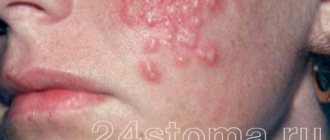
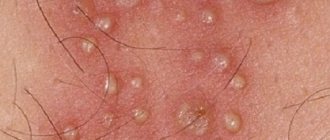
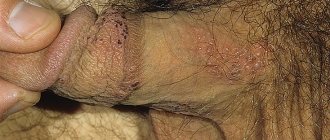
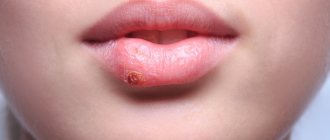
Almost everyone is familiar with a “cold” on the lips. As soon as you catch a runny nose or get nervous, an unpleasant harbinger immediately appears - a tingling sensation somewhere around the mouth.
The herpes simplex virus is present in the body of 95% of people. And only a few have immunity, the reasons for which are still unclear.
The virus enters the body in early childhood: at 3–4 years, when the antibodies against the herpes virus transmitted to the baby by the mother are depleted. Most often, infection occurs if a child is kissed by carriers of the infection. In addition to a kiss, the virus can enter the body, for example, with saliva. It penetrates the mucous membranes, reaches the nerve endings, rises into the cranial cavity, where it “hides” in a nerve plexus called the trigeminal ganglion and “sleeps” there until it is reactivated.
How does the virus become infected?
The virus can be infected in different ways: airborne droplets, contact (through shared towels, cutlery, through kissing), sexual intercourse, self-expression (when the virus from ulcers enters healthy mucous membranes and infects them). You can become infected through a blood transfusion and a child can receive the virus from the mother in utero. The incubation period (from the moment of contact until the first signs appear) is 2-14 days. A person becomes contagious as soon as sores appear on the lip, and is contagious to others until the scabs fall off .
Photo: One of the most common ways of transmitting herpes is contact.
Herpes: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Itching, soreness, redness of the skin, blisters... Really again? Those who have encountered it more than once will “recognize” these symptoms as manifestations of herpes. What kind of virus is this? For what reasons does he regularly harass some people?
Our interlocutor, candidate of medical sciences, dermatovenerologist at the Expert Tula Clinic, Vladislav Leonidovich Sheinkman, told us about this and much more.
— What is herpes and how common is it among the inhabitants of our country?
This is a group of diseases caused by herpes viruses. One of the most common types is the herpes simplex virus, which is divided into herpes types 1 and 2, as well as the varicella zoster virus and herpes zoster virus.
Almost all people in Russia are infected with the herpes simplex virus. Once the virus enters the body, it never leaves it. Usually it is in the body in an inactive, “sleeping” state and does not bother a person.
— Is herpes a fungus, a virus or a bacterium?
It's a virus.
— Where does the herpes virus hide in the body?
Herpes simplex viruses are usually found in the so-called nerve ganglia (for example, in the trigeminal ganglion, sacral ganglia).
— How does infection with the herpes virus occur? Who is at risk for herpes infection?
Infection usually occurs in childhood. There are several ways of infection. This is airborne, contact household (dishes, household items, etc.), sexual.
What is immunity and how to increase it? Allergist-immunologist at Clinic Expert Smolensk tells
Chemova Ulyana Vladimirovna
The risk of virus activation occurs in the presence of so-called cofactors. These include weakened immunity, emotional distress, stress, alcohol consumption, climate change (for example, travel), menstruation, prolonged exposure to the sun or hypothermia, the presence of infection (ARVI, pneumonia, sinusitis, etc.).
Is it possible to treat sinusitis without a puncture? Otolaryngologist at the Expert Kursk Clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences Alexandra Nikolaevna Emelyanova tells
— Tell us about the most common symptoms of herpes
Herpes occurs cyclically in the body, and its symptoms depend on the stage of the process.
The first, so-called prodromal stage, is characterized by burning, itching, and a tingling sensation in the area of future localization of herpes manifestations. The duration of this period can be several hours.
In the second stage, redness and thickening of the skin or mucous membrane appear in the form of a spot (erythematous stage). This stage of herpes lasts about a day.
At the third stage, small bubbles (2-3 mm in size) appear, which can “merge” with the serous or serous-purulent contents. Depending on the severity of the flow, the number of bubbles may vary.
In the fourth stage, the blisters break open and painful ulcers form in their place. This stage of herpes lasts several days and is the most contagious to others.
By the fifth stage, the ulcers dry out and form crusts.
