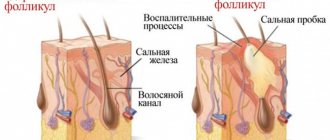
- Lactostasis is the stagnation of breast milk in the breast tissue. As a rule, it develops in the early postpartum period. It is characterized by engorgement of the mammary gland, the appearance of compaction in the tissues, a feeling of fullness, and pain on palpation.
- Mastitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the breast of an infectious nature. Most often occurs during lactation. 95% of all cases occur in the postpartum period, 5% develop in pregnant women. Provoking factors are poor breast hygiene, lactostasis, decreased resistance to infection and cracked nipples. The clinical picture of mastitis occurs in stages. At the beginning of the disease, the mammary gland is enlarged in size, swollen, redness and sharp pain on palpation are observed. Additionally, fever and symptoms of intoxication are noted. Further, the inflammation is localized and manifests itself in the form of single or multiple compactions. Without timely treatment, mastitis can result in serious complications - an abscess or phlegmon of the chest.
It is impossible to determine the cause of tightness and pain in the chest area without a visit to a specialist and additional examination. However, certain diagnostics can be carried out independently. If a woman discovers signs of a particular disease, she should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment of mastopathy
In the treatment of mastopathy, it is necessary to influence the causes of its occurrence: stabilize the menstrual cycle, treat pathologies of the thyroid gland and metabolism, and exclude “unhealthy” foods from the diet. This is often due to changes in lifestyle and established habits, sleep and eating patterns, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
How to treat mastopathy
Without normalizing the above options, treatment of mastopathy will be aimed at: reducing pain (pain relief and reducing swelling due to diuretics while limiting Na +), reducing the patient’s perception of his illness (sedatives), placebo (distracting prescriptions with unproven effectiveness).
About the treatment of breast oncology (cancer) see here.
Breast oncologists at our University Breast Center perform all types of operations for benign breast tumors: fibroadenoma, cyst, cystadenopapilloma (ductal papilloma), gynecomastia, etc.
Our Center is one of the few institutions in the city where it is possible to remove a tumor from the breast (fibroadenoma, cyst, papilloma, gynecomastia) under a compulsory medical insurance policy, voluntary medical insurance, or for a fee.
Removal of a benign breast tumor can be performed from various incisions: above the tumor, along the border of the dark part of the nipple (areola), along the border of the mammary gland (closer to the armpit), along the fold under the mammary gland. The choice is up to the patient.
Some women before surgery worry that after surgery they will have a shortage of breast tissue at the site of tumor removal. We always use breast tissue transfer techniques to evenly fill tissue gaps. If this is not enough, we have a lipofilling method in our arsenal that allows us to fill the volume deficit.
When discovering any tumor, lump or lump, every woman has an absolutely adequate question: “Isn’t this cancer?” First, do a simple test in front of a mirror: raise your arms up.
If, when you raise your arms, a retraction or area of skin appears at the site of the tumor (as in the first and third pictures), if the nipple, when you raise your arms, is pulled into the gland (as in the second picture) or is bent towards the tumor (as in the third photo) - hurry to get examined USE THIS ALGORITHM and contact an oncologist-mammologist.
The next step is to try to squeeze the breast tissue away from the tumor as in the photo:
If skin retraction appears above the tumor, also hurry up and undergo examinations using THIS ALGORITHM and contact a breast oncologist.
If you don’t find anything similar (as in the pictures above) , exhale and relax: most likely you do not have breast cancer.
Even if you squeeze your nipple and squeeze blood out of its ducts, as in the photo below , most likely it will be a benign process - ductal papilloma , and not breast cancer.
| We recommend that you be examined by specialists: |
Mastopathy
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), mastopathy is coded as N60.1 and refers to benign mammary dysplasia. This means that mastopathy is not an ancestor and does not increase the risks of its occurrence .
The World Health Organization (WHO, 1984) in the Histological Classification of Tumors (evaluates the process under a microscope) defines mastopathy as a dishormonal hyperplastic process in the mammary gland or fibrocystic disease (FCD), characterized by proliferative and regressive changes in the mammary gland tissue with an abnormal ratio of epithelial and connective tissue components.
Why does a lump appear in the breast?
Lumpiness in the chest along with painful sensations occurs with various diseases. These include:
- Benign breast tumor. Depending on the origin, adenoma, lipoma, fibroma and other neoplasms are distinguished. The tumor is a volumetric compaction. There may be one or more such formations in the breast tissue. The lump may be painful or may be painless. In some cases, breast discomfort occurs before or during menstruation.
- Breast cyst. This is a spherical or oval seal, represented by a cavity filled with liquid contents. This condition is most characterized by pain and discharge from the nipple.
- Nodular or diffuse mastopathy. It is characterized by the appearance of single or multiple compactions in the breast tissue as a result of hormonal imbalance. Symptoms of this condition are areas of palpable lumps and cysts in the tissues, pain and swelling of the mammary gland before menstruation, and discharge from the nipple.
- Malignant breast tumors. They are characterized by the appearance of a lump, a change in the shape of the mammary gland, deformation of the nipple and pathological discharge from it, as well as a change in the skin texture in the projection of the neoplasm. As the disease progresses and metastases appear, the size of nearby lymph nodes increases, their compaction and pain on palpation are noted. In the initial stages, the symptoms of breast cancer may not be pronounced enough.
