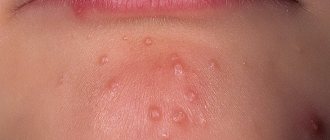
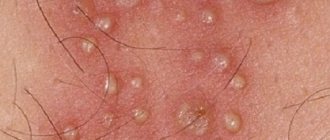
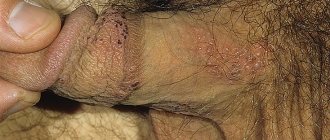
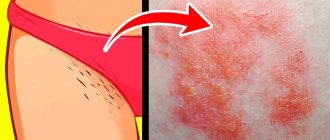
Herpes in the intimate area in men or genital herpes in men is one of the most common clinical types of sexually transmitted herpes infection (STI) and differs from them by the lifelong carriage of the pathogen in the human body.
The causative agent of genital herpes in men in 76% of cases is herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). There are cases of genital herpes caused by HSV type 1, which reflects the increased prevalence of oral-genital contact in various population groups - 24%.
Genital herpes in men is characterized by the appearance of characteristic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes in the urogenital and/or anal area.
Chronic herpetic infection is an immunodeficiency disease with lifelong persistence of the virus in the cells of the nerve ganglia with dysfunction of both the autonomic and central nervous system, characterized by periodic exacerbations with the appearance of clinical signs (“herpetic vesicles”), localized in places that are constant for each patient - “Locus minoris” . Herpetic blisters affect the mucous membranes of the urethra, genitals, anus, skin, and when the process generalizes, the liver, brain and other organs. Rashes in the form of small, tense blisters on an edematous, hyperemic base after an incubation period of 2–4 days are accompanied by a period of increase in local clinical symptoms (tingling, burning) in some cases - general symptoms (malaise, weakness, fever). The lesion, without the addition of a secondary infection, disappears on days 7-9 without a trace.
Genital herpes during pregnancy
Is genital herpes transmitted from mother to fetus in pregnant women?
If primary infection with the virus occurs during pregnancy, especially in the first half, then there is a possibility of the virus entering the fetus with the development of intrauterine infection and impaired fetal development. This is a serious complication of genital herpes, and, fortunately, it is very rare. If the virus was present in a woman’s body before pregnancy, then her immune system, already familiar with the herpes virus, effectively protects the fetus during pregnancy, and infection is possible only during childbirth, and then with the condition that at this moment the disease is in the active phase. Therefore, it is especially important not to miss relapses of genital herpes activity during pregnancy in order to begin treatment on time and prevent transmission of the virus to the child during childbirth.
Causes
Genital herpes is caused by herpes simplex viruses type 1 and 2. Primary infection with herpes simplex viruses type 1 usually occurs in childhood. According to statistics, at 6-7 years of age the incidence rate in children is about 50%. The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets. Moreover, high population density contributes to the rapid spread of infection.
Re-infection occurs through sexual intercourse. There is a high incidence rate among young people (20-30 years old). This is due to early onset of sexual activity, promiscuity, frequent changes of sexual partners, and careless attitude to barrier contraception methods. The source of infection can be not only an ulcer on the mucous membrane, but also skin with microcracks.
Risk factors for genital herpes include:
- infection through personal hygiene items;
- independent transfer of the herpes virus by hands (autoinoculation), for example, from the face to the genital mucosa
- the possibility of infection from a pregnant woman to a child during childbirth, when the child passes through the birth canal;
- transplacental method of infection (through the placenta);
- ascending through the cervical canal into the uterine cavity.
Upon contact with the herpes virus, the immune system reacts by releasing specific antibodies. If the level of immune reactions is sufficient, then there are no clinical manifestations of infection. The causative agent of genital herpes is in a latent state in the nerve ganglia (nodes, places where nerve cells accumulate). If the reactivity of the immune system decreases, the virus becomes more active and manifests itself in rashes and neurological pain.
The immune system can reduce its effectiveness through:
- hypovitaminosis;
- chronic stress;
- hypothermia;
- overheat;
- climate change;
- with ARVI.
Diagnosis of genital herpes
Which doctor should I see for genital herpes?
