To treat fungus, scabies and other skin diseases, it is not necessary to use expensive drugs. Sulfur ointment provides a good disinfecting, wound-healing, drying effect, which can be purchased at a very affordable price. This is a safe drug that can be used by adults and children starting from 2 years old. You can purchase the ointment at any pharmacy chain without a doctor's prescription.
Reasons for appearance
The lesions are caused by the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei. Any living creature that has been infected can carry it. And the more lesions on the patient’s body, the higher the risk that he can infect someone.
what does a scabies mite look like?
Infection is carried out by females and larvae. The female lives in the skin. During the daytime it is inactive, but in the evening it actively gnaws through passages, reproduces, feeds and secretes waste products. Consequently, the greatest risk of infection appears precisely in the evening and night time, when the tick is more active.
Everyone who comes into contact with the infected person is at risk. For example:
- family member
- roommate
- roommate
However, you can also become infected through indirect contact. For example in the following places:
- bathhouse
- public shower
- crowded places
Interesting. Outside a living organism, the female can live up to 3 days.
The disease spreads quickly due to the fact that the female lays eggs from which larvae hatch. After maturation, the latter crawl out to mate. The male dies and the female burrows back into human skin to continue the cycle of reproduction and spread.
Instructions for use
The ointment is used externally only. The duration of treatment is 5 days. In this case, for the first time it is recommended to apply the composition at night after a thorough shower. First you need to wash with water and soap, then dry the skin or wait for it to dry naturally.
The ointment is applied to any affected area, for example, the body, the skin of the arms, legs, as well as fingers and between them. After rubbing into the skin, you can put on clean underwear. On the second or third day of treatment it is necessary to take a break. The remaining part of the composition should not be removed from the skin.
On the fourth day, the patient needs to wash thoroughly again with soap. Rubbing in the ointment is done in the same way as the first time - in the evening. You should put on clean clothes again.
If sulfur ointment is used to treat hands, then you should not wash them for at least 3 hours. After this, the composition is applied to the hands after each washing procedure. If the ointment is washed off from other surfaces of the skin, they should be re-treated. It is important to note that the entire composition can be washed off only on the fifth day of therapy. After this they take a break. Repeated therapy can be carried out in consultation with a doctor. It is carried out until the symptoms of the disease disappear completely.
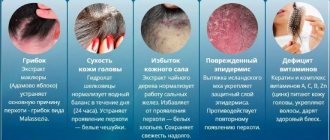
Classification of the disease and symptoms
There is a typical form of the rash with its inherent scabies, as well as apathetic forms. The latter include:
- Scabies that has no passages Appears if the cause of infection is larvae. Patients are tormented by itching due to parasites entering the body, but there are no passages because the larvae are not able to gnaw through them. However, scabies only last a couple of weeks until the insects mature and grow.
- Disease of clean people (incognito) It is distinguished by an unclear clinical picture. This disease develops in a person who washes very often, thereby washing away most of the parasites from the body.
- Scabious lymphoplasia is characterized by the formation of small dense nodes of a purple hue near the affected areas. They are very itchy. The nodes often merge into plaques, forming a dry crust. The rash remains on the skin for 2-6 weeks from the moment scabies appears. This is considered a complication, since lymphoid tissue suffers most from such damage.
- Scabious erythroderma Develops in those who develop scabies while simultaneously using antiallergic or hormonal medications. Patients do not suffer from itching and therefore do not scratch or abrade the skin, leaving most of the parasites unharmed. Consequently, their population increases faster than usual, and mites begin to spread even in places with an increased number of sebaceous glands. There are more moves than usual. The skin is dry, red and thick around the joints.
- Norwegian form Very rare. It occurs against the background of immune suppression, for example, taking drugs that enhance the production of hormones, cytostatics, or immunodeficiency. The disease is similar to erythroderma, but the number of parasites in the body is greater than with any other form of the disease. Thick gray and brown crusts (3 mm thick) appear on the affected areas. Ticks live underneath them. The entire epidermis is affected, as well as the nails. The disease becomes systemic - a person’s temperature rises, and the lymph nodes also enlarge.