And finally, at the sixth stage, the crusts fall off and the skin or mucous membrane is restored.
With type 1 herpes simplex virus, manifestations occur on the skin and mucous membranes of the upper half (for example, the lip area, nasolabial fold, neck), and type 2 - on the lower half of the body (otherwise it is called “genital herpes,” although Other areas may also be affected - for example, the buttock area, etc.).
In the recurrent form, the localization is usually stable.
— Is herpes on the lips contagious to others?
Absolutely yes.
— Does a herpetic infection always manifest itself with pronounced symptoms, or may a person not suspect that he is a carrier of the infection?
If a herpetic infection is also understood as a pure carrier state, then symptoms may not always be present. If a person has a strong immune system, he may not even know that he has such a virus.
The manifestations of exacerbation also vary from person to person. People with a normal but temporarily slightly weakened immune system, or those receiving some kind of antiviral treatment, may have a different severity of symptoms than a person with a severe illness (for example, tuberculosis), a severely weakened immune system (for example, HIV infection, chemotherapy, for organ transplants, etc.).
What are the symptoms of tuberculosis? Read more
— How is the herpes virus detected in humans?
Diagnosis of herpesvirus infection is primarily based on an examination by a dermatovenerologist.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory methods may be prescribed by the doctor. Some of them are used to detect the virus itself, while others are indicators of the immune response to the virus.
To search for the virus itself, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used, when material is taken from the site of the lesion and examined for the presence of virus nucleic acids.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is used to confirm the presence of an immune response against the virus. Imagine this situation. A person does not have any manifestations of herpes, and besides, he does not remember whether he ever had them or not. How to find out whether an organism has “met” the virus or not? If, when performing ELISA, specific antibodies are detected - immunoglobulins of class G (IgG) against the herpes virus, this means that there was once an infectious process, and the virus is currently in an inactive state. These antibodies are usually found throughout a person's life. If there is a suspicion of virus activation, then, in addition to PCR, an analysis for class M immunoglobulins (IgM) may be prescribed according to indications. The detection of this type of antibody indicates an exacerbation of the process. Outside of an exacerbation, only IgG is detected.
— For whom can the herpes virus be dangerous?
First of all, these are persons with serious diseases (for example, tuberculosis, oncological pathologies, immunodeficiencies). In them, the manifestation of herpes can be severe, affecting areas that are not usually found under other conditions (for example, the optic nerve).
— How to get rid of herpes? Is it enough to use only ointment or cauterize the wounds with brilliant green?
This depends on a number of factors - in particular the prevalence of the process, the frequency and severity of relapses. Often local treatment is not enough. There are certain standards and principles for the treatment of herpes, which consist in the use of antiviral drugs and agents to improve/correct the functions of the immune system.
— There are recommendations on the Internet to use tea bags or sage infusion to relieve itching from herpes. Do traditional methods really help in treating herpes infections?
The use of such methods may complicate the doctor’s work, i.e. making the correct diagnosis and prescribing effective treatment.
— What could be the consequences if herpes is not treated?
Mainly - frequent relapses, with the appearance of more common forms during exacerbations, with more severe symptoms.
— What specialty does a doctor treat herpes?
Dermatovenerologist.
You can make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist here
Please note: the service is not available in all cities
— Are effective methods of preventing herpes known to modern medicine?
Undoubtedly. It is necessary to identify and eliminate cofactors that lead to exacerbation of herpes. The main ones are stress, hypothermia or overheating, excessive alcohol intake, exposure to the sun, climate change and a number of others.
For reference:
Sheinkman Vladislav Leonidovich
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Smolensk State Medical Institute in 1994.
From 1994 to 1995, he completed an internship, and from 1996 to 1998, a clinical residency in the specialty “Dermatovenereology”.
Has an academic degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Currently working at Clinic Expert Tula LLC as a dermatovenerologist. Provides reception at the address: st. Boldina, 74
Why do cold sores appear on the lips?
Those who suffer from herpes have noticed that exacerbations begin along with ARVI. Herpes occurs when immunity decreases, the protective forces of which are used to suppress ARVI. Colds on the lips also appear when the body’s defenses are weakened: with chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, frequent stress, poor diet, alcohol abuse and active smoking, in women at the beginning of pregnancy and in the first 5-7 days after childbirth.
Photo: Colds on the lips can only appear if the immune system is weakened
Effect of pregnancy on virus incubation
Often, women who are in the period of bearing a child ask their attending physicians about how the incubation of herpes changes during pregnancy.
