Antihistamines in the treatment of urticaria
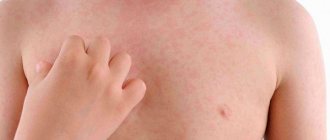
Urticaria is clinically characterized by the appearance of itchy, urticarial rashes on the skin. A wheal, the main morphological element of urticaria, is a limited swelling of the dermis with a diameter of several millimeters to several centimeters, hyperemic along the periphery and paler in the center. When edema spreads to the deep layers of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, as well as mucous membranes, Quincke's edema (angioedema) is formed.
Quincke's edema occurs quite often. It is believed that 15–20% of the population have experienced at least one episode of urticaria [15]. The prevalence of all types of urticaria in children ranges from 2.1–6.7% [8].
In recent years, the classification of urticaria has been widely discussed.
The published consensus document [12, 13] categorizes urticaria into spontaneous, physical and special types. This classification is aimed at practicing physicians and is convenient for clinicians.
The etiological factors of urticaria are presented in Table 1.
Spontaneous urticaria
Spontaneous urticaria is divided into acute and chronic according to the duration of its course. Acute urticaria lasts up to 6 weeks. Chronic urticaria persists for more than 6 weeks and has an undulating course with alternating relapses and remissions.
Acute urticaria . The main etiological factors of acute urticaria (AU) are foods and drugs. The development of urticaria is possible with allergies to epidermal allergens (cat, dog), house dust mites and pollen allergens, hymenoptera venom (bees, wasps) [2, 7, 11].
Most often, the disease is caused by the development of IgE-dependent allergic reactions. Many studies have shown a high incidence of OK in patients with atopic diseases [3, 7, 12]. An analysis of clinical symptoms in children with food allergies conducted by I. Dalal et al. found that OK alone or in combination with angioedema was the most common clinical symptom of food allergy and was observed in 74.4% of cases [7].
A study conducted by T. Zuberbier et al. found that 50.2% of patients with acute urticaria had concomitant allergic diseases - hay fever, bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis [16].
The development of urticaria may be due to the direct release of histamine and other biologically active substances from mast cells without the participation of immunological mechanisms. A number of foods, drugs, and chemicals can cause mast cell degranulation. Eating foods rich in histamine can also cause urticaria (Table 2).
Chronic urticaria (CU) . According to most authors, the most common causes of spontaneous chronic urticaria are infections - hepatitis, Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis, staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. Foods and medications can also maintain chronic symptoms of urticaria, but, unlike acute urticaria, the role of IgE-dependent reactions in the formation of symptoms is minimal [2, 6, 11, 16].
Of great interest is the frequency of detection of autoantibodies to high-affinity IgE receptors (FceRI) and to IgE in patients with CC. The autoimmune genesis of urticaria is confirmed by skin tests with autoserum. There is still no consensus regarding the role of autoantibodies in the formation of urticaria symptoms; further research is needed.
In many cases, urticaria can be caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal dysbiosis, and parasitic infestations.
Physical urticaria
Physical urticaria (PH) develops due to exposure to physical factors. The mechanism of development of the disease is not well understood. An important role of mast cell degranulation in the formation of FC symptoms has been suggested. Physical urticaria includes cold urticaria, solar urticaria, heat urticaria, dermographic urticaria, vibration urticaria and pressure urticaria.
Special forms of urticaria are cholinergic, adrenergic, aquagenic.
Treatment of urticaria
Treatment of urticaria largely depends on the form of the disease and causative factors. Nevertheless, the basic principles of therapy are the same; they include the following steps.
- Eliminating or limiting exposure to factors that cause urticaria.
- Conducting pharmacotherapy.
- Detailed examination of patients, treatment of diseases that may cause urticaria.
Pharmacotherapy . In patients with acute urticaria, exacerbation of chronic or physical urticaria, in order to relieve the acute condition, in most cases, the prescription of second-generation antihistamines is indicated. In more severe cases of the disease, parenteral administration of first-generation antihistamines is advisable (second-generation H1-blockers do not have dosage forms for parenteral administration), as well as glucocorticosteroids.
