Scabies, treatment and prevention
Any person can become infected with scabies , even clean people, although in clean people the disease proceeds differently: they have single elements of the rash and are only bothered by itching in the evening and at night. Today we will talk about how to suspect and how to treat scabies. I will give you examples of cases of scabies. A mother brought her three-year-old daughter, who attends a nursery, to see a pediatrician. Three days ago, the girl developed a rash on her wrists, interdigital spaces, palms and face, which the child scratches, especially intensely in the evening after going to bed. According to the mother, three more children in the nursery group are bothered by itching. A young man consulted a dermatologist with complaints of itching and rash in the area of the anterior surface of the abdomen, thighs and genitals. The disease is associated with food allergies or swimming in a polluted body of water during a hike, from which he returned about 10 days ago. His girlfriend has similar symptoms that arose even earlier. In the above area, the patient has many nodular elements, most of them covered with dark brown crusts. There are pustular elements in the suprapubic region and on the right thigh.
Scabies is a contagious parasitic skin disease caused by the scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabiei). The old name for the mite is scabies itch . The female scabies mite is larger than the male and has dimensions of 0.3–0.4 or 0.25–0.38 mm, makes scabies burrows in the skin at the border of the stratum corneum and granular layer of the epidermis and lays eggs there. The eggs hatch into after 2-3 days , which after 1.5-2 weeks turn into adult ticks and live for 1-2 months . Scabies mites can be contagious at any stage of their development. It is estimated that under favorable conditions, 1 female in 3 months can give birth to 6 generations of ticks in the amount of 150 million individuals. The scabies mite has low resistance to the environment. In dry and hot conditions, ticks die quickly (at 60°C - in 1 hour, at humidity below 35% - in 24 hours). In room conditions, it is enough to wait 5 days for the complete death of scabies mites .
Features of the pathogenesis of scabies Pathogenesis is the sequence of pathological (painful) changes in the body due to any disease or syndrome. Regarding scabies, you must firmly understand that all its manifestations (itching, rash) are the result of an allergy to the mite itself, its bites and waste products (saliva, eggs, excrement). Having understood this, it is easy to understand other features of scabies: the incubation (hidden) period is on average 1-2 weeks (up to 6 weeks). This time is needed for mites to settle into their new place of residence, and for the immune system to begin to respond to scabies mites and their waste. The more mites initially caught on the skin, the shorter the incubation period. When re-infected, a reaction to the pathogen appears within a few hours . Although there is no immunity to scabies, it is more difficult to become infected again , and in this case, fewer scabies mites are detected on the skin. The severity of the rash depends little on the number of mites in the skin, but is determined by the severity of the allergic reaction to their waste products. Due to severe itching and frequent scratching, a bacterial infection (for example, staphylococcus) may be attached, causing the skin rash to become more diverse, including pustules. In the morning and afternoon, ticks are inactive . The female mite, which lives no more than 4-6 weeks, digs a scabies burrow in the epidermis in the evening and at night at a rate of 2-3 mm per day, in which it lays 2-4 eggs daily . Males form short lateral branches in the female's scabies passage. Ticks dissolve the keratin of the skin using special proteolytic enzymes contained in saliva and feed on the resulting lysate (solution). At night (while the owner is sleeping), mites come to the surface of the skin to mate and explore new territories. On the surface of warm skin, mites move quite briskly - at a speed of 25 mm/min. It is clear that the easiest way to become infected with scabies is at night in a shared bed. The typical form of scabies is characterized by itching, a typical rash and the presence of scabies . However, there is scabies without burrows , so the absence of burrows does not yet prove the absence of scabies. The scabies course has a convoluted shape and consists of several segments, called the daily element of the course. The back of the stroke gradually peels off. The course itself consists of 4-7 daily elements with a total length of 5-8 mm. Usually these passages look like gray straight or zigzag scratches 1-10 mm long, at the end of which there is a transparent bubble through which a dark (sometimes written as white) point is visible - the body of the tick. Scabies are more noticeable in areas of the skin with a thin stratum corneum of the epidermis: between the fingers, the lateral surfaces of the fingers, the articular folds of the hands and elbows, the mammary glands (especially the circumference of the nipples), and the lower abdomen.