It is quite difficult to predict changes in this case.
On the one hand, the body does everything to protect the woman herself, as well as her unborn baby, from negative external influences, including viral particles.
On the other hand, pregnancy is a condition of a woman’s body, accompanied by severe immunosuppression.
Otherwise, bearing a fetus would simply be impossible.
Often it is immunosuppression that prevails in the female body.
As a result, the length of time it takes herpes from entering the body to developing symptoms is significantly shortened. It is also worth considering that herpes is quite capable of penetrating the placenta, leading to infection of the child.
Sometimes it leads to the development of congenital pathologies of varying severity.
How does herpes manifest?
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish 5 stages of the development of herpes simplex: 1. The first stage occurs when blisters appear. It manifests itself as burning and itching in the lip area, and its swelling. 2. The second stage begins with the appearance of bubbles. At first small, they grow and fill with clear liquid. After a couple of days the liquid becomes cloudy. 3. The third stage of the disease is characterized by rupture of the vesicles. In place of the burst blisters, ulcers with swelling form. This stage is dangerous due to the development of complications. The person at this moment is very contagious. 4. In the fourth stage, the ulcers become covered with a dense crust. 5. At the fifth stage, the crusts dry out and fall off. The symptoms go away. The person becomes no longer contagious.
The influence of HIV infection on the incubation period of herpes
Another common question is how the duration of incubation changes during HIV infection.
There is nothing surprising in such a question.
After all, the human immunodeficiency virus is becoming increasingly common in medical practice today.
Much in this case depends on how strongly the patient’s immunity is suppressed.
For example, if a patient regularly takes HIV medications and his lymphocyte levels remain normal, the incubation period may remain within the standard range.
If the patient ignores the doctor’s recommendations and refuses medications, the level of his defense system drops to catastrophic levels.
The result is predictable: the period of time is greatly shortened.
The disease makes itself felt much earlier than if HIV were controlled or completely absent from the body.
How can herpes be dangerous?
Herpes can cause many complications. Some of them are life-threatening.
- Bacterial complications. Most often, bacteria simply attach to the virus and the blisters fill with pus. If the blisters have already burst, then the ulcers become covered with pus, the pain in the lip becomes unbearable and a crust does not form.
- Herpetic stomatitis is a lesion of the oral mucosa. The disease begins with a sharp increase in temperature, salivation and sharp pain when chewing food. There are many blisters in the mouth, similar to herpes on the lips.
- Herpetic eye damage begins with pain in the eyes and lacrimation. A person cannot open his eyes due to severe pain. A dangerous condition that can result in blindness.
- Herpes of the esophagus. Occurs when herpes spreads from the lips. There are difficulties when swallowing, severe pain, refusal to eat and weight loss.
- Herpetic pneumonia and herpetic hepatitis occur in people with immunodeficiency and occur together with bacterial and fungal processes.
- Herpetic damage to the nervous system occurs in the form of meningoencephalitis and is the most severe form of herpes. It begins with a sharp headache, nausea and vomiting, high fever, movement disorders and convulsions. The disease is unfavorable.
Photo: To avoid complications, you need to start treating herpes in a timely manner.
Atypical forms of herpes
Sometimes genital herpes is erased. These forms of the disease account for 65% of cases of the disease:
- In women,
atypical herpes resembles inflammation of the vagina or vulva. There is pain, itching and swelling of the genital organs, profuse leucorrhoea and pain during sexual intercourse. External manifestations are limited to areas of redness or pinpoint rashes. - In men,
the atypical form of the disease is similar to inflammation of the head and foreskin (balanitis or balanoposthitis). A reddish rash appears on the mucous membrane of the penis, accompanied by pain and burning, which does not look like a herpetic rash. Inflammation of the prostate gland occurs, causing pain radiating to the anal area. Damage to the urethra leads to pain and burning when urinating, and the appearance of traces of blood in the urine.
There is a latent form of the disease in which there are no clinical manifestations, but despite this, the person remains a source of infection. But imaginary well-being does not last forever. With hypothermia, loss of strength, decreased immune defense, pregnancy, stress, severe concomitant diseases and other unpleasant conditions, the virus begins to multiply rapidly and the person becomes ill.
The disease is activated by concomitant sexually transmitted infections, especially ureaplasmosis. Due to the ability to rapidly “bloom” against a background of weakened immunity, herpes occurs in 90% of HIV patients. Therefore, if herpetic rashes appear, you need to be examined for other STDs.
