Feline lichen in humans requires immediate treatment, which in turn proceeds with maximum complexity.
Ringworm is a contagious disease that is transmitted from an infected organism to a healthy one. Pathology manifests itself in the form of small red spots with pronounced boundaries. Most often, stray dogs or cats become carriers. People who pet a sick animal have a very high risk of infection.
Ringworm can be transmitted from cat to person. When the infection came from an animal, it is microsporia; if from an unhealthy person, it is trichophytosis.
Mechanism of disease development
Ringworm in humans and cats is caused mainly by the fungus Microsporum canis, which is similar in structure to mold. Once on the skin of a person or animal, the fungal spore germinates like a seed. Special substances on the surface of the spore allow it to attach to the body, after which germ tubes emerge from it within 4–6 hours, penetrating into the upper layers of the skin.
The threads (hyphae) of the fungus grow and grow, receiving nutrients from the surrounding tissues and developing deeper and deeper layers, spreading both in length and width, and deep into the tissues. They affect the surface of the skin, hair and hair follicles. After a week, they themselves are ready to reproduce.
What is lichen
The microflora of the skin of any cat is an open system characterized by the presence of three types of microorganisms:
- resident - forming permanent and long-living colonies;
- temporary - settling on the surface of the skin, but capable of penetrating into any wounds, causing them to become infected;
- nomads - pathogenic organisms that penetrate skin barriers.
The composition of a stable microflora in healthy cats is constant and capable of preventing the appearance of colonies of pathogenic bacteria and fungi, while failures of the immune system and disturbances in the microflora cause dermatomycosis, or lichen. A disease such as lichen can cause active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, which are present in small quantities as part of the normal microflora.
How can you get infected?
Most often, children become infected with cat lichen. If the disease is not recognized in a timely manner and treatment is not started, then a rapid increase in spots on the skin will begin. They begin to become covered with dense gray scales and become very itchy. The rapid spread of fungus over a child’s skin is due to the fact that children scratch the spots, spreading the spores further throughout the skin. It happens that lichen that starts with one small spot quickly spreads throughout the skin. The diameter of cat lichen can be ten centimeters or even more.
Spots that are located nearby can merge into one large lesion and seriously complicate treatment. There is a type of cat lichen that leads to inflammation of the skin and even suppuration. In this case, there may be an increase in temperature and enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck. One of the most difficult cases of infection with cat lichen is the so-called scab. Hence the word - lousy. This type of disease is very difficult to treat.
You can become infected with cat lichen in a number of ways:
- From contact with a sick cat, fungal spores are transferred to humans and other animals.
- From a cat that appears healthy in appearance and shows no signs of illness. This is due to the fact that she has good immunity and is only a carrier of the disease.
- From a pet that was never allowed outside. The reason for this is that owners can bring fungal spores into the house on their shoes. Such spores are distinguished by their tenacity - they can be active for up to two years.
- From contact with soil, sand and grass containing lichen spores.
No matter how tenacious the spores are, they are easily washed off with soap and water. Therefore, it is necessary to thoroughly wash your hands not only after contact with an animal, but also always upon coming home from the street. Such a hygienic measure reduces the threat of contracting feline lichen to almost zero.
When the fungus develops, bald patches form on the scalp, hence the name ringworm.
Is lichen transmitted from cats to humans?
Cat lichen is dangerous for humans, as it is easily transmitted from pets to owners. You can become infected through direct contact with a cat or through various objects. The infection can be brought by a domestic cat after a walk or by its owner on shoes or clothes. Often, lichen infection occurs after contact with stray animals.
The causative agent of feline lichen is very dangerous because it is resistant to various chemicals and can also remain active in the environment for more than a year. Therefore, the cat and its owner are constantly at risk.
People from this group are most likely to be infected with shingles:
- child under 14 years of age;
- an elderly person over 60 years of age;
- women during pregnancy and lactation;
- people with reduced immunity.
Adults can also get sick, but the lichen will have a hidden course. Their immunity will quickly cope with the infectious agent.
Feline lichen in children is more complicated than in adults. According to statistics, children aged 3 to 8 years most often suffer from the disease. Their infection has an acute course, manifests itself in severe inflammation of the skin, and suppuration often forms. This is due to the fact that children have thinner and more sensitive skin, and their immunity is not yet fully developed.