Signs of Scabies We move on to the 3 main signs of scabies. 1) Increased itching in the evening and at night. This symptom is due to the life cycle of the scabies mite, which is most active in the evening and at night. 2) Typical places of rashes. Despite the fact that in clean people, rashes are rare, elements of the rash spread over time to typical places that you need to know. The appearance of the rash is less important because the rash is polymorphic (diversified). Typical sites of scabies rash in almost everyone are the interdigital spaces and the lateral surfaces of the fingers, in 50% - the area of the wrist joints, in 50% of men - the genitals, in 25% - the feet, 20% - the torso, in 17% - the arms and legs (except for hands and feet), in 10% of women - mammary glands.
Methods of infection with scabies Scabies is transmitted through prolonged direct skin-to-skin contact , so the easiest way to become infected is in bed at night. Children often become infected when they sleep in the same bed with sick parents. This is due to the biological characteristics of the mite: the scabies mite is active in the evening and at night, the mite needs about 30 minutes to penetrate the skin, the mite quickly dies in the external environment (at 21 ° C and humidity 40-80% - after 24-36 hours), and the activity loses even earlier. Infection in a group is possible through direct contact (fussing children, frequent and strong handshakes, contact sports, etc.). Infection through household items is now considered unlikely . There is a well-known experiment conducted in 1940 in Great Britain. Of 272 attempts to infect volunteers who went to bed from which patients with severe scabies had just risen, only 4 attempts led to illness.
Features of scabies in children In children during the first 6 months of life, scabies looks like urticaria (a collection of blisters, like a nettle burn). In general, the clinical picture resembles weeping eczema , which is not amenable to conventional treatment. In children under 3 years of age, the interdigital spaces and lateral surfaces of the fingers are RARELY affected. the nail plates may also become affected , which thicken and loosen with the appearance of cracks. It is characteristic that in children ALL skin of the body is affected, even the face and scalp, which does not happen in adults (accordingly, when treating scabies, children also need to treat the face and head, but adults do not). For the treatment of children, drugs with a lower (half) concentration of the active substance are usually used. The use of drugs with “children’s” concentrations to treat adults is a mistake and is one of the reasons for the ineffectiveness of the treatment. Confirmation of the diagnosis It is enough to detect scabies , but they do not happen everywhere and not in everyone. It is easier to detect scabies by staining the skin with iodine tincture - the burrows become visible in the form of brown stripes against the background of colored light brown skin. The most advanced technology is a video dermatoscope with a magnification of 600 times, which allows you to detect scabies in almost all cases. The most common confirmatory method for rapid diagnosis of scabies is scraping using 40% lactic acid . Lactic acid well loosens the stratum corneum of the epidermis, does not irritate the skin, and prevents the development of suppuration and the scattering of material during scraping. A drop of 40% lactic acid is applied to the scabies element (tract, nodule, etc.). After 5 minutes, the loosened epidermis is scraped until capillary blood appears. The material is transferred to a glass slide in a drop of lactic acid, covered with a coverslip and microscopically examined. Another common method is to remove the tick with a needle followed by microscopy. Treatment of scabies There are many medications to treat scabies. Treatment methods differ in the cost of the course and the number of skin treatments - from 2 to 5-7 during the course. For an adult, on average, 50 ml of the drug is needed per skin treatment. Principles of treatment of scabies: All patients from one epidemic. lesions must be treated simultaneously . Rub the preparation with bare hands , because the hands are most often affected by scabies. Trim your nails : there may be tick eggs underneath them due to scratching. Remember about disinfection of linen and clothes : the tick is reliably killed by boiling for 5-10 minutes in a solution of soda or washing powder, you can also iron the clothes with a hot iron, but for the laziest there is a very simple way: the linen is removed and packed in a plastic bag for 5 days or hung outdoors. After 5 days, the clothes are considered disinfected, because hungry ticks don't survive that long. Please note that you need to treat all fabrics that come into contact with the body - clothing and bedding. If you don't want to remove your bedding, give your sheets, pillowcases, and duvet covers a good run with a hot iron. If disinfection is carried out poorly, the remaining mites can infect you again.
Healthy lifestyle office
A young man consulted a dermatologist with complaints of itching and rash in the area of the anterior surface of the abdomen, thighs and genitals. The disease is associated with food allergies or swimming in a polluted body of water during a hike, from which he returned about 10 days ago. His girlfriend has similar symptoms that arose even earlier. In the above area, the patient has many nodular elements, most of them covered with dark brown crusts. There are pustular elements in the suprapubic region and on the right thigh.