- The peculiarity of children is that it spreads throughout the child’s body more strongly than through the body of an adult. In a child, lesions can be found even on the face, head, feet and palms. In infants, nails may be affected. A lot of vesicles and red bumps appear on the skin.
scabies in children - In the elderly Scabies in the elderly is characterized by few symptoms. There are fewer scabies than usual, but the number of scratches and crusts is very large.
Scabies of the elderly
The incubation period appears or disappears depending on whether a person is exposed to infection through a larva or through a female. In the latter case, there is practically no incubation period; symptoms appear immediately. If it is a larva, 2 weeks will pass from the moment of infection until the first symptoms appear (this time is necessary for the larva to grow).
Itching is the main symptom that those infected suffer from. It indicates the activity of the parasite. It can either be present only in certain areas of the skin or spread throughout the entire body (except for the face and places on the head covered with hair). One of the most basic symptoms indicating that a person is infected with scabies is that itching occurs mainly in the evening and at night.
With typical scabies, an itch also appears. It is a white stripe, 5 to 7 mm long. Scabies burrow rises above the epidermis. Most often it forms in the following places:
- folds between fingers
- wrist or elbow joint
- flexion surfaces
- front or sides of the abdomen
- armpits
- in the chest area (in females)
- near the genitals (in males)
With a standard disease, passages do not form in the following places:
- back (upper part)
- neck
- face
- scalp
The reason is that these places contain the largest number of sebaceous glands. The latter produce fat, which clogs the ventilation passages, depriving the parasites of access to oxygen.
Another symptom is when small dense tubercles appear on the body around the follicles, the so-called papules. It is in them that the larvae live until they mature. They prefer the following places:
- front and side parts of the body
- hips
- buttocks
There are other manifestations:
- Vesicles. They are bubbles with transparent contents. Formed on the hands, feet and wrists.
- Pustules. Same as vesicles, but differ in the presence of pus. This indicates bacterial infection.
- Bloody crusts.
- Scratching.
All these symptoms represent a side (allergic) reaction to parasites, their metabolic products, tissue damage and the proliferation of bacteria there.
Indications and contraindications
The main indications for use of the drug are:
- scabies;
- psoriasis (as an additional remedy);
- lichen;
- demodicosis;
- fungal infection of the feet and nails;
- The drug also helps in the treatment of seborrheic dematitis.
The product is practically harmless, so it can be used not only by adults, but also by children from 2 years of age. However, there are several contraindications:
- all stages of pregnancy;
- feeding period;
- increased sensitivity of the body to sulfur or other components;
- children under 2 years old.
Diagnostics
To determine the clinical picture, you need to do the following:
- Explain your symptoms to your doctor in detail. For example, itching only bothers you at certain times
- get tested
- examine the patient's body
- determine the source of infection
- find traces of the tick itself or its larvae
Typically, the disease is determined by the following criteria:
- purulent blisters
- dry crust
- redness on the buttocks
- scabies (the most important criterion)
To determine the itch, the lesion can be stained with iodine, oil containing minerals, or simply pressed on the epidermis with a glass slide. This will block blood from reaching the affected area and allow you to clearly see the affected area. It can also be detected using dermatoscopy (during the procedure the tick itself is detected).
Ticks can be detected using lactic acid. One drop (40%) should be applied to any lesion and wait 5 minutes. The loosened skin can then be scraped off with a sharp spoon until capillary bleeding appears. The resulting epidermis must be applied to a glass slide and looked at under a microscope. The method will allow you to identify most parasites and the products of their activity.
Side effects
If you follow the rules described in the instructions, no side effects are observed. There are also no reported cases of overdose. However, in some situations, allergy-related side effects are possible:
- redness;
- hives;
- itching;
- burning of the skin.