Diagnostics
If you suspect the presence of herpes simplex, you should not self-medicate. It is urgent, without delay or masking the rash, to come to an appointment with a dermatovenerologist. A carefully collected anamnesis (questioning of the patient) is important for establishing the correct diagnosis. Herpes, regardless of the location of the pathological process, is characterized by a wave-like course, when painful states are replaced by periods of well-being, even without treatment. The presence of blistering rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, severe subjective symptoms (itching, burning) allows doctors to visually diagnose herpes simplex, prescribe treatment in a timely manner and inform the patient about the danger of infecting a sexual partner.
Only laboratory research methods, which are fundamentally divided into two groups, can reliably confirm the herpetic nature of the disease in the absence of typical manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes:
- isolation and identification of HSV from infected material (material for analysis are scrapings from the lesion, blood, urine, saliva, tear fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, discharge of the cervical canal, vagina, urethra, rectum);
- detection of specific antibodies (protective proteins) to the herpes virus in blood serum - serodiagnosis.
Reminder in case of illness
It must be remembered that when a rash appears, a person becomes acutely contagious. Moreover, not only those around him can suffer, but also the sick person himself. For example, from a lesion on the lips with dirty hands, the herpes virus can be carried into the eyes or genitals.
Therefore, it is important to follow the following rules
- Do not touch lips affected by rashes. If you touch them, wash your hands thoroughly.
- Use your own towel and utensils.
- If your lips are affected, do not squeeze the blisters or pick off the scabs. This may cause additional skin infection.
- Refrain from kissing and oral-genital contact.
- If you wear contact lenses, do not wet them with saliva to moisten them.
- Apply antiviral cream to your lips not with your fingers, but with cosmetic sticks.
Complications of GG
People with genital herpes face an increased risk of contracting and passing on other STDs. This is because the ulceration that occurs as a result of a herpes infection makes the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals more vulnerable to sexually transmitted infections. Patients with symptomatic HH face a 2-4 times higher risk of acquiring and transmitting HIV infection.
Complications are rare:
- In some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver and eyes, even to the lining around the brain, causing meningitis.
- 1% of patients with primary HH develop autonomic dysfunction with urinary retention, erectile dysfunction, constipation, and sensory loss. Sometimes (intermittent) catheterization is necessary over several weeks.
- Mild meningitis is relatively common in primary herpes (13-20%). Herpetic encephalitis occurs less frequently and has a mortality rate of about 70%.
- Neonatal herpes simplex may develop after vaginal delivery and may be accompanied by local infection (skin, eyes, or mouth), disseminated manifestation (visceral organs), or central manifestation (CNS).
Symptoms may be especially severe in people with weakened immune systems due to existing HIV infection or immunodeficiency. An infection that affects the eyes can lead to blindness. This occurs mainly in people with weak immune systems who have had the virus for a long time. With a weak immune system, herpes increases the risk of bacterial infections, which can lead to further complications.
Another possible complication affects pregnant women. During childbirth, women can pass the virus to their newborn. Women at risk for STIs often get tested in the early weeks of pregnancy to prevent complications. A pregnant woman with symptomatic genital herpes is at risk of miscarriage or premature birth.
The infection can be transmitted to the fetus, and the baby may develop neonatal herpes. The risk of complications is especially high if a woman contracts the infection in the last trimester of pregnancy. If she has active genital ulcers near the time of delivery, a cesarean section is usually recommended to avoid exposing the newborn to the virus.
Make an appointment
Choosing an ointment for herpes -
If you have herpes, treatment in adults and children is most often carried out with one of the external agents containing 5% Acyclovir (an antiviral agent effective against the herpes virus). Preparations based on acyclovir: Acyclovir cream 5% (Russia), Acyclovir ointment 5% (Russia), Acyclovir-Hexal cream (Germany), Acyclovir-Sandoz cream (Switzerland), as well as original drugs with acyclovir - a line of branded products Zovirax (UK).
Zovirax cream: the original drug of acyclovir
Herpes cream or ointment with acyclovir should be applied to the lesion and the skin around it at least 5 times a day (but better every 2 hours while you are awake). The duration of therapy is usually 5 days, but in case of severe herpetic lesions, the duration of use can be increased to 7-10 days. It should be noted that the cream form is more preferable to the ointment, because from the ointment substance, the active substances penetrate the skin much worse.