Source: https://medvestnik.by/ru/issues/a_9425.html
Scabies mite
Scabies is a contagious parasitic skin disease caused by the scabies mite (Sarcoptes scabiei). The old name for the mite is scabies itch .
Scabies mite in the skin under an electron microscope.
The female scabies mite is larger than the male and measures 0.3–0.4 ? 0.25–0.38 mm, makes scabies in the skin at the border of the stratum corneum and granular layer of the epidermis and lays eggs there. The eggs hatch into after 2-3 days , which after 1.5-2 weeks turn into adult ticks and live for 1-2 months . Scabies mites can be contagious at any stage of their development. It is estimated that under favorable conditions, 1 female in 3 months can give birth to 6 generations of ticks in the amount of 150 million individuals.
Layers of skin. The scabies mite makes passages at the border of the stratum corneum and granular layer of the epidermis.
Scabies mite under a light (ordinary) microscope.
The scabies mite has low resistance to the environment. In dry and hot conditions, ticks die quickly (at 60°C - in 1 hour, at humidity below 35% - in 24 hours). In room conditions, it is enough to wait 5 days for the complete death of scabies mites . This feature will be useful for disinfection when treating scabies.
Features of the pathogenesis of scabies
Pathogenesis is a sequence of pathological (painful) changes in the body due to any disease or syndrome.
Regarding scabies, you must firmly understand that all its manifestations (itching, rash) are the result of an allergy to the mite itself, its bites and waste products (saliva, eggs, excrement). Having understood this, it is easy to understand other features of scabies:
- The incubation period averages 1-2 weeks (up to 6 weeks). This time is needed for mites to settle into their new place of residence, and for the immune system to begin to respond to scabies mites and their waste. The more mites initially caught on the skin, the shorter the incubation period.
- upon re-infection, a reaction to the pathogen appears within a few hours . Although there is no immunity to scabies, it is more difficult to become infected again , and in this case, fewer scabies mites are detected on the skin.
- The severity of the rash depends little on the number of mites in the skin, but is determined by the severity of the allergic reaction to their waste products.
Due to severe itching and frequent scratching, a bacterial infection (for example, staphylococcus) may be attached, causing the skin rash to become more diverse, including pustules.
Source of the figure: Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology, No. 4 (47), 2012.
In the morning and afternoon, ticks are inactive . The female mite, which lives no more than 4-6 weeks, digs a scabies burrow in the epidermis in the evening and at night at a rate of 2-3 mm per day, in which it lays 2-4 eggs daily . Males form short lateral branches in the female's scabies passage. Ticks dissolve the keratin of the skin using special proteolytic enzymes contained in saliva and feed on the resulting lysate (solution). At night (while the owner is sleeping), mites come to the surface of the skin to mate and explore new territories. On the surface of warm skin, mites move quite briskly - at a speed of 25 mm/min. It is clear that the easiest way to become infected with scabies is at night in a shared bed.
Clinical forms of scabies
There are several of them:
- typical,
- complicated by pyoderma (pustules),
- scabies of clean people,
- nodular scabies (scabious lymphoplasia),
- Norwegian scabies,
- pseudoscabies (pseudosarcoptosis).
TYPICAL FORM. It is not necessary to try to remember everything that is written just below and relates to the typical form of scabies - then I will separately focus on the important points of diagnosis.
Photo source: Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology, No. 4 (47), 2012.
Involutive - in the phase of reverse development, aging . Photo source: Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology, No. 4 (47), 2012.
The typical form is characterized by itching, a typical rash and the presence of scabies . However, there is scabies without burrows , so the absence of burrows does not yet prove the absence of scabies. The scabies course has a convoluted shape and consists of several segments, called the daily element of the course. The back of the stroke gradually peels off. The course itself consists of 4-7 daily elements with a total length of 5-8 mm. Usually these passages look like gray straight or zigzag scratches 1-10 mm long, at the end of which there is a transparent bubble through which a dark (sometimes written as white) point is visible - the body of the tick. Scabies are more noticeable in areas of the skin with a thin stratum corneum of the epidermis:
- between the fingers,
- lateral surfaces of the fingers,
- articular bends of the hands and elbows,
- mammary glands (especially nipple circumference),
- hypogastrium,
- foreskin and glans penis, etc.
