- Viral skin diseases: causes, classification
- Herpes
- Shingles (herpes zoster)
| |
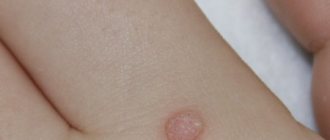
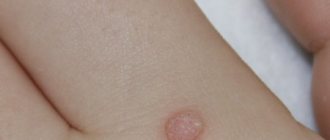
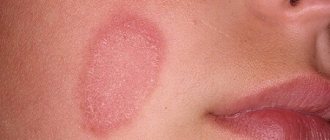
Genital warts are soft, flesh-colored, fleshy warts ranging in size from a pinhead to cauliflower-shaped growths that affect the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals, perianal area and mouth.
Mostly young people who are sexually active suffer from genital warts.
Sources of infection
Condylomas develop under the influence of the human papillomavirus. Infection with genital warts occurs through contact, usually through sexual contact. Moreover, as a result, at least 90% of sexual partners become infected from each other. Infection of newborns occurs during childbirth when passing through the birth canal of a sick mother, which can cause laryngeal papillomatosis in the child.
In various countries, genital warts are registered in 3 to 28% of patients. It should be noted that in many people the disease occurs latently. This means that the virus is in the active stage only periodically, when rashes appear, and the rest of the time the infection remains in a latent state. There is no doubt that the maximum contagiousness (possibility of infection) occurs precisely during periods of clinical manifestations of the disease.
If you like extreme sports, you don’t have to delete it!
Even if genital warts do not cause discomfort, doctors unanimously recommend removing them to avoid dangerous complications and unpleasant consequences.
In addition to further growth, neglected genital warts can pose the following threat:
- Suppuration
- in case of infection, inflammation and suppuration of the affected area are guaranteed. - Mechanical damage
- rupture of condyloma leads to the formation of painful, long-term bleeding ulcers.
- Decreased immunity
— the uncontrolled spread of the virus in the body is accompanied by severe immunity disorders, which can become a prerequisite for the development of dangerous concomitant diseases.
- Risk of cancer
— confirmed cases of malignant degeneration of genital warts have been recorded (with prolonged absence of treatment).
Localization of genital warts
• Head of the penis. • Inner layer of the foreskin. • Penile frenulum. • Skin of the scrotum and shaft of the penis. • Vagina. • Cervix. • External opening of the urethra. • Perineal skin. • Perianal area. • Rectum. • Oral cavity.
In men, genital warts most often occur on the glans penis, crown of the glans, frenulum of the foreskin and inner layer of the foreskin.
In women, the frenulum of the labia, the labia majora and minora, the clitoris, the external opening of the urethra, the vestibule of the vagina, the hymen, the vagina and the cervix are affected.
In both men and women, genital warts can occur around the anus. This localization of rashes is usually not associated with anal sexual intercourse. The fact is that the human papillomavirus does not affect a limited area, but large areas of skin (as a rule, this is the entire skin of the genital organs, the groin area, the perineum, the skin around the anus).
You should know that even with proper treatment, genital warts often recur, which is due to the persistence of the virus in seemingly healthy skin at the site of the rash. And relapse is not associated with re-infection from a sexual partner, but with reactivation of the virus. The danger of the disease lies in the transformation of condylomas into malignant neoplasms, especially if they are located in the cervical area.
Intimate condylomas
Having penetrated the body, human papillomaviruses penetrate the basal layer of the epithelium, especially in the zone of transition of stratified squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium. In a cell, HPV can exist in two forms - outside the cell’s chromosomes or integrated into the genome. Regardless of its location in the cell, the virus will be detected when the smear is tested for PCR. Being in a cell outside the chromosomes, the virus can either not cause clinical changes (latent, hidden course), or lead to increased reproduction of unchanged (!) cells and clinically manifest in the form of warts or papillomas, for example, in the same intimate places.
Another variant of virus behavior is integration into the cell genome. In this case, it either leads to the development of neoplasia (grade 1-3 dysplasia), which ultimately becomes the cause of the development of carcinoma (malignant process - invasive cancer).
