The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
This benign formation is formed due to blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland. It can be single or multiple, when the entire surface of the scrotum is covered with a large number of atheromas, resembling a pustular rash. In the latter case, the man is diagnosed with atheromatosis.
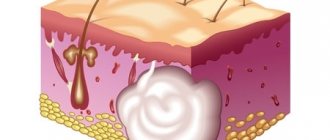
Atheroma, or sebaceous gland cyst, develops in the hair follicle. For various reasons, the excretory duct becomes blocked, and the secretion cannot find its way out. Mixing with dead skin cells, it accumulates in the sebaceous gland, stretching it and forming a compaction, the color of which is slightly lighter than the color of the surrounding skin. In the center of the atheroma, you can find a black dot - a clogged mouth of the gland.
The consistency of the formation is soft, elastic, has an even rounded contour, reaches a size of 1-1.5 cm in diameter. A primary sebaceous cyst is painless until it becomes inflamed. In contrast, secondary atheroma has a denser consistency and is painful when pressed. Secondary cysts of the sebaceous glands of the scrotum appear in large numbers in men suffering from seborrhea and hyperhidrosis, and are diagnosed as seborrheic cysts, or Fordyce cysts.
Due to friction with underwear and mechanical damage to the skin, scrotal atheromas can spontaneously open. The entry of pathogenic bacteria into the cyst against the background of reduced immunity leads to inflammation and suppuration of the formation.
Possible options for the development of atheroma:
- Healing after spontaneous opening;
- Abscess formation;
- Ulceration;
- The appearance of phlegmon.
The transformation of atheroma into a malignant tumor occurs extremely rarely, only with the addition of additional malignancy factors. It is important to differentiate atheroma from syphilitic ulcers, lipomas, fibromas. After spontaneous opening, a relapse of the disease may occur, because the remaining cells of the cyst capsule will provoke the formation of a new atheroma.
What is the cause of inflammation
There are many reasons for the appearance of a cyst: poor hygiene, disruption of the endocrine system, trauma, and damage to the hair follicle. The sebaceous gland, however, continues to function - sebum gradually accumulates under the skin. Microtrauma of the sebaceous gland leads to the same result, as a result of which its communication with the surface of the epidermis is disrupted.
Of course, the presence of excess fat under the skin cannot but have a negative impact on the functioning of the body. Sooner or later, if a person persistently refuses to remove the atheroma, an infection enters the cyst - through micropores, microtraumas on the skin, etc. The cavity is filled with pus, sometimes mixed with blood.
Causes of atheroma of the scrotum
A sebaceous gland cyst in the scrotum area is diagnosed in every fifth man. This frequency of occurrence of atheroma is associated with the structural features of the male reproductive system. The testicles, located in the scrotum, perform an important function - the production of full-fledged sperm. Many sebaceous glands maintain a stable temperature of this organ. If the rules of personal hygiene are not observed, their excretory ducts may become clogged.
Other reasons for the formation of atheroma:
- Lipid metabolism disorders;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Hyperhidrosis;
- The predominance of fatty foods in the diet.
With increased sweating, a lot of fluid is released through the sebaceous glands of the scrotum, which contains salts and hormones. Salt deposits clog the ducts and clog the pores.
In conditions of excess testosterone in the blood, the secretion of the sebaceous glands increases. Removing excess sebum becomes difficult; it accumulates in the cyst cavity. With poor diet, excessive consumption of fatty foods, spices, fried and spicy foods, specific compounds are formed in the secretions of the sweat glands that irritate the skin. This factor can also lead to the formation of atheroma.
How to understand that atheroma is inflamed
Diagnosing this formation is quite simple - by a black dot on the surface, which is the end of a clogged sebaceous duct. From time to time, contents with an unpleasant odor come out of it. In a non-inflamed state, the cyst does not cause pain, is quite elastic upon palpation and has clear boundaries.
As soon as an infection sets in, it increases in size, turns red, softens - touches bring burning pain, which is no longer possible to ignore. If this focus of infection becomes chronic, the situation may be complicated by an abscess - purulent inflammation accompanied by melting of surrounding tissues, and phlegmon - inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue.
Diagnosis and differentiation
To determine treatment tactics, the doctor must make sure the diagnosis is correct.
To do this, a visual inspection and, if necessary, laboratory tests are carried out:
- Blood test for hormones;
- Complete blood test to determine the content of leukocytes;
- A smear if there is ulceration at the site of the atheroma.
With an increased level of testosterone in the blood, we can conclude that the cause of the tumor is a hormonal imbalance. An increase in the concentration of leukocytes, which are a kind of defense of the body against pathogenic bacteria, indicates the development of an inflammatory process.