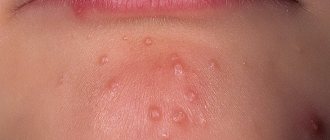
Scabies rash
scabies rash reddish nodules ), which may be scattered or multiple, confluent. Over time, papules (nodules) turn into vesicles ( vesicles ) and open with the formation of bloody or purulent crusts. Purulent crusts are the result of a secondary bacterial infection.
COMPLICATED SCABIES (in 50% of patients). Scabies can be complicated, for example, by dermatitis (mechanical scratching of the skin against the background of allergic inflammation) or pyoderma (purulent skin lesions by pyogenic cocci - staphylococci and streptococci ).
SCABIES OF CLEANS = SCABIES “INCOGNITO”: it is possible if a person washes regularly and his immune system is fine. Characterized by isolated rashes and severe itching in the evening and at night.
NODULARY (NODULAR) SCABIES = SCABIOUS LYMPHOPLASIA. It appears in the form of a few itchy round nodules (seals) with a diameter of 2-20 mm of red, pink or brown color. Scabies can be found on the surface of new nodules. Characteristic localization :
- scrotum and inguinal-scrotal folds,
- penis,
- inner thighs and buttocks,
- axillary folds,
- around the anus,
- areola.
The nodules are usually few in number. Sometimes they are the only diagnostic sign of scabies.
Scabious lymphoplasia . Photo source: https://www.skinmaster.ru/542/Chesotochnye_khody_pri_videodermatoskopii/1828
These nodes are caused by an overreaction of the immune system to ticks and their waste products. Lumps are growths of lymphoid tissue in the skin and contain lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Nodules and itching with scabious lymphoplasia can persist for several weeks and even months even after proper treatment. According to recent studies, the source of allergens in such cases are live unfertilized female scabies mites , which do not lay eggs and do not make holes in the roof of the passages, which limits the access of medicine from the surface of the skin. If we remember that female mites live up to 4-6 weeks, it becomes clear why patients may experience itching for a long time after treatment for scabies. For treatment features of scabious lymphoplasia, see below.
NORWEGIAN SCABIES. This form is the rarest, and it gets its name because it was first described in Norway a century and a half ago in patients with leprosy (leprosy). It occurs in patients who, for some reason, do not itch, although in half of the patients the itching persists. The causes of Norwegian scabies are divided into several groups:
- lack of itching due to immunodeficiency , when the immune system is so weak that mites are not able to cause a significant allergic reaction. Observed in AIDS, exhaustion, tuberculosis, during treatment with glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, etc.;
- absence of itching due to disorders of the nervous sensitivity of the skin ( polyneuropathy , leprosy, syringomyelia - the formation of cavities in the spinal cord, etc.);
- when patients want to, but cannot, itch (paralysis, myopathies, etc.);
- the rest have a hereditary predisposition (there are no above reasons).
Norwegian scabies
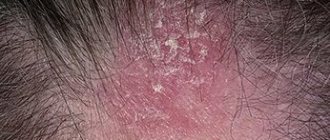
With Norwegian scabies, the skin becomes rough and thick . Even the skin of the face, hair and nails , which does not happen in adults with the typical form of scabies. Norwegian scabies is characterized by a variety of rashes, but most often these are thick, dirty yellow crusts up to 2–3 cm thick , which cover large areas of the skin like a shell. In the lower layers of the crusts there are winding passages. When the crusts are removed, extensive weeping erosions are exposed. With Norwegian scabies, the nails thicken, become loose, break easily (this resembles onychomycosis , a nail fungus), and the hair becomes dull. The patient smells sour.
Norwegian scabies is extremely contagious . up to a million on the patient’s body , while in the typical form there are usually only 15 individuals.
PSEUDOSCABIES (PSEUDOSARCOPTOSIS) is caused by scabies mites in large animals , most often dogs. These mites do not reproduce on humans and are not transmitted to other people. Psedocabies occurs much faster (several hours after infection) and is localized in places of contact with the animal (usually in open areas of the body). Treatment is usually not required .
Signs of scabies
We move on to the 3 main signs of scabies.
1) Increased itching in the evening and at night. This symptom is due to the life cycle of the scabies mite, which is most active in the evening and at night.
2) Typical rash sites.
