Types of fungal infections
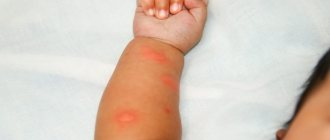
Fungal infections can appear at any age. Infants most often encounter this problem - redness and peeling appear. The symptoms are similar to those of an allergic reaction, so therapy is often carried out, which is ineffective.
The clinical picture depends on the type of disease:
- Because Candida thrives in moist and warm environments, it multiplies in the diaper area of babies. This manifests as intense, large-scale redness with scaly edges.
- Oral thrush is characterized by the appearance of a tight, gray-whitish film in the cheeks and throat. This type of disease is also caused by Candida and is most common among infants.
- Ringworm is accompanied by severe itching, the appearance of round bald spots and blackheads. There is excessive hair fragility, which results in bald spots.
- Vaginal (genital) candidiasis also occurs in childhood, although much less frequently. The victims may be babies in the first weeks of life, whose mother gave them Candida at birth. Babies still have their mother's female sex hormones (estrogens) in their bodies. They appear to inhibit the regenerative ability of the mucous membranes, which in turn contributes to the progression of the disease.
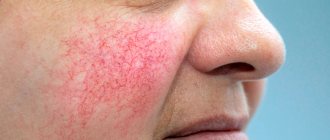
Pet-borne dermatophytes should not be underestimated. The head and torso are affected. The main carriers are cats, as well as guinea pigs and rabbits. Accompanied by severe itching, redness and excessive dryness.
Table - Classification of mycosis pathogens
| Pathogen name | Localization area | How it manifests itself |
| Tinea capitis or Microsporum (microsporia or “ringworm”) | Scalp | Ring-shaped, sharply limited red spots appear, in which the hair either breaks or falls out. Sometimes the scalp starts to ooze due to weeping. Small red pustules may appear. |
| Tinea corporis (dermatophytosis) | Torso and upper limbs | It appears as pale red areas with characteristic peeling. In addition, there is unbearable itching. Therefore, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible to avoid spreading the fungus to other parts of the child’s body through scratching. |
| Tinea pedis (onychomycosis) | Nail plates | The filamentous fungus damages the toes or nails and gives them a characteristic yellowish coloration. The plates with onychomycosis become thick and brittle, with a “loose” structure. With the exception of visual changes, symptoms such as itching do not appear, so onychomycosis is usually diagnosed in the later stages of progression. |
Reasons for the development of mycosis
Predisposing factors include taking antibiotics, poor hygiene when visiting swimming pools, increased sweating and/or poor immune system protection. In most cases, pathological disorders in the body occur due to a combination of reasons.
Varieties of opportunistic microorganisms that are causative agents of the disease:
- yeast (Candida albicans causes thrush);
- dermatophytes (provokes herpes zoster);
- mold (causative agent of aspergillosis and respiratory tract problems).
The most common is Candida albicans - it is part of the natural microflora, present in 50% of the population. It does not cause problems until it begins to multiply uncontrollably under the influence of certain factors. Most often, Candida passes from mother to baby during childbirth and breastfeeding.
Material and methods
The material was selected at a consultation with patients at the Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases with a course in cosmetology at the Medical Institute for Advanced Medical Studies (MIUV). For examination, patients were sent to the Allergy Center named after. prof. HELL. Ado. The severity of AD was assessed using the international SCORAD (Scoring atopic dermatitis) scale. The diagnosis of superficial candidiasis was made in accordance with the classification of A.M. Arievich, Z.G. Stepanishcheva (1965), and SO - A.Yu. Sergeeva, Yu.V. Sergeeva (2001). The effectiveness of AD therapy was assessed using the following clinical criteria: recovery, significant improvement, improvement, no effect. Recovery was defined as complete resolution of AD lesions. A significant improvement was considered to be persistent positive dynamics of the process, which was characterized by a 4-fold decrease in SCORAD. Improvement was understood as a slow positive dynamics of the process with a 2-fold decrease in SCORAD. In the chronic course of AD, the transformation of the continuous course of the disease into a recurrent one, as well as the lengthening of the inter-relapse period, were taken into account.
Determination of specific IgM and IgG to C. albicans
carried out by solid-phase indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) on a Multiskan Ascent spectrophotometer (Thermo Electron);
Enzyme immunoassay test systems produced by Vector-Best CJSC (Novosibirsk) were used. Determination of total IgE in blood serum was carried out by ELISA using Dia-plus test systems of NPO Biotechnology on a UniCap-100 analyzer (Phadia, Sweden), the result was expressed in IU/ml. Determination of specific IgE to lipophilic yeasts of the genus Malassezia
spp
.
carried out on a UniCap-100 device (Phadia, Sweden) using the supplied standard reagents.
Determination of the cell wall antigen-mannan of yeast-like fungi Candida
spp. carried out by ELISA using standard Candida-Ag kits (Bio-Rad, France).
The bacteriological method was used to isolate and identify opportunistic mycotic microflora. For sowing material on Malassezia
spp
.
scales of the stratum corneum of the epidermis were scraped off from an area of 1 cm2.