The study of smear data from an ulcer on the surface of the atheroma is carried out in order to determine the type of pathogenic microorganisms that caused it. The doctor must exclude the possibility of developing other pathologies with similar symptoms.
Directions for differential diagnosis (from what it is necessary to distinguish atheroma):
- Fibroma is a hypertrophied increase in connective tissue, located in the deeper layers of the skin, not fused to its surface;
- Lipoma - has a softer consistency, is less tightly fused to the surface of the skin, there is no black dot of the clogged mouth of the sebaceous gland;
- Hygroma is a cyst filled with serous fluid and fused not to the skin, but to nearby tissues.
What should I do?
If signs of inflammation appear, you should not hesitate - you must urgently go to the surgeon. But what you definitely can’t do is squeeze out or pick at the formation, trying to make a hole in it. If a breakthrough occurs and the pus is outside, the wound needs to be treated and wait until it heals. After this, the capsule and contents can be removed. The cyst should not be heated or steamed at any stage - this can cause infection.
At an emergency consultation with a surgeon, it may be recommended to relieve inflammation with levomekol or ichthyol ointment. The product is applied to a clean bandage and applied to the cyst, and then secured with a bandage. The compress is applied three times a day until the process subsides.
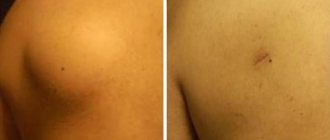
What is
Atheroma is a neoplasm, not classified as malignant, formed as a result of clogging of the sebaceous gland duct. Moreover, it can appear anywhere on the skin - on the scalp, neck, chin, cheeks, eyelids, chest, back, groin, ears, fingers, and so on. That is, in any place where there are sebaceous glands.
Atheroma is not an infectious or inflammatory disease, is not sexually transmitted, and also does not pose a threat to the health and life of the patient, except in cases of infection.
In men, it is considered normal for such lumps to appear in the genital area - the scrotum and penis. Small atheromas open on their own and do not cause discomfort to the owner, unlike large ones, which cannot go unnoticed due to their pain.
The appearance of such a neoplasm resembles a capsule filled with remnants of the epithelium and white or yellow fat cells.
Features of treatment
It is impossible to treat atheroma in such an acute condition. As soon as the inflammatory process can be stopped, the patient will be offered one of the removal methods. Large formations are removed surgically under local anesthesia. By cutting the skin, the doctor removes the capsule, applies cosmetic sutures, after which a scar remains on the skin.
If the cyst is small, a laser will be offered - without contact with the patient's blood. After this procedure, no traces remain. Sometimes it is advisable to combine these two methods - perform surgical excision and treat the capsule with a laser.
If an abscess has formed inside, the surgeon opens the atheroma under local anesthesia, removes the pus and rinses it. To prevent repeated suppuration, a special drainage is inserted into the cavity for several days, and antibiotics are also prescribed. In this case, the formation can be removed no earlier than three months after the wound has completely healed.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of a sebaceous gland cyst on the scrotum, you must carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene. Toilet of the genitals using soap or special cosmetics for intimate hygiene is a mandatory event. Steam baths can be used to cleanse the skin and prevent the appearance of atheroma.
Reasonable consumption of fats and carbohydrates will help not only maintain optimal weight, but also avoid clogging of the sebaceous glands. An additional measure to prevent scrotal atheroma is wearing loose underwear made from natural fabrics to prevent overheating of the groin area.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors
Where to remove a wen on the scrotum in Moscow
It is best to do this in a clinic specializing in outpatient urology, where all the necessary techniques and equipment are available.
Doctors with experience in removing such formations will perform the procedure quickly, painlessly and, if possible, without leaving a trace.
The Private Practice clinic paid close attention to the aesthetic side of the issue, so that the removal field did not leave any rough marks on the skin of the scrotum. Plus, the technique used does not require hospitalization of the patient and allows you to get rid of wen on the skin of the testicles even on the day of treatment.
Removal of a sebaceous gland cyst on the scrotum using an electrocoagulator
- For small atheromas, a ball electrode or electric knife is used, which, in coagulation mode, completely evaporates the cyst with the formation of a protective crust.
- If there are large wen of 1 cm or more, then they have to be removed by incising the skin over the atheroma and removing its contents. Next, the gland capsule is coagulated and 1-2 sutures and an aseptic dressing are applied.
- When taking biopsy material for histological examination, the atheroma is completely excised using a loop electrode and sent to the laboratory for analysis.