It is worth paying attention to the composition, for example, the effective concentration of acyclovir is exactly 5% (although in pharmacies you can also find products with a 3% concentration). In addition, the composition should preferably contain propylene glycol and/or cetomacrogol, which increase the penetration of acyclovir molecules through the surface layers of the skin. This is important because Acyclovir itself penetrates quite poorly through the epidermis of the skin and the resulting crusts.
For women, it may be important to be able to apply cosmetics on top of the absorbed cream. In this case, you should choose a cream that contains dimethicone (silicone). Today, dimethicone in combination with propylene glycol and cetomacrogol is found in the following products - Zovirax cream, Zovirax Active-Duo cream, Acyclovir-Sandoz cream.
The best remedy for herpes with acyclovir is
Today, the best drug for external use against herpes is Zovirax Duo-Active cream, which contains a combination of 5% acyclovir and 1% hydrocortisone. Acyclovir blocks the multiplication of the virus, and hydrocortisone reduces inflammation and swelling. Moreover, if the use of the cream begins even before the appearance of herpetic blisters, then hydrocortisone sometimes makes it possible to prevent their formation altogether. But if bubbles do form, their number and size will be smaller, which in itself will significantly speed up healing.
Disadvantages of acyclovir-based drugs - acyclovir is an outdated drug, but in principle it works well for most patients (with some exceptions). For example, in patients with good immunity, resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir occurs on average in only 3% of cases, which is quite small. However, the problem is in patients with weakened immune systems + frequent courses of acyclovir use in the past - in such groups of patients, resistance to acyclovir can be observed in 10 to 27% of cases.
In addition, acyclovir molecules have a very low tropism for the herpes virus, which means that acyclovir usually simply does not find a certain percentage of viral particles in cells (for example, drugs based on penciclovir / famciclovir have a much higher tropism in the virus). In addition, acyclovir molecules tend to penetrate poorly through the skin, as well as through the resulting crusts (to the site of virus reproduction). In order to somehow reduce this problem, some manufacturers add propylene glycol and cetomacrogol to external products containing acyclovir.
Alternative external remedies for herpes -
First of all, this is the Fenistil-Pentivir cream, which contains the antiviral component Penciclovir. Compared to acyclovir, penciclovir is several times more effective (including due to the significantly greater tropism of penciclovir for the herpes virus, and due to better penetration into cells affected by the virus). It should also be noted that the resistance of the herpes virus to penciclovir is extremely low - it is no more than 0.2%.
The drug is applied to the lesion every 2 hours (8 times a day), but the course of use is usually only 4 days. Such a short course is due to the fact that after the last application of the cream, the clinically active concentration of penciclovir will remain in the cells for about 2 more days (i.e., the therapeutic effect after a 4-day course will last about 6 days). Clinical studies have also found that repeated outbreaks of herpes occur less frequently when using Fenistil-pencivir than when using other drugs. However, in recent months this drug has disappeared from Russian pharmacies, most likely due to the re-registration procedure.
We have already said above that patients with weakened immune systems often develop resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir. What should such patients do? International recommendations in this case speak of the need to use courses of famciclovir in tablets - these are drugs such as Favirox or Famvir. Tablet preparations based on valacyclovir (if resistance to acyclovir is suspected) does not make sense to use, because valacyclovir is a precursor to acyclovir. The latter means that if there is resistance to acyclovir, there will be resistance to valacyclovir.
Cream Devirs for herpes –
Maybe there are some other topical products that would be effective against herpes and do not contain acyclovir? In pharmacies you can find such a prescription drug - Devirs cream (manufactured by Vertex, Russia), containing the antiviral component ribavirin. According to the instructions, this drug can be used in patients over 18 years of age - for genital herpes, for the treatment of labial herpes, herpes localized on the face and body.
Unfortunately, there are very few clinical studies on the effectiveness of local ribavirin-based products, and all of them, in our opinion, have a rather weak degree of evidence. Getting acquainted with the studies, we noticed that this drug was very rarely used in studies in the form of monotherapy (usually it was combined with either oral ribavirin or oral acyclovir), which already indicates the rather weak effectiveness of the cream. Therefore, our editors cannot recommend this drug for widespread use, especially for the treatment of herpes lips and small lesions on the face. But the drug may well be used as part of complex therapy, for example, for genital herpes.
Isolation and identification of HSV
In specialized virology laboratories, HSV is isolated using the culture method. Its essence lies in the fact that the material for research (the contents of herpetic eruptions, human secretions) is placed on specially grown cells in which the virus begins to multiply. Then, after 5 days, the presence of HSV is determined by characteristic changes. Thus, we can say for sure that this disease is of a herpetic nature.