Treatment of patients with chronic urticaria requires great patience and close cooperation between the doctor and the patient. The quality of life of patients is seriously affected: itching can affect daily activity, disrupt sleep, rashes on the face embarrass the patient, severely limit his communication and professional activities. Patients require frequent and long-term use of antihistamines. First generation antihistamines have a number of undesirable effects that limit their use. The sedative effect and impairment of cognitive and psychomotor functions of the central nervous system are well known [4]. Low selectivity and binding of M-cholinergic receptors manifest themselves in dry mucous membranes of the oral cavity; in patients with bronchial asthma, the viscosity of sputum increases, which negatively affects the course of the disease. Urinary retention, constipation, and a possible increase in intraocular pressure limit the prescription of drugs to patients with concomitant diseases. An equally serious disadvantage of first-generation H1-blockers is their short-term action, the need for 3-4 doses per day, and fairly high doses. A decrease in therapeutic effectiveness with long-term use dictates the need to change the drug every 10–14 days.
Second generation antihistamines (desloratadine, loratadine, fexofenadine, cetirizine, ebastine) do not have these disadvantages. All drugs have a high safety profile, no serious side effects, and are easy to use. New antihistamines are prescribed once a day, regardless of food intake; there is no need to change drugs, since high therapeutic effectiveness remains with long-term use. It is possible to prescribe second-generation H1-blockers to patients with concomitant diseases for whom first-generation drugs were contraindicated.
Of course, second generation antihistamines differ from each other. General practitioners, dermatologists, and pediatricians are faced with the question: which drug should be prescribed to the patient?
In recent years, quite a large number of studies have been conducted in an attempt to determine which antihistamine is superior to others. Using the results of comparisons in practical work is difficult, since individual parameters were studied in sample groups of sick or healthy individuals, and adequate dosages of the drugs being compared were not always used. However, most researchers conclude that the newer non-sedating antihistamines are comparable in effectiveness, safety, and ease of use. Patient preference may be the determining factor when choosing between second-generation antihistamines [9, 10, 15].
Considering the participation of histamine in the formation of all symptoms of urticaria [1], second-generation antihistamines are the first choice drugs. In addition to the direct antihistamine effect, new H1 blockers have anti-inflammatory activity. Taking them regularly eases the course of the disease and improves the quality of life of patients.
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
We conducted a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the effectiveness and safety of the drug kestine (ebastine) in patients with chronic urticaria. The study included 40 patients with chronic urticaria aged 16–61 years. Women - 35, men - 5.
Before inclusion in the study, patients had not received systemic antihistamines for 7 days or more. Throughout the study, patients did not receive macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin) and azoles (intraconazole, ketoconazole). The patients did not have severe concomitant diseases. According to the ECG, there was no prolongation of the QT interval.
For 8 weeks, 30 patients received kestin 20 mg/day and 10 patients received placebo.
Patients noted in a diary every evening the severity of itching, the number and size of urticarial rashes. The dynamics of symptoms were assessed by a doctor during visits. The doctor and patients recorded the occurrence of adverse events, their manifestations and the necessary therapy. There were 3 visits in total: the first visit was the starting one, the second was 4 weeks later, and the third visit was 8 weeks after inclusion in the study.
Considering that itching is the main symptom of urticaria, which significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life, Tables 4 show the dynamics of the severity of itching in patients after 4 and 8 weeks of therapy. In the group receiving kestin, all patients showed regression in the severity of this symptom. Among patients receiving placebo, the effectiveness of therapy was significantly lower - 5 (50%) patients were prematurely excluded from the study due to lack of effect over the same time. The overall effectiveness assessment indicates the high effectiveness of kestin 20 mg/day in patients with chronic urticaria compared to placebo (Table 6).