Hidden form
A less common variant of the clinical course of intimate condylomas in women and girls. Latent course of human papillomavirus infection without any changes in the skin or other manifestations, i.e. in this case, visible growths of genital warts in the intimate area or any other area of the body are not always observed. At the same time, the virus behaves “autonomously”, without interfering with the life activity of healthy human cells (there are types of papillomaviruses that do not manifest themselves in the human body throughout his entire life).
Active form
In this form, the body reacts to its presence in the cells and makes attempts to “limit” the further spread of the papillomavirus. This is achieved due to the compensatory proliferation of cells in the basal layer of the skin, resulting in the creation of a kind of “sarcophagus” of cells. As you probably guessed, this formation is called a “genital wart” or “intimate condyloma.” In this case, the virus integrates with the genome of human cells, as a result of which they are modified, which leads to dysplasia of the affected tissue area, or even cancer (the most common location of this process is the cervix, provoked by HPV types 16 and 18). A woman can be infected with several types of HPV at the same time.
As a rule, from the moment of infection to the appearance of papilloma (whether it is a wart or genital wart in the intimate area) time passes from several weeks to 9-10 months, and until the appearance of cervical or rectal cancer - from 5 to 15 years, depending on the type of HPV , its concentration (viral load) and, of course, the state of the human immune system. The relevance of condylomas in women is also due to the fact that highly oncogenic types of the virus increase the risk of developing precancerous diseases of the vulva and vagina by 60 times. Removal of condylomas in a clinic by a gynecologist (not self-medication at home!) is the main way to prevent this complication!
Questions - answers
1. WHERE CONDYLOMA GROWS. In women, they appear most often on the external genitalia in the area of the labia minora, less often on the labia majora, often in the vagina, on the cervix, in the urethra, perineum and near the anus. They are much less common on the clitoris, mouth, throat and anal canal. In masturbating girls or virgins who practice sexual games “without penetration” into the vagina, a gynecological examination can often reveal papillomatosis of the vestibule and hymen. See photos of condylomas in women.
2. CAN CONDYLOMAS GO AWAY BY THEMSELVES AND DISAPPEAR? At a young age, the immune system works very well, there are no chronic diseases, so condyloma in an intimate place can either suddenly appear or suddenly disappear. Especially if it is caused by non-oncogenic types of HPV and in a low titer (see quantitative analysis for condylomas in the table below).
3. WHEN ARE INTIMATE CONDYLOMAS CONtagious? If HPV enters a healthy body with good immunity, it may not appear clinically for some time. Sometimes this period lasts months and years (the incubation period can last from several weeks to 2-3 years). If the HPV that enters the human body is not an oncogenic type, it does not pose any threat to the carrier itself and is not transmitted to others. But as soon as an exacerbation begins, and genital warts or papillomas grow in the intimate area or on the skin, it begins to be transmitted to the contactee upon any contact.
4. CONDYLOMAS WITHOUT HPV - DOES IT HAPPEN? Are genital warts possible without HPV? In women and men, these formations are a consequence of the human papillomavirus entering the body. However, when asking questions to a gynecologist or on medical forums, many people discuss a negative HPV test, but there are papillomas or condylomas. Let’s clarify this situation and give a few reasons why this could be:
- Violation of the rules for collecting material for analysis;
- The NGE laboratory conducts this range of research;
- Failures in the technological process of performing the analysis;
- More than 100 types of HPV are known to medicine, and many of them can cause various formations on the body. As a rule, laboratories diagnose only 14 main, clinically significant, types of high oncogenic risk, for example, 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 56, etc. Therefore, negative HPV in the presence of condylomas indicates that your disease is caused by non-oncogenic types of the virus. This is prognostically more favorable (of course, if paragraphs 1-3 are irrelevant).