The likelihood of contracting feline ringworm increases in the following cases:
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- colds or chronic diseases in which the immune system is weakened;
- frequent contact with animals;
- the presence of wounds, scratches, abrasions, microcracks on the skin;
- increased humidity in the room;
- frequent stress;
- long course of antibiotics;
- a large number of allergens in the room.
These factors increase the risk of human infection with lichen, since the fungus enters a favorable environment where it actively develops.
Symptoms
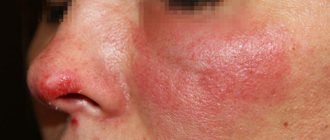
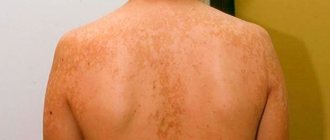
What does feline lichen look like in humans (see photo? The incubation period lasts from 5 days to 2 months, in most cases, symptoms of the disease appear on days 6–7. Microsporia has various clinical signs depending on the location. When smooth skin is affected, it first appears a pink round spot that gradually increases in size. A hyperemic rim of small papules forms along its edge, the skin peels off in the center. New rims may form around the primary plaque, forming a “ring within a ring”, and the merging of several fragments is often observed. The person is bothered by minor itching .
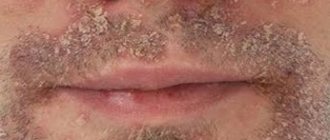
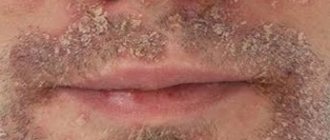
Cat lichen on the head looks like a bald spot with a flaky center and redness of the skin. The lesions have an irregular shape, unclear boundaries, and can increase in size, affecting a large area and causing hair breakage near the skin at a height of 1–2 mm. The remaining hairs are covered with whitish scales and form stubs with a dark center.
Ringworm in a child during adolescence can occur in a chronic form; girls are more often affected. The formation of microsporia in boys is characterized by a milder course; plaques can resolve on their own when the composition of sebum changes against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
In chronic disease, the occipital, temporal region of the scalp, skin of the buttocks, joints, shoulder girdle, nail plates, palms and feet are affected. On the smooth dermis, plaques look like bluish spots with slight peeling; onychomycosis causes thickening, destruction of nails, changes in their color, lamination, the appearance of spots and tubercles. With severe immunodeficiency, ulcers and abscesses can form.
Pathogens of dermatophytosis
The development of lichen is provoked by filamentous fungi. Depending on the main reservoir, they are divided into anthropophilic, zoophilic, and geophilic. The first can spread from person to person, the second can spread from animals to people, and the third lives in the soil.
Most often, ringworm in cats is caused by a fungus called Microsporumcanis (Latin for canine microsporia). According to statistics, it provokes the development of lichen in 92% of cats and 65% of dogs. According to scientists, other representatives of dermatophytes are transmitted to pets from the rodents they hunt.
Infection with lichen through soil occurs quite rarely.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the pathology, you should consult a dermatologist. He conducts an initial examination of the lesions.
To confirm the assumption of ringworm, the following studies are carried out:
- Inspection using a Wood's lamp emitting ultraviolet light. On the head, in areas affected by the fungus, the hair has a slight greenish tint. This method is good because it is possible to determine the disease, even if only one hair is infected.
- The diagnosis can be clarified using bacteriological examination. For scraping, hair scales and stumps are taken, which are examined under a microscope for the presence of microorganisms in them. Fungal spores and mycelium are usually found in the upper layers of the skin.
The areas affected by ringworm glow under a fluorescent lamp
It is also necessary to differentiate from skin pathologies with similar external signs:
- when the disease is localized on the scalp, differentiation is made with alopecia;
- the cutaneous location of ringworm should be distinguished from eczema and psoriasis;
- the chronic form is differentiated from candidiasis, acne, psoriasis and eczema of the nails, as well as lichen planus are excluded.
Possible complications
After ringworm, complications can occur, both mild and serious. It all depends on the pathogen and the degree of neglect of the skin lesion, on the effectiveness of therapeutic measures. If treatment is not started immediately, deep damage to the hair follicles by the fungus may occur, then there is a possibility that hair may no longer appear in these places.
This does not harm health, but it brings significant discomfort to a person in an aesthetic sense. Therefore, if you suspect lichen, start proper treatment immediately and do not expect the disease to go away on its own.
Taking medications for ringworm on your own can only cause harm and lead to serious complications.