When such symptoms occur, symptomatic treatment is indicated. If allergic reactions are accompanied by complications, you must stop the course and consult a doctor. A change in therapy may be needed.
It should also be noted that sulfur has a fairly high toxic effect. Inhalation of the ointment is unacceptable - it is necessary to protect the lungs and nasopharynx. If during treatment you discover other side effects that are not listed in the description, you should consult a doctor.
How to treat
For proper treatment, specific therapy must be carried out to confirm scabies. If the doctor was unable to identify the mite and scabies, a trial treatment will be prescribed. In addition, preventive treatment is prescribed to all family members and people in contact with the patient.
The doctor will prescribe medications that kill ticks. Most often they are:
- aerosols
- ointments
- creams
- suspensions
- emulsions
The prescribed drugs will be based on the following substances:
- benzyl benzoate
- permitrina
- sulfur
- piperonyl butoxide
- esbiola
Sometimes treatment includes washing with soap or treating the skin with emollient ointments before using the drug.
Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine and treatment method. It is based on the following criteria:
- clinical picture
- complications
- person's age
- pregnancy
Self-medication can cause complications, apathetic forms of infection or a protracted course of the disease.
“Sulfur ointment”: description
The drug is an ointment that contains the active substance – sulfur in precipitated form. Also contains petrolatum base, water and emulsifier. It is packaged in 25 g jars. It should be stored in a cool place at a temperature of up to 15 degrees Celsius, or in the refrigerator. Avoid exposure to sunlight and keep away from children. The shelf life is 2 years from the date of production.
The ointment has a wide range of effects. It heals wounds, eliminates itching, relieves skin irritation, and disinfects the surface. Destroys bacteria, fungi, and parasites. It is used for various diseases and infectious lesions of the skin.
Despite a considerable number of medications, scabies is sometimes difficult to treat. What to do in such cases?
All drugs used to treat scabies affect only the metamorphic stage of mite development and do not affect the embryonic stage, which lasts no more than 4 days. Repeated treatment of the skin on the fourth day ensures sanitation, as it destroys the larvae that hatched from the eggs. Thus, none of the drugs currently used in Russia should be used once.
Scabies
is a common disease in dermatologist practice, sometimes complicating other skin diseases and not always easy to diagnose. In recent years, Moscow has seen a consistently high incidence of scabies. During the summer and autumn months, cases of scabies occur during almost every appointment. The basis for diagnosis is the clinical picture and the results of a microscopic examination of material taken from the lesions, obtained by scraping. In most cases, it is not difficult to make a diagnosis, with the exception of atypical manifestations of scabies, as well as the combination of various chronic skin diseases with it. In this work we will not dwell on the clinical manifestations of scabies - they are well known. Let us only note that in clean people, who shower daily with soap or shower gel and often wash their hands, rashes are scanty, typical scabies on the hands are rare, and the spread of rashes occurs very slowly. The pharmacy network has many products for the treatment of scabies, and yet the majority of patients (79.5%) turned to our Scientific Dermatology Center for help due to the ineffectiveness of previous treatment. This situation prompted us to analyze why it is so difficult to cure scabies.
First of all, let's talk about choosing a treatment method. In Russian pharmacies for the treatment of scabies there are domestic drugs - benzyl benzoate emulsion 20% (JSC Retinoids), solutions according to Demyanovich (60% sodium hyposulfite solution and 6% hydrochloric acid solution), simple sulfuric ointment (33%), Medifox concentrate containing 5% permethrin (Fox and Co.) and Wilkinson ointment (Permpharmacia) (contains liquid tar, calcium carbonate, purified sulfur, naphthalan ointment, green soap and water) and foreign - Spregal aerosol (Lab.SKAT , France) and benzyl benzoate ointment 20% (Latvia, Estonia).
Of the domestic drugs, in our opinion, the most effective remedy is a 20% benzyl benzoate emulsion. It is easily applied to the skin, does not stain bed linen and clothes, and is easily removed when washed. A minor drawback of the drug is that it does not have a strong specific odor.