How much does it cost to remove atheroma of the scrotum with an electric knife? Small elements - from 500 rubles. cyst excision – 2500 rub.
After removal of the wen, careful wound care is necessary to prevent the development of inflammatory complications:
- Do not wet the removal area for at least 7 days
- Do not engage in sexual activity or vigorous physical exercise, which injures the crusts and contributes to the accumulation of sweat on the skin of the scrotum.
- Don't tear off the crusts
- Treat the crusts with fucorcin solution 2 times a day or apply bandages with antibacterial ointment solutions to the wound
- Apply a sterile protective dressing
- At the first signs of inflammation (redness, swelling, pain, pus), immediately contact the clinic’s doctor on duty.
If you follow these rules, you can get rid of wen on the skin of the scrotum without any problems or consequences, with an excellent cosmetic effect. Even after removing large sebaceous gland cysts with suturing, barely noticeable linear scars ultimately remain, which over time are difficult to detect in the folds of the skin of the testicles.
Prevention of atheromas on the genitals in men
It is almost impossible to regulate the process of sebum formation and the patency of the ducts of the glands of the skin of the scrotum. Often, the appearance of wen has genetically determined factors, such as an increased content of androgen receptors on the surface of the sebaceous glands.
Regular hygiene of the genital organs, normal nutrition rich in vitamins A, D, C, and B are of great importance for the prevention of recurrence of atheromas.
In severe cases, our doctors select drugs based on retinoids to reduce the activity of the sebaceous glands and normalize the keratinization of the epithelium of their ducts. This helps reduce the appearance of new elements, but has certain side effects.
Methods for removing sebaceous gland cysts in the skin of the scrotum
- Surgical - dissection of the gland shell with a scalpel, removal of fat, pus, capsule, suturing.
- Electrosurgical and radio wave - dissection of the skin over the wen with an electric knife, removal of the contents of the atheroma, destruction of its capsule and duct to prevent relapse. Or simply evaporate the atheroma when it is small. Suturing the wound is necessary only for large elements.
- Laser removal - dissection of the gland capsule with a laser or laser vaporization of small elements to form a sterile protective crust.
The choice of technique is up to the doctor, taking into account, of course, the wishes of the patient. Much depends on which method the doctor is better at. In our clinic, doctors more often use electrosurgical, radio wave and laser removal of sebaceous gland cysts, because they go away without bleeding, the wound after manipulation is absolutely sterile due to the high temperature of the laser and electrode, there is often no need to apply sutures, which facilitates further management and care wound.
How to get rid of wen on the scrotum
This can be done during the patient’s initial visit to the clinic.
After examination and diagnosis, the man donates blood to the hospital complex, which is ready in 20-30 minutes thanks to express diagnostics.
Next, each element is anesthetized using infiltration anesthesia so that there is no sensation during removal.
The next stage is the immediate removal and application of a bandage or suture if the atheroma was large.
How to remove wen in the skin of the scrotum at home
It’s better not to do this on your own. We know of cases where people try to squeeze out atheromas, pierce them with a needle or a knife. All this usually led to serious inflammatory complications and suppuration. There is a risk of losing the testicle when bacterial microflora spreads to its membranes.
Such experiments have two outcomes:
- In the best case, after inflammation, the wound heals, but atheroma relapses, that is, the wen appears again because the gland capsule remains in the skin, and sebum continues to be produced.
- The patient is admitted to the hospital with purulent melting, phlegmon of the scrotum and the risk of testicular amputation.
At the initial stages of the inflammatory process, after self-removal of wen, men turn to us. Most often, we can help them at the outpatient stage. Antibacterial therapy is prescribed, pus and the atheroma itself are removed. In severe cases, it is necessary to send the patient to the hospital.
Possible complications
Complications after removal of atheroma are rare. However, during the operation, blood vessels may be damaged, resulting in bleeding. To eliminate the consequences, the surgeon will sew up the damaged area and apply coagulants to ensure blood clotting.
After removal of the atheroma, suppuration of the suture may also occur due to possible interaction with bacterial flora. In this case, redness and itching will appear at the operation site. This inflammation, like any other, is treated conservatively.
The patient is prescribed antibiotics, additional examinations and observation. If the condition worsens and there is obvious progression of inflammation, immediate surgical intervention is required.
After each operation for atheroma, there is a possibility of re- development of the tumor. This phenomenon is called relapse. This occurs due to incomplete excision of damaged tissue. There is also the possibility of inflammation of the scar, which can develop into soft tissue phlegmon. This complication is considered extremely dangerous and requires immediate hospitalization.