During the entire observation period, no sedation, serious adverse events, or prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG were recorded in both groups.
Thus, second-generation antihistamines are highly effective and safe drugs. They are the first choice drugs for controlling urticaria symptoms in most patients. At the same time, it should be emphasized that achieving pharmacological control of the symptoms of urticaria does not exclude the need to conduct a thorough diagnostic search and identify possible causes of the development of urticaria.
I. V. Sidorenko , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor T. V. Zakharzhevskaya , Candidate of Medical Sciences A. V. Karaulov , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of MMA named after. I. M. Sechenova, Moscow
Rating of remedies for urticaria
The VyborExpert project team has done a lot of work to study doctors’ recommendations on the best way to treat urticaria in children and adults. I also reviewed offers from pharmaceutical companies popular in pharmacies. Several dozen applicants were considered, each assessed on a group of criteria:
- Type – antihistamines, hormonal, sedatives, sorbents, external, internal;
- Release form: tablets, capsules, ointments, creams, syrups, solutions;
- Treatment regimen – method of administration, frequency, course duration;
- Efficacy – speed of onset of relief, digestibility, bioavailability;
- Age – admission to children, adults, elderly people;
- Contraindications – a list of restrictions for use;
- Risks – the likelihood of side effects;
- Special instructions - pregnancy, lactation, compatibility with other medications;
- Manufacturer – imported, domestic drug;
- Price - the cost of packaging, whether it is enough for the course, the relationship with effectiveness.
As a result, we selected 7 nominees who received the best recommendations from dermatologists and experts. They demonstrate maximum demand and high patient ratings. Real reviews helped determine the strengths and weaknesses of each candidate and confirmed its benefits in the fight against urticaria.
What is the best remedy for hives?
As soon as the first signs of urticaria appear on the skin, you need to select medications to combat it. Follow doctor's orders. The expert rating compiled by the Vyborexperta.ru project is aimed at narrowing the search range in pharmacies. Comparative analysis showed:
- Suprastin is the first aid for suppressing allergies without side effects;
- Advantan is a highly safe hormonal ointment against complex forms of the disease;
- Polysorb is a fast-acting enterosorbent for adults, children, and pregnant women;
- Persen Forte is a herbal sedative to eliminate nervousness as a cause of urticaria.
The presented review of effective remedies for rashes in adults and children is not unconditional; the final word belongs to the doctor. Where to buy them, which pharmaceutical manufacturer to give preference to is a purely individual decision.
The best enterosorbents for urticaria
In addition to combating the visible manifestations of an allergic reaction, urticaria is treated from the inside. To do this, enterosorbents are used, which will remove allergens, toxins and other harmful substances from the body. We analyzed the latest offers on the pharmaceutical market, the level of demand, and doctors’ recommendations. Based on reviews, effective remedies for urticaria were selected.
Smecta
An effective sorbent for cleansing the body of toxins and allergens. An antidiarrheal drug with adsorbent properties, where the active ingredient is dioctahedral smectite. Efficiency is observed against viruses and pathogenic microorganisms. Available in individual packaging of 3 g, one dose, inside there is a powder with orange or vanilla flavoring. It differs from many analogues in that it is used from the first days of life, during pregnancy and lactation. The component also stimulates the production of mucus in the intestines, increasing the protective functions of the immune system. In difficult situations, treatment with Smecta is prescribed for 7 days. The price of 10 bags is 140-170 rubles.
Advantages:
- For all ages;
- Pleasant taste;
- Allowed for pregnant and breastfeeding women;
- Increased intestinal immunity;
- Rapid removal of allergens;
- Inexpensive.
Flaws:
- Lumps during dilution;
- Reduced absorption of other drugs.
Adult patients are prescribed to take up to 6 sachets during the day, a child can take no more than 2 doses (you can mix the powder with food and drinks). For better absorption, it is better to carry out manipulations between meals. Smecta is not prescribed to those who suffer from chronic constipation or intestinal obstruction.