Despite the fact that in clean people, rashes are rare, elements of the rash spread over time to typical places that you need to know. The appearance of the rash is less important because the rash is polymorphic (diversified).
Typical places of rash due to scabies (according to the analysis of 1105 maps of the KKVD in Minsk):
- almost everyone has interdigital spaces and lateral surfaces of the fingers,
- in 50% - the area of the wrist joints,
- 50% of men have genitals,
- 25% have feet,
- 20% - torso,
- in 17% - arms and legs (excluding hands and feet),
- 10% of women have mammary glands.
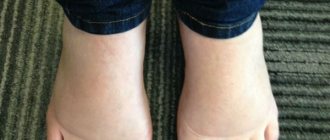
Typical sites of scabies rash
And also: flexion folds of the forearms and shoulders, buttocks, hips and popliteal cavities.
Thus, scabies without involving the hands is uncommon. Such scabies is possible if the patient is clean and the mites have not yet spread to the hands (for example, through sexual transmission). Another conclusion can be made, confirmed by practice: dermatologists rarely make a diagnosis of scabies at the very beginning of the disease (when the hands and wrists do not itch yet), attributing itching (for example, in the legs) to allergies or insect bites. And only after repeated requests from an itchy patient, when most of the typical places are affected, is it possible to suspect scabies, refer the patient for analysis and make a correct diagnosis.
3) Group nature of itching.
If other family members begin to itch in the evenings and at night, then it’s time to see a dermatologist.
Comparison of rashes from flea bites and scabies
Methods of infection with scabies
Scabies is transmitted through prolonged direct skin-to-skin contact , so the easiest way to become infected is in bed at night. Children often become infected when they sleep in the same bed with sick parents. This is due to the biological characteristics of the tick:
- scabies mite is active in the evening and at night,
- It takes about 30 minutes for a tick to penetrate the skin,
- in the external environment, the tick dies quickly (at 21 ° C and humidity 40-80% - after 24-36 hours), and loses activity even earlier.
Infection in a group is possible through direct contact (fussing children, frequent and strong handshakes, contact sports, etc.). Infection through household objects is now considered unlikely . There is a well-known experiment conducted in 1940 in Great Britain under the leadership of Mellanby. Of 272 attempts to infect volunteers who went to bed from which patients with severe scabies had just risen, only 4 attempts led to illness.
The clinical form of the disease also matters. If in the typical form there are about 15 mites on the patient’s skin, then in the Norwegian form of scabies there are several hundred thousand (up to a million). The rarity and unusual appearance of patients with Norwegian scabies (thick dirty yellow crusts, damage to hair and nails, frequent absence of itching) lead to the fact that the diagnosis is made only when others begin to itch.
The Department of Skin and Venereal Diseases of the Belarusian State Medical University analyzed more than a thousand medical records of patients treated for scabies at the Minsk City Skin and Venereal Dispensary. It turned out that 80% of the sick were young people under 29 years of age . Every fifth is a child. 80-85% are cases in the family, and patients from organized groups account for up to 20%.
Features of scabies in children
In children during the first 6 months of life, scabies looks like urticaria (a collection of blisters, like a nettle burn). In general, the clinical picture resembles weeping eczema , which is not amenable to conventional treatment. In children under 3 years of age, the interdigital spaces and lateral surfaces of the fingers are RARELY affected. the nail plates may also become affected , which thicken and loosen with the appearance of cracks.
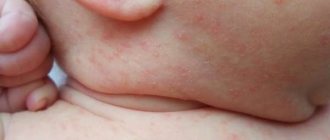
Rash in a child due to scabies
It is characteristic that in children ALL skin of the body is affected, even the face and scalp, which does not happen in adults (accordingly, when treating scabies, children also need to treat the face and head, but adults do not). For the treatment of children, drugs with a lower (half) concentration of the active substance are usually used. The use of drugs with “children’s” concentrations to treat adults is a mistake and is one of the reasons for the ineffectiveness of the treatment.
Diagnosis confirmation
It is enough to detect scabies , but they do not occur everywhere and not in everyone. It is easier to detect scabies by staining the skin with iodine tincture - the burrows become visible in the form of brown stripes against the background of colored light brown skin. The most advanced technology is a video dermatoscope with a magnification of 600 times, which allows you to detect scabies in almost all cases.
Magnification by 10 and 3 times . Photo source: Ukrainian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology, Cosmetology, No. 4 (47), 2012.