To identify the causative agent of HSV, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is widely used, which makes it possible to find out what type of herpes virus is present in the body. The material for research is taken with a special brush from the rash sites. The PNR method is highly sensitive and is performed within 24–48 hours.
What to do if herpes incubation takes a very long time
Doctors have long noticed that not all patients develop herpes according to the standard pattern.
This fact further complicates treatment during the incubation period.
It is worth keeping in mind: if the patient has a strong body, an active immune system, symptoms of the disease may not appear for a very, very long time.
Do you need to worry if there are no symptoms of the disease, although they should be, since infection has definitely occurred?
Until rashes begin to appear, the patient can be calm about his health.
Herpes is not an infection that undermines the body unnoticed.
Its symptoms are quite vivid and difficult to ignore.
If there are no symptoms, then the virus is dormant and does not pose a threat to the body.
Since it is completely impossible to remove a pathogenic microorganism from the body, all that remains is to make efforts to prevent it from becoming more active.
Principles of treatment
Herpes can and should be treated. Currently, medicine has a whole arsenal of drugs that, in most cases, make it possible to obtain a lasting clinical effect in those who suffer from recurrent herpes and to successfully control periods of activation of the disease in asymptomatic forms. It is impossible to achieve complete removal of the virus from the body using currently existing treatment methods; it is possible to maintain the body in a state where the virus does not have a chance to activate. Currently, there are two main directions of treatment for herpes simplex:
- The use of antiviral drugs, the main place among which is occupied by acyclovir-containing (ACV) drugs. In case of exacerbation of herpes, the first aid remedy is medications containing acyclovir: ZOVIRAX, VAPTREX, ACICLOVIR-ACRI, VIROLEX. They are available in the form of tablets and creams. The same drugs are used locally in the form of cream and ointment. Taking these medications should begin in the first hours of an exacerbation.
- A complex treatment method that includes immunotherapy in combination with antiviral therapy. As a rule, the disease occurs against the background of suppressed immune reactions, so immunotherapy plays an important role in the treatment of herpes. If relapses of the disease are seasonal (autumn, spring) and they are accompanied by symptoms of ARVI, then to antiviral treatment with drugs containing acyclovir, it is advisable to add a course of drugs that stimulate the synthesis of interferon (a substance produced by the body and providing an antiviral effect): herbal immunostimulants (for example, IMMUNAL) and synthetic drugs such as ARBIDOL, AMEXIN, VIFERON, KIPFERON. Moreover, they can be used for preventive purposes about a month before the onset of autumn slush and spring hypovitaminosis). If relapses of herpes (at any location) occur more than 3-4 times a YEAR, this is a reason to consult a doctor. This means that the body's defenses (immunity) cannot cope with the infection. In such cases, after studying the immune status, the patient is prescribed complex treatment, including antiviral and immune drugs. In patients with recurrent herpes, the drugs TACTIVIN, TIMALIN, THIMOGEN, MYELOPID, etc. are successfully used (treatment must be carried out after an immunological study).
Serodiagnosis
Antibodies to the herpes virus appear in the blood serum by 4-7 days after the initial infection, reach a peak after 2-3 weeks and can persist throughout life. The diagnosis is made by the characteristic increase in antibodies and determination of their class. For example, the detection of a certain level of immunoglobulin M (antibodies) indicates a primary infection of a person or an exacerbation of herpes. The detection of a certain level of immunoglobulin G indicates that the human body has encountered the virus and has developed antibodies - the person is infected, but not infectious to others. The result is known the next day. The analysis can be repeated at intervals of several days.
What tests will help detect infection during the incubation period?
Tests during the incubation period, as doctors note, are particularly difficult.
This is due to the fact that viral infections are already difficult to diagnose.
If we are talking about the incubation period, everything becomes even more difficult.
You should immediately forget about such popular and simple methods as microscopy and smear culture.
Of course, seeding is performed in some laboratories with special conditions, but it is more for research purposes.
The most reliable options are ELISA and PCR.
Moreover, as doctors note, PCR usually provides more information, which in itself is more reliable. This is due to the fact that the technique does not detect traces of a pathogenic microorganism in the blood, but detects it itself.
However, it is worth considering that PCR also has limitations.
If at the time of examination there are not enough viral particles in the body (the threshold value is below the detectable value), then the analysis will be false negative.