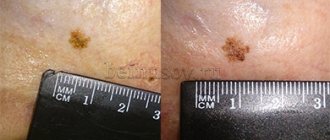
Reasons for the appearance of a halo around a nevus
There are several reasons why a white spot appears around a mole.
- Heredity . If parents have moles on their bodies surrounded by a light spot, then there is a high probability that their children will also experience a similar phenomenon.
- Ultraviolet . When the sun's rays hit the skin, it can cause various changes. A white rim around a mole can also appear under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Some people experience this after sunbathing on the beach or in a solarium.
- Hormonal changes in the body. Changes in hormonal levels caused by various processes occurring in the body are another reason for the formation of a white spot on the skin. This can happen during pregnancy, menopause, in adolescence during puberty, after suffering stress or serious illness, as well as as a result of long-term use of hormonal drugs. Sometimes a severe hormonal imbalance in the body can cause a mole to completely disappear from the skin. However, this does not happen at one moment, but gradually: first a white halo appears around it, which increases in size and absorbs the nevus until it disappears completely.
- Radioactive radiation. If a person has been exposed to radiation, they may develop white spots around the nevus. Since radioactive radiation often leads to the formation of malignant tumors, a light rim around moles may indicate the beginning of this process.
- Mechanical impact. If a mole frequently rubs against clothing or is squeezed by it, white areas may form around it.
- Degeneration of a nevus into a malignant formation. The most dangerous reason for the appearance of a halo around a mole is the beginning of the process of its degeneration into skin cancer. Therefore, it is very important to recognize the threat in time and begin treatment.
Causes of a white spot
The formation of nevi on the human body closely correlates with an increase in the concentration of melanin in cellular structures. Dermatologists agree that the reasons for the development of white spots are the following factors:
- factor of heredity. If mom/dad develops pigmentation during their life, the disorder will recur in children;
- exposure to ultraviolet light. Systematic visits to the solarium or daily sunbathing on the beach contribute to the development of pathology. In such cases, the skin must be protected. Use glasses, sunscreen, large hats and beach umbrellas;
- hormonal dysfunction. The disease is often observed in adolescents and during pregnancy in women. The disease develops during menopause. Severe stress and dangerous diseases negatively affect the condition of the human body;
- dysfunction of the skin.
A white halo around a mole is not always a sign of the development of a malignant tumor. If even slight pigmentation appears, you should consult a professional dermatologist. The specialist will diagnose the body and select the optimal recovery plan. Treatment should be orderly and comprehensive.
Far from the full number of nevi are localized on the human body from the moment of birth. The lion's share of formations is formed in the first 30-60 days. With age, the number of birthmarks increases exponentially (tanning in this case is completely prohibited).
Types of nevi with a white halo
There are several types of birthmarks, surrounded by a light rim.
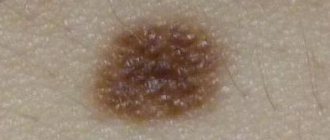
- Nevus of Sutton. It is an ordinary mole, around which there are white areas of skin that have an irregular shape or merge with each other. Such formations often appear in adolescence and can be single or multiple. They do not pose a threat to health and extremely rarely degenerate into a malignant formation.
- Nevus of Setton. This mole looks like a separate pigment spot surrounded by a large light halo. The size of the rim can reach 1 cm in diameter. In some cases, the skin around moles has a white-brown, mottled tint. Such a nevus also does not cause any inconvenience to a person.
- Vitiligo . This is a genetic disease, as a result of which the human body stops producing the pigment melanin. As a result, white spots appear around moles and in general on any areas of the skin. This disease can occur in both children and adults.
READ ALSO: Decorating the Christmas tree
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
The symptoms of the pathology have pronounced characteristics. White spots localized near moles cause a number of unpleasant moments for a person:
- stable itching, provoking scratching of the affected area of the epidermis at a certain point;
- peeling of the epithelial layer in the area of the nevus. Cracks may appear near the hair, on the back, face;
- pigmentation disappears gradually, starting from the middle;
- Sometimes a person experiences sharp pain.
A flat spot is not a cause for concern. The form of the disease informs doctors that the nevus has not transformed into a malignant structure. Examination of the affected area becomes inevitable if the spot changes in shape and color.
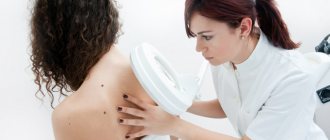
Doctors visually examine patients and collect materials to study histological parameters. Tissue analysis will reveal the exact reasons for the transformation of a nevus into melanoma. An effective technique is dermatoscopy. It is better not to risk it and visit a qualified dermatologist in the clinic.
In babies, a white or pinkish halo often appears around a mole. As a rule, this is associated with hormonal dysfunctions of a fragile body. Infants should be protected from ultraviolet radiation. Systematic consumption of vitamin D and microelements will not hurt.
Are white spots around a mole dangerous?
White patches of skin in themselves do not pose a health threat. But if there are other symptoms indicating the development of a pathological process, then you should immediately show the nevus to a doctor. So, the following signs are cause for concern:
- the shape and size of the nevus changes;
- the edges become uneven;
- cracks, peeling, nodules, and bumps appear on the surface of the mole;
- it is swollen and inflamed;
- pain, burning, itching and other unpleasant sensations are felt;
- blood, pus or exudate is released from the mole;
- the nevus changed color.
If you have one or more symptoms, you should consult a doctor. All these phenomena may indicate malignant degeneration of the birthmark, so it is very important to conduct an examination as early as possible.
Treatment of nevus with a white rim
If you don't like a mole with a white halo, you can get rid of it. To do this, you need to see a dermatologist. To begin with, he will prescribe a special examination for you, which will determine whether the nevus is a benign formation and whether it can be removed.