5. IS IT POSSIBLE TO COMPLETELY CURE HPV IN WOMEN? There are currently no treatments for condylomas with reliably proven effectiveness. Systemic therapy for HPV infection has not been developed and is only necessary in the case of complicated HPV infection (papillomas, condylomas, dysplasia, erosion), or long-term, recurrent HPV infection, especially when high cancer risk types of the virus are identified. For example, in the presence of HPV and condylomas, it is necessary to remove formations as a source of infection and carry out complex antiviral therapy.
As for the use of immunomodulators, their use should be balanced, reasoned and after a blood test for immune status. Afterwards, dynamic monitoring should be carried out - regular HPV Digen test, PAP test (cervical oncocytology), colposcopy and vulvoscopy to identify possible foci of relapse of genital papillomatosis. Consider getting vaccinated against HPV. The Gardasil vaccine, of course, will not protect against the type that already exists, but it will help prevent infection with other dangerous types of HPV.
6. HOW TO REMOVE CONDILOMAS AT HOME? If you really want to, you can find tips on how to remove genital warts at home. For example, on the Internet there are tips on how to cauterize intimate warts with acid, lubricate them with ointments and creams, herbal recipes from “grandmother..., grandfather...” and other all-scientific and sometimes downright harmful recommendations. I will quote one patient of our gynecology, who tried to get rid of papillomas between her legs on her own, received a rather strong side effect from the so-called “folk recipes” and came to the conclusion that “... a woman has only one pussy and she must be treated with care, with trepidation, and trust her health, well-being and appearance only to medical professionals!”
7. CAN CLEANING THE BODY FROM PARASITES HELP? Attempts to cleanse the body of papillomas in the intimate area instead of removing them, as well as to expel other parasites (germs, worms, viruses, including HPV) with various microwaves, UHF currents, exposure to resonant frequencies and other similar undertakings - shamanism, quackery or It's just pure fraud. By expelling uninvited intestinal inhabitants with a pharmaceutical drug, you will certainly be doing your body a favor, but you will not get rid of HPV and genital warts from your intimate area!
8. EROSION AND CONDYLOMA In gynecology, cervical erosion is a collective concept that simply describes certain changes in the cervical mucosa, but is not a diagnosis as such. Accordingly, not all erosion requires treatment. In order to determine what exactly led to its formation, it is necessary to do a cytological examination of the scraping and an extended colposcopy. If you just have ectopia (false erosion associated with hormonal characteristics in the period up to 22 - 25 years, in women who have not given birth), it is uncomplicated and small in size, then it does not require treatment. If you are diagnosed not with ectopia, but with any transformation of the mucous membrane, especially in the presence of intimate warts or papillomas, you need to be examined for HPV types (Digen test) and hidden infections. The next step may be a biopsy of the cervix (taking a section of tissue). Histological examination allows us to understand the nature of changes in the cervix, confirm or refute the presence of flat “cervical” warts, which will give the correct final diagnosis and help the doctor choose the optimal method of treatment or cauterization of condylomas.
Treatment of condylomas
Genital warts must be removed.
Currently, there are several ways to remove genital warts. The choice of method is carried out individually for each patient, depending on the clinical situation.
To remove condylomas, the following can be used: • cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen (removal by exposure to low temperature); • electrocoagulation (removal of condylomas by exposure to high temperature); • laser therapy (removal of condylomas using a laser); • cauterization with chemicals (removal of condylomas is facilitated by various potent substances that are applied to the site of inflammation or administered by injection); • removal of condylomas using a radio wave method (removal of condylomas using a radio wave scalpel.
Radio wave surgery method
Radio wave surgery is the optimal method for removing tumors in the anogenital area due to good aesthetic results and wound healing without scarring.
The method is based on the effect of radio frequency waves on biological tissues. This leads to increased molecular vibrations, local heating and evaporation of neoplasm cells. Due to the high temperature, blood vessels are immediately sealed, which prevents bleeding.