Polysorb
Another popular remedy for urticaria in adults and children is Polysorb from a Russian pharmaceutical company. The main substance is colloidal silicon dioxide, which binds and then removes all harmful substances from the body. It differs from analogues in its strong sorption and detoxification properties. Thanks to this, the medication is widely used in complex treatment. Release form: odorless, tasteless powder for dilution with water and oral administration. Enterosorbent is approved for children of any age; in this case, the dosage is selected taking into account weight. The instructions allow the use of Polysorb by pregnant and breastfeeding women. One can of 12 g costs 50-80 rubles.
Advantages:
- Treats any form of skin disease;
- Quick elimination of the clinical picture;
- Allowed for children, pregnant and breastfeeding women;
- Safety;
- Ease of use;
- Inexpensive.
Flaws:
- There are contraindications;
- Makes it difficult to have bowel movements.
At least 60 minutes should pass between Polysorb, other drugs and food. If the cause of the allergic reaction is food, then the sorbent is taken before eating. The maximum duration of the course is 2 weeks. Polysorb is not recommended for people with acute inflammation of the digestive system, intestinal atony, or intestinal obstruction.
The best remedies for psoriasis
The best sedative for urticaria
Frequent companions of urticaria are nervousness, irritability, and insomnia. To reduce excitability without causing complications, the dermatologist prescribes sedative medications. Preference is given to safe sedatives that do not harm the nervous system and other internal organs. After analyzing expert advice, patient reviews, and clinical studies, we have chosen one undoubted leader in this rating category.
Persen Forte
A sedative from a Slovenian pharmaceutical company with an increased concentration of active substances. The main difference between this nominee and all those described above is its herbal composition without synthetic additives. To relieve irritability and have an antispasmodic effect, Persen Forte included lemon balm, peppermint, and valerian. It is prescribed for any diseases accompanied by increased irritability. Release form: small red-brown capsules for swallowing orally. Treatment is allowed from 12 years of age. The package contains 40 tablets, their price is 300-350 rubles. Pregnant and breastfeeding women need a doctor's permission.
Advantages:
- Plant origin;
- Convenient capsules;
- Getting rid of nervousness;
- Quick tangible effect;
- No addiction syndrome;
- Doesn't make you sleepy.
Flaws:
- Price;
- Adults only.
Take Persen Forte if urticaria is caused by stress, 1-2 capsules up to 3 times a day. The course of treatment depends on the complexity of the disease, from 2 to 8 weeks. Despite its plant origin, patients observe the effect already in the first days of therapy. In rare cases, a long course provokes constipation.
First aid for hives
When a rash occurs in children, the first action is to eliminate the allergen or extremely limit contact with it. If food is the cause, the stomach should be rinsed. If you are allergic to chemicals, cosmetics, or matter, take a shower; if you are allergic to medications, stop using them and replace them with others.
Timely provision of first-aid to a child with urticaria is of great importance in preventing the worsening of the disease.
If urticaria occurs in children: emergency care, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- When initial signs of manifestation occur, it is important to assess the patient’s condition.
If a single rash is localized, it is slightly itchy and does not enlarge subsequently, it is enough to treat the area with an allergic ointment (Fenistil, Zinc). The drugs effectively eliminate itching and have a drying, astringent effect. Also give him an antihistamine tablet.
- Drink enterosorbent (Polysorb, Activated carbon). Sometimes, the use of fast-acting laxatives (Magnesium sulfate) becomes an effective measure. However, it is necessary to replace the lost fluid.
- A preventive measure for anaphylaxis at the time of an insect bite is the immediate removal of the sting and prevention of the distribution of poison into the blood. Place ice on the bite area. When there is a history of complex allergic manifestations, take an antihistamine (Suprastin, Diazolin).
First aid for rashes and its complications is performed depending on individual symptoms. Therefore, eliminating weak signs of disease with strong doses of steroid medications is very unwise and dangerous.