Benzyl benzoate ointment 20% is no less effective than emulsion and may be the drug of choice. An ointment containing 10% benzyl benzoate is also available in pharmacies. This concentration is not sufficient for the treatment of adult patients, but is convenient for use in children.
Treatment with solutions according to Demyanovich (prescription form) by sequentially rubbing in a 60% sodium hyposulfite solution (solution No. 1), and then a 6% hydrochloric acid solution (solution No. 2) is also quite effective (the entire treatment lasts about an hour). Leather treatment is carried out in a warm room, which is then ventilated. Before use, solution No. 1 is slightly warmed and thoroughly rubbed into the skin with your hands, starting with the hands, left and right arms, then the torso, left and right legs, including the toes and soles. Rubbing into each area lasts 2-3 minutes, the whole procedure takes about 10-15 minutes. Then they take a break until the skin dries and crystals appear on it and perform the second treatment. After a 10-minute break, begin rubbing in solution No. 2, which is carried out in the same sequence, 1 minute at a time. in each area, only 3-4 times with drying intervals of approximately 5 minutes. The next day the procedure is repeated. After 3 days, take a shower. The sodium hyposulfite solution has a sulfur odor, and after treatment an unpleasant sensation remains. The need to not wash for 3 days also reduces the consumer properties of the drug.
Sulfur and sulfur-tar ointments are time-tested effective remedies. Their disadvantage is the Vaseline base, which is not absorbed, unpleasant to the touch, and gives the skin an unkempt appearance. For scabies, rub sulfur or sulfur-tar ointment onto the entire skin for 5-7 days. This disrupts sweating, both ointments stain laundry and have a pungent odor. These shortcomings often do not suit patients. It seems to us advisable to use sulfur ointment for the purpose of “follow-up treatment” on certain areas of the skin, especially with scabious lymphoplasia, the treatment experience of which shows that a combination of sulfur ointment with weak corticosteroid ointments has a good effect (in the morning - 1% hydrocortisone ointment, in the evening - 33% sulfur ointment) for 7-10 days. The same disadvantages are characteristic of Wilkinson's ointment.
We have no experience with the drug Medifox.
Among foreign drugs, 5% cream with permethrin is recognized as the most effective and least toxic. The French drug Spregal, produced in the form of an aerosol, is easy to use and does not have an unpleasant odor; Disadvantages include the possibility of penetration through the skin into the blood, the development of allergic reactions associated with the aerosol entering the respiratory tract, high consumption of the drug and its high cost. For the treatment of scabies, a single treatment is recommended. Our experience shows that treatment alone is not enough, and relapses occur. Esdepalletrin, the main active ingredient in Spregal, belongs to the neurotoxic group and is unlikely to affect tick eggs. It seems to us that it is more appropriate to repeat the treatment on the 4th day in order to influence the metamorphic stages of the mites. Repeated treatment of the skin on the fourth day ensures sanitation of the skin, as it destroys the larvae hatched from the eggs.
Thus, none of the drugs currently used in Russia should be used once. Literary data confirm our opinion - among 195 patients examined after treatment with 5% permethrin cream, only 46.7% turned out to be healthy after a single treatment (Yonkosky D., Ladia L., Gackenheimer L., Schultz MW Scabies in nursing homes: An eradication program with permethrin 5% cream / J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 1990, v.23, n.6, part 1, p.1133-1136). All commercially available anti-scabies products are effective when used correctly. The choice of treatment method is determined by the doctor’s experience, the availability of the drug in the pharmacy chain, its cost, ease of use and other consumer properties.