At the site of removal, a dry crust forms, under which epithelization of the wound occurs. After the scab falls off, a pink skin forms in its place, which over time transforms into normal integumentary tissue. In our clinic, for radio wave removal of condylomas, we use the latest generation Surgitron device Surgitron DF-120 (USA) with an innovative “fulgurate” mode specifically for the removal of condylomas.
Removal of genital warts with a laser or radio wave scalpel
These methods of removing condylomas are today one of the most modern, effective and preferred methods for getting rid of uncomfortable and unaesthetic genital warts.
Removal is performed using an erbium or CO2 laser or a radio wave scalpel under local anesthesia (a 1-2% solution of local anesthetic (for example, lidocaine) is injected into the area around the condyloma or under it.
The radio wave scalpel used in this case does not burn, but cuts off the damaged area, while it preserves it after removal and allows for a histological examination necessary to clarify the diagnosis. The method is painless and fast, it is based on high energy radio waves. Another advantage of laser and radiosurgery is its unsurpassed efficiency: condylomas do not grow again after removal.
After removal of genital warts, a special, gentle regimen is required. After removal of genital warts, solariums and saunas are contraindicated, heavy lifting is prohibited, and abstinence from sexual activity is advisable. Depending on the treatment method, the regimen is observed for 1 to 4 weeks.
Each method of genital wart removal has its own indications and limitations for use, which must be taken into account by the attending physician when drawing up an individual treatment plan. After removal of multiple and widespread condylomas, the patient may be prescribed complex therapy aimed at reducing the viral load in the body and strengthening general immunity.
What are the methods for removing condylomas?
In medical practice, there is more than one method for removing such formations. Each of them is highly effective. During removal, doctors use chemicals and physical solutions.
The main removal methods are:
- chemical exposure;
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- radio wave removal;
- laser removal.
Let's look at each technique separately.
Chemical exposure
Removal using this method involves the use of special solutions that cauterize the condylomas. As a rule, this is Solcoderm or Condilin.
There is a special applicator for applying Condilin. The solution is applied twice a day (morning and evening). The course of treatment is three to four days. Afterwards there is a break for several days, then the procedure is repeated. Treatment is carried out for no more than one month.
Solcoderm is also applied twice a day. It is necessary to treat condylomas until they turn yellow or pale gray.
If the number of tumors is not small, then the course of therapy is repeated.
Condilin and Solcoderm have a cauterizing effect. After completing the course of therapy, the condylomas dry out and are torn away from the skin on their own. At the same time, not a trace remains of them.
This method of removing tumors is only suitable for small tumors, and they should not merge with each other.
The effectiveness of treatment is 85 percent.
Cryodestruction of condylomas
Removal occurs using a coolant. As a rule, liquid nitrogen is used in medical practice. The doctor freezes the formations, then they die and fall off.
The process itself takes no more than three minutes. After this treatment, no rough scars remain. During the therapy, the patient does not experience pain, so it is carried out in a hospital setting and without anesthesia.
Anesthesia can be administered to patients who have a very low pain threshold.
The downside of the freezing effect is the fact that the skin is restored only after six months.
Electrocoagulation of condylomas
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Removal occurs under the influence of high temperatures, which are created using high-frequency waves. New growths in the anal area are burned out with an electric knife. After the procedure, scabs form at the site of the condyloma, which fall off within five to six days.
Compared to other procedures, electrocoagulation is a painful process. The patient is first given local anesthesia. The skin is completely restored within ten days.
Doctors may prescribe a similar procedure for patients with severe genital warts.
Removal by radio waves
During this procedure, high-frequency radio waves affect condylomas. During radio wave exposure, tissues begin to emit heat and at the same time destroy formations.
This procedure is used not only in this case. It is widely used, as it is painless, non-traumatic and without excess blood. Also, there are no scars left after the operation.
The procedure itself takes no more than half an hour, and even large areas of damage can be treated.
How to prepare for the procedure?
There are no difficulties here. At the first visit, the doctor must examine the condylomas, take tissues for testing, and find out whether the patient has any contraindications to their removal by one method or another. If there are no contraindications to the removal of condylomas, the patient comes at the appointed time for the procedure.