The most common confirmatory method for rapid diagnosis of scabies is scraping using 40% lactic acid . Lactic acid well loosens the stratum corneum of the epidermis, does not irritate the skin, and prevents the development of suppuration and the scattering of material during scraping. A drop of 40% lactic acid is applied to the scabies element (tract, nodule, etc.). After 5 minutes, the loosened epidermis is scraped until capillary blood appears. The material is transferred to a glass slide in a drop of lactic acid, covered with a coverslip and microscopically examined.
Another common method is to remove the tick with a needle followed by microscopy.
Treatment of scabies
There are many medications to treat scabies. Treatment methods differ in the cost of the course and the number of skin treatments - from 2 to 5-7 during the course. For an adult, on average, 50 ml of the drug is needed per skin treatment. I'll tell you about the most famous drugs:
1) BENZYL BENZOATE in the form of emulsion and ointment (20% for adults and 10% for children): this is the most popular drug for the treatment of scabies in Russia and Belarus . Absorbs well and leaves no marks on laundry. It is cheap (1 euro - 150 ml, enough for 3 treatments).
Treatment requires 2 treatments (the second on the 4th day). On the first day in the evening (any treatment for scabies should begin only in the evening !), first wash in the shower with soap and a washcloth . Washing mechanically removes mites from the surface of the skin and loosens the epidermis, which facilitates the penetration of anti-scabiosis agents. After washing with bare hands, thoroughly rub the benzyl benzoate emulsion or ointment over the entire body, with the exception of the head and face in adults. When the skin is dry, you can go to bed (your hands should also be treated). 10-12 hours after treatment, you can take a shower (the drug has a specific smell), although it is more effective not to wash. Underwear is changed (disinfected), and bed linen is changed upon request.
On the 4th day the treatment is repeated. This is necessary to destroy all new ticks that hatched from eggs in three days, because... Benzyl benzoate has no effect on tick eggs. 12 hours after treatment, wash with soap and a washcloth, be sure to change bed linen and clothes.
2) PERMETHRIN (cream, ointment, lotion, spray): highly effective and the most popular drug in the West . The most commonly used is 5% permethrin cream. Requires 2 treatments. It is slightly more expensive than benzyl benzoate. Since permethrin (in a lower concentration) is also used for the treatment of head and pubic lice (lice), it is necessary to choose a drug with permethrin for the treatment of scabies, taking into account the indications in the package insert for the drug.
3) SPREGAL: an expensive French drug in the form of an aerosol, which is enough for 3 treatments. Contains poisons that are neurotoxic to ticks: esdepalletrin (esbiol) and piperonyl butoxide. It is easy to use, leaves no traces, is almost odorless, but it cannot be inhaled, and treatment with spregal costs several times more than any other product.
Although the instructions indicate that Spregal even acts on mite eggs (unlike other anti-mite medications) and therefore a single treatment of the body is sufficient, many dermatologists recommend standard double treatment of the skin with an interval of 3 days to avoid relapses of scabies. I also recommend double processing .
Other methods of treating scabies are used less frequently:
- Demjanovich method (60% sodium hyposulfite and 6% hydrochloric acid): effective, but each treatment takes about an hour. Pretty long.
- simple sulfur ointment (adults 20-33%): rub in daily for 5-7 days. The product is proven, but there are a number of shortcomings. The ointment has a pungent odor and is based on Vaseline, which is not absorbed, is disgusting to the touch and stains your laundry. Few people like this. In the West, sulfur ointment is no longer used.
- There are other, lesser-known treatments.
Principles of scabies treatment:
- All patients from the same epidemic. lesions must be treated simultaneously .
- Rub the preparation with bare hands , because the hands are most often affected by scabies.
- Trim your nails : there may be tick eggs underneath them due to scratching.
- Remember about disinfection of linen and clothes : the tick is reliably killed by boiling for 5-10 minutes in a solution of soda or washing powder, you can also iron the clothes with a hot iron, but for the laziest there is a very simple way: the linen is removed and packed in a plastic bag for 5 days or hung outdoors. After 5 days, the clothes are considered disinfected, because hungry ticks don't survive that long.
Please note that you need to treat all fabrics that come into contact with the body - clothing and bedding. If you don't want to remove your bedding, give your sheets, pillowcases, and duvet covers a good run with a hot iron. If disinfection is carried out poorly, the remaining mites can infect you again.