So, if all the drugs are quite effective, why is it sometimes so difficult to cure scabies? The most common error in treatment is the excessive use of antiparasitic drugs, with the subsequent development of postscabiosis dermatitis. It usually happens like this: the patient has finished treatment, but the itching continues to bother him, and not all the rashes have gone away. The patient’s conclusion is that the drug was not effective enough, and the causative agents of the disease are more resistant. The usual actions in this situation are repeating the course of treatment or changing the drug. Sometimes insufficiently experienced doctors make this mistake. In fact, the persistence of itching after treatment is the body's reaction to the killed mite and does not require additional treatment. After a repeated course of treatment, the itching often becomes more intense and new rashes appear. This is no longer scabies, this is allergic contact dermatitis. The term “post-scabiosis dermatitis” refers to inflammatory changes in the skin that occur after treatment for scabies, either according to generally accepted regimens, or excessive treatment. In our opinion, this dermatitis has some features compared to other contact dermatitis. The skin of the torso (especially places of pressure and friction with clothing) and proximal extremities is mainly affected. Against the background of erythema with unclear boundaries, there are small, barely noticeable cracks and erosions along the skin lines, as well as fine-plate peeling. A small number of nodular elements are sometimes noticeable along the periphery of the lesions. In addition, if the patient came in a short time after the development of dermatitis, then there are residual manifestations of scabies on the skin in the form of papules, erosions, excoriations and crusts.
As a rule, dermatitis in patients observed at our Center (121 people) occurred after excessive use of drugs on the recommendation of a doctor or on the patient’s own initiative. The most common recommendations from doctors are to use the drugs daily for several days or repeat the course of treatment if itching and rashes continue, or change the drug in the same situation. Thus, 9 patients received 2 courses of treatment with benzyl benzoate emulsion 20%, a week of daily lubrication was prescribed for 2 patients, 20 consecutive days for 1 patient, 5 courses for 1 patient, 10 courses for 1 more, 2 patients were treated for several months in a row. Despite the development of dermatitis, the manifestations of scabies usually quickly regressed under the influence of drugs. At the same time, we observed dermatitis and scabies after applying the drug Spregal: in one case a single dose, in another - multiple times. In both patients, microscopy of skin scrapings revealed scabies mites.
After the first application of antiparasitic agents, dermatitis was not observed in any patient, despite the fact that many of them experienced a burning sensation immediately after application. Apparently, the frequency of application is more important. In some cases, dermatitis also occurred in individuals receiving the usual course of treatment with benzyl benzoate according to a 4-day regimen. This may be due to increased sensitivity of the skin of some patients to benzyl benzoate. In 5 cases, dermatitis developed in persons with allergic dermatoses. Their presence can be regarded as a risk factor. Treatment of post-scabiosis dermatitis was carried out with antihistamines and sedatives, calcium preparations; for widespread rashes, zinc talker and paste were used externally; for localized and severely dry skin, weak corticosteroid ointments (hydrocortisone 1%, sinaflan) were used. Fukortsin was applied to crusts and excoriations. For secondary infection, Fukortsin (Fukaseptol) and Hyoxysone ointment were used.
Another reason for treatment failure is scabious lymphoplasia or nodular scabies. Scabious lymphoplasia is clinically characterized by the presence of intensely itchy nodular elements on the skin up to 1 cm in size, dense to the touch, purplish-bluish in color, round in shape, often covered with a bloody crust. The pathogenesis of scabious lymphoplasia is based on immuno-allergic reactions with hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue. We observed such elements in 29 patients (25 men and 4 women). Localization of nodular elements: scrotum - 16, inguinal-scrotal folds - 12, penis - 11, inner thighs - 7, buttocks - 6, inguinal folds - 6, axillary region - 3, lower abdomen - 2, area around the anus - 2 , navel area - 1, places of pressure and friction with clothing - 1 patient. Simultaneously, lymphoplasia and postscabiosis dermatitis were observed in 5 patients. Lymphoplasia was more often observed with a long course of the disease and with excessive treatment - the use of one course of treatment with benzyl benzoate emulsion 20% for 4-7 days in a row - in 7 patients, including 2 times a day - in one patient, the use of 2 courses of benzyl benzoate emulsion 20% 4 days in a row - in 1 patient, use of 5 courses of benzyl benzoate emulsion 20% - in 2. 12 patients were treated with 2 drugs sequentially, for example, 1 course of benzyl benzoate emulsion 20%, then 2 courses of Sarcoptol ointment; 10 days of using benzyl benzoate emulsion 20%, then sulfur ointment - 10 days; 1 course of application of benzyl benzoate emulsion 20%, then Spregal aerosol.