Before removing condylomas, the doctor treats the skin around the growth with a disinfectant and, if necessary, uses anesthesia - this can be injections or local anesthesia using a spray or cream.
The entire procedure for removing one condyloma takes several minutes, after which the affected area is re-treated with an anesthetic. If necessary, the doctor applies a bandage and then gives recommendations on caring for the wound. Often, along with this, the specialist prescribes antiviral drugs that prevent relapses.
When is the procedure for removing condylomas contraindicated?
The main contraindication to removal of condylomas by any method is a diagnosed malignant tumor, no matter where it is located. If tests confirm the degeneration of condyloma, its removal is only possible through surgery. In addition, contraindications include:
- periods of bearing and feeding a child;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune and endocrine systems; tendency to thrombosis;
- inflammatory processes in the body; exacerbation of infectious diseases;
- diabetes mellitus, mental disorders;
- the presence of a pacemaker (when removed by radio waves or laser).
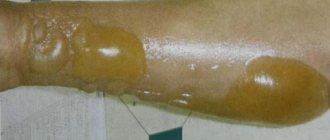
Features and diagnosis of giant condylomas
Giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma has a characteristic clinical feature: progressive growth. There is a pronounced tendency for recurrence of this disease, even after complete excision of the existing formation. Predominantly exophytic growth is observed against the background of the presence of invasive growth. The result is the fusion of individual parts of the new growth, which forms its external similarity to the cauliflower inflorescence.
Buschke-Levenshtein's condyloma, from the point of view of histological picture, is diverse: areas of benign condylomas alternate with areas of atypical cells or squamous cell carcinoma.
To confirm this diagnosis, specialists must carry out differential diagnosis, the purpose of which is to exclude the following probable diagnoses:
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- condyloma lata, which accompanies syphilis;
- ordinary genital warts.
Difficulties in diagnosis may arise due to the transformation of giant or ordinary condyloma acuminata into an atypical tumor. The disease requires multiple sectional biopsies and computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
To completely exclude oncology, complete excision of the tumor is performed with histological examination.
The difference between papilloma and condyloma
During life, a variety of formations appear on the human body. The most common benign formations include the following:
- nevi;
- papillomas;
- warts;
- others.
It should be understood that not all formations are safe. It is always preferable to consult a dermatologist to determine the danger of a particular skin formation.
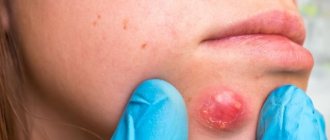
Papillomas are delicate papillary formations on human skin that appear as a result of infection of the skin, most often with certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted by contact from the skin of an infected person to the skin of an uninfected person. Papillomas can remain on a person’s body throughout his life; these tumors are considered safe. Dermatologists still strongly recommend removing papillomas due to the possibility of damaging them or accidentally tearing them off, which can lead to negative consequences.
Condyloma is a rough scallop formation on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, anogenital area and oral cavity. Condylomatosis is a disease that is caused mainly by HPV types 6 and 11. In this case, the mode of transmission is sexual (sexual transmission). Condylomas (warts) develop as a result of a decrease in the body’s protective abilities, and are subject to mandatory removal, which is one of the stages of complex treatment of this problem.
The main difference between condyloma and papilloma is their location on the human body. Also, these neoplasms have different structural features. In any case, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. If you are interested in an effective solution to the problem, it is preferable to contact a specialized specialist: in the genital area, this is a gynecologist, on the skin of another area, a dermatologist.
Prevention of condylomatosis
Condylomatosis is a consequence of infection of the body with the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is mainly transmitted through sexual contact. It appears in the form of warts called condylomas. Such formations can appear on the external and internal genital organs, in the anal area, and oral cavity.
Therefore, to prevent condylomatosis, you should avoid:
· presence of sexually transmitted infections;
· neglect of protective equipment during sexual intercourse;
· smoking;
· mechanical trauma to the skin or mucous membrane of the genital organs.