Diffuse FAM
NB! This abbreviation is very often used after any examination of the breast (ultrasound, mammography, examination). This is due to the fact that in budget clinics, if the doctor does not find any pathology during the examination and does not make at least some diagnosis, the insurance company does not pay for this consultation and examination to the institution. Therefore, there is an unspoken instruction to doctors to “put at least something.” This is how it is implemented. It is impossible to write “Normal variant” or “No pathology detected”!
In private centers, in most cases, there is an unobtrusive recommendation to encourage repeat visits of patients and their additional examinations. Therefore, they also “find” FAM, FCM or mastopathy during a simple preventive examination without the patient’s complaints - in order to be able to prescribe a “control” examination, examination or even treatment with dietary supplements (which are often sold right there) with a second “appearance in 3-4 months” .
Causes of mastopathy
WHO considers the cause of mastopathy or fibroadenomotosis dishormonal changes that can occur with:
- disruption of hormone synthesis during an unstable menstrual cycle
- for problems with the thyroid gland
- in case of metabolic disorders with excess body weight (adipose tissue itself synthesizes estrogens - ovarian hormones of the first phase of the cycle).
- late birth and short duration of breastfeeding.
WHO does not consider options for dishormonal changes due to consumption of cheap foods with hormones - broiler meat, animals and fish that received hormonal growth stimulants; animal tissues with a high content of endogenous hormones - udder, adipose tissue, uterus, ovaries, milk - which are not thrown away, but processed and used for the manufacture of cheap semi-finished products. A number of plant products contain substances that are not actually hormones, but which our body perceives as hormones - hops in beer, soy, palm oil components. When consumed regularly, they can also cause dishormonal changes and provoke not only mastopathy.
Normally, a passage of secretion occurs in the mammary gland: hormones of the corpus luteum - phase II of the cycle initiate the proliferation of cells of the mammary gland lobules (which secrete milk during feeding) - as preparation for a possible pregnancy - without pregnancy, their regression occurs. The cells of the lobules die and the products of their death move along the ducts towards the nipple, where what is left of them is absorbed in the sinuses. In mastopathy, due to dishormonal changes, the process of proliferation in the lobules is more pronounced. As a result, more regression products of these cells appear, which form clusters (cysts). Severe regression promotes aseptic inflammation and the formation of connective tissue. With a deficiency of vitamins A, E and D, rough scar tissue forms at the site of regression, disrupting the movement of secretions and aggravating the problem in subsequent cycles.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding help normalize the condition of the mammary glands, while abortion provokes a non-physiological hormonal shock to the mammary gland tissue.
The synthesis of all hormones occurs mainly at night from 23:00 to 3:00, provided that the person is already sleeping at this time. For this process to occur normally, you need to go to bed after 10:00 p.m. It is believed that this process is also negatively affected by excessive lighting. At night, during sleep, all the damage that happened to the body during the day is restored. Lack of sleep and light pollution from artificial lighting disrupt the natural process of hormone synthesis and body restoration, causing illness.
Also, excess Na+ content also contributes to fluid retention in the body. Each sodium ion can hold up to 4 water molecules. Sodium ions are part of sodium glutamate (a flavor enhancer - a food additive for cheap food) and salt (NaCl), which is found in abundance in processed foods, sauces and seasonings.
Signs of mastopathy
WHO considers all the problems mentioned in the paragraph above to be the cause of mastopathy - when, under the influence of these hormonal changes in the mammary gland, glandular tissue is stimulated (proliferation), and after the stimulation stops, excessively proliferating tissues die with the formation of cysts, after which - the formation of scar tissue. As a result, multiple cysts appear in the breast, and the connective tissue causes fibrosis.
All this leads to an increase in the density of the mammary glands and the occurrence of pain - first before menstruation, and with an unstable cycle - it may not depend on it.
Pain in mastopathy is never one-sided and precisely localized: the entire chest hurts, right and left, maybe somewhere a little stronger (for example, in the upper outer quadrants - where there is more glandular tissue), but ALL! It bothers me while lying and standing, without changing from body position.
If signs of mastopathy appear or intensify while taking hormonal drugs (contraceptives), it means they were chosen incorrectly - coordinate their use with a gynecologist. At the same time, being treated at the same time by a mammologist is absurd.
If the pain is local in nature - on the one hand, and you can accurately show its location, but no compaction is detected in this place - most likely it is associated with intercostal neuralgia due to physical inactivity and problems with the thoracic spine. This pain will go away depending on the position of the body (tilting left and right, bending over, lying down and standing up) and inexperienced specialists and patients often confuse it with mastopathy. According to the results of breast examinations (mammography, ultrasound), nothing is found with her either.
FAM (fibroadenomotosis) or FCM (fibrocystic mastopathy)
FAM stands for fibroadenomotosis. This is the same as FCM - fibrocystic mastopathy. This term refers to a pathological process in the mammary gland (breast), characterized by the appearance of cysts and fibrous tissue. More cysts - cystic FAM or FCM, more fibrous tissue - fibrous FAM or FCM.
If the process evenly affects the entire tissue of the gland, it is a diffuse form. If the process is local - focal FAM or local. Local fibrous FAM is often mistaken for cancer. Suspicion is excluded by MRI and biopsy, or by surgery to remove a suspicious tumor.
Very often, the diagnosis of FAM is made not because of the presence of pathology, but in order to properly fill out documents for the visiting patient at an appointment at a budget clinic: if you write on the card that “no pathology was detected,” the insurance company will not pay for the appearance at the clinic.
The most common cause of FAM is hormonal changes (read more HERE).