Cases of scabious lymphoplasia were treated with a combination of corticosteroid ointment (usually hydrocortisone 1%) applied to the skin in the morning and sulfur ointment applied in the evening. Additionally, cauterization of individual elements with liquid nitrogen 1-2 times a week and antihistamines were sometimes prescribed. Despite the treatment, scabious lymphoplasia sometimes persisted for quite a long time - a month or more.
We attach great importance to the period of observation of the patient, considering it advisable to examine him if scabies is diagnosed on the 7th day after the start of treatment, and then every 7-10 days until the rashes are completely resolved. Regarding the frequency of observation of patients, our opinion is somewhat at odds with the authors of the Methodological Recommendations (Scabies. Methodological Recommendations for Doctors // TsKVI Ministry of Health of the USSR. - M., 1992), in which it is recommended to examine the patient immediately after treatment and after 2 weeks, and with T. V. Sokolova, who recommends examining the patient only 2 weeks after the first treatment (Sokolova T.V. Incubation period and diagnosis of scabies. Vestn. Dermatol. 1992, 2, pp. 9-12), although from the point of view of the biology of the scabies mite this is justified. In our opinion, it is advisable to do the first examination after a week, since 4 days are not enough for complete resolution of the rash, even with successful therapy. In addition, if a patient develops postscabiosis dermatitis, then after a week it is easy to differentiate it from residual manifestations of scabies. And, finally, this examination is necessary from a psychological point of view - at this stage it is important to explain to the patient the essence of the changes taking place, to encourage him, to point out the good effect of the treatment and to prevent the repeated use of antiparasitic drugs in order to “consolidate the effect” or “follow-up treatment”. The next examination, if there are no complications, is scheduled after 10-14 days to determine cure or reinfestation. With the development of scabious lymphoplasia, it is advisable to examine the patient every week until the rash completely resolves.
The effectiveness of treatment is largely due to the simultaneous treatment of the patient and contact persons. Scabies is an ectoparasitic disease caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei hominis. This disease is specific to humans and is not transmitted to people from pets. Transmission of pathogens occurs primarily at night, when ticks are active. The most common source of infection was sexual partners, other family members, and dorm roommates. Often, infection occurred during a business trip, while on vacation, or with relatives. Sometimes the disease occurred after the arrival of guests, in 3 cases - after a stay in the hospital, in 2 cases - in maternity hospitals. In this regard, it is very important, if possible, to identify the source of infection, asking the patient not only about the presence of the disease in close relatives, but also taking into account all the above circumstances. It is better to treat all sick people at the same time to avoid reinfection. The incubation period can be practically absent when infected by adult female ticks, and up to 2 weeks when infected by larvae. All healthy persons in close contact with sick people are recommended to undergo one-day preventive treatment with any of the drugs.
In conclusion, I would like to note the importance of disinfection measures. Their absence often leads to re-infection with scabies. These activities are easy to perform. Bedding, towels, washcloths, and linen are disinfected by boiling for 5-10 minutes in a solution of soda or washing powder, and when washing in an automatic washing machine, it is enough to turn on the longest wash cycle at maximum temperature. Blankets and pillows, as well as outer clothing, are disinfected by hanging them outdoors for 5 days. Toys, items that cannot be washed, and shoes can be temporarily excluded from use for 5 days by placing them in a plastic bag. Mattresses and upholstered furniture can be treated with any aerosol preparation designed to kill crawling insects.
Prof. V.I.
Albanova Print