At the Yauza Clinical Hospital, this disease begins with a clinical examination by a specialized specialist (gynecologist or urologist), and is confirmed by laboratory tests. If necessary, consultation with related specialists (immunologist) is carried out.
What tests should be taken for genital herpes?
Laboratory diagnostics solves 2 problems:
- determine the presence of the herpes simplex virus or contact with it: to do this, study the blood, vaginal discharge, urethra, sperm, urine of the patient for the presence of antibodies to the herpes simplex virus, or particles of the virus itself;
- to prove the “involvement” of these rashes with genital herpes: material taken directly from blisters or ulcers is examined.
Also, to select effective therapy, it is necessary to accurately determine the type of pathogen - this question is answered by polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Make an appointment
Treatment of genital herpes
How to treat genital herpes? Unfortunately, there is currently no way to completely destroy the virus in the body and cure genital herpes once and for all. However, specialists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital have developed a treatment regimen that keeps the pathogen in an inactive state and significantly reduces the likelihood of developing a relapse of genital herpes in men and women.
Goals of therapy:
- Removal of local manifestations - rash, painful ulcers, itching.
- Speedy relief of relapse.
- Strengthening the immune system, maintaining long-term stable remission.
The complex of treatment measures includes:
- Antiviral drugs – oral and topical, which are selected individually. One of the most effective in treating a genital virus is acyclovir (tablets, injections, cream, ointment).
- Prescription of immunomodulators, immunostimulants.
- Patients with rare exacerbations are treated with episodic therapy. For those whose disease is severe (frequent relapses due to the individual characteristics of the immune system - its low activity against the herpes virus), a long course of pharmacotherapy is indicated - systemic therapy.
Despite the fact that there are no methods for completely curing herpes yet, the doctor will select medications that will reduce the frequency of relapses. This way, you can live a full life without regular exacerbations of the disease. Make an appointment with a specialist to avoid complications and relapses.
Symptoms and signs
Human herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 can equally cause primary and secondary infections. Typically, the course of the disease depends on the state of the person’s immune system and the genetic characteristics of the virus. Primary infection with HSV-1 and HSV-2 is characterized by general symptoms and a high percentage of complications, while recurrent herpes, on the contrary, has less pronounced symptoms and periodic remissions. Frequent exacerbations of the process are usually characteristic of patients with immunodeficiencies. HSV-1 is milder than HSV-2.
Treatment of genital herpes during pregnancy
First of all, it should be noted that there is a group of antiviral drugs that can be used with complete safety for the developing fetus.
Indications for treatment:
- primary infection during pregnancy,
- relapses of the disease and
- prevention of relapses before childbirth.
Taking into account the possibility of an asymptomatic course of the disease during a relapse, it is necessary to conduct periodic examinations of the woman throughout pregnancy and, especially in the last weeks before childbirth.
By contacting the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, you are guaranteed to receive qualified advice from a specialized specialist, an accurate diagnosis of your condition, effective treatment of the identified disease, and prevention of exacerbations of genital herpes and its complications. Take care of your health - make an appointment with a gynecologist or urologist right now!
Kinds
Doctors distinguish between primary and secondary types of the disease.
Primary is the one that is diagnosed for the first time. It is characterized by a bright clinical picture and a rapid course.
Secondary is one that is diagnosed more than once; these are relapses of chronic pathology. The frequency of resumption of symptoms depends on the person’s immunity; symptoms are often blurred and short-lived.
Secondary genital herpes is distinguished by the frequency of exacerbations:
- Mild form – no more than 3 relapses in 12 months;
- Moderate – up to 6 exacerbations in 12 months;
- Severe form – more than 6 relapses per year.
Doctors also classify the disease according to the specific symptoms.
How to prevent getting genital herpes
People with outbreaks of genital herpes are highly contagious. During the active phase of the disease, any sexual contact should be avoided, especially if there are ulcers. Using a condom does not prevent the spread of the disease because not all sores are covered by a condom.
Although the likelihood of infection is greatest when ulcers are present, people who have had HS can always be contagious to some extent, even if they have received medical treatment. The virus can be activated and transmitted to a sexual partner even when the skin looks completely normal.