- Treatment of complicated scabies is best done with benzyl benzoate ointment or Spregal.
- Norwegian scabies is treated in a hospital.
This disease is characterized by the development of a characteristic rash in the area of the trunk and limbs in the form of scabies, nodules and blisters, scratching and the formation of bloody crusts against the background of infection with a parasite such as Sarcoptes scabiei (scabies mite). If the disease is caused by parasites common among animals, the disease is called pseudosarcoptosis. Specific complications of the disease are secondary bacterial and fungal infections, as well as the layering of allergic dermatitis.
The causative agent of scabies is the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei - the scabies mite. The pathogen is transmitted through close intimate contact, when living together, or through skin-to-skin contact while in bed. Transmission usually occurs in a focus, which is characterized by a group of people in which there is a source of the pathogen and transmission routes - the maximum activity of the pathogen is observed at night, so the direct route of transmission is through close intimate contact. Transmission of the pathogen is also possible through close household contact with household items of infected patients, but this route of transmission is only possible if the patient has a large number of scabies. It is especially dangerous to have two or more sources of scabies in a group that were infected under different circumstances. Persons living together in restrictive conditions (shared dormitories, boarding schools, nursing homes, barracks and many other situations) also play a particularly important role in the transmission of this disease. There are rarely cases of scabies infection in public places with limited crowds of people - in baths, saunas, swimming pools, trains, hotels). The main reasons for the spread of scabies are failure to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards, contact with a source of infection, and severe somatic diseases (such as diabetes), which facilitate the penetration of the pathogen into the skin. The main manifestation of scabies is the appearance of a scabies tract - a chronic inflammatory area with a predominance of lymphocytes in the stratum corneum of the skin. Depending on the clinical symptoms, there are typical scabies, scabies without burrows, Norwegian scabies, scabies without burrows, scabies lymphoplasia of the skin, complicated scabies with the addition of bacterial or fungal flora, as well as pseudosarcoptosis (infection with scabies mites from animals).
The symptoms of the disease depend on the form of the course. The most common form of scabies is the typical one, in which it is customary to allocate an incubation period (from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease) - about 2 weeks. When the disease manifests itself, scabies burrows form, nodules form on the torso and limbs, blisters, pronounced scratches and bloody crusts form in their place. A characteristic specific symptom is the absence of rashes in the interscapular space. Among the subjective changes, patients usually complain of severe itching, usually worsening at night. The rash is caused by a pronounced reaction of the body to the waste products of the tick. The main morphological element is “itch burrows,” which can be of several types: typical burrows are represented by white lines on the limbs and genitals, which are combined with a large number of nodules, vesicles and crusts. Diagnostically significant symptoms can be identified: pustules and crusts in the elbow area (Ardi's symptom), bloody crusts in the elbow area (Gorchakova), bloody crusts in the buttocks area (Michaelis), scabies in the form of an elevation (Sezary). When diagnosing “scabies without passages,” small nodules and blisters are detected. One of the most severe variants of the disease is Norwegian scabies. This is a rare and highly contagious form that occurs as a result of a pronounced decrease in immunity. The manifestation of the disease is a generalized lesion of the skin with the appearance of massive gray-white or dark dense crusts that limit movement. In children, the course of the disease is characterized by damage to the skin of the face and scalp.
A dermatovenerologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of scabies. If, based on the examination, the nature of the disease can be assumed, then it can be confirmed in several ways. The causative agent must be identified: to stain the “scabies tracts”, an iodine solution is used, as well as oil vitropressure; Using a needle, the scabies mite is removed, when applying lactic acid, the contents of the skin are “scraped off”, and dermatoscopy (examination of the skin through a microscope) is carried out to identify scabies mites.
For treatment, methods are used to destroy the causative agent of scabies. Treatment regimens include benzyl benzoate preparations (ointments, emulsions), permethrin, sulfur ointment, esdepalletrin with the addition of piperonyl butoxide. Treatment for Norwegian is somewhat different - in the evening the patient is treated with a scabicide, in the morning with one of the keratolytic drugs - products with salicylic acid (5% sulfur-salicylic ointment, 5-10% salicylic ointment) and urea. Treatment is carried out until the crusts are completely removed. The prognosis with correctly prescribed treatment is favorable.