Treatment
For many, it is very important to know whether a disease is transmitted to humans from an animal or not. Also, when infected, how to treat feline lichen is of great importance. At the initial signs of pathology, you should immediately contact a dermatologist to determine the diagnosis. And never self-medicate. The use of folk recipes and ineffective drugs will lead to the proliferation of lichen throughout the body, then the therapy will be very long.
A single examination is not enough for a doctor to make a diagnosis. Pathogenic bacteria quickly mutate, and this will require testing to determine the type of fungal infection and the severity of its development. During the period of treatment for deprivation, it is advisable not to contact family and friends. At the same time, treat the cat responsible for the infection.
The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment for cat lichen, which involves the use of medications:
- Antifungal drugs for external use in the form of ointment, gel (Ketonazole, Clotrimazole, Lamisil).
- Antifungal drugs for oral administration (Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Terbinafine) - for microsporia on the head.
- Immunomodulators (Amiksin, Likopid, Tamerit, etc.).
- Solutions containing iodine (Iodopirone, Iodinol, Degmicide).
Before starting therapeutic measures, you should cut off the hair from the damaged area of the head so that the fungus does not spread to a healthy area. This must be done every week.
Also, for lichen, vitamins are prescribed in parallel to strengthen the immune system. In addition to medications, you must:
- Follow a diet - do not eat fried, salty, spicy foods.
- Avoid bathing procedures and rubbing the skin with a washcloth.
- You can only wash your hair with antifungal shampoos (Nizoral).
- Regularly treat clothing and personal items with disinfectants.
For a speedy recovery, you should strictly follow all the specialist’s instructions, take medications in the prescribed dosage, treat affected areas in a timely manner, and eat healthy.
Folk remedies
In addition to drug treatment prescribed by a doctor, folk remedies are sometimes used:
- A mixture of iodine and vodka in a 1:1 ratio has an excellent effect. This solution is safe for both exposed skin and the scalp, but it fights fungus very well.
- A product made from birch tar and fish oil, taken in equal proportions, destroys stripping stains very well. It is rubbed into the affected areas 2 times a day.
- It is recommended to use tar soap for treatment, and the darker it is, the more healing properties it has. It is used instead of the usual one for hygiene procedures. You can rub a slightly moistened piece onto the stain and leave for 5-10 minutes, then rinse well with running water.
- Apple cider vinegar is very useful in the treatment of lichen. A small piece of gauze is moistened with it and this compress is applied to the areas of infection 5-6 times a day for 10-15 minutes.
- A compress of honey with grated beets is also effective - the mixture is applied to the affected area, covered with a film on top and left for several hours.
Prevention
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Therefore, we advise you to follow simple rules so as not to become infected with diarrhea:
- do not touch stray animals with bare hands;
- if pets have contact with yard animals, regularly bring them to the veterinary clinic for examination;
- wash your hands thoroughly after going outside;
- If you suspect a lichen disease, contact a dermatovenerologist in a timely manner.
Take care of your health and consult a doctor promptly if you have any suspicious symptoms.
Ringworm in humans Pityriasis versicolor Lichen planus Solar lichen Herpes zoster Pink lichen of Zhiber
How to recognize lichen in a pet
The main symptom of lichen is damage to the skin. Typical manifestations are:
- the appearance of spots on the body. With a multi-colored form, pigmentation can be pale pink, brown, yellow, with ringworm - the skin is reddened, with Zhiber's lichen - pink spots;
- increased fat content of wool, deterioration of its quality;
- focal hair loss. With the cutting form, there is a large number of broken hairs around the area;
- the appearance of scales on reddened and bald areas;
- deterioration of the claws, their deformation.
Against the background of such symptoms, the cat usually becomes restless, trying to constantly scratch the affected area - the skin damaged by the fungus itches. A depressed furry friend may be accompanied by a refusal to eat.
It is more difficult to notice lichen in furry cats, but upon careful examination it is not difficult to see the problem
It is worth considering that in cats with long hair, it is not always possible to notice the affected areas early, since baldness does not occur immediately, and long hairs can cover the areas suffering from lichen. In short-haired breeds, lesions become noticeable faster. It is not difficult to recognize lichen in a timely manner; to do this, you need to regularly examine your pet, sorting through the fur and assessing the condition of the skin.
If you find suspicious changes on the skin, immediately contact a veterinary clinic. Self-medication in such a situation is unacceptable, since only a doctor can accurately determine the type of lichen or differentiate another disease from it based on the results of laboratory tests.