The material was collected with a cotton swab moistened with sterile olive oil. The material was subcultured three times on Notman-agar (LNA) selective medium. The inoculated dishes were incubated in a thermostat at 32°C for 2 weeks. Species identification of representatives of the genus Malassezia
spp.
were carried out according to morphological (colony morphology, cell size and shape), physiological (growth at 37 and 40 °C) and chemotaxonomic (catalase reaction, utilization of Tween 20, Tween 40, Tween 60, Tween 80) characteristics. The results were assessed in the number of CFU/cm2. Definition of Candida
spp
.
from skin and CO was carried out by inoculating the material on sugar broth.
Symptoms of fungal infections
The nature and severity of pathological changes depend on the virulence (pathogenicity) and type of pathogen, as well as on the reactivity of the body, the area of localization and the area of the lesion. Signs of the disease cannot be identified independently. When primary symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor rather than begin self-medication.
The main symptoms of fungus in children:
- Body and scalp. Accompanied by redness, peeling and baldness (hair is broken off at a height of 4-5 mm), as well as the appearance of grayish-white scales.
- Feet, hands and interdigital space. Toenail fungus in children is characterized by excessive dryness, redness, moderate weeping and peeling. There are also bubbles and cracks that itch unbearably.
- Mucous membranes of the oral cavity and genitals. Thrush or candidiasis is accompanied by the appearance of a white, cheesy coating. Extensive superficial ulcerations and vesicular rashes are accompanied by burning and itching.
None of the known fungal diseases develops lasting immunity, so repeated infections are not excluded. That is why parents should know what fungus looks like in children and consult a doctor when the first symptoms appear.
Prevention of dermatitis in children
To prevent dermatitis, it is important to follow the rules of hygiene and nutrition for the child, to give preference to clothing made from natural fabrics, hypoallergenic household products and cosmetics. To build strong immunity, children benefit from air baths and hardening procedures. For proper skin care, it is recommended to use cosmetics created specifically for children - preferably without parabens, phthalates, with a hypoallergenic composition and labeled 0+ . Correctly selected products strengthen the baby’s skin barrier, care for the skin without interfering with its natural development.
_____________________________________________ 1 - Clinical study 1035F4 2 - Clinical study 1016F10.01.02 3 - Sunflower oil distillate and inflammation. June 2010. 4 — Clinical study of Cream for “milk crusts” 1042F3.01.24
Diagnosis of mycosis
To make a diagnosis, an examination is carried out by a dermatologist or mycologist. The first step is a microscopic examination of the scales of the epidermis, hair and nails.
Laboratory testing allows you to determine the presence of spores or hyphae, which is necessary to clarify the type of pathogen and make an accurate diagnosis. The dermatologist also performs an examination under a Wood's lamp. This approach allows us to determine the type of disease and differentiate it from dermatitis.
Treatment of fungal infections
Thrush is treated with antifungal agents that are applied to the skin or mucous membranes. Systemic therapy is also prescribed. If you treat only the symptoms, a relapse will soon occur. The cause of the disease should be combated by strengthening the body’s protective functions.
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is necessary only in case of severe disease and in the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Treatment of fungal infections in children has the following approach:
- prescribing monotherapy or a combination of systemic and external antimycotic agents;
- the use of immunostimulants, glucocorticoids and antihistamines.
To increase the effectiveness of drug therapy, multivitamin complexes and physiotherapeutic procedures (DMV, therapy, darsonvalization, magnetic therapy, medicinal electrophoresis) are prescribed. Treatment should be carried out 2-3 times a day. The hair is shaved and the crusts are carefully removed.
When localized on the feet and hands, it is recommended to use special pastes, creams and ointments based on clotrimazole, neftifine or terbinafine. If a bacterial infection occurs, it becomes necessary to use antibiotics. For protracted and severe fungus of the nails, face and body skin, and hair in a child, antimycotic drugs containing fluconazole, itraconazole or griseofulvin are indicated.
For onychomycosis, it is necessary to use the drug until the nail grows completely. If drug treatment is ineffective, then surgical removal of the nail plates is performed.
To permanently defeat an infectious disease, you need to use the right medications and adhere to a certain diet. Self-medication in this case can lead to the development of serious complications.
Foods that should be excluded from the diet:
- Sugar, in any variety - honey, cane sugar, dextrose, fruit, malt and beet sugar, maple syrup, etc.
- Refined carbohydrates - white bread, buns, cakes or cookies, light noodles, white rice, etc.
- Products containing yeast.
When treating fungal infections in children, it is recommended to keep the affected area dry by frequently changing underwear or diapers. After showering and bathing, it is advisable to pat your skin well with a soft terry towel.
Possible complications
Complications of atopic dermatitis in children:
- Asthma and allergic rhinitis (hay fever). Sometimes eczema precedes these diseases. More than half of young children with atopic dermatitis develop asthma and allergic rhinitis by age 13.
- Chronic itching and flaking. This disorder can cause the affected area to change color and become thicker.
- Skin infections. Infection increases the risk of contracting bacteria and viruses, such as the herpes simplex virus.
- Allergic contact dermatitis. This disease often occurs in patients with atopic dermatitis.
- Sleep problems. The characteristic severe itching can lead to insomnia.
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis
A test for general and specific Ig E is prescribed to determine the cause of skin inflammation. The doctor makes the diagnosis by examining the affected areas and taking a medical history. The specialist may also use patch tests or other tests to rule out other skin conditions.
If parents suspect that a certain food was the cause of a rash on the child’s body, then they need to inform the doctor about this and ask about the possibility of identifying potential food allergens. In this case, a diet is prescribed for treatment.