For this reason, safe sex practices (using a condom) should be practiced between outbreaks to reduce the risk of spreading the disease to a sexual partner. There is no vaccine to prevent genital herpes infection.
Routes of infection
Although the disease is most often classified as a sexually transmitted disease, it can also be contracted through household objects: by sharing utensils, towels and linen, as well as by kissing. The greatest chance of becoming infected with genital herpes is during its exacerbation. In this case, any contact with the patient may be dangerous and even such a means of protection as a condom, alas, may be powerless against the virus.
FACT:
The highest incidence of genital herpes occurs in people aged 20 to 30 years.
Complications of GG
People with genital herpes face an increased risk of contracting and passing on other STDs. This is because the ulceration that occurs as a result of a herpes infection makes the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals more vulnerable to sexually transmitted infections. Patients with symptomatic HH face a 2-4 times higher risk of acquiring and transmitting HIV infection.
Complications are rare:
- In some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver and eyes, even to the lining around the brain, causing meningitis.
- 1% of patients with primary HH develop autonomic dysfunction with urinary retention, erectile dysfunction, constipation, and sensory loss. Sometimes (intermittent) catheterization is necessary over several weeks.
- Mild meningitis is relatively common in primary herpes (13-20%). Herpetic encephalitis occurs less frequently and has a mortality rate of about 70%.
- Neonatal herpes simplex may develop after vaginal delivery and may be accompanied by local infection (skin, eyes, or mouth), disseminated manifestation (visceral organs), or central manifestation (CNS).
Symptoms may be especially severe in people with weakened immune systems due to existing HIV infection or immunodeficiency. An infection that affects the eyes can lead to blindness. This occurs mainly in people with weak immune systems who have had the virus for a long time. With a weak immune system, herpes increases the risk of bacterial infections, which can lead to further complications.
Another possible complication affects pregnant women. During childbirth, women can pass the virus to their newborn. Women at risk for STIs often get tested in the early weeks of pregnancy to prevent complications. A pregnant woman with symptomatic genital herpes is at risk of miscarriage or premature birth.
The infection can be transmitted to the fetus, and the baby may develop neonatal herpes. The risk of complications is especially high if a woman contracts the infection in the last trimester of pregnancy. If she has active genital ulcers near the time of delivery, a cesarean section is usually recommended to avoid exposing the newborn to the virus.
Make an appointment
How does the disease manifest itself?
The incubation period of the genital virus (herpes simplex virus) ranges from 3 to 7 days. The first manifestations of the virus are the formation of blisters on the glans penis and the inner layer of the foreskin, less often on the scrotum and perineum. When bubbles break through, erosions are formed in their place, tending to merge. In severe cases, the lesions occupy a large area. The same phenomena occur on the mucous membrane of the urethra. In this case, patients experience pain and burning in the urethra when emptying the bladder and discharge from the urethra. At the same time, a patient with genital herpes may have an increase in body temperature and enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes.
Forecast and prevention of genital herpes
As a preventative measure to prevent primary infection of HS, it is recommended to use condoms during sex, especially during casual sexual intercourse. But you should know that the use of protective contraception does not reduce the risk of infection through microcracks and other damage in areas of the skin not covered by a condom. If you suspect the penetration of a virus, you can treat the skin with local antiseptic preparations.
GG is characterized by relapses with decreased immunity. To prevent the disease, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- take vitamins;
- get enough rest and eat right;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- the area of blisters and ulcers should be dry and clean to avoid infection;
- If symptoms appear, consult a doctor promptly.
People infected with this virus should try to avoid direct contact with others to protect them from infection. Avoid scratching or touching herpes lesions as this may spread the infection to other areas of the skin.
You can see prices for services
Vaccination
An antiherpetic vaccine helps get rid of frequent relapses (Vitagerpavak, Gerpovax are registered in the Russian Federation).
Figure 3 - Gerpovax
Injections are carried out only during the period of remission according to the following scheme:
- 1The first 5 doses intradermally 1 time every 3-7 days.
- 2A repeat course is possible after 7-10 days.
- 3After 6 months, revaccination according to a similar scheme of 1-2 courses.
Non-drug treatment may include plasmapheresis. With its help, detoxification and immunocorrection are carried out. The method is approved for use in pregnant women.