If everything is in order, you will be asked to choose one of the methods for removing the birthmark. Modern medicine offers several methods:
- electrocoagulation – cauterization of the nevus with electric current;
- cryodestruction – freezing with liquid nitrogen;
- laser method - removal of formation using a laser;
- radio wave method - exposure to high-frequency radio waves;
- surgical method - excision of the mole with a scalpel.
Each of these methods has its pros and cons. The doctor will tell you which one to choose, taking into account your problem.
Preventing the appearance of white spots
To avoid the formation of light areas around the birthmark, you need to follow some recommendations.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun. If you have sensitive skin or a lot of moles on your body, then you should not stay in the open sun for long. Do not go to the beach between 11:00 and 17:00. At this time the sun is most aggressive. The best time for sunbathing is in the morning or late afternoon. Be sure to apply sunscreen to your skin.
- If the mole has already turned white, cover this area of skin with clothing so that it is not exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Depigmented areas burn easily in the sun.
- Try not to injure moles, because any mechanical damage can negatively affect their condition.
Now you know that a white circle around a birthmark is harmless in most cases. But if a mole begins to bother you and cause inconvenience, try not to delay contacting a doctor. It’s better to be on the safe side than to get sick.
Congenital nevi (moles)
Balybina Yulia Gennadievna
Dermatologist
April 24, 2021
Congenital nevi (moles) are considered to be those with which a child is born, or those that appear in the first year of life. They differ from the usual dark spots that appear in all people later, as they are quite active. If the baby has skin lesions, they should be examined by a dermatologist.
The cells of such nevi can be located deep - in the lower third of the reticular layer of the dermis, sometimes in the subcutaneous fat, muscles, and even bones. Or they may have a superficial location. Superficial nevi often have dark shades of brown. This may contribute to the appearance of melanocytic dysplasia (malignancy).
This process occurs due to the influence of internal factors, such as hormonal stimulation, or external ones, for example, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, due to trauma.
The risk of dangerous behavior of congenital nevi directly depends on:
- size
- heredity, cases of melanoma in family history
- skin phototype (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6)
- harmful environmental factors
- hormonal stimulation
- traumatization
For each child with a congenital nevus, management tactics are selected individually by a dermatologist/dermato-oncologist, taking into account all the data.
The size of the education matters most. Therefore, let’s look at the classification by size and the risks within each group:
— Congenital nevus is small. Has a size of less than 15 mm. The risk of developing a malignant process in this group, according to one data, is less than 1%; according to others, from 1 to 4% throughout life. When present, melanoma most often appears after age 20. In childhood, it is characterized by a calm course, so routine observation by a dermatologist is usually sufficient.
— Congenital nevus averages from 15 to 100 mm. Before the onset of hormonal changes in puberty, on average up to 12 years, the risk of malignancy is low. Further, during life, according to various sources, from values less than 1% to 5%.
The tactics for managing such nevi, removal or observation, are determined by the doctor, taking into account the presence or absence of severe somatic diseases, skin characteristics, for example, a tendency to form scars, and aesthetic goals.
In general, I consider it safer to remove it at the age of 7 to 12 years in the absence of contraindications. Contraindications may be, for example, for the use of general anesthesia or in the form of severe skin pathology.
It is also important to consider the location of the nevus. After removal of the nevus, a scar remains; if it is on the face, you need to make a very balanced decision about the operation. On the scalp, if located deeply, removal may leave a hairless area.
— A special place in the classification is occupied by large formations, from 100 to 200 mm, and giant, more than 200 mm formations. They can occupy an entire anatomical region. They have the greatest risk of malignancy compared to those indicated above. The main distinctive feature of large nevi is that against their background, melanoma can form in the first years of a child’s life. The average risk of developing malignant cells during the first 20 years of life is about 5%. Therefore, I consider the main tactic to be removal.
Such nevi are observed when removal is impossible. This may be due to the complexity of the location, or due to excessively large sizes, when there are not enough skin grafting options.
In cases where the nevus is located on the scalp and spine, it is additionally recommended to do an MRI to exclude nerve damage. In some of these cases, neurocutaneous melanosis must be excluded. This pathology is a separate topic.
It must be borne in mind that even in cases where a difficult decision is made to remove large and giant nevi, this will not be a guaranteed fact that melanoma will not appear in other areas.
The main thing parents need to remember:
- If a newborn baby or a baby under one year old has moles, an examination by a dermatologist/dermato-oncologist is mandatory.
- Small congenital nevi should be observed by a specialist until the age of 20 (unless there are reasons to remove them earlier). In cases where the characteristics of the nevus change after 20 years, it may need to be removed.
- Medium congenital nevi are routinely removed between the ages of 7 and 12 years, in the absence of contraindications. Earlier removal may be recommended based on the results of follow-up examinations.
- Large and giant nevi should be removed, if possible, with the participation of a plastic surgeon under general anesthesia. If removal is impossible - observation and inspection once every 3-6 months. When a suspicious area appears, a fragmentary histological examination is performed.
- For skin with congenital nevi, it is necessary to adhere to general measures of protection from ultraviolet radiation: avoid direct sunlight, do not be in the open sun from 11 am to 5 pm, use photoprotection products with SPF 50+ and mechanical protection with clothing and hats.
- Try not to injure moles.
- When prescribing stimulant medications, discuss with a dermatologist the feasibility and safety of taking them, taking into account the presence of a congenital nevus.
Fortunately, large nevi are rare. Moles can be beautiful and even piquant, giving your appearance a special twist. The main thing is to have information about possible risks and keep them under the supervision of a competent specialist. At our center, doctors are ready to provide qualified assistance and answer all your questions.